Medication
Fexinidazole is an oral treatment for gambiense human African trypanosomiasis It was included in 2019 in the WHO Essential medicines list and WHO human African Trypanosomiasis treatment guidelines. This molecule is indicated as first line for first stage and non-severe second stage.
Self-care
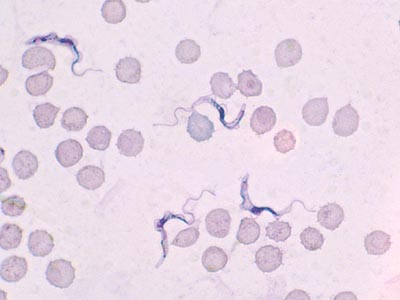
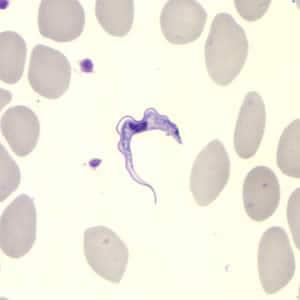
Trypanosoma brucei ssp. in a thin blood smear stained with Giemsa. Credit: DPDx Early diagnosis is difficult because signs and symptoms in the first stage are non-specific and because diagnostic measures are insensitive. Diagnosis requires confirming the presence of the parasite in any body fluid.
Nutrition
Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense is found in 13 countries in eastern and southern Africa. Nowadays, this form represents under 5% of reported cases and causes an acute infection. First signs and symptoms are observed a few months or weeks after infection. The disease develops rapidly and invades the central nervous system.
What is the best treatment for trypanosomiasis?
The disease has two forms, Trypanosoma brucei (T b) rhodesiense and T b gambiense; and is almost always fatal if untreated. Despite a recent reduction i …
How is Trypanosoma brucei SSP diagnosed?
What is Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense?
How many forms of Trypanosoma brucei are there?
See more
Can you cure trypanosomiasis?
There is no test of cure for African trypanosomiasis. After treatment, patients should be closely followed for 24 months and monitored for relapse. Recurrence of symptoms will require examination of body fluids, including CSF, to detect the presence of trypanosomes.
Is Trypanosoma brucei curable?
rhodesiense (https://www.who.int/data/gho/data/themes/topics/human-african-trypanosomiasis ). Sleeping sickness is curable with medication but is fatal if left untreated.
How is East African sleeping sickness treated?
Medication for the treatment of East African trypanosomiasis is available through CDC. Hospitalization for treatment is usually necessary. Periodic follow-up exams that include a spinal tap are required for 2 years.
What is the drug of choice for Trypanosoma brucei Gambiense 2nd stage?
Treatment of second-stage gambiense HAT relied on melarsoprol, an arsenic-based derivative, for over 50 years. Melarsoprol is associated with a wide range of adverse effects, the most feared being an encephalopathic syndrome that kills 3–6% of patients.
How is brucei diagnosed?
Although general laboratory studies may be helpful in the diagnosis of African trypanosomiasis (sleeping sickness), a definitive diagnosis of T brucei infection requires actual detection of trypanosomes in blood, lymph nodes, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), skin chancre aspirates, or bone marrow.
Can you survive sleeping sickness?
How is trypanosomiasis treated? Trypanosomiasis is curable if treatment is given quickly, however if left untreated the disease is fatal. The type of treatment given depends on the stage of the disease. Generally, the earlier the disease is identified, the easier it is to treat.
How is trypanosomiasis treated in cattle?
If detected early, Trypanosomosis can be treated with trypanocidal drugs for therapeutic and prophylactic purposes. Therapeutic drugs for cattle include diminazene aceturate, homidium chloride and homidium bromide. Prophylactic drugs for cattle include homidium chloride, homidium bromide and isometamidium.
Is there a vaccine for sleeping sickness?
There is no vaccine or medicine that prevents African trypanosomiasis. Travelers can protect themselves by preventing tsetse fly bites.
Is there a vaccine for Chagas disease?
Currently, there is no vaccine to prevent Chagas disease and chemotherapy is the only alternative for curing infected individuals. The success of treatment depends on stage of the disease, age of the patient and biochemical characteristics of the parasite strain (WHO, 2017).
Does ivermectin treat African sleeping sickness?
African trypanosomiasis (sleeping sickness) Tsetse flies (Glossina palpalis) fed on ivermectin-treated animals die within 5 days, demonstrating that ivermectin has promise to help control these African trypanosomiasis vectors.
How do you control trypanosomiasis?
Prevention & ControlWear long-sleeved shirts and pants of medium-weight material in neutral colors that blend with the background environment. Tsetse flies are attracted to bright or dark colors, and they can bite through lightweight clothing.Inspect vehicles before entering. ... Avoid bushes. ... Use insect repellent.
Which one is correct about Trypanosoma?
Solution : (a)Trypanosoma is an obligate parasite, it is digenetic polymorphic (Trypanosoma is adult form in human, whereas, crithidal and leptomonal are developmental forms in tse-tse fly).
Where is trypanosomiasis transmitted?
b. gambiense causes a slowly progressing African trypanosomiasis in western and central Africa and T. b.
What is the parasite that causes sleep sickness?
Parasites - African Trypanosomiasis (also known as Sleeping Sickness) minus. Related Pages. African Trypanosomiasis, also known as “sleeping sickness”, is caused by microscopic parasites of the species Trypanosoma brucei. It is transmitted by the tsetse fly ( Glossina species), which is found only in sub-Saharan Africa.
How does Trypanosoma brucei rhodesienseand T. bruce
Trypanosoma brucei rhodesienseand T. brucei gambiense, the causative agents of Human African Trypanosomiasis, are transmitted by tsetse flies. Within the vector, the parasite undergoes through transformations that prepares it to infect the human host. Sequentially these developmental stages are the replicative procyclic ...
What are the genes that are upregulated in tsetse flies?
In experimentally infected mature tsetse flies, genes related with DNA/RNA binding, protein phosphorylation, and initiation of transcription, as well as with cytoskeleton and actin binding cell-remodeling functions are upregulated.
What are the stages of encephalitic sickness?
The sickness has two clear cut clinical stages, i.e., a hemolymphatic initial systemic stage and a second phase characterized by the invasion of the brain by parasites. This encephalitic stage involves sensory, motor and psychiatric disturbances, with alterations of sleep representing the most typical manifestations.
How does the host contribute to the infection dynamics?
However, the human host contributes to the infection dynamics through the selection of distinct antigen types, his/her genetic susceptibility (trypanotolerance) and the potential influence of host-dependent effects on parasite pathogenicity.
What is the best treatment for T B rhodesiense?
Melarsoprol is the only available treatment for late-stage T b rhodesiense infection, but can be lethal to 5% of patients owing to post-treatment reactive encephalopathy. Eflornithine combined with nifurtimox is the first-line treatment for late-stage T b gambiense.
What is the cause of African trypanosomiasis?
Human African trypanosomiasis, or sleeping sickness, is caused by infection with parasites of the genus Trypanosoma, transmitted by the tsetse fly. The disease has two forms, Trypanosoma brucei (T b) rhodesiense and T b gambiense; and is almost always fatal if untreated.
Is trypanosomiasis fatal?
The disease has two forms, Try panosoma brucei (T b) rhodesiense and T b gambiense; and is almost always fatal if untreated. Despite a recent reduction in the number of reported cases, patients with African trypanosomiasis continue to present major challenges to clinicians.
What is the prehospital care for African trypanosomiasis?
Prehospital care of African trypanosomiasis (sleeping sickness) centers on management of the acute symptoms of fever and malaise in conjunction with close monitoring of the patient’s neurologic status. In the emergency department, if central nervous system (CNS) symptoms are severe, airway management to prevent aspiration becomes important, along with an immediate blood smear, complete blood count (CBC), and lumbar puncture for trypanosome detection.
What is the CNS in emergency?
In the emergency department, if central nervous system (CNS) symptoms are severe, airway management to prevent aspiration becomes important, along with an immediate blood smear, complete blood count (CBC), and lumbar puncture for trypanosome detection.
