
What are the treatment options for Type 1 diabetes?
When medicines and lifestyle changes are not enough to manage your diabetes, a less common treatment may be an option. Other treatments include bariatric surgery for certain people with type 1 or type 2 diabetes, and an "artificial pancreas" and pancreatic islet transplantation for some people with type 1 diabetes.
What type of diabetes medicine should I take?
Other factors, such as your other health conditions, medication costs, and your daily schedule may play a role in what diabetes medicine you take. If you have type 1 diabetes, you must take insulin because your body no longer makes this hormone.
What do diabetics need to know about diabetes treatment?
Diabetic patients need complicated treatment for their metabolic problems as well as for related comorbidities. They have to treat, often intensively, hypertension, dyslipidaemia, bone disease, anaemia, and frequently established cardiovascular disease (CVD).
Can my doctor prescribe treatment for type 2 diabetes?
If you have type 2 diabetes, your doctor may prescribe one or more treatments to help manage your blood sugar levels and reduce your risk of complications. Read on to more learn about some of the most common treatments and recommendations for people who are newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes.
What is the best treatment for type 1 diabetes?
Intensive insulin therapy is recommended for most people with type 1 diabetes, although simpler insulin treatments may still be recommended for some people. Intensive insulin treatment — Intensive insulin treatment is best for keeping blood sugar in near-normal or "tight" control.
What is the first treatment for type 1 diabetes?
Insulin injected subcutaneously is the first-line treatment of type 1 diabetes mellitus (DM). The different types of insulin vary with respect to onset and duration of action. Short-, intermediate-, and long-acting insulins are available.
What type of medication is used for type 1 diabetes?
Insulin. Insulin is the most common type of medication used in type 1 diabetes treatment. If you have type 1 diabetes, your body can't make its own insulin. The goal of treatment is to replace the insulin that your body can't make.
Can type 1 diabetes be treated without insulin?
For people with “traditional” T1D, particularly those diagnosed in childhood or adolescence, to survive without insulin, “they would need to stay on carbohydrate restriction and stay very hydrated,” Kaufman says. But their survival rate is “multiple days, to a few weeks, getting sicker and weaker as time goes on.
Can type 1 diabetes be treated with tablets?
If you have type 1 diabetes, you'll need to use insulin to treat your diabetes. You take the insulin by injection or by using a pump. If you have Type 2 diabetes, you may have to use insulin or tablets, though you might initially be able to treat your diabetes by eating well and moving more.
How is type 1 diabetes permanently treated?
Currently, there is no cure for type 1 diabetes. Insulin injection is the only medication; however, it accompanies serious medical complications. Current strategies to cure type 1 diabetes include immunotherapy, replacement therapy, and combination therapy.
Which insulin is best for type 1 diabetes?
Insulin glargine (Lantus) – this takes effect after an hour and can last for 24 hours. Insulin determir (Levemir) – this has a shorter effect than Lantus and so if often injected twice per day. Insulin degludec (Tresiba) – this is often prescribed to reduce nocturnal hypoglycaemia in people over the age of 18.
Diabetes Treatment: Lowering Blood Sugar
Several classes of type 2 diabetes medicines exist. Each class of medicine works in different ways to lower blood sugar. A drug may work by: 1. Sti...
Compare Diabetes Medications
Here's an at-a-glance comparison of common diabetes medications. More medications are available depending on your needs and situation. Ask your doc...
How to Choose Your Diabetes Medication
No single diabetes treatment is best for everyone, and what works for one person may not work for another. Your doctor can determine how a specific...
What is the treatment for diabetes?
Other treatments include bariatric surgery for certain people with type 1 or type 2 diabetes, and an "artificial pancreas" and pancreatic islet transplantation for some people with type 1 diabetes.
What is the treatment for poorly controlled type 1 diabetes?
Pancreatic islet transplantation is an experimental treatment for poorly controlled type 1 diabetes. Pancreatic islets are clusters of cells in the pancreas that make the hormone insulin. In type 1 diabetes, the body’s immune system attacks these cells. A pancreatic islet transplant replaces destroyed islets with new ones that make and release insulin. This procedure takes islets from the pancreas of an organ donor and transfers them to a person with type 1 diabetes. Because researchers are still studying pancreatic islet transplantation, the procedure is only available to people enrolled in research studies. Learn more about islet transplantation studies#N#External link#N#.
What is the best way to treat diabetes?
Taking insulin or other diabetes medicines is often part of treating diabetes. Along with healthy food choices and physical activity, medicine can help you manage the disease. Some other treatment options are also available.
How to control glucose levels during pregnancy?
If you have gestational diabetes, you should first try to control your blood glucose level by making healthy food choices and getting regular physical activity. If you can’t reach your blood glucose target, your health care team will talk with you about diabetes medicines, such as insulin or the diabetes pill metformin, that may be safe for you to take during pregnancy. Your health care team may start you on diabetes medicines right away if your blood glucose is very high.
How to take insulin?
Inhaler. Another way to take insulin is by breathing powdered insulin from an inhaler device into your mouth. The insulin goes into your lungs and moves quickly into your blood. Inhaled insulin is only for adults with type 1 or type 2 diabetes.
What is premixed insulin?
Your doctor might also recommend premixed insulin, which is a mix of two types of insulin. Some types of insulin cost more than others, so talk with your doctor about your options if you're concerned about cost. Read about financial help for diabetes care .
Why do you need insulin?
Type 1 diabetes. If you have type 1 diabetes, you must take insulin because your body no longer makes this hormone. You will need to take insulin several times during the day, including with meals. You also could use an insulin pump, which gives you small, steady doses throughout the day.
How to reduce the risk of diabetic neuropathy?
Lifestyle and home remedies. These measures can help you feel better overall and reduce your risk of diabetic neuropathy: Keep your blood pressure under control. If you have high blood pressure and diabetes, you have an even greater risk of complications.
What is the recommended blood sugar level for diabetics?
But, in general, the American Diabetes Association recommends the following target blood sugar levels for most people with diabetes: Between 80 and 130 mg/dL, which is 4.4 and 7.2 millimoles per liter (mmol/L) before meals.
What test is done to diagnose diabetic neuropathy?
Along with the physical exam, your doctor may perform or order specific tests to help diagnose diabetic neuropathy, such as: Filament test. Your doctor will brush a soft nylon fiber (monofilament) over areas of your skin to test your sensitivity to touch. Sensory testing.
What antidepressants help with nerve pain?
Some antidepressants ease nerve pain, even if you aren't depressed. Tricyclic anti depressants may help with mild to moderate nerve pain. Drugs in this class include amitriptyline, desipramine (Norpramin) and imipramine (Tofranil). Side effects can be bothersome and include dry mouth and drowsiness.
What is the test called for blood pressure?
Called electromyography, this test is often done with nerve conduction studies. It measures electrical discharges produced in your muscles. Autonomic testing. Special tests may be done to determine how your blood pressure changes while you are in different positions, and whether you sweat normally.
What is the name of the doctor who treats metabolic disorders?
An endocrinologist is a doctor who specializes in treating metabolic disorders, such as diabetes. You may also be referred to a neurologist, which is a doctor who specializes in treating nervous system problems. To prepare for your appointment, you may want to: Be aware of any pre-appointment restrictions.
How to treat gastroparesis?
Diet changes and medications may help relieve gastroparesis, diarrhea, constipation and nausea. Low blood pressure on standing (orthostatic hypotension). Treatment starts with simple lifestyle changes, such as avoiding alcohol, drinking plenty of water, and changing positions such as sitting or standing slowly.
Scope
These recommendations are intended to apply to nonpregnant adults with type 1 or type 2 diabetes.
Target audience
These recommendations are intended for the use of health care professionals who care for patients with diabetes and hypertension, including specialist and primary care physicians, nurses and nurse practitioners, physicians’ assistants, educators, dietitians, and others.
Method
These recommendations are based on the American Diabetes Association Technical Review “Treatment of Diabetes in Adult Patients with Hypertension” ( 1 ). A technical review is a systematic review of the medical literature that has been peer-reviewed by the American Diabetes Association’s Professional Practice Committee.
Evidence review: hypertension as a risk factor for complications of diabetes
Diabetes increases the risk of coronary events twofold in men and fourfold in women. Part of this increase is due to the frequency of associated cardiovascular risk factors such as hypertension, dyslipidemia, and clotting abnormalities.
Evidence for target levels of blood pressure in patients with diabetes
The UKPDS and the Hypertension Optimal Treatment (HOT) trial both demonstrated improved outcomes, especially in preventing stroke, in patients assigned to lower blood pressure targets. Optimal outcomes in the HOT study were achieved in the group with a target diastolic blood pressure of 80 mmHg (achieved 82.6 mmHg).
Evidence for non-drug management of hypertension
Dietary management with moderate sodium restriction has been effective in reducing blood pressure in individuals with essential hypertension. Several controlled studies have looked at the relationship between weight loss and blood pressure reduction.
Evidence for drug therapy of hypertension
There are a number of trials demonstrating the superiority of drug therapy versus placebo in reducing outcomes including cardiovascular events and microvascular complications of retinopathy and progression of nephropathy.
How does diabetes medicine work?
Each class of medicine works in different ways to lower blood sugar. A drug may work by: Stimulating the pancreas to produce and release more insulin. Inhibiting the production and release of glucose from the liver.
Can you take a single medication for type 2 diabetes?
However, you may need medications to achieve target blood sugar (glucose) levels. Sometimes a single medication is effective. In other cases, a combination of medications works better. The list of medications for type 2 diabetes is long and potentially confusing.
Is diabetes a single treatment?
No single diabetes treatment is best for everyone, and what works for one person may not work for another. Your doctor can determine how a specific medication or multiple medications may fit into your overall diabetes treatment plan and help you understand the advantages and disadvantages of specific diabetes drugs. Oct. 24, 2020.
What is the name of the regimen that contains both long-acting and short-acting insulin?
The regimen containing both long-acting and short-acting insulin is called a basal-bolus insulin regimen; it provides physiological replacement of insulin. If a patient used insulin prior to admission, the same dose can be restarted in the hospital.
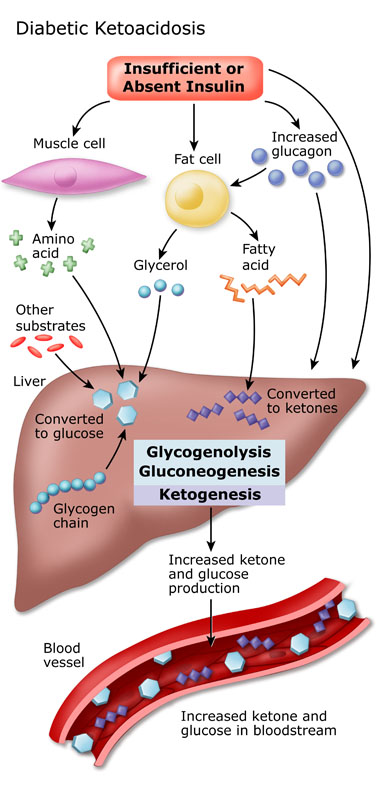
What are the therapeutic goals of DKA?
The therapeutic goals of DKA management include optimization of 1) volume status; 2) hyperglycemia and ketoacidosis; 3) electrolyte abnormalities; and 4) potential precipitating factors. The majority of patients with DKA present to the emergency room. Therefore, emergency physicians should initiate the management of hyperglycemic crisis while a physical examination is performed, basic metabolic parameters are obtained, and final diagnosis is made. Several important steps should be followed in the early stages of DKA management: 1 collect blood for metabolic profile before initiation of intravenous fluids; 2 infuse 1 L of 0.9% sodium chloride over 1 hour after drawing initial blood samples; 3 ensure potassium level of >3.3 mEq/L before initiation of insulin therapy (supplement potassium intravenously if needed); 4 initiate insulin therapy only when steps 1–3 are executed.
How many hospitalizations for diabetic ketoacidosis in 2009?
In 2009, there were 140,000 hospitalizations for diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) with an average length of stay of 3.4 days.1The direct and indirect annual cost of DKA hospitalizations is 2.4 billion US dollars.
Why is bicarbonate not indicated in mild and moderate forms of DKA?
Bicarbonate therapy is not indicated in mild and moderate forms of DKA because metabolic acidosis will correct with insulin therapy.3, 8The use of bicarbonate in severe DKA is controversial due to a lack of prospective randomized studies.
Is ketoacidosis a type 1 or 2 diabetes?
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a rare yet potentially fatal hyperglycemic crisis that can occur in patients with both type 1 and 2 diabetes mellitus. Due to its increasing incidence and economic impact related to the treatment and associated morbidity, effective management and prevention is key. Elements of management include making ...
Can DKA cause hypokalemia?
A “normal” plasma potassium concentration still indicates that total body potassium stores are severely diminished, and the institution of insulin therapy and correction of hyperglycemia will result in hypokalemia.
When should diabetes be treated?
The treatment of diabetes should start before the development of complications. Also, if a patient during dental treatment has symptoms of hyperglycemia (red dry skin, rapid breathing, dehydration, acetone breath), he should be immediately treated.
What is the cause of diabetes?
It is believed that this type of diabetes occurs as a result of an autoimmune destruction of insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas (pancreatic islets, also called islets of Langerhans – tiny clusters of cells scattered throughout the pancreas).
How does diabetes affect dental health?
In addition, some of them such as gingivitis and periodontitis have adverse effect on disease control. Daily implementation of the oral hygiene measures and regular dental checkups will preserve oral health of patients with diabetes and will contribute significantly to the health of the whole organism.
What are the most common oral complications of diabetes?
Oral manifestations of diabetes are gingivitis and periodontitis, dry mouth, increased susceptibility to infections especially fungal, increased susceptibility to caries, burning sensation of oral mucosa and difficult wound healing. Gingivitis and periodontitis are the most common oral complications of diabetes.
Why does diabetes occur?
Diabetes is caused by two reasons: when the pancreas stops completely or partially to produce hormone insulin (Type 1 diabetes) or when the insulin is not effective in the body (Type 2 diabetes). Type 1 diabetes (formerly called insulin dependent type) occurs in 10% of patients, most often in children and adolescents.
How many people have Type 2 diabetes?
Type 2 diabetes (formerly called non-insulin dependent type) occurs in 90% of patients, mainly adults over forty years of age. The disease occurs when the pancreas is not anymore able to produce sufficient amounts of hormone insulin to meet the needs of the organism or when the target cells become resistant to insulin ...
What bacteria are more destructive in diabetics?
In patients with poorly controlled diabetes the number of destructive bacteria (spirochetes and movable rods) is increased than in patients with well-controlled diabetes and non-diabetic individuals.
What is the best diet for diabetics?
In general, the American Diabetes Association (ADA) recommends: eating a wide variety of nutrient-rich foods, such as whole grains, legumes, vegetables, fruits, lean proteins, and healthy fats. evenly spacing your meals throughout the day.
What is type 2 diabetes?
Overview. Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition in which the body doesn’t use insulin properly. This causes blood sugar levels to rise, which can lead to other health problems. If you have type 2 diabetes, your doctor may prescribe one or more treatments to help manage your blood sugar levels and reduce your risk of complications.
How to check blood sugar at home?
To check your blood sugar at home, you can prick your fingertip and test your blood with a blood glucose monitor. Or, you can invest in a continuous glucose monitor, which continuously tracks your blood sugar levels using a small sensor inserted under your skin.
What is the goal of blood work for diabetes?
Blood sugar testing. The main goal of diabetes treatment is to keep your blood sugar levels in target range. If your blood sugar falls too low or rises too high, it can cause health problems. To help monitor your blood sugar levels, your doctor will order blood work on a regular basis.
How to get a diabetic to exercise?
According to the ADA, most adults with type 2 diabetes should: 1 get at least 150 minutes of moderate to vigorous intensity aerobic exercise per week, spread over multiple days 2 complete two to three sessions of resistance exercise or strength training per week, spread over non-consecutive days 3 try to limit the amount of time you spend engaging in sedentary behaviors 4 try not to go more than two days in a row without physical activity
Can Type 2 diabetes change overtime?
They will also ask you to schedule regular checkups and blood tests. If you notice changes in your symptoms or blood sugar levels, let your doctor know. Type 2 diabetes can change overtime. Your doctor may adjust your treatment plan to meet your evolving needs. Last medically reviewed on June 17, 2019.
Can insulin be injected?
insulin, which may be injected or inhaled. other injectable drugs, such as a GLP-1 receptor agonist or amylin analogue. In most cases, your doctor will start by prescribing oral medication. Over time, you might need to add insulin or other injectable drugs to your treatment plan.
What is the best food for diabetics?
Here are the 16 best foods for people living with diabetes, both type 1 and type 2. 1. Fatty Fish. Some people consider fatty fish to be one of the healthiest foods on the planet. Salmon, sardines, herring, anchovies and mackerel are great sources of the omega-3 fatty acids DHA and EPA, which have major benefits for heart health.
Does eating fish lower blood sugar?
Research indicates that people who eat fatty fish regularly have a lower risk for acute coronary syndromes, like heart attacks, and are less likely to die from heart disease ( 7, 8. Trusted Source. ). Studies show that eating fatty fish may also help regulate your blood sugar.
Can you eat avocados with diabetes?
This makes them an ideal snack for people with diabetes, especially since obesity increases your chances for developing diabetes. Avocados may have properties specific to preventing diabetes. ). More research is needed in humans to establish the connection between avocados and diabetes prevention.
Does broccoli help with blood sugar?
Broccoli may also help manage your blood sugar levels. One study found that consuming broccoli sprouts led to a 10 percent reduction in blood glucose in people with diabetes ( 55 ). This reduction in blood glucose levels is likely due to sulforaphane, a chemical in cruciferous vegetables like broccoli and sprouts.
Can diabetics eat nuts?
Nuts may also help people with diabetes improve their heart health. A 2019 study involving over 16,000 participants with type 2 diabetes found that eating tree nuts — such as walnuts, almonds, hazelnuts and pistachios — lowered their risk of heart disease and death ( 49 ).
Does eating healthy help with diabetes?
The bottom line. When diabetes is not well managed, it increases your risk for several serious diseases. But eating foods that help keep blood sugar, insulin, and inflammation manageable can dramatically reduce your risk for complications.
Does vitamin C help with diabetes?
Vitamin C acts as a potent antioxidant and also has anti-inflammatory qualities. Increasing dietary intake of vitamin C-rich foods can help people with diabetes increase their serum vitamin C levels while reducing inflammation and cellular damage ( 11. Trusted Source. ).

Diagnosis
Treatment
- Diabetic neuropathy has no known cure. The goals of treatment are to: 1. Slow progression of the disease 2. Relieve pain 3. Manage complications and restore function
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
- These measures can help you feel better overall and reduce your risk of diabetic neuropathy: 1. Keep your blood pressure under control.If you have high blood pressure and diabetes, you have an even greater risk of complications. Try to keep your blood pressure in the range your doctor recommends, and be sure to have it checked at every office visit. 2. Make healthy food choices.…
Alternative Medicine
- There are also many alternative therapies that may help with pain relief on their own or in combination with medications. But check with your doctor before using any alternative therapy or dietary supplement to make sure to avoid any potential interactions. For diabetic neuropathy, you may want to try: 1. Capsaicin.Capsaicin cream, applied to the s...
Coping and Support
- Living with diabetic neuropathy can be difficult and frustrating. If you find yourself feeling depressed, it may help to talk to a counselor or therapist. Support groups also can offer encouragement and advice about living with diabetic neuropathy. Ask your doctor if there are any in your area, or for a referral to a therapist. The American Diabetes Association offers online sup…
Preparing For Your Appointment
- If you don't already see an endocrinologist, you'll likely be referred to one if you start showing signs of diabetes complications. An endocrinologist is a doctor who specializes in treating metabolic disorders, such as diabetes. You may also be referred to a neurologist, which is a doctor who specializes in treating nervous system problems. To prepare for your appointment, y…