
How to treat and bring down high blood sugar levels?
Tips for healthful living with diabetes
- Eat a consistent diet. Maintain a steady carbohydrate intake, avoiding “empty calorie” foods, such as processed foods, whenever possible.
- Get consistent exercise. ...
- Reduce stress. ...
- Stay hydrated. ...
- Get a good night’s rest. ...
- See your doctor. ...
- Maintain a healthy weight. ...
- Stick to your medication and insulin regimen. ...
How to reduce your blood sugar levels naturally?
They noted that temperature difference is related to blood pressure control, so following more natural light patterns might ... In the meantime, good ways to keep your blood sugar levels under control and reduce your risk of developing type 2 diabetes ...
What medications can cause hyperglycemia?
- Azathioprine
- Chemotherapeutic medications
- Cimetidine ( Tagamet)
- Morphine
- Methadone
- Anesthetic s
- Tranquilizer s
How to lower blood sugar quickly in an emergency?
How to Lower Blood Sugar Quickly in an Emergency: Tips and More
- Take your insulin as prescribed. High blood sugar occurs when your body has too little insulin, or your body can’t use insulin properly.
- Exercise. ...
- Eat a consistent diet. ...
- Get consistent exercise. ...
- Reduce stress. ...
- Stay hydrated. ...
- Get a good night’s rest. ...
- See your doctor. ...
- Maintain a healthy weight. ...
- Stick to your medication and insulin regimen. ...

What is the correct treatment for hyperglycemia?
Treatment usually includes: Fluid replacement. You'll receive fluids — usually through a vein (intravenously) — until you're rehydrated. The fluids replace those you've lost through excessive urination, as well as help dilute the excess sugar in your blood.
What is the first line treatment for hyperglycemia?
Insulin, rather than oral hypoglycemic agents, is often indicated for initial treatment of symptomatic or severe hyperglycemia (fasting plasma glucose >250 mg/dL [13.9 mmol/L], random glucose consistently >300 mg/dL [16.7 mmol/L], A1C >10 [85.8 mmol/mol]), depending on the severity of the baseline metabolic disturbance ...
What is the most widely used treatment to manage type 1 diabetes?
Metformin is the most widely used drug, together with sodium-glucose co-transporters 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors, amylin analogues, glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists, and dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors.
How do you treat hypoglycemia in type 1 diabetes?
Most episodes of asymptomatic or symptomatic hypoglycemia are effectively self-treated with glucose tablets or carbohydrate containing juice, soft drinks, candy, other snacks or a meal by the person with T1DM [1,2]. 20 g, repeated in 15 to 20 minutes if necessary, is a reasonable dose of carbohydrate [64].
Do you give insulin for hyperglycemia?
Insulin, given either intravenously or subcutaneously, is the preferred regimen for effectively treating hyperglycemia in the hospital.
What type of insulin is used for hyperglycemia?
Regular and analog human insulins are used for correction of hyperglycemia, unless bovine or pork insulin is the only available insulin.
What is the first line treatment for type 1 diabetes?
Insulin injected subcutaneously is the first-line treatment of type 1 diabetes mellitus (DM). The different types of insulin vary with respect to onset and duration of action. Short-, intermediate-, and long-acting insulins are available.
What are the treatment management strategies for patients with type 1 diabetes?
Treatment for type 1 diabetes includes:Taking insulin.Carbohydrate, fat and protein counting.Frequent blood sugar monitoring.Eating healthy foods.Exercising regularly and maintaining a healthy weight.
What is the latest treatment for diabetes type 1?
Researchers have recently successfully treated Type 1 diabetes by transplanting insulin-producing pancreas cells into the patient.
Can type 1 diabetes have hyperglycemia?
People with type 1 diabetes (T1D) can have episodes of hyperglycemia every day. Although this can be frustrating, it rarely creates a medical emergency. Not taking enough insulin can lead to hyperglycemia (like missing a dose or not taking enough insulin for the carbs you ate).
How is hypoglycemia treated in emergency?
Immediate hypoglycemia treatmentEat or drink 15 to 20 grams of fast-acting carbohydrates. These are sugary foods or drinks without protein or fat that are easily converted to sugar in the body. ... Recheck blood sugar levels 15 minutes after treatment. ... Have a snack or meal.
How is hypoglycemic episode treated?
The immediate treatment for hypoglycaemia is to have some food or drink that contains sugar, such as dextrose tablets or fruit juice, to correct your blood glucose levels. After having something sugary, you may need to have a longer-acting "starchy" carbohydrate food, such as a sandwich or a few biscuits.
What is the target glucose level for diabetics?
The American Diabetes Association defines a fasting glucose target as 80 to 130 mg/dl. A fasting glucose level above 130 mg/dl is considered to be hyperglycemia.
Why is my blood sugar high in type 1 diabetes?
One of the hallmarks of type 1 diabetes is hyperglycemia, or high blood glucose (sugar). There’s a very good reason that glucose levels climb high in type 1 diabetes, and that’ s a lack of insulin. When the pancreas shuts down insulin production, blood glucose levels start to climb. If there is sufficient insulin in the bloodstream, say, from an insulin injection or insulin infusion from a pump, glucose levels (hopefully) return to a safe level. If there is little or no insulin available, the situation becomes serious, both in the short term and the long term.
What happens when the pancreas shuts down insulin production?
When the pancreas shuts down insulin production, blood glucose levels start to climb. If there is sufficient insulin in the bloodstream, say, from an insulin injection or insulin infusion from a pump, glucose levels (hopefully) return to a safe level. If there is little or no insulin available, the situation becomes serious, ...
What is the blood glucose level after a meal?
A blood glucose level that’s above 180 mg/dl one to two hours after eating a meal (postprandial) is considered to be hyperglycemia. Symptoms of hyperglycemia usually appear when glucose levels are at least 180 to 200. Keep in mind that you may not have all of the symptoms of hyperglycemia. Checking your blood glucose with a meter is crucial ...
How do you know if you have hyperglycemia?
The most common signs and symptoms of hyperglycemia are: · Feeling thirsty. · Feeling hungry (even “hangry”) · Frequent urination. · Blurry vision. · Feeling very tired and lethargic. · Headache. If your blood sugars are high for a longer period of time, you might realize that you’ve lost weight — despite eating your usual meals and snacks, ...
Why do people not give insulin?
Some people may omit insulin injections in public situations, such as in a restaurant or at work due to inconvenience, embarrassment or a desire to not let others know about their diabetes. Alcohol abuse is another instance that can lead to hyperglycemia.
Can you have hyperglycemia if you have a low?
You might also have hyperglycemia if you over-treat a low. Psychosocial issues may lead to hyperglycemia, too. Diabulimia, an eating disorder in a person with diabetes (typically type 1 diabetes) is a form of bulimia whereby the person intentionally restricts or omits insulin in order to lose weight.
How to treat hyperglycemia?
Treating Hyperglycemia. The first thing you should do to treat hyperglycemia is take insulin. Your doctor should explain to you your “correction factor,” which is the amount of insulin you will need to bring your blood sugar level down a certain amount (for example, 1 unit might lower your blood sugar by 50 mg/dL).
What to do if blood sugar is high after taking insulin?
It’s important to drink a lot of water or other carbohydrate-free beverages while treating hyperglycemia, and you should call your doctor if your blood sugar stays high after taking insulin.
How Does Hyperglycemia Happen?
Hyperglycemia happens when your body has too little insulin to use the sugar in your blood.
Why is it important to control blood sugar in children with T1D?
Controlling blood sugar is very important in children with T1D. Long-term hyperglycemia damages the eyes, heart, kidneys, and nerves, so it is important to maintain good glucose control to minimize the chances of this damage.
How long does it take for blood sugar to go up after eating?
Doctors may say you have hyperglycemia if your blood sugar is higher than 130 mg/dL after not eating or drinking for at least 8 hours (called fasting hyperglycemia) or if your blood sugar is higher than 180 mg/dL 2 hours after a meal (called postprandial or after-meal hyperglycemia). For people with diabetes, blood sugar control over ...
What is the medical term for high blood sugar?
Hyperglycemia is the medical term for high blood sugar (high blood glucose). It happens when sugar stays in your bloodstream instead of being used as energy. For people without diabetes, a healthy blood sugar level is about 70 to 140 milligrams per deciliter of blood (mg/dL). For people with diabetes, though, the target or healthy blood sugar range ...
What are the signs of hyperglycemia?
Having sweet-smelling or “fruity” breath. Cuts or sores that do not heal, infections, and unexplained weight loss may also be signs of long-term hyperglycemia. If you notice any of these symptoms, you should check your blood sugar. If your blood sugar is very high, you should also test for ketones in either your blood or urine.
What type of medication is prescribed for type 1 diabetes?
Other medications. Additional medications also may be prescribed for people with type 1 diabetes, such as: High blood pressure medications. Your doctor may prescribe angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors or angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs) to help keep your kidneys healthy.
How to manage diabetes?
Make a commitment to manage your diabetes. Take your medications as recommended. Learn all you can about type 1 diabetes. Make healthy eating and physical activity part of your daily routine. Establish a relationship with a diabetes educator, and ask your health care team for help.
Why is A1C important?
Compared with repeated daily blood sugar tests, A1C testing better indicates how well your diabetes treatment plan is working. An elevated A1C level may signal the need for a change in your insulin regimen, meal plan or both.
What does A1C mean?
It measures the percentage of blood sugar attached to the oxygen-carrying protein in red blood cells (hemoglobin). The higher your blood sugar levels, the more hemoglobin you'll have with sugar attached. An A1C level of 6.5 percent or higher on two separate tests indicates diabetes.
How long does it take to retest for Type 1 diabetes?
Retest again in 15 minutes to make sure it has risen to a safe level. Working. Type 1 diabetes can pose some challenges in the workplace. For example, if you work in a job that involves driving or operating heavy machinery, hypoglycemia could pose a serious risk to you and those around you.
How to get a diabetic to exercise?
Physical activity. Everyone needs regular aerobic exercise, and people who have type 1 diabetes are no exception. First, get your doctor's OK to exercise. Then choose activities you enjoy, such as walking or swimming, and make them part of your daily routine.
What does a blood sugar level of 200 mean?
Regardless of when you last ate, a random blood sugar level of 200 mg/dL (11.1 mmol/L) or higher suggests diabetes, especially when coupled with any of the signs and symptoms of diabetes, such as frequent urination and extreme thirst. Fasting blood sugar test. A blood sample will be taken after an overnight fast.
What is the first course of treatment for hyperglycemia in pregnancy?
The first course of treatment can include medical nutrition therapy, physical activity, and weight management, depending on pre-pregnancy weight and blood sugar monitoring.
What are the factors that affect the treatment of hyperglycemia?
The treatment of hyperglycemia depends on a variety of factors, including duration, frequency, and severity of hyperglycemia, as well as age, overall health, and cognitive function.
Why do women with gestational diabetes need insulin?
Women diagnosed with gestational diabetes may also need insulin to reduce the risk of hyperglycemia and keep blood sugars tightly controlled.
How to prevent type 2 diabetes?
Exercise. The ADA states that breaking up extended sedentary activity and avoiding extended periods of sitting may prevent type 2 diabetes for those at risk and may also aid in glycemic control for those with diabetes. 4 That's because exercise can help reduce hyperglycemia by burning glucose . For example, going for a walk after ...
What is the treatment for gestational diabetes?
Hyperglycemia in pregnancy can result in a diagnosis of gestational diabetes. The first type of treatment is medical nutrition therapy, physical activity, and weight management depending on pre-pregnancy weight and blood sugar monitoring.
What BMI is needed for type 2 diabetes?
The ADA suggests that, " Metabolic surgery should be recommended as an option to treat type 2 diabetes in screened surgical candidates with BMI ≥40 kg/m 2 (BMI ≥37.5 kg/m 2 in Asian Americans) and in adults with BMI 35.0–39.9 kg/m 2 (32.5–37.4 kg/m 2 in Asian Americans) who do not achieve durable weight loss and improvement in comorbidities (including hyperglycemia) with nonsurgical methods." 14
What foods affect blood sugar?
Eating excessive amounts of carbohydrates, such as refined grains (white bread, rolls, bagels, cookies, rice, pasta, crackers, sweets), sugary foods, and sweetened beverages can increase the risk of hyperglycemia.
How to manage hyperglycemia in type 1 diabetes?
People with both type 1 and type 2 diabetes can manage hyperglycemia by eating healthy, being active, and managing stress. In addition, insulin is a critical part of managing hyperglycemia for people with type 1 diabetes, while people with type 2 diabetes may need oral medications and eventually insulin to help them manage hyperglycemia.
What to do if you don't have diabetes?
If you don’t have diabetes and have any of the signs and symptoms of hyperglycemia, call your healthcare provider. Together you can work to manage your hyperglycemia.
How long does it take for blood glucose to go up after eating?
A person has hyperglycemia if their blood glucose is greater than 180 mg/dL one to two hours after eating. If you have hyperglycemia and it’s untreated for long periods of time, you can damage your nerves, blood vessels, tissues and organs.
What is the blood glucose level of a diabetic?
The condition is most often linked with diabetes. Hyperglycemia is blood glucose greater than 125 mg/dL (milligrams per deciliter) while fasting (not eating for at least eight hours; a person with a fasting blood glucose greater than 125 mg/dL has diabetes). A person has impaired glucose tolerance, or pre-diabetes, ...
What are the risk factors for hyperglycemia?
Major risk factors for hyperglycemia are: You have a family history of type 2 diabetes. You are African American, Native American, Hispanic or Asian American. You are overweight. You have high blood pressure or cholesterol. You have polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS). You have a history of gestational diabetes.
What causes insulin resistance?
Endocrine conditions, such as Cushing syndrome, that cause insulin resistance. Pancreatic diseases such as pancreatitis, pancreatic cancer and cystic fibrosis. Certain medications (such as diuretics and steroids). Gestational diabetes, which happens in 4% of pregnancies, and is due to decreased insulin sensitivity.
What does it mean when you have high blood sugar?
Hyperglycemia (High Blood Sugar) Hyperglycemia (high blood glucose) means there is too much sugar in the blood because the body lacks enough insulin. Associated with diabetes, hyperglycemia can cause vomiting, excessive hunger and thirst, rapid heartbeat, vision problems and other symptoms. Untreated hyperglycemia can lead to serious health ...
What is the link between hyperglycemia and diabetes?
The link between hyperglycemia and diabetes. Hyperglycemia, or high blood glucose, is a symptom that characterizes diabetes. Insufficient insulin production, resistance to the actions of insulin, or both can cause diabetes to develop. When a person eats carbohydrates, the body breaks them down into simple sugars that enter the bloodstream.
Why do people with diabetes need extra medication?
People with diabetes may need to take extra medication to keep their blood sugar levels stable during times of illness or stress.
How to monitor blood sugar at home?
A person can monitor their blood sugar at home with the help of a fingerstick or a continuous glucose monitoring system.
What is the fasting glucose level for prediabetes?
Doctors tend to diagnose prediabetes at a fasting glucose level of 100 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dl) and diabetes at 126 mg/dl. People with prediabetes would score 140–200 on an oral glucose tolerance test. Those with diabetes would score 200 and higher.
What is the name of the disease that characterizes diabetes?
Treatments. Summary. Hyperglycemia, or high blood glucose, is a symptom that characterizes diabetes. Insufficient insulin production, resistance to the actions of insulin, or both can cause diabetes to develop. When a person eats carbohydrates, the body breaks them down into simple sugars that enter the bloodstream.
What are the symptoms of type 2 diabetes?
Typical signs and symptoms of hyperglycemia include: frequent urination. increased thirst.
Is high blood sugar a sign of diabetes?
Hyperglycemia and diabetes. People with diabetes have consistently high blood sugar and ongoing monitoring is often necessary. People with prediabetes, in which blood sugar levels are higher than normal but not as high as they would be in diabetes, are at risk of developing diabetes.
How do I treat hyperglycemia?
You can often lower your blood sugar level by exercising. However, if your blood sugar is above 240 mg/dl, check your urine for ketones. If you have ketones, do not exercise.
How to lower blood sugar levels with ketones?
Exercising when ketones are present may make your blood sugar level go even higher. You'll need to work with your doctor to find the safest way for you to lower your blood sugar level. Cutting down on the amount of food you eat might also help. Work with your dietitian to make changes in your meal plan.
What is the term for high blood glucose?
Hyperglycemia (High Blood Glucose) Hyperglycemia is the technical term for high blood glucose (blood sugar). High blood sugar happens when the body has too little insulin or when the body can't use insulin properly.
What happens if you have type 2 diabetes?
If you have type 2, your body may have enough insulin, but it is not as effective as it should be. You ate more than planned or exercised less than planned. You have stress from an illness, such as a cold or flu. You have other stress, such as family conflicts or school or dating problems.
Do diabetics need a medical ID?
Many people with diabetes, particularly those who use insulin, should have a medical ID with them at all times.
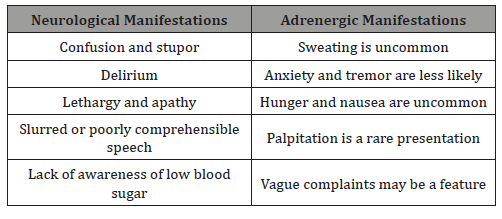
Diagnosis
Treatment
- Home treatment
Talk to your doctor about managing your blood sugar and understand how different treatments can help keep your glucose levels within your goal range. Your doctor may suggest the following treatments: 1. Get physical.Regular exercise is often an effective way to control your blood suga… - Emergency treatment for severe hyperglycemia
If you have signs and symptoms of diabetic ketoacidosis or hyperglycemic hyperosmolar state, you may be treated in the emergency room or admitted to the hospital. Emergency treatment can lower your blood sugar to a normal range. Treatment usually includes: 1. Fluid replacement.You'l…
Clinical Trials
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Coping and Support
- Treatment for type 1 diabetes includes: 1. Taking insulin 2. Carbohydrate, fat and protein counting 3. Frequent blood sugar monitoring 4. Eating healthy foods 5. Exercising regularly and maintaining a healthy weight The goal is to keep your blood sugar level as close to normal as possible to delay or prevent complications. Generally, the goal is to...
Preparing For Your Appointment
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiestesting new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.
Home Remedies and Lifestyle
- Careful management of type 1 diabetes can reduce your risk of serious — even life-threatening — complications. Consider these tips: 1. Make a commitment to manage your diabetes.Take your medications as recommended. Learn all you can about type 1 diabetes. Make healthy eating and physical activity part of your daily routine. Establish a relationship with a diabetes educator, and …
Prescriptions
- Diabetes can affect your emotions both directly and indirectly. Poorly controlled blood sugar can directly affect your emotions by causing behavior changes, such as irritability. There may be times you feel resentful about your diabetes. People with diabetes have an increased risk of depression and diabetes-related distress, which may be why many diabetes specialists regularly include a s…
Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
- If you suspect that you or your child might have type 1 diabetes, get evaluated immediately. A simple blood test can let your doctor know if you need further evaluation and treatment. After diagnosis, you'll need close medical follow-up until your blood sugar level stabilizes. A doctor who specializes in hormonal disorders (endocrinologist) generally coordinates diabetes care. Your h…
Emergency Situations
Surgeries
- Insulin
Insulin is the hormone responsible for controlling blood sugar levels in the body. People who have type 1 diabetes do not produce their own insulin. Therefore, most people with type 1 diabetes should be treated with multiple daily injections of meal time (or prandial) insulin and basal insuli… - Pramlintide
This medication is approved for use in patients with type 1 diabetes. It is used to delay gastric emptying and reduce blood sugars by reducing the secretion of glucagon.12 It can help people with type 1 diabetes lose weight (if they are overweight), as well as reduce blood sugars and low…
Complementary and Alternative Medicine
- Hyperglycemia in pregnancy can result in a diagnosis of gestational diabetes. The first course of treatment can include medical nutrition therapy, physical activity, and weight management, depending on pre-pregnancy weight and blood sugar monitoring. Lifestyle changes, specifically diet and exercise, are an essential component and all women need to control blood sugar.14Ho…