
Medication
Mar 01, 2021 · To relieve symptoms of hives at home you can: Wear loose-fitting, breathable clothing. Use cold compresses. Stay cool in general. Take a bath. Avoid known allergens and hives triggers. Stay moisturized Alternative treatments.
Self-care
Jan 01, 2022 · First-line pharmacotherapy for acute and chronic urticaria is nonsedating second-generation antihistamines (histamine H 1 blockers), which can …
Nutrition
Prednisolone in the dose of 20-30 mg for three days is effective to control severe attacks of urticaria and angioedema. Low dosage alternate day dosing may be used in patients with CU who do not respond to other therapies. [ 13]
See more
Apr 04, 2022 · What can I do to manage urticaria? Cool your skin. This may help decrease itching. Apply a cool pack to your hives. Dip a hand towel in cool water, wring... Do not rub your hives. This can irritate your skin and cause more hives. Wear loose clothing. Tight clothes may irritate your skin and cause ...
How to treat urticaria with home remedies?
The most common medications for urticaria include 2): Sleep-causing (sedating) type-1 antihistamines such as diphenhydramine, hydroxyzine, or cetirizine Non-sleep-causing (non-sedating) type-1 antihistamines such as loratadine, fexofenadine, or desloratadine Type-2 antihistamines such as anitidine, cimetidine, or famotidine Doxepin
Can urticaria go away without treatment?
Meanwhile, a 2016 review concluded that acupuncture might help relieve chronic urticaria, though there is not enough evidence to confirm that this is a safe, effective treatment.
What are some common treatments for urticaria?
Oct 14, 2021 · Treatment of urticaria can be as simple as eliminating whatever it was that caused the hives to start in the first place. If the itching and …
How I cured my chronic urticaria?
Jun 02, 2017 · You can treat the hives with calamine lotion as necessary. Diphenhydramine (Benadryl) This oral antihistamine can reduce the rash and other symptoms, like itching, by working from the inside out....
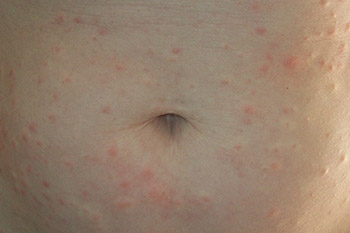
How Is The Cause of Urticaria Diagnosed?
Your healthcare provider will examine you and ask about your symptoms. He may also ask about your family medical history, medicines you take, and f...
How Is Urticaria Treated?
Hives often go away without treatment. Chronic urticaria may need to be treated with more than one medicine, or other medicines than listed below....
What Steps Do I Need to Take For Signs Or Symptoms of Anaphylaxis?
1. Immediately give 1 shot of epinephrine only into the outer thigh muscle. 2. Leave the shot in place as directed. Your healthcare provider may re...
What Safety Precautions Do I Need to Take If I Am at Risk For Anaphylaxis?
1. Keep 2 shots of epinephrine with you at all times. You may need a second shot, because epinephrine only works for about 20 minutes and symptoms...
What Can I Do to Manage Urticaria?
1. Cool your skin. This may help decrease itching. Apply a cool pack to your hives. Dip a hand towel in cool water, wring it out, and place it on y...
Call 911 For Signs Or Symptoms of Anaphylaxis
such as trouble breathing, swelling in your mouth or throat, or wheezing. You may also have itching, a rash, or feel like you are going to faint.
When Should I Seek Immediate Care?
1. Your heart is beating faster than it normally does. 2. You have cramping or severe pain in your abdomen.
When Should I Contact My Healthcare Provider?
1. You have a fever. 2. Your skin still itches 24 hours after you take your medicine. 3. You still have hives after 7 days. 4. Your joints are pain...
How to treat idiopathic urticaria?
A stepwise approach to treating chronic idiopathic urticaria, based on published treatment guidelines, is shown in Figure 9. 1, 7, 16 Second-generation antihi stamines are considered first-line therapy . For better symptom control, the medication should be dosed daily, rather than on an as-needed basis. 20 Treatment guidelines suggest that if normal doses are not successful, titration up to two to four times the usual dose is the next step. 1, 7, 16 With higher doses, there is greater possibility of adverse effects, which should be discussed with patients.
What is the initial workup for urticaria?
The initial workup for urticaria and angioedema is a history and physical examination to determine a possible etiology ( Table 3). Patients should be asked about timing and onset of symptoms, associated symptoms (which may suggest anaphylaxis), likely triggers, medications and supplements (especially new or recently changed dosages), recent infections, and travel history. Physicians should perform a complete review of systems. Physical examination should include identifying and characterizing any current lesions, testing for dermatographism (urticaria, often linear, that forms with stroking or rubbing of unblemished skin), and checking for signs of systemic illness.
What is urticaria hives?
Urticaria is often referred to as hives, but that term can have a variety of meanings in the general population. Common conditions that can be confused with urticaria are listed in Table 2. 12, 13 These conditions are diagnosed primarily by history and physical examination. Some conditions can produce urticarial lesions, but they have a different underlying pathophysiology, as well as prognosis and treatment. These include cutaneous mastocytosis (urticaria pigmentosa), urticarial vasculitis, cryoglobulinemia, and several rare disorders. These conditions may be distinguished based on differences in presentation. For example, cutaneous mastocytosis is noted for orange to brown hyperpigmentation of the lesions, urticaria limited to smaller diameters, and Darier sign (a wheal and flare reaction produced by stroking the lesion). Likewise, classic urticarial vasculitis is distinguished by individual wheals that last for more than 24 hours, are painful, and leave residual hyperpigmentation or purpura 12 ( Figures 7 and 8). However, the sensitivity of these characteristics may be low. 14
What is the prevalence of urticaria?
Urticaria has a lifetime prevalence of approximately 20 percent in the general population. It is caused by immunoglobulin E– and nonimmunoglobulin E–mediated mast cell and basophil release of histamine and other inflammatory mediators. Diagnosis is made clinically.
How long does urticaria flare up?
In chronic urticaria, flare-ups recur more days than not for more than six weeks.
What is the difference between urticaria and angioedema?
The difference between the two conditions is whether the mast cells are in the superficial dermis, which results in urticaria, or in the deeper dermis and subcutaneous tissues, which produces angioedema. Immunoglobulin E (IgE) mediation of this histamine release is often ascribed, but non-IgE and nonimmunologic mast cell activation can also be a cause. Bradykinin-mediated increase in vascular permeability is another cause of angioedema associated with the use of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors. Chronic urticaria may have a serologic autoimmune component in some patients, including antibodies to IgE and the high-affinity IgE receptor. However, the exact mechanism of action and significance of these antibodies remain unclear. 3, 4
Is urticaria idiopathic or idiopathic?
Chronic urticaria is usually idiopathic and requires only a simple laboratory workup unless elements of the history or physical examination suggest specific underlying conditions. Treatment includes avoidance of triggers, although these can be identified in only 10 to 20 percent of patients with chronic urticaria.
What is the best medicine for urticaria?
The following are common medicines used to treat urticaria: Antihistamines decrease mild symptoms such as itching or a rash. Steroids decrease redness, pain, and swelling.
How to get rid of hives on skin?
Cool your skin. This may help decrease itching. Apply a cool pack to your hives. Dip a hand towel in cool water, wring it out, and place it on your hives. You may also soak your skin in a cool oatmeal bath. Do not rub your hives. This can irritate your skin and cause more hives. Wear loose clothing.
How long do hives last?
Hives can change size and shape, and appear anywhere on your skin. They can be mild or severe and last from a few minutes to a few days. Hives may be a sign of a severe allergic reaction called anaphylaxis that needs immediate treatment. Urticaria that lasts longer than 6 weeks may be a chronic condition that needs long-term treatment.
What are some foods that cause allergies?
Food allergies, such as to nuts, eggs, or shellfish. Food dyes, additives, or preservatives. Medicine allergies, such as to ibuprofen or antibiotics. Infections, such as a cold or mono. Bug bites.
How long does epinephrine last?
You may need a second shot, because epinephrine only works for about 20 minutes and symptoms may return. Your healthcare provider can show you and family members how to give the shot. Check the expiration date every month and replace it before it expires. Create an action plan.
Can you refuse treatment?
You always have the right to refuse treatment. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Can you exercise after eating?
If you have had exercise-induced anaphylaxis, do not exercise right after you eat. Stop exercising right away if you start to develop any signs or symptoms of anaphylaxis. You may first feel tired, warm, or have itchy skin. Hives, swelling, and severe breathing problems may develop if you continue to exercise.
How to treat urticaria?
Wear loose clothing. Take an antihistamine, such as Benadryl, to counter the histamine (chemical allergic reaction). Avoid alcohol, tobacco, and exercise. You might need extra treatment if you have a severe case of urticaria or if the bumps occur in a sensitive area, like the throat, lips, or eyes.
What is the best medication for urticaria?
The most common medications for urticaria include 2): Sleep-causing (sedating) type-1 antihistamines such as diphenhydramine, hydroxyzine, or cetirizine. Non-sleep-causing (non-sedating) type-1 antihistamines such as loratadine, fexofenadine, or desloratadine.
What is urticaria hives?
Urticaria also called hives, is a skin reaction usually caused by allergy or from stress, characterized by swelling, bumps, itching and burning that appear and disappear anywhere on the body 1). The important symptom of urticaria is itch (pruritus). Urticaria or hives are sometimes referred to as welts or wheals surrounded by ...
How do you know if you have hives?
Common symptoms are itching, redness, and swelling. Symptoms can appear right after an allergic exposure or later on, and can occur in any order. Individual lesions of hives appear as distinct (well-defined), pink-to-red swellings ranging in size from 2 mm to over 30 cm, also are known as welts or wheals.
How long does it take for urticaria to disappear?
Another sign of urticaria is if you press the red bump and the middle part turns white (known as blanching). Individual lesions of hives disappear within 24 hours, though a single episode may last much longer. Dermographism is a type of urticaria that appears within a few minutes of scratching the skin.
How long does it take for hives to go away?
Swelling of the eyes, mouth, hands, feet, or genitals can sometimes occur with hives. This swelling, called angioedema, usually goes away within 24 hours. Hives is usually an itchy rash that can also burn or sting.
How does the body respond to allergies?
Your body responds to allergies by releasing chemicals into your blood. These chemicals, such as histamine, trigger the bumps and swelling known as hives. In up to 90% of outbreaks of hives, a trigger is never found despite extensive testing; these cases are referred to as idiopathic urticaria. In approximately 50% of idiopathic urticaria ...
How to treat urticaria?
Treatment for acute urticaria includes non-sedating antihistamines taken regularly for several weeks. Antihistamines, such as cetirizine or fexofenadine, help by blocking the effects of histamines and reducing the rash and stopping the itching. Various antihistamines can be purchased in pharmacies or online.
How long does urticaria last?
Acute urticaria is the most common type. Symptoms last less than 6 weeks, and they typically affect the face and neck, fingers, toes, and the genitals of males. However, any part of the body can be affected. Chronic urticaria continues for more than 6 weeks.
What is a red rash that is triggered by an allergen?
Hives are a red, raised, itchy skin rash that is sometimes triggered by an allergen. An allergen is something that produces an allergic reaction. It is also known as urticaria, welts, weals, or nettle rash. When an allergic reaction occurs, the body releases a protein called histamine.
How long do hives last?
They can appear on just one part of the body, or on several parts. Symptoms normally disappear within 24 hours, but sometimes another weal appears as the last one fades. In some cases, hives can continue for several days. People with chronic hives can have symptoms for months or years.
What is the best medicine for hives?
Antibiotics, for example, Dapsone, can reduce redness and swelling. Omalizumab, or Xolair, is an injectable drug that blocks immunoglobin E, a substance that plays a role in allergic responses. It can reduce symptoms of chronic idiopathic urticaria, a type of hives of unknown origin that can last for months or years.
Can acupuncture help with hives?
Those with severe symptoms may need to see a specialist. Acupuncture may help treat hives, but a systematic review. Trusted Source. published in 2016 concluded that “Acupuncture might be effective and safe for chronic urticaria in relieving symptoms, based on a low level of evidence.”.
What is a rash on the skin called?
Swellings , known as wheals, appear as a rash on the skin. They are usually pink or red, with an oval or round shape. They can range from a few millimeters to several inches across. They can be extremely itchy, and they have a red flare around them.
What is the best treatment for hives?
Over-the-counter options. If home and natural remedies aren’t enough to help your hives, over-the-counter (OTC) treatments may be your best bet. Not only can OTC options relieve itching and irritation, they can target your body’s histamine response, which is what causes hives to appear.
How to reduce side effects of corticosteroids?
thinning skin. To reduce side effects, take oral corticosteroids at a lower dose and transition to corticosteroid creams with your doctor’s supervision.
What is a rash on your body?
Hives (urticaria) is a rash on your body. Although hives are often associated with allergic reactions, they can also be triggered by: stress. medications. insect bites or stings. sunlight. cold temperatures. infection. other underlying conditions.
How long does it take for hives to go away?
Hives generally fade within 24 hours and don’t require treatment. However, you should seek immediate medical attention if you experience any of the following: dizziness. swelling in your throat or face. difficulty breathing. These may be signs of a severe allergic reaction and require emergency care.
What are the signs of a severe allergic reaction?
difficulty breathing. These may be signs of a severe allergic reaction and require emergency care. If your hives are milder, continue reading to learn how to ease any discomfort and speed up the healing process.
How to get rid of a swollen swollen swollen swollen
Use a cold compress. Applying something cool to your skin can help relieve any irritation. To do this, grab a bag of frozen veggies or wrap a handful of ice in a towel and apply to the affected area for up to 10 minutes. Repeat as needed throughout the day.
Does witch hazel help with irritation?
The natural tannins found in the herb witch hazel can help relieve irritation. You may want to prepare your own witch hazel mixture to use as an astringent to maximize the tannins.
What is the best medication for hives?
Anti-inflammation medications. Oral corticosteroids, such as prednisone, can help lessen swelling, redness and itching. These are generally for short-term control of severe hives or angioedema because they can cause serious side effects if taken for a long time. Antidepressants.
How to treat hives from a swollen ear?
Avoid scratching or using harsh soaps. Soothe the affected area with a bath, fan, cool cloth, lotion or anti-itch cream. Keep a diary of when and where hives occur, what you were doing, what you were eating, and so on. This may help you and your doctor identify triggers. Avoid known triggers.
How long do hives last?
Chronic hives can go on for months and years. They can interfere with sleep, work and other activities. The following precautions may help prevent or soothe the recurring skin reactions of chronic hives: Wear loose, light clothing. Avoid scratching or using harsh soaps.
What are some examples of antihistamines?
Examples include: Loratadine (Claritin) Fexofenadine (Allegra) Cetirizine (Zyrtec) Desloratadine (Clarinex) If the nondrowsy antihistamines don't help you, your doctor may increase the dose or have you try the type that tends to make people drowsy and is taken at bedtime.
What is the best medicine for hives?
Quercetin and evening primrose are two supplements for hives that will calm and get rid of your hives faster. ( 19 ) Quercetin is a natural antihistamine and an anti-inflammatory. Test tube studies have revealed that quercetin prevents immune cells from releasing histamines, which cause allergic reactions like hives.
What to do when you have hives?
With some simple natural remedies, you can calm a hives outbreak on yourself or your child quite quickly. Inexpensive, common household items like oatmeal, witch hazel and baking soda are really effective at calming the itching and redness that usually accompany hives.
What causes hives in the body?
Illness, including lupus, autoimmune diseases, leukemia. Hives resulting from physical causes, like pressure, cold, or sun exposure, are called physical hives. Heat urticaria or heat hives are caused by an increase in body temperature from things like hot showers or baths, spicy foods or exercise.
How long do hives last?
Other times, hives can last for hours and even several weeks to months. Acute episodes of urticaria last for six weeks or less. Hives that last for six weeks or less are acute hives. Those that remain for more than six weeks are chronic hives.
How do you know if you have hives?
Symptoms of hives can include: ( 5) Swelling of the surface of the skin into red or skin-colored welts (called wheals) with clearly defined edges. Wheals are typically round or oval and can get bigger, spread, and join together to form larger areas of flat, raised skin.
Can stress cause hives?
Can stress cause hives? The answer is definitely “yes.” Hives and stress can go hand-in-hand. When you experience excessive short or long term stress, it takes a toll on body’s immune system. Since the stress is throwing off your immune system, your body responds by internally sending out histamine to fend off your current health problem, which in this case is stress. Histamine release doesn’t make stress go away, but it can cause hives to start popping up in various places. Basically, this is an allergic reaction to stress and your body is sending out visible signals (hives) to let you know that it’s time to chill out. ( 18)
What to do if you have hives and a fever?
Seek urgent medical attention for yourself or your child if hives are severe and/or cover a large area of your body, or if you have other symptoms, such as difficulty breathing or a fever. Chronic urticaria or chronic hives should be evaluated by an allergist or immunologist to determine proper hives treatment.
