
Medication
Treatment for Vulvar Cancer. Specific treatment for vulvar cancer will be determined by your doctor(s) based on: Your overall health and medical history. Extent of the disease. Your …
Procedures
One option for treatment is partial radical vulvectomy (removal of the tumor, nearby parts of the vulva, and other tissues containing cancer). Surgery may also include removal of the lymph …
Therapy
Your healthcare provider will discuss exactly which type of treatment and order of treatment is best suited for your stage of vulvar cancer. Vulvar cancer treatment options include the …
Nutrition
Mar 21, 2022 · Vulvar cancer may be treated with a number of options, depending on the type and stage of the cancer, as well as the patient’s age and overall health. Surgery is typically a …
See more
The ultimate goal of this research is gene therapy. Gene therapy involves replacing the damaged genes in cancer cells with normal genes in order to stop the abnormal behavior of these cells. …
How do I choose the best treatment for vulvar cancer?
Dec 03, 2021 · Treatment may include: Surgery. Radiation therapy. Chemotherapy. Combination treatment. Your doctor's treatment plan will be based on the results of your tests, the type of …
What is the goal of surgery for vulvar cancer?
Jan 16, 2018 · A partial vulvectomy (surgery to remove the tumor and a rim of healthy tissue around it), along with lymph node removal is the usual treatment for melanoma on the vulva. In …
What is vulvar cancer?
What is immune immunotherapy for vulvar cancer?
See more
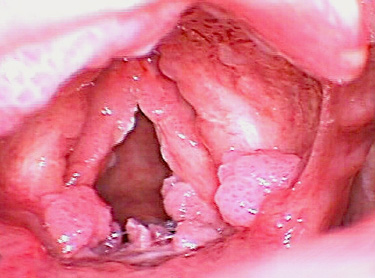
How quickly does vulvar cancer grow?
What are the warning signs of vulvar cancer?
- Constant itching.
- Changes in the color and the way the vulva looks.
- Bleeding or discharge not related to menstruation.
- Severe burning, itching or pain.
- An open sore that lasts for more than a month.
- Skin of the vulva looks white and feels rough.
How long can you live with vulvar cancer?
...
5-year relative survival rates for vulvar cancer.
Can you survive vulvar cancer?
How do you get vulvar cancer?
- Increasing age. ...
- Being exposed to human papillomavirus (HPV). ...
- Smoking. ...
- Having a weakened immune system. ...
- Having a history of precancerous conditions of the vulva.
Does vulvar cancer spread fast?
Is vulvar cancer serious?
What is the recovery time for vulvar cancer surgery?
What kind of doctor treats cancer?
If your doctor or gynecologist suspects or diagnoses cancer, you'll likely be referred to a gynecologic oncologist who specializes in surgery for gynecologic cancers. Because appointments can be brief, and it can be difficult to remember everything you want to discuss, it's a good idea to be prepared.
What tests can be done to determine the stage of cancer?
Your doctor may do a more thorough examination of your pelvis for signs that the cancer has spread. Imaging tests.
Why is radiation used for cancer?
Radiation therapy is sometimes used to shrink large vulvar cancers in order to make it more likely that surgery will be successful . Radiation therapy is sometimes combined with chemotherapy, which can make cancer cells more vulnerable to the radiation.
What is the procedure to remove lymph nodes?
Removing a few nearby lymph nodes (sentinel node biopsy). To determine whether cancer has spread to the lymph nodes, the surgeon may use a procedure called sentinel node biopsy. This procedure identifies the lymph nodes most likely to contain cancer so they can be removed and analyzed.
How does immunotherapy work?
Immunotherapy uses your immune system to fight cancer. Your body's disease-fighting immune system may not attack your cancer because the cancer cells produce proteins that help them hide from the immune system cells. Immunotherapy works by interfering with that process.
Can radiation kill cancer cells?
Radiation therapy is sometimes combined with chemotherapy, which can make cancer cells more vulnerable to the radiation. If cancer cells are discovered in your lymph nodes, your doctor may recommend radiation to the area around your lymph nodes to kill any cancer cells that might remain after surgery.
What is vulvar cancer?
Vulvar cancer is a rare disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the vulva. Having vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia or HPV infection can increase the risk of vulvar cancer. Signs of vulvar cancer include bleeding or itching in the vulvar area.
Can vulvar cancer cause early symptoms?
Vulvar cancer often does not cause early signs or symptoms. Signs and symptoms may be caused by vulvar cancer or by other conditions. Check with your doctor if you have any of the following:
What is it called when cancer spreads to another part of the body?
When cancer spreads to another part of the body, it is called metastasis . Cancer cells break away from where they began (the primary tumor) and travel through the lymph system or blood.
Where does stage 2 cancer spread?
In stage II, the tumor is any size and has spread into the lower part of the urethra, the lower part of the vagina, or the anus. Cancer has not spread to the lymph nodes.
What is stage 3 cancer?
In stage III, the tumor is any size and may have spread into the lower part of the urethra, the lower part of the vagina, or the anus. Cancer has spread to one or more nearby lymph nodes. Stage III is divided into stages IIIA, IIIB, and IIIC.
What is the treatment for cancer after surgery?
After the doctor removes all the cancer that can be seen at the time of the surgery, some patients may be given chemotherapy and/or radiation therapy after surgery to kill any cancer cells that are left. Treatment given after the surgery, to lower the risk that the cancer will come back, is called adjuvant therapy.
What is a PDQ cancer summary?
This PDQ cancer information summary has current information about the treatment of vulvar cancer. It is meant to inform and help patients, families, and caregivers. It does not give formal guidelines or recommendations for making decisions about health care.
How rare is vulvar cancer?
Vulvar cancer is very rare, accounting for 0.6 percent of all cancers in women. In the U.S., close to 5,000 women are diagnosed with vulvar cancer each year. The HPV vaccine can prevent the strains of HPV responsible for most cervical, vaginal and vulvar cancers.
What are the risk factors for vulvar cancer?
The following factors may increase a woman’s risk of developing vulvar cancer: Age: Of the women who develop vulvar cancer, over 80 percent are over 50, and half are over 70. Infection with certain types of HPV. HIV infection.
What is the procedure to remove cancer cells?
Vulvectomy: All tissues of the vulvar are surgically removed. The extent of the tissue removed is based on the size and location of the lesion. Radiation therapy: X-rays, gamma rays and charged particles are used to fight cancer.
What is the treatment for cancer?
The extent of the tissue removed is based on the size and location of the lesion. Radiation therapy: X-rays, gamma rays and charged particles are used to fight cancer. Chemotherapy: Anticancer drugs are used to treat cancerous cells. It's very important that your particular findings be put into context by an expert.
What is a gynecologic oncologist?
Gynecologic oncologists are subspecialists with advanced training in the diagnosis, treatment and surveillance of female cancers, including vulvar cancer.
What is a VIN?
Vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia (VIN): VIN occurs when there are abnormal cells on the surface layer of vulvar skin. These cell changes are a precancerous condition, so there is an increased risk for vulvar cancer in women with VIN, although most cases do not progress to cancer. Other genital cancers. Smoking.
What is recurrent vulvar cancer?
Recurrent vulvar cancer. When cancer comes back after treatment, it's called recurrent cancer. Treatment options depend on how soon the cancer comes back and whether the recurrence is local (in the vulva), regional (in nearby lymph nodes), or distant (has spread to organs such as the lungs or bones). If the recurrence is local, it may still be ...
What is the most important factor in choosing a treatment for vulvar cancer?
Other factors that affect this decision include the exact location of the cancer on the vulva, the type of vulvar cancer, your age, your preferences, and your overall health. Because vulvar cancer is rare, it's hard to study it well.
What is stage 2 cancer?
Stage II. Stage II cancers have spread to structures near the vulva, such as the anus, the lower vagina, and/or the lower urethra. One option for treatment is partial radical vulvectomy (removal of the tumor, nearby parts of the vulva, and other tissues containing cancer). Surgery may also include removal of the lymph nodes in ...
Where does stage 2 cancer spread?
Stage II cancers have spread to structures near the vulva, such as the anus, the lower vagina, and/or the lower urethra. One option for treatment is partial radical vulvectomy (removal of the tumor, nearby parts of the vulva, and other tissues containing cancer). Surgery may also include removal of the lymph nodes in the groin on both sides ...
Can radiation help with bladder cancer?
There is no standard treatment for them. Surgery is not expected to cure these cancers, but may be helpful in relieving symptoms, such as bowel or bladder blockages. Radiation may also be helpful in shrinking the cancer and improving symptoms. Chemo may also be an option.
Can radiation cure cancer?
Surgery is not expected to cure these cancers, but may be helpful in relieving symptoms, such as bowel or bladder blockages. Radiation may also be helpful in shrinking the cancer and improving symptoms. Chemo may also be an option. Experts recommend that these women enroll in a clinical trial.
What is it called when cancer comes back?
When cancer comes back after treatment, it's called recurrent cancer. Treatment options depend on how soon the cancer comes back and whether the recurrence is local (in the vulva), regional (in nearby lymph nodes), or distant (has spread to organs such as the lungs or bones). If the recurrence is local, it may still be possible to remove ...
What is the most common treatment for cancer of the vulva?
Surgery is the most common treatment for cancer of the vulva. The goal of surgery is to remove all the cancer without any loss of your sexual function. Types of surgery include:
What is the best treatment for vulvar lesions?
Biologic therapy. Biologic therapy is a type of treatment that uses lab-made substances or substances in your body to help your body’s immune system or fight cancer. Imiquimod cream (Aldara®, Zyclara®) is an example of a biologic therapy used to treat precancerous vulvar lesions.
What is vulvar cancer?
Vulvar Cancer. Vulvar cancer is a rare cancer of a woman’s vulva. There are about 6,000 new cases of vulvar cancer in the U.S. each year. About half the cases are caused by human papillomavirus and half are caused by lichen sclerosus. Symptoms include changes in vulvar skin color and lumps or open sores.
How many cases of vulvar cancer are there in the US?
There are about 6,000 new cases of vulvar cancer in the U.S. each year. About half the cases are caused by human papillomavirus and half are caused by lichen sclerosus. Symptoms include changes in vulvar skin color and lumps or open sores. Treatments include surgery, radiation and chemotherapy.
What are the symptoms of vulvar?
Symptoms include changes in vulvar skin color and lumps or open sores. Treatments include surgery, radiation and chemotherapy. Appointments & Access. Contact Us. Overview. Symptoms and Causes. Diagnosis and Tests. Management and Treatment. Prevention.
Where does vulvar cancer occur?
Vulvar cancer most often develops on the inner or outer vaginal lips, but can arise in any location of the vulva. Vulvar cancer usually develops slowly over several years. Precancerous lesions usually develop first and are discovered as abnormal cell growth in the outer most layer of skin.
How does radiation kill cancer cells?
Radiation therapy kills cancer cells using high-energy x-rays or other types of radiation. External radiation therapy uses a machine to deliver radiation through your skin to the targeted cancer site. Internal radiation therapy uses a radioactive substance sealed in needles, seeds, wires or catheters that are placed directly into or near the cancer. Choice of radiation therapy delivery method depends on the type and stage of the cancer being treated.
How to treat vulvar cancer?
Surgery is typically a component of the treatment plan. Chemotherapy and radiation therapy may also be recommended in situations where the cancer cannot be completely ...
Can radiation therapy help with vulva cancer?
Radiation treatment for vulvar cancer requires accuracy and precision. With sophisticated radiation therapy delivery systems, our radiation oncologists are better able to target difficult-to-reach tumors in the vulva. Also, our radiation oncologists can direct higher radiation doses at vulvar cancer cells, while reducing exposure to normal, healthy tissue.
Can cancer be removed with radiation?
Chemotherapy and radiation therapy may also be recommended in situations where the cancer cannot be completely removed with surgery, if there is a high risk for recurrence or if the cancer has spread to the lymph nodes. A gynecologic oncologist specializing in cancer ...
What is HDR brachytherapy?
High-dose rate (HDR) brachytherapy is a type of internal radiation therapy that delivers radiation from implants placed close to, or inside, the tumor (s) in the body. HDR brachytherapy may be combined with other treatments, such as TomoTherapy® or intensity modulated radiation therapy (IMRT), to treat vulvar cancer.
What is EBRT radiation?
External beam radiation therapy (EBRT) directs a beam of radiation from outside the body at cancerous tissues inside the body. It is a cancer treatment option that uses doses of radiation to destroy cancerous cells and shrink tumors. Benefits of EBRT for vulvar cancer may include: EBRT is an outpatient procedure.
What drugs are used to treat vulvar cancer?
Researchers are learning more about the gene and protein changes that take place in vulvar cancer cells. Drugs that target changes like these are already being used to treat other cancers. There have been case reports of using these drugs known as targeted therapies to treat vulvar cancers, too. These drugs do not have the same kind of side effects as traditional chemo drugs do. So far, the drugs cetuximab and erlotinib have been tried and doctors have reported some success in a few patients. Sometimes cetuximab is combined with cisplatin chemotherapy for treatment. These drugs need further study.
Is vulvar cancer rare?
Vulvar cancer is rare, which makes it hard to study. Still, research is being done to find new ways to prevent and treat cancer of the vulva. There are some promising new developments.
Can vulvar cancer spread to lymph nodes?
Vulvar cancer can spread to lymph nodes in the groin. Better ways to look for this spread and identify nodes with cancer might help doctors treat these nodes and decrease the risk of cancer coming back there. It could also allow them to save the healthy nodes and decrease the risk of long-term swelling in the groin and legs, called lymphedema.
What is clinical trial?
Clinical trials are being done to determine the best way to use and combine surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. These trials will provide information about whether certain groups of patients benefit from radiation after surgery and whether patients with cancer that has spread to lymph nodes benefit from chemotherapy or pelvic radiation therapy.
What is internal radiation therapy?
The use of internal radiation therapy, called brachytherapy, along with external beam radiation is being studied. This form of radiation is done by placing tiny pieces of radioactive material right into the tumor. It's already used to treat other types of cancer, and women with certain vulvar tumors might benefit from it, too.
What is the goal of gene therapy?
Gene therapy involves replacing the damaged genes in cancer cells with normal genes in order to stop the abnormal behavior of these cells.

Diagnosis
Treatment
Clinical Trials
Coping and Support
Specialist to consult
Preparing For Your Appointment
- Diagnosing vulvar cancer
Tests and procedures used to diagnose vulvar cancer include: 1. Examining your vulva.Your doctor will likely conduct a physical exam of your vulva to look for abnormalities. 2. Using a special magnifying device to examine your vulva.During a colposcopy exam, your doctor uses a … - Determining the extent of the cancer
Once your diagnosis is confirmed, your doctor works to determine the size and extent (stage) of your cancer. Staging tests can include: 1. Examination of your pelvic area for cancer spread.Your doctor may do a more thorough examination of your pelvis for signs that the cancer has spread. …