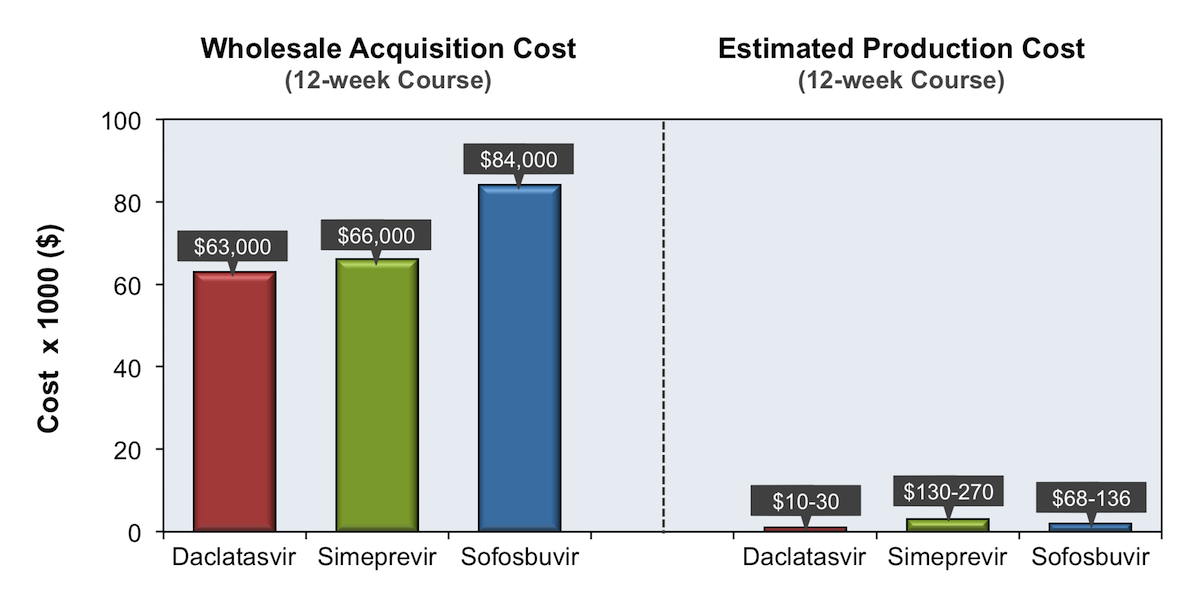
New DAAs have been highly effective in treating chronic HCV infection, but the high cost of these medications has served as a major barrier to more widespread treatment access. The wholesale acquisition cost for the newer DAAs ranges from $417 to $1,125 per day.
Full Answer
Who pays for HCV treatment?
Dec 13, 2019 · Following availability of new DAAs, average yearly OOP spending on HCV medications increased from $41 to $94 per HCV-diagnosed member in the study population, with about 32% of members receiving...
Is HCV treatment cost-effective?
Jun 01, 2018 · The table below highlights the average cost of treatment for the combination DAAs currently available. Most of these drugs take at least 12 weeks to cure HCV, while the most recently approved drug ...
When was HCV treatment approved by the FDA?
example, the wholesale acquisition cost of a 12-week course of sofosbuvir is $84,000 and the estimated production cost is $68 to $136.[1] The pharmaceutical companies justify the significant discrepancy in wholesale acquisition cost and production cost based on a need to recoup large expenses incurred during the
What is wholesale acquisition cost (WAC)?
Prescription Drug Wholesale Acquisition Cost (WAC) Increases This table is a list of wholesale acquisition cost (WAC) increases that exceed the WAC increase threshold of 16% for the period including the current quarter and the previous two calendar years for prescription drug products with a WAC greater than $40 for a course of therapy.

What is the cost of HCV treatment?
The cost of hep C treatment varies depending on the type of drug. However, an 8- to 12-week course can range from $54,000 to $95,000 (or higher). For example, the price of a 12-week course of Zepatier can be as much as $54,600, and a 12-week course of Harvoni can cost as much as $94,500.Sep 2, 2021
How much does Sovaldi cost in America?
Official Answer. The wholesale cost of Sovaldi is $1000 per 400mg tablet. A 12-week treatment course of Sovaldi costs around $84,000 and a 24-week course, $168,00.Apr 23, 2020
Are hep C drugs expensive?
Hepatitis C drugs are pricey Antiviral drugs for hepatitis C are very effective, but they come at a steep cost. Just one Sovaldi pill costs $1,000. A full 12-week course of treatment with this drug costs $84,000.Feb 5, 2019
How much is ribavirin cost?
Wholesale Prices of RibavirinDrug NameDosePrice Per Month for Generic*Ribavirin800–1,400 mg daily800 mg: $1,192 1,000 mg: $1,490 1,200 mg: $1,787 1,400 mg: $2,0852 more rows
Why is Sovaldi so cheap in India?
The newspaper says that current treatments for the disease in India run about $6,000 and require a 24- to 48-week course of injectables that come with serious side effects. So Sovaldi will be cheaper and easier to administer, with fewer side effects and the ability to cure many of the cases.
What is the cost of Sovaldi in India?
Gilead Sciences makes the hepatitis C drugs – Sovaldi and Harvoni – but $85,000 is an only in America price. Sovaldi sells for about $1,000 a pill in the U.S., while a generic version costs only $4 a pill in India.Jul 19, 2017
How can I get hep C treatment for free?
Patient assistance programs (PAPs) offer free hepatitis C drugs to lower-income people who are uninsured or underinsured, and who do not qualify for insurance programs such as Medicaid or Medicare.
What is the best hep C treatment?
Hepatitis C is treated using direct-acting antiviral (DAA) tablets. DAA tablets are the safest and most effective medicines for treating hepatitis C. They're highly effective at clearing the infection in more than 90% of people.
Is hep C treatment covered by insurance?
Luckily, hep C treatment is covered by most insurance plans, so for many people, the cheapest way of getting it will be through insurance (although you'll probably need prior authorization). If your hep C treatment is not covered by your insurance, ask your doctor about an appeal.Jan 27, 2019
What is the brand name for ribavirin?
Ribavirin is an antiviral medication used together with an interferon alfa product (such as Peg-Intro or Intron A) to treat chronic hepatitis C. Ribavirin is available under the following different brand names: Rebetol, Ribasphere, RibaPak, Copegus, Virazole, and Moderiba.
What are the side effects of ribavirin treatment?
Ribavirin may cause side effects. Tell your doctor if any of these symptoms are severe or do not go away:cough.upset stomach.vomiting.diarrhea.constipation.heartburn.loss of appetite.weight loss.More items...•Jun 15, 2016
How much does aerosolized ribavirin cost?
RIBAVIRIN is an antiviral medicine. It is used with other medicines to treat hepatitis C. It will not work for colds, flu, or other viral infections. The lowest GoodRx price for the most common version of ribavirin is around $94.15, 92% off the average retail price of $1,255.45.
How to pay for HCV?
If you’re concerned about paying for HCV medications, remember that you aren’t alone as you seek treatment. There are people and organizations that can help you, including the following: 1 Your doctor. They can help you by ordering and documenting the tests you’ll need so you can qualify to get your medications, especially if you’re working with a liver or infection specialist. 2 Most drug manufacturers. There are patient assistance programs that offer free or reduced-cost medications for people who meet their criteria. 3 Patient advocacy groups. These groups provide assistance with all aspects of HCV treatment. For instance, if your insurer denies treatment, you can appeal the decision with help from one of these groups. Your doctor can also help in this situation.
How many people die from hepatitis C each year?
Americans have chronic hepatitis C. About 19,000 of these people die each year from cirrhosis or liver cancer. Fortunately, recent advancements in the fight against this virus have changed the outlook for people with HCV. New drugs have transformed the disease from one that can, at best, be controlled to one that can be cured for most people who ...
What is the liver infection?
Hepatitis C is a viral infection that attacks the liver. Infection with hepatitis C can lead to serious liver disease, including cirrhosis and cancer. Hepatitis C virus (HCV) is transmitted by exposure to blood or other bodily fluids that contain HCV.
What is a direct acting antiviral?
of people who take them, depending on the type of HCV infection and treatment exposure. These new drugs are called direct-acting antivirals (DAAs). The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved the first of these medications for HCV treatment in 2011. Several more medications have been approved since that time.
Is generic medicine cheaper than brand name?
It also means there are no generic versions of these drugs yet. Generics are typically much cheaper than brand- name versions. The FDA determines how long this period of exclusivity will last. During this time, the pharmaceutical companies have a lot of freedom in establishing prices.
What are the criteria for liver disease?
These criteria may be based on: the severity of liver disease. whether the person avoids alcohol and drug use. whether the drug’s prescribed by a doctor who specializes in liver diseases. the life expectancy of the person seeking treatment. whether less expensive treatments could be used first.
Can hepatitis C be treated with drugs?
Today there are several drug options available that can cure hepatitis C infection — that’s the great news. What’s less great is the high cost of these drugs. However, there are many options you can explore to find help paying for these medications.
Prescription Drug Wholesale Acquisition Cost (WAC) Increases
This table is a list of wholesale acquisition cost (WAC) increases that exceed the WAC increase threshold of 16% for the period including the current quarter and the previous two calendar years for prescription drug products with a WAC greater than $40 for a course of therapy.
Office of Statewide Health Planning & Development
California's Office of Statewide Health Planning and Development (OSHPD) is the leader in collecting data and disseminating information about California's healthcare... read more
What is wholesale acquisition cost?
The wholesale acquisition cost (WAC) is the manufacturer’s list price of the drug when sold to the wholesaler, while the DIRP is the manufacturer’s list price when sold to non-wholesalers. WAC is the most common benchmark used today by pharmacies to buy drugs from wholesalers. Typically a 20% mark-up is applied to the manufacturer-supplied WAC ...
What is coinsurance in pharmacy?
Many patients have coinsurance or copayments, where they only pay for a portion of their prescription cost. The insurance company then pays the rest of the cost (the reimbursement) to the pharmacy. Insurance companies include: prescription benefit managers (PBMs) like Express Scripts, CVS Health, or OptumRx.
How is Awp calculated?
The drug manufacturer may report the AWP to the individual publisher of drug pricing data, such as MediSpan or First Data Bank. The AWP may also be calculated by the publisher based upon a mark-up specified by the manufacturer that is applied to the wholesale acquisition cost (WAC) ...
What is wholesale acquisition cost?
The wholesale acquisition cost (WAC) is an estimate of the manufacturer’s list price for a drug to wholesalers or direct purchasers, but does not include discounts or rebates.3 Without including rebates and other incentives provided by manufacturers, it is hard to estimate the actual cost of the drug.
What is a low copay?
Low copays disguise the actual cost of medications, increasing patients’ demand for prescriptions. For example, a patient may be prescribed a medication with a U&C price of $100 for a month’s supply, but with a contracted third-party plan the patient may only be responsible for a $20 copayment to the pharmacy.
What is the relationship between supply and demand?
Basic microeconomics explains the relationship of supply and demand with the pricing of goods and services. Changes in supply and demand influence market price, and then a price change influences consumer decisions to purchase. In the case of drug pricing, there are several factors that have complicated this particular market.
How does a pharmacy benefit manager work?
In the prescription-drug market, most patients are enrolled with a third-party plan (government and/or insurance company) that utilizes a pharmacy benefits manager (PBM) to help manage this process. The patient pays the third party in the form of premiums along with a contribution from the government or the patient’s employer as a part of the total work compensation to the PBM. At the point of sale when patients pick up their prescription from the pharmacy, they usually pay a smaller portion of the transaction and the PBM reimburses the pharmacy for the balance. Low copays disguise the actual cost of medications, increasing patients’ demand for prescriptions. For example, a patient may be prescribed a medication with a U&C price of $100 for a month’s supply, but with a contracted third-party plan the patient may only be responsible for a $20 copayment to the pharmacy. This reduction in price helps drive consumer demand for this prescription medication. When patients are responsible for a larger proportion of the cost, they are less likely to utilize the health care service.6
What is EAC in pharmacy?
The EAC is meant to reflect the cost of the drug to the provider from the wholesaler, but is not a published figure. The average actual cost (AAC) is considered the final cost paid by pharmacies to their wholesalers after all discounts have been deducted and is derived from actual audits of pharmacy invoices.
What is EOB in insurance?
When the patient receives an explanation of benefits (EOB) from the insurance company, the apparent total cost of the medication may be higher than what the pharmacy is actually paid due to the markup by the PBM within the spread. This value may vary depending on the drug product.
What is an AMP?
The AMP was originally mandated as a part of the Omnibus Budget Reconciliation Act of 1990 (OBRA ’90), and the actual definition continues to evolve.3 AMP is meant to calculate the cost of a drug directly from a manufacturer after any rebate or discount is included.

Cost-Effectiveness
- Cost-effectiveness analysis (CEA) compares the relative costs and outcomes of 2 or more interventions. CEA explicitly recognizes budget limitations for healthcare spending and seeks to maximize public health benefits within those budgetary constraints. The core question that CEA …
Affordability
- An intervention that is cost-effective is not necessarily affordable. Affordability refers to whether a payer has sufficient resources in its annual budget to pay for a new therapy for all who might need or want it within that year. Several characteristics of CEA limit its ability to speak to the budgetary impact of interventions being implemented in the real world. 1. Perspective on cost CEA seeks t…
Cost vs Affordability For HCV Treatment
- Despite a growing body of evidence that HCV treatment is cost-effective and may even be cost saving over the long term in some cases, many US payers—especially those offering Medicaid insurance products—continue to limit access to HCV treatment. Access has improved as cost has decreased but limitations remain. Proposed reductions in healthcare spending for Medicaid wou…
Cost-Effectiveness of Screening For HCV
- Several cost-effectiveness studies demonstrate that routine, one-time testing for HCV among all adults in the US would likely identify a substantial number of cases of HCV that are currently being missed, and that doing so would be cost-effective. One study employed simulation modeling to compare several versions of routine guidance, including routine testing for adults over the ages …
Conclusions
- Many studies have demonstrated the economic value of HCV screening (Chaillon, 2019); (Eckman, 2019); (Tasillo, 2019); (Assoumou, 2018); (Barocas, 2018); (Schackman, 2018); (Schechter-Perkins, 2018); (Lyons, 2016); (Hsieh, 2016); (Schackman, 2015) and treatment (Goel, 2018); (Chhatwal, 2017); (He, 2017); (Chahal, 2016); (Chhatwal, 2015); (Chidi, 2016); (Martin, 201…