
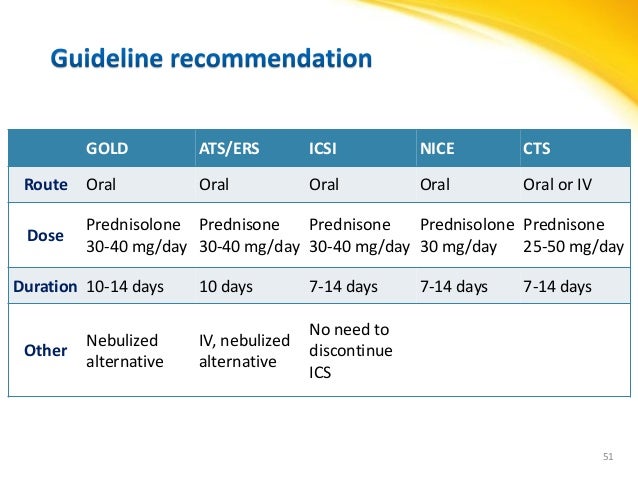
Medication
Long-term control medications such as inhaled corticosteroids are the most important medications used to keep asthma under control. These preventive medications treat the airway inflammation that leads to asthma symptoms. Used on a daily basis, these medications can reduce or eliminate asthma flare-ups.
Procedures
The main injections for asthma are: benralizumab (Fasenra) omalizumab (Xolair) mepolizumab (Nucala) reslizumab (Cinqaero) These medicines are known as biologic therapies. They are not suitable for everyone with asthma and can only be prescribed by an asthma specialist. The main side effect is discomfort where the injection is given.
Self-care
Short-acting beta-agonists are the first choice for quick relief of asthma symptoms. They include albuterol ( ProAir HFA, Proventil HFA, Ventolin HFA ), epinephrine ( …
Nutrition
Scheduled, daily inhaled corticosteroid (ICS) treatment is the currently preferred pharmacologic controller therapy for persistent asthma in individuals of all ages. Intermittent ICS dosing includes courses of ICS treatment used for brief periods, usually in response to symptoms or as an add-on with or without a long-acting beta 2 -agonist (LABA).
See more
Feb 16, 2005 · Systemic treatment with corticosteroids was introduced into the treatment of asthma in the mid-20th century; inhaled corticosteroids have been in use for over 35 years. The last 40 years have also seen the development of the first targeted asthma treatments: cromones, antileukotrienes, and anti-IgE.
What is the best natural remedy for asthma?
Sep 12, 2018 · Allergen-specific immunotherapy represents a potentially disease-modifying therapy for many patients with asthma, but should only be prescribed by physicians with appropriate training in allergy.
Which is more effective at treating asthma?
What is the ultimate goal of treatment in asthma?
Which is the best for asthma?
What is the most common treatment for asthma?
The most common asthma treatments are inhalers. These are considered the best asthma treatments for most people. This is because inhalers help get the medicine to the airways where it's needed. Almost everyone with asthma has a preventer inhaler and a reliever inhaler.
What are 4 treatments for asthma?
There are four types of asthma inhaler devices that deliver medicine: metered dose inhalers (MDI), dry powder inhalers (DPI), breath actuated inhalers, and soft mist inhalers.
What is a good treatment for asthma?
Short-acting beta-agonists are the first choice for quick relief of asthma symptoms. They include albuterol (ProAir HFA, Proventil HFA, Ventolin HFA), epinephrine (Asthmanefrin, Primatene Mist), and levalbuterol (Xopenex HFA).May 10, 2020
What is first line treatment for asthma?
Strength of RecommendationKey clinical recommendationsLabelReferencesInhaled corticosteroids are recommended as first-line treatment in children with acute asthma.A2,8,9The combination of a beta2 agonist and an inhaled corticosteroid is superior to the addition of a leukotriene modifier.A2,20–222 more rows•Sep 15, 2004
What are 5 treatments for asthma?
Types of long-term control medications include:Inhaled corticosteroids. These are the most common long-term control medications for asthma. ... Leukotriene modifiers. These include montelukast (Singulair), zafirlukast (Accolate) and zileuton (Zyflo). ... Combination inhalers. ... Theophylline. ... Biologics.
What is the typical treatment for asthma and how does it improve asthma symptoms?
Quick-relief inhalers (bronchodilators) quickly open swollen airways that are limiting breathing. In some cases, allergy medications are necessary. Long-term asthma control medications, generally taken daily, are the cornerstone of asthma treatment.Mar 5, 2022
What is the safest asthma medication?
There isn't one drug that's considered the safest asthma medication. Asthma drugs are usually used in combination with others for the best results in controlling symptoms and reducing attacks.Aug 26, 2021
How do inhalers help asthma?
The medicine helps open the airway and lets more air move in and out of your lungs and helps you breathe more easily. People with asthma use inhalers during an attack when their airways swell and become narrower. These attacks cause the person to cough, wheeze and have trouble breathing.Nov 17, 2020
What helps asthma without an inhaler?
What helps an asthma attack without an inhaler?Sit up straight to help keep the airway open (your child shouldn't lie down)Remain calm (distraction with TV or music can help)Try to breathe slowly and steadily (yoga breathing techniques and other techniques can help)Move away from triggers like cigarette smoke, etc.
What is the gold standard for asthma treatment?
The gold standard in asthma therapy is still a low-dose ICS as a controller together with an on-demand Short-acting beta-2-agonist (SABA). An LTRA (Leucotriene-receptor antagonist) can be tried as a second choice.Jul 1, 2016
What is the drug of choice for mild asthma?
Theophylline. You take this bronchodilator daily in pill form to treat mild asthma. Theophylline (Theo-24, others) relaxes the airways and decreases the lungs' response to irritants. It can be helpful for nighttime asthma symptoms.
How long does asthma stay open?
They act quickly and should be taken at the first sign of symptoms. They keep the airways open for four to six hours.
What is a metered dose inhaler?
There are four types of asthma inhaler devices that deliver medicine: metered dose inhalers (MDI), dry powder inhalers (DPI), breath actuated inhalers, and soft mist inhalers. Metered dose inhalers have medicine plus a propellant. The propellant sprays the medicine out of the inhaler in a short burst.
Why are anti-inflammatory medications called controllers?
Anti-inflammatories (steroidal) come in many different forms. They are also called controllers because they help to control or prevent asthma symptoms. They reduce swelling and extra mucus inside the airways. They will not relieve sudden symptoms.
What are the changes in the airways?
There are three changes in the airways when you have asthma: This swelling, clogging, and muscle tightening makes your airways smaller or narrower. This makes it harder for air to flow easily through your airways, and it becomes harder to breathe. There are asthma medicines that target these three changes.
Why is it important to improve indoor air quality?
Improving the indoor air quality in your home is an important part of asthma control. Your indoor air can be more polluted than outside air. Our interactive Healthy Home can show you ways to improve the indoor air quality of your home. A healthier home can reduce your exposure to allergens and irritants.
How does a syringe work?
They work by targeting a cell or protein in your body to prevent airway swelling. They are for moderate-to-severe asthma that is hard to treat with ICS and/or other medicines, or people with asthma dependent on OCS. They are for specific types of asthma and will not work for everyone.
Can asthma be treated?
Unfortunately, there is no cure for asthma. For that reason, you may have asthma symptoms when exposed to triggers. This is the case even if you don’t have symptoms very often. Your triggers can change over time, and your treatment will depend on two things: how severe your asthma is, and how often you have symptoms.
How to manage asthma?
Taking an active role in managing your asthma treatment will help you maintain better long-term asthma control, prevent asthma attacks and avoid long-term problems. Create a written asthma action plan with your doctor. This written plan will serve as an asthma treatment guide tailored to your specific needs. It will help you follow these three ...
What are the best medications for asthma?
There are two main types of medications used to treat asthma: 1 Long-term control medications such as inhaled corticosteroids are the most important medications used to keep asthma under control. These preventive medications treat the airway inflammation that leads to asthma symptoms. Used on a daily basis, these medications can reduce or eliminate asthma flare-ups. 2 Quick-relief inhalers contain a fast-acting medication such as albuterol. These medications are sometimes called rescue inhalers. They're used as needed to quickly open your airways and make breathing easier. Knowing when to use these medications can help prevent an impending asthma attack.
What is the best test for asthma?
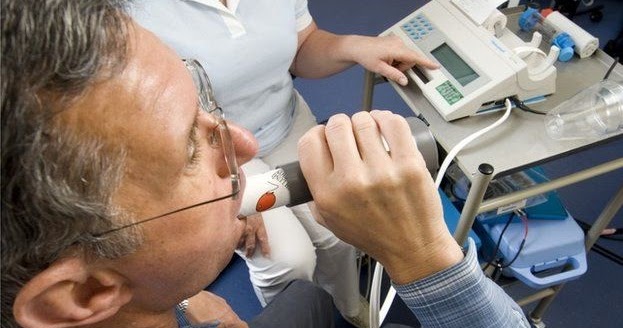
If your lungs aren't working as well as they should be, your asthma may not be under control. There are two main lung function tests: Peak flow. This test is done at home with a simple hand-held device called a peak flow meter. A peak expiratory flow measurement indicates how fast you can force air out of your lungs.
What to do if your lungs aren't working?
When your lungs aren't working as well as they should be, you may need to adjust your medications according to the plan you made with your doctor ahead of time. Your written asthma action plan will let you know exactly when and how to make adjustments.
How to keep a record of asthma?
It will help you follow these three important steps and keep a good record of your asthma treatment: 1. Track your symptoms. Write down your symptoms in an asthma diary each day. Recording symptoms can help you recognize when you need to make treatment adjustments according to your asthma action plan. Use your asthma diary to record:
What is a quick relief inhaler?
Quick-relief inhalers contain a fast-acting medication such as albuterol. These medications are sometimes called rescue inhalers. They're used as needed to quickly open your airways and make breathing easier. Knowing when to use these medications can help prevent an impending asthma attack.
How to keep asthma under control?
Long-term control medications such as inhaled corticosteroids are the most important medications used to keep asthma under control. These preventive medications treat the airway inflammation that leads to asthma symptoms. Used on a daily basis, these medications can reduce or eliminate asthma flare-ups.
What is the best treatment for asthma?
Inhalers, which are devices that let you breathe in medicine, are the main treatment. Tablets and other treatments may also be needed if your asthma is severe. You'll usually create a personal action plan with a doctor or asthma nurse.
Why do you need a preventer inhaler?
You use a preventer inhaler every day to reduce the inflammation and sensitivity of your airways, which stops your symptoms occurring. It's important to use it even when you do not have symptoms. Speak to a GP or asthma nurse if you continue to have symptoms while using a preventer inhaler.
What is a spacer inhaler?
a sore throat. You can help prevent these side effects by using a spacer, which is a hollow plastic tube you attach to your inhaler, as well as by rinsing your mouth after using your inhaler. Asthma UK: preventer inhalers.
Can you take biologics with asthma?
These medicines are known as biologic therapies. They are not suitable for everyone with asthma and can only be prescribed by an asthma specialist. The main side effect is discomfort where the injection is given. Asthma UK: biologic therapies for severe asthma.
Is bronchial thermoplasty safe?
A procedure called bronchial thermoplasty may be offered as a treatment for severe asthma. It works well and there are no serious concerns about its safety. You will be sedated or put to sleep using a general anaesthetic during a bronchial thermoplasty.
Can breathing exercises help with asthma?
There's little evidence to suggest many of these treatments help. There's some evidence that breathing exercises can improve symptoms and reduce the need for reliever medicines in some people, but they should not be used instead of your medicine. Asthma UK: complementary therapies for asthma.
Can you use a reliever and preventer inhaler?
If using reliever and preventer inhalers does not control your asthma, you may need an inhaler that combines both. Combination inhalers are used every day to help stop symptoms occurring and provide long-lasting relief if they do occur. It's important to use it regularly, even if you do not have symptoms.
What is asthma treatment?
Asthma Treatment. Asthma Medications. Asthma and Anxiety. If you or a loved one has asthma, you should know about the best treatments for short-term relief and long-term control. This will help you and your doctor manage the symptoms. If you have symptoms or an asthma attack, it's important to know when to call your doctor to prevent an emergency.
What is the best medication for asthma?
Short-acting beta-agonists are the first choice for quick relief of asthma symptoms. They include albuterol (ProAir HFA, Proventil HFA, Ventolin HFA), epinephrine (Asthmanefrin, Primatene Mist), and levalbuterol (Xopenex HFA). Anticholinergics such as ipratropium (Atrovent) lessen mucus in addition to opening your airways.
What is the best way to reduce swelling in the airways?
Leukotriene modifiers relax the smooth muscles around your airways and ease swelling. You can take them as pills or liquids. These include montelukast (Singular), zafirlukast (Accolate), and zileuton (Zyflo). Cromolyn prevents your airways from swelling when they come into contact with an asthma trigger.
What to do if your rescue inhaler doesn't work?
Likewise, if you’re having to use your rescue inhaler too often, see your doctor. You may need to change your asthma treatment for better control.
What is the best long term control medicine?
Inhaled corticosteroids are the most effective long-term control medicines. These aren’t the same as anabolic steroids that people use to grow muscle. They include beclomethasone (Qvar RediHaler), budesonide (Pulmicort Flexhaler), ciclesonide (Alvesco), fluticasone (Flovent HFA), and mometasone (Asmanex Twisthaler).
Can steroids cause thrush?
Many medications have side effects. For example, inhaled steroids can cause mild problems, such as thrush infections and a sore throat, or more serious ones including eye disorders and bone loss. Keep your doctor up to date with how well your treatment is working and whether you have side effects.
What is the best way to open your airways?
Caffeine. It’s a mild bronchodilator, meaning it can open your airways, but it doesn’t work as fast as medications. Avoid caffeine for several hours before any medical appointment that might include a lung function test. Choline. This helps your body work the way it should.
What is the best treatment for asthma?
For individuals with mild persistent asthma, either of the following two treatments are recommended as part of Step 2 therapy: 1) a daily low-dose ICS and as-needed SABA for quick-relief therapy, or 2) intermittent as-needed SABA and ICS used one after the other for worsening asthma.
What is the focus of the 2020 Asthma Management Guidelines?
This Clinician’s Guide summarizes the 2020 Focused Updates to the Asthma Management Guidelines: A Report from the National Asthma Education and Prevention Program Coordinating Committee Expert Panel Working Group to help clinicians integrate the new recommendations into clinical care. The full 2020 Report, which is focused on selected topics rather than a complete revision of the 2007 Expert Panel Report 3: Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Asthma (EPR-3), can be found at nhlbi.nih.gov/asthmaguidelines. This summary guide should be used in conjunction with the full report. The Guide is organized by the following topics:
How old do you have to be to take ICS?
In individuals ages 12 years and older with mild persistent asthma, the Expert Panel conditionally recommends either daily low-dose ICS and as-needed SABA for quick-relief therapy or as-needed ICS and SABA used concomitantly.
When to use subcutaneous immunotherapy?
In individuals ages 5 years and older with mild to moderate allergic asthma , the Expert Panel conditionally recommends the use of subcutaneous immunotherapy as an adjunct treatment to standard pharmacotherapy in those individuals whoseasthma is controlled at the initiation, build up, and maintenance phases of immunotherapy.
What is ICS therapy?
Scheduled, daily inhaled corticosteroid (ICS) treatment is the currently preferred pharmacologic controller therapy for persistent asthma in individuals of all ages. Intermittent ICS dosing includes courses of ICS treatment used for brief periods, usually in response to symptoms or as an add-on with or without a long-acting beta2-agonist (LABA). Recommendations for ICS treatment are organized by age.
When should I use FeNO?
In individuals ages 5 years and older with persistent allergic asthma, for whom there is uncertainty in choosing, monitoring, or adjusting anti-inflammatory therapies based on history, clinical findings, and spirometry, the Expert Panel conditionally recommends the addition of FeNO measurement as part of an ongoing asthma monitoring and management strategy that includes frequent assessments.
Does FeNO test for asthma?
FeNO measurement may support a diagnosis of asthma in individuals for whom the diagnosis is uncertain, even after a complete history, physical examination, and spirometry testing including bronchodilator responsiveness.
How to treat asthma?
The treatment of asthma involves the treatment of the patient during fits and between the fits. The general indications are: 1 To allay the spasm during the paroxysm; 2 To find out and remove the exciting cause … 3 To treat complications and sequelae and to improve the general health.
How effective are corticosteroids for asthma?
Inhaled corticosteroids have been recommended and used in the treatment of asthma for just over 30 years; they are very effective as “asthma-controller” therapies, but there are no convincing data that they are disease-modifying treatments.
How long does a bronchodilator last?
These agents had rapid onset of action, produced bronchodilation lasting 4 to 6 hours, and became the “bronchodilator of choice.”. Since the mid-1980s, bronchoconstriction that could be relieved by the inhalation of a specific β 2 agonist was commonly included as a diagnostic criterion of asthma.
When did corticosteroids start being used?
Western medicine began to use adrenergic stimulants approximately 100 years ago, but they were likely used in Asian medicine long before that. Systemic treatment with corticosteroids was introduced into the treatment of asthma in the mid-20th century; inhaled corticosteroids have been in use for over 35 years.
Who wrote the book "Asthma"?
In Stedman's Twentieth Century Practice, published in 1896, Sir Thomas Granger Stewart and George Alexander Gibson ( 3) wrote about asthma: The treatment of asthma involves the treatment of the patient during fits and between the fits. The general indications are: To allay the spasm during the paroxysm;
When was asthma first discovered?
Although asthma has been described as a medical entity since the time of Aretaeus, the Cappadocian, in approximately 100 a. d. ( see review by Marketos and Ballas [ 1 ]), the constellation of physical findings and signs that we currently recognize as asthma dates from the work of John Floyer ( 2) in 1698.
Do corticosteroids cause cataracts?
Inhaled corticosteroids have side effects. When used on a regular basis for long periods of time, there are documented adverse effects, such as loss of stature ( 35, 36 ), decreased bone mineralization, glaucoma, and cataracts ( 37 – 39 ). Inhaled corticosteroids have been recommended and used in the treatment of asthma for just over 30 years;
What is the best medication for asthma?
Inhaled rapid-acting beta2-agonists are the preferred reliever medications for the treatment of acute symptoms, and should be prescribed to all patients with asthma. In Canada, several short-acting beta2-agonists (SABAs; e.g., salbutamol, terbutaline) and one LABA (formoterol) are approved for this indication.
What is the goal of asthma management?
The primary goal of asthma management is to achieve and maintain control of the disease in order to prevent exacerbations (abrupt and/or progressive worsening of asthma symptoms that often require immediate medical attention and/or the use of oral steroid therapy) and reduce the risk of morbidity and mortality.
What is the most common respiratory disease in Canada?
Background. Asthma remains the most common chronic respiratory disease in Canada, affecting approximately 10% of the population [1]. It is also the most common chronic disease of childhood [2].
How old do you have to be to take ICS?
For most children, ICS dose escalation (to a moderate dose) is the preferred approach to achieve control, while the addition of another class of medications (usually a LABA) is recommended for patients over 12 years of age [15, 16, 23].
What is the differential diagnosis of asthma?
The differential diagnosis of asthma is unique for infants and young children and includes anatomic defects (laryngo- or tracheomalacia, congenital heart defects), physiological defects (primary ciliary dyskinesia) and genetic conditions such cystic fibrosis and primary immunodeficiency, to name just a few conditions.
Is asthma a respiratory disorder?
Asthma is the most common respiratory disorder in Canada, and contributes to significant morbidity and mortality. A diagnosis of asthma should be suspected in patients with recurrent cough, wheeze, chest tightness and dyspnea, and should be confirmed using objective measures of lung function (spirometry preferred).
Diagnosis
Clinical Trials
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Alternative Medicine
Specialist to consult
Coping and Support
- Physical exam
Your doctor will perform a physical exam to rule out other possible conditions, such as a respiratory infection or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Your doctor will also ask you questions about your signs and symptoms and about any other health problems.
Preparing For Your Appointment
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiestesting new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.
Treatment
- Although many people with asthma rely on medications to prevent and relieve symptoms, you can do several things on your own to maintain your health and lessen the possibility of asthma attacks.
Preparation
- Certain alternative treatments may help with asthma symptoms. However, keep in mind that these treatments are not a replacement for medical treatment, especially if you have severe asthma. Talk to your doctor before taking any herbs or supplements, as some may interact with the medications you take. In most cases, more research is needed to see how well alternative reme…
Overview
- Asthma can be challenging and stressful. You may sometimes become frustrated, angry or depressed because you need to cut back on your usual activities to avoid environmental triggers. You may also feel limited or embarrassed by the symptoms of the disease and by complicated management routines. But asthma doesn't have to be a limiting condition. The best way to overc…
Symptoms
- You're likely to start by seeing your family doctor or a general practitioner. However, when you call to set up an appointment, you may be referred to an allergist or a pulmonologist. Because appointments can be brief, and because there's often a lot of ground to cover, it's a good idea to be well prepared. Here's some information to help you get ready for your appointment, as well a…
Prevention
Uses
Results
- A nebulizer is a machine with tubing that takes liquid medicine and turns it into a mist that you inhale. Nebulizers are an option for anyone who has difficulty using an asthma inhaler.
Medical uses
- Yes. Asthma symptoms often occur at night. Many people wake up with asthma symptoms such as coughing or wheezing. You can control nighttime symptoms by taking asthma controller medicines on a regular basis.