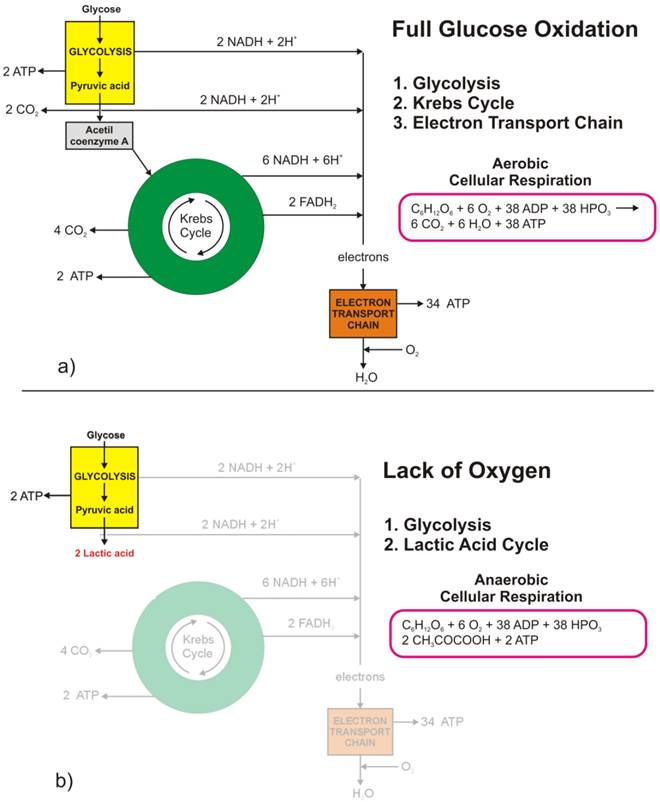
The term Warburg effect in oncology describes the observation that cancer cells, and many cells grown in vitro, exhibit glucose fermentation even when enough oxygen is present to properly respire. In other words, instead of fully respiring in the presence of adequate oxygen, cancer cells ferment.
What is the Warburg method for reversing cancer?
A Look at the Evidence
- Obesity — having too much body fat — is a clear risk factor for cancer.
- Obesity is caused by consuming more calories than are expended over time.
- Eating lots of refined carbohydrates, including foods with added sugar, can lead to obesity.
- Body fat promotes inflammation, which can damage DNA and lead to cancer.
What is the Warburg method?
What is the Warburg method for reversing cancer? In oncology, the Warburg effect is the observation that most cancer cells predominantly produce energy by a high rate of glycolysis followed by lactic acid fermentation in the cytosol, rather than by a comparatively low rate of glycolysis followed by oxidation of pyruvate in mitochondria as in ...
What is the best natural cure for cancer?
The Top 10 Natural Cancer Cures
- Physical Activity. Participating in any type of physical activity will help most people who are following a protocol that they believe is consistent with the best natural cancer cure that ...
- Nutrition. ...
- Acupuncture. ...
- Yoga. ...
- Meditation. ...
- Music therapy. ...
- Massage. ...
What is the Warburg effect?
Zhang, Q., Qin, Y., Zhao, J. et al. Correction: Thymidine phosphorylase promotes malignant progression in hepatocellular carcinoma through pentose Warburg effect. Cell Death Dis 13, 134 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-022-04557-7

What is the Warburg effect cancer?
In oncology, the Warburg effect (/ˈvɑːrbʊərɡ/) is the observation that most cancer cells produce energy predominantly not through the 'usual' citric acid cycle and oxidative phosphorylation in the mitochondria as observed in normal cells, but through a less efficient process of 'aerobic glycolysis' consisting of high ...
How does Warburg effect help cancer cells?
The Warburg effect with aerobic glycolysis efficiently produces ATP synthesis and consequently promotes cell proliferation by reprogramming metabolism to increase glucose uptake and stimulating lactate production. High-proliferating cancer cells use increased fatty acid synthesis to support the rate of cell division.
What is the Warburg effect for dummies?
The Warburg Effect is defined as an increase in the rate of glucose uptake and preferential production of lactate, even in the presence of oxygen.
Is the Warburg effect true?
The Warburg effect has been confirmed in previous studies including those of DeBerardinis et al. [10], where cells were incubated under oxygenated conditions in 10 mM C-13-labelled glucose.
What does curcumin do to cancer cells?
Laboratory and animal research suggests that curcumin may prevent cancer, slow the spread of cancer, make chemotherapy more effective and protect healthy cells from damage by radiation therapy. Studies of curcumin in people are still in the early stages.
How do you inhibit the Warburg effect?
Curcumin inhibits Warburg effect in cancer cells Sub-toxic concentrations of 0–20 μM curcumin for 24 hours were used for the study. Significant inhibition in glucose uptake and lactate release was observed across the four cell lines, however, no appreciable decrease in Warburg effect was observed in HEK 293 cells (Fig.
What cells use the Warburg effect?
In contrast to normal differentiated cells, which rely primarily on mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation to generate the energy needed for cellular processes, most cancer cells instead rely on aerobic glycolysis, a phenomenon termed “the Warburg effect.” Aerobic glycolysis is an inefficient way to generate adenosine ...
What is the Reverse Warburg effect?
The Reverse Warburg Effect describes when glycolysis in the cancer-associated stroma metabolically supports adjacent cancer cells. This catabolite transfer, which induces stromal-cancer metabolic coupling, allows cancer cells to generate ATP, increase proliferation, and reduce cell death.
What is the Warburg effect and what is its clinical relevance?
The Warburg effect represents high levels of glycolysis and thus enables the clinical application of metabolic imaging, such as 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography (FDG-PET), which is a non-invasive imaging technique that allows quantification of tumor activity on the basis of altered tissue glucose ...
What did Otto Warburg get a Nobel Prize?
The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 1931 was awarded to Otto Heinrich Warburg "for his discovery of the nature and mode of action of the respiratory enzyme."
What is the Warburg effect and what is its clinical relevance?
The Warburg effect represents high levels of glycolysis and thus enables the clinical application of metabolic imaging, such as 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography (FDG-PET), which is a non-invasive imaging technique that allows quantification of tumor activity on the basis of altered tissue glucose ...
Why do cancer cells prefer glycolysis?
Cancer cells have significant heterogeneity in glucose metabolism. Most cancer cells rely largely on aerobic glycolysis as it accounts for 56–63% of their ATP budget. So, cancer cells plunder more glucose from microenvironment and secrete more lactic acid to meet requirement of energy and material metabolism.
What is the Warburg Method?
By Alina Walker on Wednesday, May 1, 2019. Warburg Method is a guide packed with treatments for several diseases and ailments. It has been compiled over the years and a lot of research has went into it. The book comes for absolutely no cost which is why it is so preferable and can be relied on as clearly, it’s an attempt to reveal ...
How does the Warburg method help?
Warburg Method can give readers this life by detailing them on not only the tips and tricks that can help them improve their health by reversing illnesses but also by telling them the exact strategies, the exact ingredients which they’ll need for benefiting their health.
Who was the German scientist who discovered the cure for cancer?
This guide is called the Warburg Method, based on the name of the German scientist, chemist, and doctor, Otto Warburg. Dr. Warburg worked in the Nazi regime and was instructed by Adolf Hitler himself to find a cure for cancer. He had, as a matter of fact, discovered the cure for cancer without the use of radiations, ...
Why is the Warburg Way called the Warburg Way?
The therapy is called The Warburg Way ™ because it is based upon a 1927 observation by Dr. Otto Warburg, a Nobel laureate. Dr. Warburg observed that cancer cells required much more glucose than normal cells to meet their energy requirements, and that depriving them of glucose in the blood by administering insulin starved these cells ...
What kinds of tumors have been treated?
What kinds of tumors have been treated?#N#The treatment has successfully provided relief to patients with solid tumors, including breast, prostate, thyroid, neck, esophagus, stomach, colon, liver, pancreas, bone, ovarian, uterine, lung, pancreatic, and glioblastoma. It has not yet been applied to palliative care for leukemia and other blood-based malignancies.
What did Warburg conclude about the cancerous cells?
He concluded that the cancerous cells did not have much mitochondrial respiration, which resulted in their uncontrolled growth and multiplication. This is known as the Warburg effect. However, a lot still remains to be ascertained about Warburg’s theory.
Who is the scientist who solved the cancer mystery?
When the cancer mystery is finally solved, Otto Heinrich Warburg certainly deserves part of the credit. His contribution is more than noteworthy.
What was Einstein's influence on Otto Warburg?
In fact, Einstein’s influence is very evident in some of Otto’s theories and works. Otto Warburg applied himself to serious scientific study and was religiously devoted to his laboratory. He held many impressive titles: he was a medical doctor, a physiologist, and a Nobel Laureate.
What is the theory of cancer?
According to the theory, cancer is initiated by incorrect respiration occurring in some cells.
Why is cancer caused by a pyruvate?
According to Otto Warburg, cancer is caused by incorrect respiration occurring in the cells. In healthy cells, glucose is ideally broken down in two cycles. During the first half, a pyruvate is formed, and it is then oxidized to release more energy. This is however not the case for cancerous cells.
How is cancer initiated?
According to the theory, cancer is initiated by incorrect respiration occurring in some cells. The theory has sparked some interesting debates, but suffice it to say that Warburg was on to something.
Why is cancer thought to occur?
Generally, cancer is thought to occur due to genetic mutation by malignant transformation. Currently, the general notion around the world regarding Warburg’s theory is that his observations are characteristics of cancerous mutations, and not the cause of the disease.
What is the Warburg theory of cancer?
The Warburg Theory of Cancer or “Warburg hypothesis” (as distinguished from the Warburg effect) postulates that the driver of tumorigenesis is an insufficient cellular respiration caused by insult to mitochondria.
What did Warburg discover?
Warburg’s discovery has opened up new ways in the fields of cellular metabolism and cellular respiration. He has shown, among other things, that cancerous cells can live and develop, even in the absence of oxygen. “But, even for cancer. There is only one primary cause. Summarized in a few words, the cause of cancer is the replacement ...
What is the Warburg effect?
The Warburg Effect describes the observation that cancer cells, and many cells grown in-vitro, exhibit glucose fermentation even when enough oxygen is present to properly respire. In other words, instead of fully respiring in the presence of adequate oxygen, cancer cells ferment.
Why did Otto Warburg win the Nobel Prize for his work?
Dr. Otto Warburg received the Nobel prize in 1931 for the discovery that unlike all other cells in the human body, cancer cells do not breathe oxygen. Cancer cells are anaerobic, which means that they derive their energy without needing oxygen. It turns out that cancer cells cannot survive in the presence of high levels of oxygen.
Where was Otto Warburg's lecture?
Dr. Otto Warburg lecture delivered to Nobel Laureates on June 30, 1966 at Lindau, Lake Constance, Germany. There are prime and secondary causes of diseases.
Is cancer an aerobe?
All normal body cells are thus obligate aerobes, whereas all cancer cells are partial anaerobes. From the standpoint of the physics and chemistry of life this difference between normal and cancer cells is so great that one can scarcely picture a greater difference.
How does Warburg slow down cancer?
The hope of scientists at the forefront of the Warburg revival is that they will be able to slow — or even stop — tumors by disrupting one or more of the many chemical reactions a cell uses to proliferate, and, in the process, starve cancer cells of the nutrients they desperately need to grow.
What percentage of cancers are caused by Warburg's effect?
The cancer cells were ravenous for glucose. Warburg’s discovery, later named the Warburg effect, is estimated to occur in up to 80 percent of cancers.
Why does Warburg effect occur?
In the years following his breakthrough, Warburg became convinced that the Warburg effect occurs because cells are unable to use oxygen properly and that this damaged respiration is, in effect, the starting point of cancer.
What is the Warburg theory?
Imagine two engines, the one being driven by complete and the other by incomplete combustion of coal,” Warburg wrote in 1956, responding to a criticism of his hypothesis that cancer is a problem of energy. “A man who knows nothing at all about engines, their structure and their purpose may discover the difference.
What is the term for the metabolic catalysts that Warburg spent his career analyzing?
The metabolic catalysts that Warburg spent his career analyzing began to be referred to as “housekeeping enzymes ” — necessary to keep a cell going but largely irrelevant to the deeper story of cancer. “It was a stampede,” says Thomas Seyfried, a biologist at Boston College, of the move to molecular biology.
How does cancer grow?
Instead, the cancer cells fueled their growth by swallowing up enormous amounts of glucose (blood sugar) and breaking it down without oxygen. The result made no sense. Oxygen-fueled reactions are a much more efficient way of turning food into energy, and there was plenty of oxygen available for the cancer cells to use.
Who was the first to believe that cancer could be treated by disrupting its source of energy?
An Old Idea, Revived: Starve Cancer to Death. In the early 20th century, the German biochemist Otto Warburg believed that tumors could be treated by disrupting their source of energy. His idea was dismissed for decades — until now.