
Mayoclinic.org
1. Avoid products with added salt...
2. Choose lower potassium foods...
3. Limit the amount of protein you eat...
Learn More...Allremedies.com
1. Blueberries...
2. Apple...
3. Cabbage...
4. Cauliflower...
5. Chamomile Tea...
6. Goldenrod Tea...
7. Aloe Vera...
8. Vitamin C...
Learn More...Trueremedies.com
1. Drink Enough Water...
2. Reduce Salt Consumption...
3. Garlic...
4. Onion...
5. Fishes...
6. Blueberries...
7. Apple...
8. Cabbage...
Learn More...Curejoy.com
1. Baking soda...
2. Dandelion leaves...
3. Asparagus...
4. Ayurvedic remedies...
Learn More...Effectiveremedies.com
1. Soot Trees and Black Beans...
2. Houttuynia...
3. Red Sandalwood...
4. Flame Of The Forest...
5. Goldenrod Tea and Chamomile Tea...
6. Fruits And Vegetable Juices...
7. Cucumber...
8. Apple Cider Vinegar...
Learn More...When does an uti turn into a kidney infection?
Sometimes a urinary tract infection can get out of hand as the harmful bacteria crawl their way through the bladder and up to the kidneys. With a kidney infection, its going to be that dull, continuous pain, says Santiago. UTIs that turn into kidney infections are also more likely to cause fever, chills, and nausea. 3. Trauma
What is the best home remedy for kidney infection?
Remedies to help alleviate symptoms
- Drink plenty of water. Flushing bacteria from the kidneys is an important goal when a person has a kidney infection. ...
- Drink cranberry juice. ...
- Rest. ...
- Use warm, moist heat. ...
- Take green tea extract or drink green tea. ...
- Use over-the-counter pain relievers, but avoid aspirin. ...
Is oregano oil good for kidney infection?
Oregano oil has strong anti-bacterial ability, so it can prevent urinary tract infection and kidney infection effectively. - Antioxidant effect. Oregano oil is one source of antioxidant substances that can help remove free radicals from the body and protect the remaining kidney functioning tissues. Besides, it can also help improve patients ...
Can a person have a kidney infection without a fever?
Yes it is possible to have either a kidney infection or urinary tract infection with no fever. Many years ago I had one with absolutely no other signs besides a nasty backache. I thought nothing of it as I have back problems anyway.
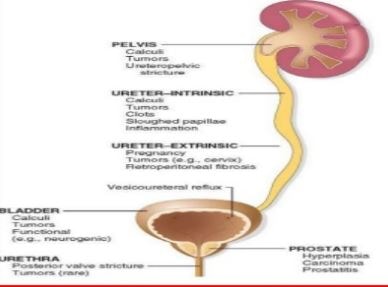
Can you take antibiotics if you have chronic kidney disease?
Antibiotics with Kidney Disease: If you need to receive any antibiotics, the dose may need to be adjusted and likely decreased to match your lower kidney function. Some antibiotics are safe to take when you have kidney disease and others should be avoided.
How does CKD affect UTI?
CKD could be a risk factor for UTI, which may be present with asymptomatic bacteriuria or symptomatic UTIs requiring treatment. In addition to reduced host immunity6, comorbidities especially diabetes, advanced age, and urinary tract obstruction are common risks for UTI and CKD progression accordingly7.
Is ciprofloxacin safe in kidney disease?
Our study suggests that ciprofloxacin is relatively safe regarding its renal toxicity and can be used in SK patients with UTI. Caution, however, is required for risk persons, such as stage 5 CKD patients.
What antibiotics treat kidney disease?
Penicillins are generally well tolerated in patients with kidney disease. Hypersensitivity reactions are commonly reported, and an association between penicillins and interstitial nephritis exists, but patients with kidney disease are not considered to be at higher risk (10).
What is best antibiotic for urinary tract infection?
Drugs commonly recommended for simple UTIs include:Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole (Bactrim, Septra, others)Fosfomycin (Monurol)Nitrofurantoin (Macrodantin, Macrobid)Cephalexin (Keflex)Ceftriaxone.
Is nitrofurantoin safe in CKD?
Use of nitrofurantoin can be problematic for patients with renal dysfunction. Reduced renal function may lead to toxicity due to an increase in nitrofurantoin serum levels. Impaired renal function also decreases the efficacy of nitrofurantoin as an antibacterial medicine in the urinary tract.
Is bactrim safe in CKD?
The double-strength tablet of trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole (Bactrim, Septra), which is commonly prescribed, should be avoided unless the patient's creatinine clearance is known to exceed 50 mL per minute; the single-strength tablet of trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole is preferable.
Is levofloxacin safe in kidney disease?
Since levofloxacin is excreted mainly by the kidneys, the dose of Levofloxacin Tablets should be adjusted in patients with renal impairment.
Is cephalexin safe for CKD patients?
Renal Impairment KEFLEX should be administered with caution in the presence of impaired renal function (creatinine clearance < 30 mL/min, with or without dialysis).
What antibiotics should I avoid with kidney disease?
Aminoglycoside antibiotics are known for causing kidney injury—even at low doses. People with chronic kidney disease, dehydration, or those who have been taking these antibiotics for a long time are at particularly high risk. The most toxic aminoglycoside is neomycin, followed by gentamicin, tobramycin, and amikacin.
Which medicine is best for chronic kidney disease?
Medications like allopurinol lower the levels of uric acid to help prevent gout, but they may also cause side effects like rashes or nausea. Initial studies suggest that allopurinol can slow down the progression of chronic kidney disease and prevent cardiovascular complications.
What medications should be avoided with kidney disease?
What medications to avoid with kidney diseasePain medications also known as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) ... Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) ... Cholesterol medications (statins) ... Antibiotic medications. ... Diabetes medications. ... Antacids. ... Herbal supplements and vitamins. ... Contrast dye.
What is the best medication for pyelonephritis?
In short, the management of pyelonephritis in patients with GFR in the 10- to 50-ml/min range requires only reduction of dosage to avoid high serum concentrations and the concomitant increased risk for concentration-dependent adverse drug events. Ciprofloxacin or levofloxacin are suggested as first choices for empiric therapy.
What is the MIC of 90% of UTI?
The MIC for 90% of the bacteria that commonly cause UTI is usually <16 μg/ml. Hence, there is a large safety range as long as the kidney can concentrate urine to some degree. Even though it is unlikely that cystitis would require parenteral therapy, it is pertinent to comment on the data in Table 1.
How are aminoglycosides excreted?
The aminoglycosides are excreted by glomerular filtration. Roughly 5% of filtered drug is reabsorbed by the cells of the proximal renal tubules ( 31 ). The result is very high urine concentrations ( Table 1 ). There are few data on urine concentrations in patients with renal disease. One paper reported a peak urine concentration of sisomicin (an aminoglycoside that is not available in the United States) of only 1.8 μg/ml in the ureteral urine from a severely damaged kidney ( 32 ).
Which antimicrobials are effective for urethritis?
In summary, antimicrobials with anticipated effectiveness in patients with urethritis/cystitis and chronic renal insufficiency are selected fluoroquinolones (ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin) and trimethoprim alone. Nitrofurantoin should not be used because of low urine drug concentrations.
Is gemifloxacin an empiric therapy?
Hence, moxifloxacin or gemifloxacin should not be used because of their low urine concentrations ( Table 1 ). The dose of drug is adjusted for the degree of renal insufficiency as suggested by the drug package insert or standard reference sources ( 15, 16 ). The primary goal is to achieve predictably effective serum and urine concentrations. Ciprofloxacin urine concentrations, 24 h after an adjusted dose, are reported as above the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of urinary pathogens in patients with a creatinine clearance of <50 ml/min ( 17, 18 ).
Is pyelonephritis a parenchymal infection?
A long-standing issue is whether UTI represent surface mucosal (uroepithelial) or parenchymal infections or both. Infections of the urethra are viewed as superficial, whereas pyelonephritis is considered a parenchymal infection. Cystitis ranges from mild (superficial) to invasion of the wall of the bladder.
Can UTI be treated with renal insufficiency?
Clinical trials of new drugs that are under evaluation for efficacy for UTI usually exclude patients with chronic renal insufficiency . As a result, there are few data on the urine concentrations of drugs that are licensed for the treatment of UTI in patients with underlying renal disease. Of interest, there are only a few reports of clinical or microbiologic antimicrobial treatment failures in patients with renal insufficiency and cystitis or pyelonephritis. Perhaps this is not a serious problem, or, more likely, the sporadic nature of the problem has failed to generate a coordinated multicenter evaluation.
How to help people with kidney disease?
They can understand what you're feeling and offer unique support. Ask your doctor about support groups in your area. Or contact organizations such as the American Association of Kidney Patients, the National Kidney Foundation or the American Kidney Fund for groups in your area .
What is the treatment for end stage kidney disease?
At that point, you need dialysis or a kidney transplant. Dialysis.
What is the procedure to remove a sample of kidney tissue?
Other imaging tests may be used in some cases. Removing a sample of kidney tissue for testing. Your doctor may recommend a kidney biopsy to remove a sample of kidney tissue. Kidney biopsy is often done with local anesthesia using a long, thin needle that's inserted through your skin and into your kidney.
What is a kidney biopsy?
Kidney biopsy. During a kidney biopsy, your doctor uses a needle to remove a small sample of kidney tissue for lab testing. The biopsy needle is inserted through your skin and is often directed using the guidance of an imaging device, such as ultrasound. As a first step toward diagnosis of kidney disease, your doctor discusses your personal ...
What is the best way to diagnose kidney failure?
Imaging tests. Your doctor may use ultrasound to assess your kidneys' structure and size. Other imaging tests may be used in some cases.
What tests are done to determine if you have kidney disease?
For kidney disease diagnosis, you may also need certain tests and procedures, such as: Blood tests. Kidney function tests look for the level of waste products, such as creatinine and urea, in your blood.
What is the first step in a kidney diagnosis?
As a first step toward diagnosis of kidney disease, your doctor discusses your personal and family history with you. Among other things, your doctor might ask questions about whether you've been diagnosed with high blood pressure, if you've taken a medication that might affect kidney function, if you've noticed changes in your urinary habits, ...
Rapid Response
In his review of urinary tract infection, Car recommends reducing the dose of amoxicillin in renal failure, and avoiding the use of tetracyclines and nitrofurantoin.1Unfortunately, “renal failure” has no accepted definition in terms of glomerular filtration rate (GFR).
Treatment of urinary tract infections: implications of chronic kidney disease
In his review of urinary tract infection, Car recommends reducing the dose of amoxicillin in renal failure, and avoiding the use of tetracyclines and nitrofurantoin.1Unfortunately, “renal failure” has no accepted definition in terms of glomerular filtration rate (GFR).

Diagnosis
Treatment
- Depending on the cause, some types of kidney disease can be treated. Often, though, chronic kidney disease has no cure. Treatment usually consists of measures to help control signs and symptoms, reduce complications, and slow progression of the disease. If your kidneys become severely damaged, you might need treatment for end-stage kidney disease.
Clinical Trials
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiestesting new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
- As part of your treatment for chronic kidney disease, your doctor might recommend a special diet to help support your kidneys and limit the work they must do. Ask your doctor for a referral to a registered dietitian who can analyze your diet and suggest ways to make your diet easier on your kidneys. Depending on your situation, kidney function and ...
Coping and Support
- Receiving a diagnosis of chronic kidney disease can be worrisome. To help you cope with your feelings, consider: 1. Connecting with other people who have kidney disease.They can understand what you're feeling and offer unique support. Ask your doctor about support groups in your area. Or contact organizations such as the American Association of Kidney Patients, the National Kid…
Preparing For Your Appointment
- You'll likely start by seeing your primary care doctor. If lab tests reveal that you have kidney damage, you might be referred to a doctor who specializes in kidney problems (nephrologist).