
First aid and treatment for hydrogen sulfide poisoning
- oxygen inhalation Remove the person from the alleged site of poisoning.
- Free him from tight clothing: take off his tie, unbutton his shirt, blouse.
- If possible, oxygen inhalation should be performed.
- Rinse the mucous membranes with running water for 10 minutes. ...
- If the poison got inside - you need to do a gastric lavage with warm water.
Full Answer
What PPE is needed when working with hydrogen sulfide (H2S)?
Use respiratory and other personal protective equipment. If engineering and administrative controls cannot reduce hydrogen sulfide below OSHA's permissible exposure limit, employers must provide respiratory protection and other personal protective equipment (PPE), such as eye protection and possibly fire-resistant clothing.
How much H2S is fatal?
H2S is immediately fatal when concentrations are over 500-1000 parts per million (ppm) but exposure to lower concentrations, such as 10-500 ppm, can cause various respiratory symptoms that range from rhinitis to acute respiratory failure.
How do you remove hydrogen sulfide?
The signaling molecule hydrogen sulfide (H 2 S) plays a critical role in antibiotic ... Blocking its action would represent then a way to remove an important defense against antibiotics, but available CSE inhibitors have a low potency against bacterial ...
Who is at risk of hydrogen sulfide exposure?
[1] The biggest risk from hydrogen sulfide happens on farms with manure storage areas, in sewage treatment plants, and in factories that use the gas for industrial processes. In these places, the gas can reach levels that cause serious harm and death in hours or even minutes.
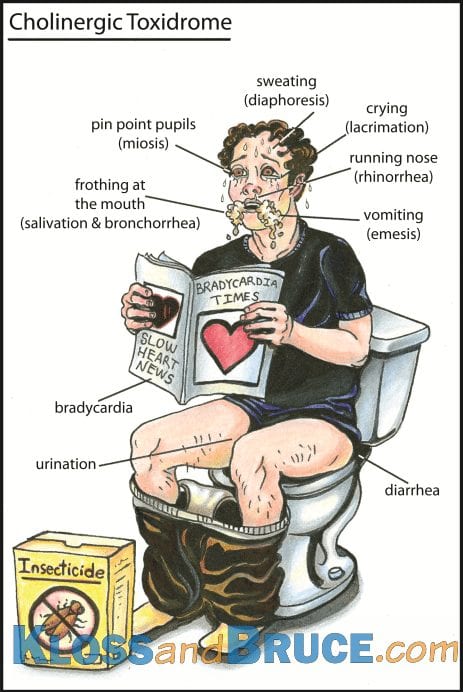
How is hydrogen sulfide poisoning treated?
Nitrite therapy (found in the cyanide antidote kit) has been suggested as a therapy for hydrogen sulfide exposure. Amyl nitrite is given by inhalation (for 30 seconds every minute until an intravenous line is established) followed by intravenous sodium nitrite (300 mg over absolutely no less than 5 minutes).
How do you neutralize hydrogen sulfide?
When dealing with a hydrogen sulfide gas leak, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration recommends using water to spray down the gas, then adding sodium bicarbonate to neutralize it.
How do you know if you have hydrogen sulfide poisoning?
Symptoms of acute exposure include nausea, headaches, delirium, disturbed equilibrium, tremors, skin and eye irritation, and convulsions. Inhaling high concentrations can produce extremely rapid unconsciousness and death. Dermal exposure to the liquefied gas can cause frostbite injury.
Can you survive hydrogen sulfide?
Fifty percent of people exposed to hydrogen sulfide for just five minutes at 800 ppm will not survive, and a single breath at 1000 ppm causes immediate death. Common effects of inhaling low concentrations of hydrogen sulfide (10 ppm or less) are burning eyes, coughing and shortness of breath.
What are the long term effects of H2S exposure?
Prolonged exposure may cause nausea, tearing of the eyes, headaches or loss of sleep. Airway problems (bronchial constriction) in some asthma patients. Possible fatigue, loss of appetite, headache, irritability, poor memory, dizziness. Slight conjunctivitis ("gas eye") and respiratory tract irritation after 1 hour.
How do you neutralize Sulphur?
Baking soda is well known for erasing odours. And the best thing is that it's very easy to use and efficient too. If the smell is coming from your clothes then, soak them in baking soda before washing. You can also sprinkle baking soda in all the corners of your house to get rid of the sulphur scent.
How is sewer gas poisoning treated?
If there's only a mild sewer gas leak, the first step for treatment is to air out the house and call a plumber to come and inspect and fix the leak. Getting some fresh air can help reduce your symptoms, too. Higher levels of exposure to sewer gas require immediate medical attention.
How long does hydrogen sulfide stay in your system?
Any absorbed hydrogen sulfide does not accumulate in the body as it is rapidly metabolised in the liver and excreted in the urine. Hydrogen sulfide usually breaks down in air in about 3 days and is dispersed by wind. Therefore exposure is only likely to continue if there is an ongoing source.
What steps is your employer required to take to protect you against hydrogen sulfide exposure?
For exposures below 100 ppm, use an air-purifying respirator with specialized canisters/cartridges for hydrogen sulfide. A full face respirator will provide eye protection....Control ExposuresUse exhaust and ventilation systems to reduce hydrogen sulfide levels. ... Train and educate workers about hazards and controls.More items...
How do you test for hydrogen sulfide?
1:425:57Hydrogen sulfide test (Biochemical assay) - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThe hydrogen sulfide will combine with the iron to form ferric sulfide which is a black precipitateMoreThe hydrogen sulfide will combine with the iron to form ferric sulfide which is a black precipitate any blackening of the medium indicates the reduction of sulfur.
What causes hydrogen sulfide in the body?
Your body makes small amounts of hydrogen sulfide. Hydrogen sulfide is produced by the natural bacteria in your mouth. It is also produced when some types of proteins are broken down by bacteria in the intestines.
What are the symptoms of hydrogen sulfide exposure?
Symptoms of acute exposure include nausea, headaches, delirium, disturbed equilibrium, tremors, convulsions, and skin and eye irritation. Inhalation of high concentrations of hydrogen sulfide can produce extremely rapid unconsciousness and death. Exposure to the liquified gas can cause frostbite injury.
What is hydrogen sulfide?
Hydrogen sulfide's can cause inhibition of the cytochrome oxidase enzyme system resulting in lack of oxygen use in the cells. Anaerobic metabolism causes accumulation of lactic acid leading to an acid-base imbalance. The nervous system and cardiac tissues are particularly vulnerable to the disruption of oxidative metabolism and death is often the result of respiratory arrest. Hydrogen sulfide also irritates skin, eyes, mucous membranes, and the respiratory tract. Pulmonary effects may not be apparent for up to 72 hours after exposure.
How long does hydrogen sulfide affect the respiratory system?
Hydrogen sulfide also irritates skin, eyes, mucous membranes, and the respiratory tract. Pulmonary effects may not be apparent for up to 72 hours after exposure. Children do not always respond to chemicals in the same way that adults do. Different protocols for managing their care may be needed.
Why are children exposed to the same levels of hydrogen sulfide as adults?
Children exposed to the same levels of hydrogen sulfide as adults may receive larger doses because they have greater lung surface area: body weight ratios and increased minute volumes:weight ratios. In addition, they may be exposed to higher levels than adults in the same location because of their short stature and the higher levels of hydrogen sulfide found nearer to the ground. Children may be more vulnerable to corrosive agents than adults because of the relatively smaller diameter of their airways.
Is hydrogen sulfide absorbed by the lungs?
Inhalation is the major route of hydrogen sulfide exposure. The gas is rapidly absorbed by the lungs. The odor threshold (0.5 ppb) is much lower than the OSHA ceiling (20 ppm). However, although its strong odor is readily identified, olfactory fatigue occurs at high concentrations and at continuous low concentrations.
Is hydrogen sulfide a reliable indicator of hydrogen sulfide?
For this reason, odor is not a reliable indicator of hydrogen sulfide's presence and may not provide adequate warning of hazardous concentrations. Hydrogen sulfide is slightly heavier than air and may accumulate in enclosed, poorly ventilated, and low-lying areas.
Does hydrogen sulfide have a rotten egg smell?
Hydrogen sulfide has a characteristic rotten-egg odor; however, olfactory fatigue may occur and consequently it may not provide adequate warning of hazardous concentrations. Hydrogen sulfide is well absorbed through the lungs; cutaneous absorption is minimal. Exposure by any route can cause systemic effects.
What is the best treatment for hydrogen sulfide poisoning?
Recommended treatment typically includes using the hydroxocobalamin or sodium nitrate from a cyanide antidote kit. It is important to note that this treatment is considered advanced first aid and should only be performed by someone trained to manage hydrogen sulfide exposure. If you work around hydrogen sulfide, a trained medic may have this in their first aid kit.
How to help someone with hydrogen sulfide?
Get to Fresh Air. The best thing you can do for someone suffering from hydrogen sulfide exposure is to move them to a well-ventilated place with fresh air. Removing them from the area stops any further poisoning and gives them a moment to breathe normally.
What to do if hydrogen sulfide is not cut off?
When seconds count, the arrival of a HAZMAT team and an ambulance can mean life and death. If the gas has not been cut off, it will form an increasingly deadly haze that is both invisible and imperceptible to smell. A specialized team can enter the area with proper equipment and air tanks to manage the situation.
What is the best way to clean your eyes from hydrogen sulfide?
Eye Shower. Hydrogen sulfide burns eyes, causing intense stinging, damage, and even blindness. After moving to a safe place, use a chemical shower to wash the victim’s eyes and body. They should carefully remove their clothes, as the fabric likely absorbed and retained some gas.
Is hydrogen sulfide dangerous?
It should be noted, however, that if a victim of hydrogen sulfide exposure is stumbling or collapses, it may be too dangerous to retrieve them without a self-contained breathing apparatus and a protective suit. When there’s that much gas in the area, you should leave rescue to trained professionals.
Can you use hydrogen sulfide in first aid?
It is important to note that this treatment is considered advanced first aid and should only be performed by someone trained to manage hydro gen sulfide exposure. If you work around hydrogen sulfide, a trained medic may have this in their first aid kit.
Is it too late to treat hydrogen sulfide?
TREATMENT FOR HYDROGEN SULFIDE EXPOSURE. Hydrogen sulfide exposure presents many frightening symptoms. Sometimes it’s too late for preventative measures and you must treat the immediate symptoms. When that happens, you must act fast. While treatment is best left to the professionals, there are a few early treatment options for hydrogen sulfide ...
What is the best way to carry a victim out of the site of exposure?
Assess whether the patient has the ability to be carried off; if the victim is suspected of an injury sustained from exposure, ensure proper care for mobilization such as a neck brace and a spinal stretcher to be used to carry the victim out of the site of exposure
What is the purpose of IV fluids?
IV fluids and vasopressors are used to treat victims with abnormal low blood pressure (hypotensive) – Vasopressor: a type of drug (depending on the ingredients) that constrict the smooth muscles that make up the blood vessels, reducing the circumference of the blood vessels causing an increase in blood pressure.
Can liquefied gas cause frostbite?
Since direct exposure to the liquefied gas can cause frostbite, determine whether the patient has frostbite – if so, carefully apply blankets to the affected area to help warm the exposed area encourage circulation
How does hydrogen sulfide affect the human body?
The health effects of hydrogen sulfide depend on how much H2S a worker breathes and for how long. However, many effects are seen even at low concentrations. Effects range from mild, headaches or eye irritation, to very serious, unconsciousness and death.
Is a sandbox flammable?
It is highly flammable and toxic, even at low concentrations. It is heavier than air and may travel along the ground. It can build up in low-lying areas, and in confined spaces (including enclosed, poorly ventilated areas, such as manure pits, sewers, manholes, and underground vaults).
Is H2S flammable?
It is extremely flammable and highly toxic. Hydrogen sulfide is used or produced in a number of industries, such as.
Is hydrogen sulfide dangerous?
Because it is heavier than air, hydrogen sulfide can collect in low-lying and enclosed spaces, such as manholes, sewers, and underground telephone vaults. Its presence makes work in confined spaces potentially very dangerous. The health effects of hydrogen sulfide depend on how much H2S a worker breathes and for how long.
What is hydrogen sulfide used for?
Hydrogen sulfide is used in many industries. For example, it’s used to produce textiles. Some examples of workers at risk of being exposed to hydrogen sulfide include the following:
What is HHE in health?
The Health Hazard Evaluation Program (HHE) conducts onsite investigations of possible worker exposure to chemicals. Search the HHE database for more information on chemical topics.
How does hydrogen sulfide affect you?
Hydrogen sulfide gas causes a wide range of health effects. Workers are primarily exposed to hydrogen sulfide by breathing it. The effects depend on how much hydrogen sulfide you breathe and for how long. Exposure to very high concentrations can quickly lead to death.
What happens if you breathe hydrogen sulfide?
What about longer term health effects? Some people who breathed in levels of hydrogen sulfide high enough to become unconscious continue to have headaches and poor attention span, memory, and motor function after waking up. Problems with the cardiovascular system have also been reported at exposures above permissible exposure limits. People who have asthma may be more sensitive to hydrogen sulfide exposure. That is, they may have difficulty breathing at levels lower than people without asthma.
What is the NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards?
NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) Publication No. 2005-149. Provides physical descriptions, exposure limits, measurement methods, personal protection and sanitation, first aid, respirator recommendations, exposure routes, symptoms, target organs, and other information about hydrogen sulfide.
Is hydrogen sulfide flammable?
Hydrogen sulfide is a highly flammable, explosive gas, and can cause possible life-threatening situations if not properly handled. In addition, hydrogen sulfide gas burns and produces other toxic vapors and gases, such as sulfur dioxide.
Can hydrogen sulfide cause frostbite?
In addition to exposure to hydrogen sulfide in the air, exposure to liquid hydrogen sulfide can cause "blue skin" or frostbite. If clothing becomes wet, avoid ignition sources, remove the clothing and isolate it in a safe area to allow it to evaporate.
What is the effect of H2S on the human body?
The clinical effects of H2S depend on its concentration and the duration of exposure. H2S is immediately fatal when concentrations are over 500-1000 parts per million (ppm) but exposure to lower concentrations, such as 10-500 ppm, can cause various respiratory symptoms that range from rhinitis to acute respiratory failure. H2S may also affect multiple organs, causing temporary or permanent derangements in the nervous, cardiovascular, renal, hepatic, and hematological systems. We present a case of occupational exposure to H2S leading to multi-organ involvement, acute respiratory failure, organizing pneumonia, and shock resembling acute sepsis. The patient also developed mild obstructive and restrictive pulmonary disease and peripheral neuropathy.
Why is H2S considered a knock down gas?
Hence, H2S has been referred to as the “knock down gas” because inhalation of high concentrations can cause immediate loss of consciousness and death.2,3How ever, prolonged exposure to lower concentrations, such as 10-500 ppm, can cause various respiratory symptoms that range from rhinitis to acute respiratory failure.
Is H2S a toxic substance?
Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) is responsible for many incidents of occupational toxic exposure, especially in the petroleum industry. The clinical effects of H2S depend on its concentration and the duration of exposure. H2S is immediately fatal when concentrations are over 500-1000 parts per million (ppm).
Is H2S a hazard?
There are many cases of H2S exposure in the agricultural industry4and their prevalence has increased markedly with the development of porcine confinement facilities.1,5H2S is the primary chemical hazard of natural gas production.6We report a severe case of hydrogen sulfide (H2S) intoxication. The patient survived long enough to observe the sequelae of this entity, which can include neuropsychiatric morbidity.
What is the best treatment for sulfide poisoning?
Two cyanide antidotes—hydroxocobalamin and sodium nitrite—have been tested as sulfide antidotes; hydroxocobalamin binds sulfide and nitrite generates both methemoglobin, which binds sulfide, and nitric oxide, which could displace sulfide from cytochrome C oxidase15,22,23,24. Both agents have shown some benefit in animal models, but both have to be administered either before or immediately after sulfide exposure15,25,26. A sulfide-poisoned person treated with hydroxocobalamin died, but he was moribund when the hydroxocobalamin was given27. Sodium nitrite may be beneficial in sulfide-poisoned humans, but only when administered within minutes of exposure28.
How does sulfide become toxic?
At about 3–30-fold higher concentrations, sulfide becomes toxic by binding to and inhibiting cytochrome C oxidase in complex IV of the electron transport chain , the last complex in the chain prior to ATP synthesis by complex V3,4,5.
What is cobinamide used for?
Cobinamide Rescues Flies and Mice Exposed to H2S Gas.
How long does it take for flies to recover from H2S exposure?
We found that within one to two minutes of exposing flies to H2S, the flies fell motionless; this recapitulates the rapid “knock-down” and unconscious state experienced by humans exposed to H2S gas1,15. After 20 min of H2S exposure, the flies were transferred to ambient air, and, over the ensuing hour, ~20% of flies recovered, with few flies recovering beyond that time (Fig. 3a). In contrast, ~65% of flies that had been grown on food containing 100 or 200 μM cobinamide recovered from the H2S exposure, while flies grown on food containing 100 or 200 μM hydroxocobalamin showed either no improvement compared to control flies or a 40% recovery rate, respectively (Fig. 3a,b). The improved recovery of cobinamide-fed flies compared to hydroxocobalamin-fed flies was not due to greater cobinamide absorption, because the two drugs yielded similar concentrations of ~2 μM; exclusive of the heads, total body cobinamide and hydroxocobalamin concentrations were measured (Supplementary Fig. 3).
What is the effect of sulfur on mitochondria?
Sulfide’s inhibition of complex IV of the mitochondrial electron transport system could cause cellular toxicity via reduced ATP production and/or generation of oxidative stress .
Is H2S soluble in water?
Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) is readily water soluble , and, at physiological pH, about two-thirds exists as hydrogen sulfide ion (HS—) and one-third as undissociated H2S1. We use the generic term “sulfide” to refer to both species. Sulfide is an endogenous signal transmitter via protein sulfhydration, and, at low intracellular concentrations—0.01 to 1 μM—donates electrons to complex II of the mitochondrial electron transport chain, thereby stimulating ATP production2,3,4,5,6. At about 3–30-fold higher concentrations, sulfide becomes toxic by binding to and inhibiting cytochrome C oxidase in complex IV of the electron transport chain, the last complex in the chain prior to ATP synthesis by complex V3,4,5. Cyanide, which also inhibits cytochrome C oxidase, increases mitochondrial generation of superoxide and induces oxidative stress in cells7,8. Sulfide could also be expected to induce oxidative stress, but the sulfur in sulfide is in the −2 oxidation state, the most reduced form of sulfur. Sulfide, therefore, has reducing potential—the two-electron redox potential of H2S is +0.17 V at pH 7—and sulfide’s effect on the cellular redox state is controversial7,9,10,11,12,13,14.
Is hydrogen sulfide toxic?
Hydrogen sulfide is a highly toxic gas —second only to carbon monoxide as a cause of inhalational deaths. Its mechanism of toxicity is only partially known, and no specific therapy exists for sulfide poisoning. We show in several cell types, including human inducible pluripotent stem cell (hiPSC)-derived neurons, ...
