
Explore
Feb 10, 2005 · For patients with newly diagnosed deep vein thrombosis (DVT), good evidence indicates that outpatient treatment is safe and effective using low-molecular-weight heparin and an oral anticoagulant until the international normalized ratio (INR) is in therapeutic range.
What is the optimal duration of treatment for DVT?
The initial treatment of both DVT and PE is anticoagulation. Anticoagulants, commonly referred to as “blood thinners,” do not actually thin blood. Instead, they block the action of various clotting factors and prevent blood clots from growing. In this way, they allow the body’s own natural processes to destroy clots over time.
What is DVT and how can you treat it?
Jan 16, 2016 · Anticoagulation options for acute VTE include unfractionated heparin, low molecular weight heparin, fondaparinux and the direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs). DOACs are as effective as conventional therapy with LMWH and vitamin K antagonists. Thrombolytic therapy is reserved for massive pulmonary embolism (PE) or extensive deep vein thrombosis (DVT).
What is DVT and how dangerous is it?
Percutaneous transcatheter treatment of patients with deep venous thrombosis (DVT) consists of thrombus removal with catheter-directed thrombolysis, mechanical thrombectomy, angioplasty, and/or stenting of venous obstructions.
What you can do to Prevent DVT?
Oct 08, 2020 · Use of direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs) are recommended as first-line treatment of acute DVT or PE. DOAC therapy is preferred over vitamin K antagonists (VKAs) for most patients without severe renal insufficiency (creatinine clearance <30 ml/min), moderate-severe liver disease, or antiphospholipid antibody syndrome.
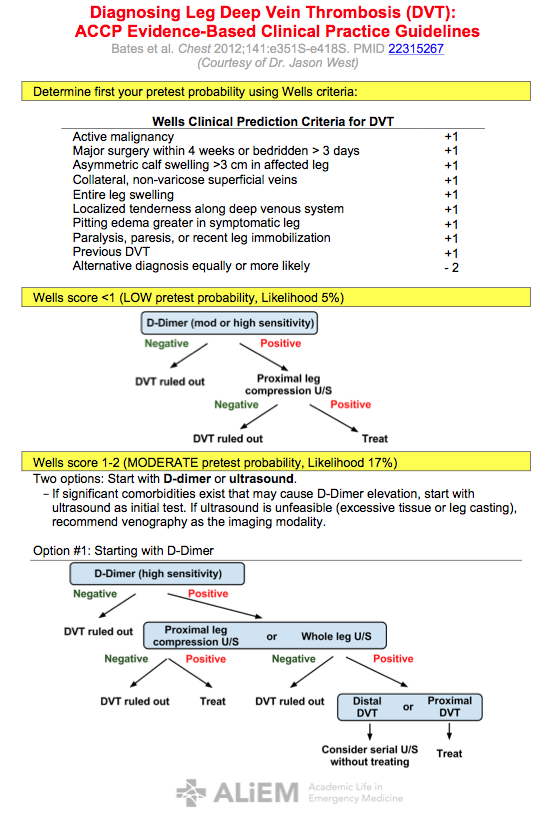
What is the first line treatment for DVT?
How long is treatment for DVT in leg?
Can DVT be treated without surgery?
How do you treat a DVT in the leg?
- Wear graduated compression stockings. These specially fitted stockings are tight at the feet and become gradually looser up on the leg, creating gentle pressure that keeps blood from pooling and clotting.
- Elevate the affected leg. ...
- Take walks.
What is the best medication for DVT?
...
Blood thinners include:
- Apixaban (Eliquis)
- Betrixaban (Bevyxxa)
- Dabigatran (Pradaxa)
- Edoxaban (Savaysa)
- Fondaparinux (Arixtra)
- Heparin.
- Rivaroxaban (Xarelto)
- Warfarin.
Can you fully recover from DVT?
What is the main cause of DVT?
What are the 10 signs of a blood clot?
- Pain in the side of your belly, legs, or thighs.
- Blood in your urine.
- Fever.
- Nausea or vomiting.
- High blood pressure.
- Sudden severe leg swelling.
- Trouble breathing.
What are the signs of DVT?
How long does it take for a DVT to dissolve?
How urgent is treatment for DVT?
Can a DVT dissolve on its own?
What is the procedure to remove a clot in a patient with DVT?
In rare cases, a surgical procedure to remove the clot may be necessary. Thrombectomy involves removal of the clot in a patient with DVT. Embolectomy involves removal of the blockage in the lungs caused by the clot in a patient with PE.
What is a DVT test?
DVT. Duplex ultrasonography is an imaging test that uses sound waves to look at the flow of blood in the veins. It can detect blockages or blood clots in the deep veins. It is the standard imaging test to diagnose DVT. A D-dimer blood test measures a substance in the blood that is released when a clot breaks up.
What anticoagulants are used to prevent bleeding?
Fondaparinux (injected under the skin). Anticoagulants that are taken orally (swallowed) include. Warfarin, Dabigatran, Rivaroxaban, Apixaban, and. Edoxaban. All of the anticoagulants can cause bleeding, so people taking them have to be monitored to prevent unusual bleeding.
How do thrombolytics work?
Thrombolytics (commonly referred to as “clot busters”) work by dissolving the clot. They have a higher risk of causing bleeding compared to the anticoagulants, so they are reserved for severe cases.
What are the symptoms of DVT?
There are other conditions with signs and symptoms similar to those of DVT and PE. For example, muscle injury, cellulitis (a bacterial skin infection), and inflammation (swelling) of veins that are just under the skin can mimic the signs and symptoms of DVT. It is important to know that heart attack and pneumonia can have signs ...
Where is contrast venography injected?
Contrast venography is a special type of X-ray where contrast material (dye) is injected into a large vein in the foot or ankle so that the doctor can see the deep veins in the leg and hip.
Do blood thinners thin blood?
Although called blood thinners, these medications do not actually thin the blood. They reduce the ability of the blood to clot, preventing the clot from becoming larger while the body slowly reabsorbs it, and reducing the risk of further clots developing. The most frequently used injectable anticoagulants are.
What is the initial treatment for DVT?
What is the initial treatment of DVT? The initial treatment of both DVT and PE is anticoagulation. Anticoagulants , commonly referred to as “blood thinners,” do not actually thin blood. Instead, they block the action of various clotting factors and prevent blood clots from growing.
What is the FDA approved drug for DVT?
Three LMWHs have been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the prevention of DVT and PE: dalteparin (Fragmin®), tinzaparin (Innohep®), and enoxaparin (Lovenox®). Only two of these medications, tinzaparin and enoxaparin, have been approved for the treatment of DVT and PE. Fondaparinux (Arixtra®) is a new type ...
Why is Tyler sharing her Stop the Clot story?
Tyler is sharing her Stop the Clot® story to highlight important information about #bloodclot risks connected to estrogen-based birth control and to encourage people to be aware of their bodies. Learn more: http://bit.ly/2qJhcMQ #stoptheclot #stoptheclotstory
Do anticoagulants help with DVT?
In this way, they allow the body’s own natural processes to destroy clots over time. In the last 10 years, the anticoagulants that have been used for the initial treatment of DVT and PE have changed somewhat.
What is the pain associated with a DVT?
Pain associated with DVT is often described as being a cramp or ache in the calf or thigh. Pulmonary embolism is often heralded by development of dyspnea and pleuritic chest or back pain. Pulmonary embolism can also cause progressive fatigue, dyspnea on exertion, syncope or pre-syncope or sudden death. Since these symptoms can be caused by many diseases, the likelihood of VTE can be estimated by assessing a patient’s thrombosis risk factors (Table 2) [1, 2]. The presence of these disease processes should be elicited in the history when assessing a patient for VTE.
How long does it take to treat VTE?
The next 3–6 months, we consider the “short term” treatment phase of therapy. After 3–6 months, we apply the term “long term” treatment of VTE when the benefit/risk of continued treatment becomes a critical aspect of the decision making process. Figure 1illustrates this continuum of care.
What is a VTE?
Venous thromboembolism (VTE) which consists principally of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE) is a common cause of morbidity and mortality. Consequently, health care providers in all clinical settings will be faced with managing patients with this illness. Numerous evidence-based guidelines are available to assist providers in clinical decision-making. However, there are many clinical scenarios where a paucity of data exist. The purpose of this guidance document is to provide advice to providers on all aspects of the treatment of VTE based upon the best available information including situations where evidence is limited.
Where is the Division of Hematology?
Division of Hematology, Department of Medicine and Pathology, The Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD USA
What is the primary objective of deep vein thrombosis?
The primary objectives for the treatment of deep venous thrombosis (DVT) are to prevent pulmonary embolism (PE), reduce morbidity, and prevent or minimize the risk of developing the postthrombotic syndrome (PTS).
What is the most basic mechanical method for thrombectomy?
The most basic mechanical method for thrombectomy is thromboaspiration, or the aspiration of thrombus through a sheath. Mechanical disruption of venous thrombosis has the potential disadvantage of damaging venous endothelium and valves, in addition to thrombus fragmentation and possible pulmonary embolism.
What are the goals of endovascular therapy?
The goals of endovascular therapy include reducing the severity and duration of lower-extremity symptoms, preventing pulmonary embolism, diminishing the risk of recurrent venous thrombosis, and preventing postthrombotic syndrome.
Why is anticoagulation important?
Long-term anticoagulation is necessary to prevent the high frequency of recurrent venous thrombosis or thromboembolic events. Anticoagulation does have problems. Although it inhibits propagation, it does not remove the thrombus, and a variable risk of clinically significant bleeding is observed.
How long does anticoagulation therapy last?
Anticoagulant therapy is recommended for 3-12 months depending on site of thrombosis and on the ongoing presence of risk factors. If DVT recurs, if a chronic hypercoagulability is identified, or if PE is life threatening, lifetime anticoagulation therapy may be recommended. This treatment protocol has a cumulative risk of bleeding complications of less than 12%.
What is heparin used for?
Heparin Use in Deep Venous Thrombosis. Heparin products used in the treatment of deep venous thrombosis (DVT) include unfractionated heparin and low molecular weight heparin (LMWH) The efficacy and safety of low-molecular-weight heparin (LMWH) for the initial treatment of DVT have been well established in several trials.
Does anticoagulation help with DVT?
The immediate symptoms of DVT often resolve with anticoagulation alone, and the rationale for intervention is often reduction of the 75% long-term risk of PTS. Systemic IV thrombolysis once improved the rate of thrombosed vein recanalization; however, it is no longer recommended because of an elevated incidence of bleeding complications, slightly increased risk of death, and insignificant improvement in PTS. The lack of a significantly reduced incidence of PTS after systemic thrombolysis (40-60%) likely reflects the inadequacy of the relatively low threshold volume of thrombus removal that was considered successful.
How long does it take to treat DVT?
The ASH guidelines define the treatment period of acute DVT/PE as “initial management” (first 5-21 days), “primary treatment” (first 3-6 months), and “secondary prevention” (beyond the first 3-6 months).
What is the first line of treatment for acute DVT?
Patients with submassive (intermediate-high risk) or massive PE as well as patients at high risk for bleeding may benefit from hospitalization. Use of direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs) are recommended as first-line treatment of acute DVT or PE.
How many times does DVT occur annually?
The ASH assembled a multidisciplinary writing committee to provide evidence-based guidelines for management of DVT and PE, which occur 300,000-600,000 times annually in the United States.
Is thrombolysis a good treatment for proximal DVT?
For most patients with proximal DVT, the ASH guidelines suggest anticoagulation therapy alone over thrombolytic therapy. Thrombolysis is reasonable to consider in patients presenting with limb-threatening DVT (phlegmasia cerulea dolens) or for select younger patients at low bleeding risk with iliofemoral DVT.
Can you use compression stockings for DVT?
For patients with acute DVT who are not at high risk for post-thrombotic syndrome, the ASH guidelines recommend against the routine use of compression stockings. However, select patients may benefit from compression stockings to help with edema and pain associated with acute DVT. Share via:
Can you take aspirin with DVT?
For patients with DVT/PE with stable cardiovascular disease, the ASH guidelines suggest suspending aspirin therapy when initiating anticoagulation. The combination of anticoagulation plus aspirin increases the risk of bleeding without clear evidence of benefit for patients with stable cardiovascular disease.
Is thrombolysis considered a high risk procedure?
Thrombolysis is reasonable to consider for patients at low bleeding risk who are at high risk for decompensation. For patients with extensive DVT in whom thrombolysis is considered appropriate, the ASH guidelines suggest using catheter-directed thrombolysis over systemic thrombolysis.
What is the treatment for DVT?
Once you receive a diagnosis of DVT, you’ll likely be prescribed medications known as anticoagulants, or blood thinners. These work to keep the clot from growing and to prevent further clots.
What is a DVT?
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a medical condition that happens when a blood clot forms in a vein. A deep vein blood clot can occur anywhere in the body, but most often forms in the calf or thigh. Treating DVT is important because of the risk of a life-threatening complication known as pulmonary embolism. This occurs when the blood clot breaks ...
How long do you have to take warfarin?
They’ll give you detailed instructions for taking additional doses at home. You may have to take the anticoagulant medication for three to six months, sometimes longer. Make sure to follow your doctor’s instructions carefully. Taking too much of an anticoagulant medication like warfarin can thin the blood too much and lead to bleeding problems.
Why is it important to make changes to your lifestyle to prevent DVT?
Along with managing your symptoms , it’s important to make changes to your lifestyle in order to prevent DVT happening again. Certain people are at a higher risk of developing DVT, including: people who are having surgery in the lower extremities. heavy smokers.
What is the best medicine for stroke?
Acetyl salicylic acid, which is derived from salicylate and is commonly known as aspirin, is used to prevent stroke. Ginger is a common ingredient in many recipes. It can also be made into a tea. Ginger has many other health benefits as well.
How to lower blood pressure?
Lower your blood pressure with dietary changes, like reducing your salt and sugar intake.
How to get blood out of your leg?
Wear graduated compression stockings. These specially fitted stockings are tight at the feet and become gradually looser up on the leg, creating gentle pressure that keeps blood from pooling and clotting. Elevate the affected leg. Make sure your foot is higher than your hip. Take walks.
What is a personal history of DVT?
A personal or family history of DVT or PE. If you or someone in your family has had one or both of these, you might be at greater risk of developing DVT.
How old do you have to be to get DVT?
Age. Being older than 60 increases your risk of DVT, though it can occur at any age.
What is it called when a DVT and pulmonary embolism occur together?
When DVT and pulmonary embolism occur together, it's called venous thromboembolism (VTE).
How long does it take for blood clots to go away after birth?
Women with an inherited clotting disorder are especially at risk. The risk of blood clots from pregnancy can continue for up to six weeks after you have your baby. Birth control pills (oral contraceptives) or hormone replacement therapy. Both can increase your blood's ability to clot.
What causes pain in the leg vein?
A blood clot in a leg vein may cause pain, warmth and tenderness in the affected area.
What causes blood clots?
The main causes of DVT are damage to a vein from surgery or trauma and inflammation due to infection or injury.
What does it feel like to have a deep vein thrombosis?
The pain often starts in your calf and can feel like cramping or soreness. Red or discolored skin on the leg. A feeling of warmth in the affected leg. Deep vein thrombosis can occur without noticeable symptoms.
How to help yourself after a DVT?
In addition to taking your medication as your doctor instructed, you can do a few other things to make another DVT less likely. Get up and around as soon as you safe ly can after an injury or surgery. Staying active helps your blood flow like it should.
How to keep a DVT from getting bigger?
You probably take medicine that makes your blood slower to clot. These drugs, called anticoagulants or blood thinners, can keep a DVT from getting bigger while your body breaks it down. They also can help keep another clot from forming. Some are given as shots, and some are pills.
How long does it take for a blood clot to heal?
Most people are fully healed from a deep vein thrombosis ( DVT) within a few weeks or months. But if you’re recovering from this type of blood clot (which happens in a large vein, most often in your leg), you might be worried about how it will change your life and whether it will happen again. Learning about the condition and taking charge ...
Why do people with DVT have long term complications?
Up to half of people with DVT will have long-term complications because of damage to the leg vein (post-thrombotic syndrome), where blood remains too long (chronic venous insufficiency).
How long does it take to get a blood thinner for DVT?
Some are given as shots, and some are pills. It usually takes about 3 months to treat a DVT. If you aren’t likely to have another one, you may be able to stop taking blood thinners at that point. People whose chances are higher may need to stay on them for years. Talk with your doctor about what’s best for you.
How to get rid of leg pain?
On long trips, get up and walk the aisle of the plane or stop the car to take a walk every hour or two. If you can’t move around, flex and point your toes, or tighten and release your leg muscles. Stay a healthy weight. Don’t smoke.
Can anticoagulants cause stroke?
Because anticoagulants can cause uncontrolled bleeding, your odds of a stroke or other bleeding problem should be part of your decision. Your treatment plan will be different depending on which medication you take. For decades, warfarin ( Coumadin , Jantoven) has been the go-to drug for treating a DVT.
