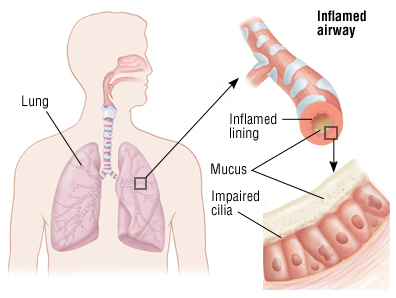
Medication
Feb 01, 2022 · Treatment of acute bronchitis is typically divided into two categories: antibiotic therapy and symptom management.
Nutrition
Dec 02, 2020 · Antibiotics are drugs that kill or prevent the growth of bacteria. Acute bronchitisis usually caused by viruses, though, so antibioticswon’t help. Many studies have shown that antibioticshardly affect the course of the illness. In the studies, antibiotics reduced the duration of the cough by half a day on average.
Do any bronchitis home remedies actually work?
Blood tests, breathing tests, and imaging tests may also be used. In most cases, antibiotics are not needed to treat acute bronchitis. If it progresses to pneumonia, then antibiotics may be necessary. Treatment is aimed at managing the symptoms.
What helps you feel better when you have bronchitis?
Jun 30, 2021 · In most cases, acute bronchitis resolves on its own. Treatment mainly focuses on managing symptoms and supportive care, such as drinking lots of fluid and resting. Even when the acute bronchitis is caused by bacteria, antibiotics are not …
Will bronchitis go away on its own?
Mar 08, 2019 · This condition is called bronchitis, and it causes symptoms that can include coughing, shortness of breath, and low fever. Acute bronchitis typically lasts less than 10 days, but the coughing can ...
What is the best antibiotic for bronchitis?
6 rows · May 15, 2002 · Because acute bronchitis most often has a viral cause, symptomatic treatment with protussives, ...
See more
The typical therapies for managing acute bronchitis symptoms have been shown to be ineffective, and the U.S. Food and Drug Administration recommends against using cough and cold preparations in children younger than six years. The supplement pelargonium may help reduce symptom severity in adults. As patient expectations for antibiotics and ...
What is the best treatment for acute bronchitis?
- Drink lots of fluids, especially water. Try eight to 12 glasses a day to help thin out that mucus and make it easier to cough up. ...
- Get plenty of rest.
- Use over-the-counter pain relievers with ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin), naproxen (Aleve), or aspirin to help with pain.
What is the first line treatment for acute bronchitis?
What antibiotics treat acute bronchitis?
- Extended macrolides like Zithromax (azithromycin)
- Fluoroquinolones like Cipro (ciprofloxacin) and Levaquin (levofloxacin)
- Aminopenicillins like Principen (ampicillin), Moxatag (amoxicillin), and Hetacin (hetacillin)
- Cephalosporins.
How do doctors treat bronchitis?
Do I need antibiotics for bronchitis?
Does azithromycin treat acute bronchitis?
Can amoxicillin treat bronchitis?
What is the best antibiotic for chest infection?
What is the treatment for acute bronchitis?
Treatment of acute bronchitis is typically divided into two categories: antibiotic therapy and symptom management. Physicians appear to deviate from evidence-based medical practice in the treatment of bronchitis more than in the diagnosis of the condition.
Can antibiotics be used for bronchitis?
Antibiotics are generally not indicated for bronchitis, and should be used only if pertussis is suspected to reduce transmission or if the patient is at increased risk of developing pneumonia (e.g., patients 65 years or older).
How long does bronchitis last?
Symptoms of bronchitis typically last about three weeks. The presence or absence of colored (e.g., green) sputum does not reliably differentiate between bacterial and viral lower respiratory tract infections. Viruses are responsible for more than 90 percent of acute bronchitis infections.
Is cough a primary diagnosis?
Cough is the most common symptom bringing patients to the primary care physician's office , and acute bronchitis is usually the diagnosis in these patients . Acute bronchitis should be differentiated from other common diagnoses, such as pneumonia and asthma, because these conditions may need specific therapies not indicated for bronchitis.
How long does a cold last?
The common cold often causes coughing; however, nasal congestion and rhinorrhea are also usually present, and a cold typically lasts only seven to 10 days. Symptoms of acute bronchitis typically persist for approximately three weeks. 3.
How to diagnose acute bronchitis?
Healthcare providers can often diagnose acute bronchitis by taking a medical history and doing physical exam. Blood tests, breathing tests, and imaging tests may also be used . In most cases, antibiotics are not needed to treat acute bronchitis. If it progresses to pneumonia, then antibiotics may be necessary.
Can bronchitis be prevented?
Acute bronchitis can’t always be prevented. However, there are shots you can get to prevent its complications, such as pneumonia. Check with your healthcare provider about getting the flu and pneumococcal shots. Getting a flu shot every year can help prevent both the flu and pneumonia.
How long does bronchitis last?
Acute bronchitis may also be called a chest cold. Most symptoms of acute bronchitis last for up to 2 weeks. The cough can last for up to 8 weeks in some people. Chronic bronchitis lasts a long time. It is more common among smokers.
What causes bronchitis?
Acute bronchitis is usually caused by a viral infection. This is most often the same viruses that cause colds and the flu. It may also be caused by a bacterial infection, or by physical or chemical agents that are breathed in.
What is an oximeter?
An oximeter is a small machine that measures the amount of oxygen in the blood. To get this measurement, a small sensor is taped or clipped on a finger or toe. When the machine is on, a small red light can be seen in the sensor. The sensor is painless and the red light does not get hot. Cultures of nasal discharge and sputum.
What is the purpose of a swab test?
Testing the sputum you cough up or swab from your nose may be done to find and identify the microorganism causing the infection. Pulmonary function tests. These are tests that help to measure the ability of the lungs to move air in and out of the lungs.
Do antibiotics help with bronchitis?
In most cases, antibiotics are not needed to treat acute bronchitis. That’s because most of the infections are caused by viruses. Antibiotics are not effective against viruses. If it has progressed to pneumonia, then antibiotics may be necessary. Treatment is aimed at treating the symptoms, and may include:
How to get rid of bronchitis?
Below are some ways you can feel better while your body fights off acute bronchitis: Get plenty of rest. Drink plenty of fluids. Use a clean humidifier or cool mist vaporizer. Use saline nasal spray or drops to relieve a stuffy nose. For young children, use a rubber suction bulb to clear mucus.
Can antibiotics help with bronchitis?
Transcript. txt icon. [TXT – 294 B] Acute bronchitis usually gets better on its own—without antibiotics. Antibiotics won’t help you get better if you have acute bronchitis. When antibiotics aren’t needed, they won’t help you, and their side effects could still cause harm.
How long does a chest cold last?
That’s what makes you cough. A chest cold, often called acute bronchitis, lasts less than 3 weeks and is the most common type of bronchitis.
Can you give a child aspirin?
Children younger than 6 months: only give acetaminophen. Children 6 months or older: it is OK to give acetaminophen or ibuprofen. Never give aspirin to children because it can cause Reye’s syndrome, a rare but very serious illness that harms the liver and brain. Cough and cold medicines:
What temperature should a 3 month old have?
See a doctor right away if your child is younger than 3 months old and has a fever of 100.4 °F (38 °C) or higher. See a doctor if you have any of the following: Temperature of 100.4 °F or higher. Cough with bloody mucus. Shortness of breath or trouble breathing.
What is the best treatment for bronchitis?
Examples of medication that can help control cough or clear mucus include: 2. Antitussives, also called cough suppressants, like Tessalon Perles ( benzonatate) or Delsym (dextromethorphan)
How to treat bronchitis at home?
Home Remedies and Lifestyle. Supportive care and symptom management are the primary treatment focus for acute bronchitis. In most cases, the infection just has to run its course. Supportive care at home include: 2. Resting and getting plenty of fluids . Drinking lots of water, which helps loosen chest congestion.
What is the best cough medicine for bronchitis?
Over-the-counter medications for cough can help with acute bronchitis. Examples of medication that can help control cough or clear mucus include: 2 1 Antitussives, also called cough suppressants, like Tessalon Perles ( benzonatate) or Delsym (dextromethorphan) 2 Expectorants, which help clear mucus from the airways, like Mucinex (guaifenesin) 3 A pain reliever and fever reducer, such as acetaminophen (Tylenol)
Can you take over the counter medication for bronchitis?
Acute bronchitis doesn't generally require treatment and resolves on its own. However, you can use over-the-counter medications to alleviate your symptoms, such as pain relievers and cough suppressants. The best things to do are getting plenty of rest and fluids and letting your infection run its course.
Can antibiotics help with bronchitis?
Even if your acute bronchitis is caused by bacteria, antibiotics generally won't help. Rest, supportive care, and over-the-counter medications to treat your cough and fever are generally the best strategies to treat acute bronchitis.
What is the cause of coughing?
Complementary Medicine. Coughing is one of the top complaints that brings people to their doctor's office, and acute bronchitis, also called a chest cold, is a common culprit. This condition is usually caused by a virus, but it can also be caused by bacteria. 1.
Can you prevent bronchitis?
There’s no way to completely prevent acute bronchitis because it has a variety of causes. However, you can decrease your risk by following the tips listed here. If you have a weakened immune system due to a health condition or older age, you should take special care to avoid getting acute bronchitis.
Can you take antibiotics for bronchitis?
It’s important to know, though, that antibiotics aren’t recommended for people with acute bronchitis. Most cases of the condition are caused by viruses, and antibiotics don’t work on viruses, so the drugs wouldn’t help you.
How long does bronchitis last?
Acute bronchitis typically lasts less than 10 days, but the coughing can continue for several weeks. Chronic bronchitis, on the other hand, can last for several weeks and usually comes back. This condition is more common in people with asthma or emphysema. Read on to learn more about symptoms, causes, and treatment of acute bronchitis.
Can bronchitis go away without treatment?
In many cases, acute bronchitis will go away without treatment. But if you see your doctor because of symptoms of acute bronchitis, they will start with a physical exam. During the exam, your doctor will listen to your lungs as you breathe, checking for symptoms such as wheezing.
What causes acute bronchitis?
Causes of acute bronchitis include viral and bacterial infections, environmental factors, and other lung conditions. Viral infection: Viruses cause 85 to 95 percent. Trusted Source. of acute bronchitis cases in adults. The same viruses that cause the common cold or flu can cause acute bronchitis.
Can bronchitis be caused by a viral infection?
Bacterial infection: In rare cases, bacterial bronchitis can develop after a viral infection of bronchitis. This can result from infections by bacteria such as Mycoplasma pneumoniae, Chlamydia pneumoniae, and Bordetella pertussis (which causes whooping cough ).
Can smog cause bronchitis?
Irritants: Breathing in irritants such as smoke, smog, or chemical fumes can cause inflammation in your trachea and bronchial tubes. This can lead to acute bronchitis. Other lung conditions: People with chronic bronchitis or asthma sometimes develop acute bronchitis.
Can you take antibiotics for bronchitis?
However, studies indicate that many physicians treat bronchitis with antibiotics.
What are the signs of bronchitis?
The physical examination of patients presenting with symptoms of acute bronchitis should focus on vital signs, including the presence or absence of fever and tachypnea, and pulmonary signs such as wheezing, rhonchi, and prolonged expiration.
What is the most common cause of bronchitis?
Acute bronchitis is usually caused by a viral infection. 9 In patients younger than one year, respiratory syncytial virus, parainfluenza virus, and coronavirus are the most common isolates. In patients one to 10 years of age, parainfluenza virus, enterovirus, respiratory syncytial virus, and rhinovirus predominate.
Is coughing a sign of bronchitis?
Although most physicians consider cough to be necessary to the diagnosis of acute bronchitis, they vary in additional requirements. Other signs and symptoms may include sputum production, dyspnea, wheezing, chest pain, fever, hoarseness, malaise, rhonchi, and rales. 16 Each of these may be present in varying degrees or may be absent altogether.
Is bronchitis a viral infection?
Because acute bronchitis is most often caused by a viral infection, usually only symptomatic treatment is required. Treatment can focus on preventing or controlling the cough (antitussive therapy) or on making the cough more effective (protussive therapy). 18
Can bronchodilators cause asthma?
Acute bronchitis and asthma have similar symptoms. Consequently, attention has recently been given to the use of bronchodilators in patients with acute bronchitis. Although relatively few studies have examined the efficacy of oral or inhaled beta agonists, one study 21 found that patients with acute bronchitis who used an albuterol metered-dose inhaler were less likely to be coughing at one week, compared with those who received placebo.
What is the most common symptom of bronchitis?
Cough is the most common symptom bringing patients to the primary care physician's office, and acute bronchitis is usually the diagnosis in these patients. Acute bronchitis should be differentiated from other common diagnoses, such as pneumonia and asthma, because these conditions may need specific therapies not indicated for bronchitis. Symptoms of bronchitis typically last about three weeks. The presence or absence of colored (e.g., green) sputum does not reliably differentiate between bacterial and viral lower respiratory tract infections. Viruses are responsible for more than 90 percent of acute bronchitis infections. Antibiotics are generally not indicated for bronchitis, and should be used only if pertussis is suspected to reduce transmission or if the patient is at increased risk of developing pneumonia (e.g., patients 65 years or older). The typical therapies for managing acute bronchitis symptoms have been shown to be ineffective, and the U.S. Food and Drug Administration recommends against using cough and cold preparations in children younger than six years. The supplement pelargonium may help reduce symptom severity in adults. As patient expectations for antibiotics and therapies for symptom management differ from evidence-based recommendations, effective communication strategies are necessary to provide the safest therapies available while maintaining patient satisfaction.
How long does bronchitis last?
Symptoms of bronchitis typically last about three weeks. The presence or absence of colored (e.g., green) sputum does not reliably differentiate between bacterial and viral lower respiratory tract infections. Viruses are responsible for more than 90 percent of acute bronchitis infections.