Explore
- Apple cider vinegar, blackstrap molasses, and cayenne pepper are very popular natural blood thinners.
- Warming spices such as curry powder, ginger, and cinnamon, turmeric, oregano, dill, licorice, and mint also have blood-thinning properties.
- Many fruits will help to aid in thinning the blood. ...
How to treat thrombosis naturally?
Special Measures
- Prolonged Travel. Long trips by airplane or car can substantially increase your risk of DVT. ...
- Pregnancy, Birth Control Pills, and Hormone Replacement Therapy. Females who are pregnant or taking birth control pills or hormone replacement therapy have an elevated risk for DVT.
- Heart Failure. ...
- Recent Hospitalization or Surgery. ...
- Previous DVT. ...
How to spot and prevent deep vein thrombosis?
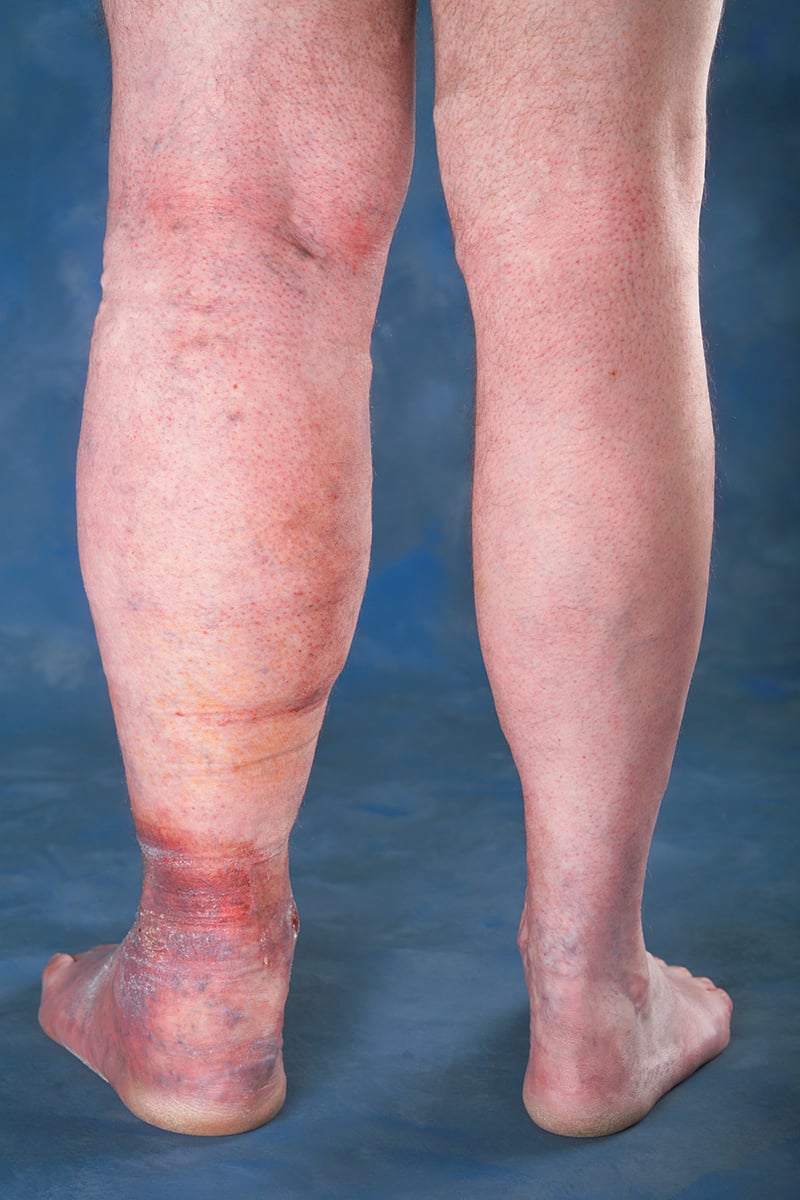
Symptoms of DVT in the leg are:
- throbbing or cramping pain in 1 leg (rarely both legs), usually in the calf or thigh
- swelling in 1 leg (rarely both legs)
- warm skin around the painful area
- red or darkened skin around the painful area
- swollen veins that are hard or sore when you touch them
How do we diagnose and treat deep vein thrombosis?
Home treatment of DVT is possible and effective, safe and cost-effective. On the average, 40 percent of expenses per patient were saved when compared with hospital stay in spite of more expensive LMWH. The patients who received LMWH spent a mean of 1.2 days in the hospital, as compared with 12.7 day …
Can you treat deep vein thrombosis at home?
What is the name of the blood thinner that is used to treat blood clots?
What is the term for a blood clot in the vein?
How is heparin given?
How do platelets and factors work together?
Why do you need blood tests for warfarin?
How to reduce the risk of bleeding from warfarin?
What are the advantages and disadvantages of heparin?
See more
About this website
How long does thrombosis take to go away?
It takes about 3 to 6 months for a blood clot to go away. During this time, there are things you can do to relieve symptoms. Elevate your leg to reduce swelling.
Is thrombosis life threatening?
Thrombosis occurs when blood clots block veins or arteries. Symptoms include pain and swelling in one leg, chest pain, or numbness on one side of the body. Complications of thrombosis can be life-threatening, such as a stroke or heart attack.
What causes thrombosis?
Conditions like atherosclerosis, where arteries stiffen because of a buildup of plaque (a waxy substance related to cholesterol) inside them, often cause clots. This happens when a clot forms over a rupture or break in a section of plaque.
Can thrombosis heal on its own?
Deep vein thrombosis usually occurs in the lower leg. It often goes unnoticed and dissolves on its own. But it may cause symptoms like pain and swelling. If someone is diagnosed with DVT, they will need treatment to avoid serious complications such as pulmonary embolism.
What are the 10 signs of a blood clot?
This is dangerous, so look out for these symptoms:Pain in the side of your belly, legs, or thighs.Blood in your urine.Fever.Nausea or vomiting.High blood pressure.Sudden severe leg swelling.Trouble breathing.
What is the difference between clot and thrombus?
Blood clots are clumps that occur when blood hardens from a liquid to a solid. A blood clot that forms inside one of your veins or arteries is called a thrombus. A thrombus may also form in your heart.
What are 5 causes of a thrombus?
What Causes a Thrombus?Injury to the leg veins.Illness that affects the veins.Immobility.Broken bone.Certain medications.Obesity.Inherited (genetic) disorders.Autoimmune disorders that increase the risk of blood clots.More items...•
What is the most common cause of thrombus?
Anything that prevents your blood from flowing or clotting normally can cause a blood clot. The main causes of DVT are damage to a vein from surgery or trauma and inflammation due to infection or injury.
How do you check for thrombosis?
Duplex ultrasonography is an imaging test that uses sound waves to look at the flow of blood in the veins. It can detect blockages or blood clots in the deep veins. It is the standard imaging test to diagnose DVT. A D-dimer blood test measures a substance in the blood that is released when a clot breaks up.
What are the first signs of a blood clot?
Symptoms of a blood clot include:throbbing or cramping pain, swelling, redness and warmth in a leg or arm.sudden breathlessness, sharp chest pain (may be worse when you breathe in) and a cough or coughing up blood.
What causes thrombosis in the legs?
What causes a venous blood clot? Blood clots in the veins are usually caused by slowed blood flow to the legs and feet, which can cause the blood to clot. Venous blood clots may also be caused by damage to a vein from an injury or infection.
Does aspirin dissolve blood clots?
It can help prevent a heart attack or clot-related stroke by interfering with how the blood clots. But the same properties that make aspirin work as a blood thinner to stop it from clotting may also cause unwanted side effects, including bleeding into the brain or stomach.
List of 14 Deep Vein Thrombosis Medications Compared - Drugs.com
Blood clotting in the veins of the inner thigh or leg. In air travel, DVT is the economy-class syndrome. Even in young, health travelers the long stretches immobilised in cramped seats in cabins with very low humidity set the stage for the formation of a thrombus.
Blood Clots: How They Get Dissolved - WebMD
Any clot that forms in your body, from an injury to a DVT, needs to get cleared out at some point. Here’s how it happens and what treatments can help.
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) Treatment: Treating Blood Clots in Legs - WebMD
Treating DVT at Home. When you go home after DVT treatment, your goals are to get better and prevent another blood clot.You’ll need to: Take medications as directed. After a DVT, you'll take ...
Blood Clot Treatment | Johns Hopkins Medicine
Blood clots can be very serious, so symptoms of blood clots should be evaluated by a doctor immediately. If not treated, a clot can break free and cause a pulmonary embolism—where the clot gets stuck in a blood vessel in the lung, causing severe shortness of breath and even sudden death. Treatment ...
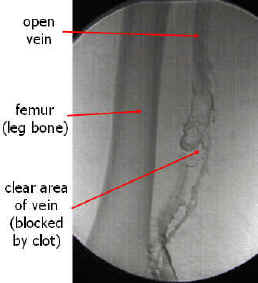
Endovascular Treatment of Thrombosis and Embolism
Deep venous thrombosis (DVT) is a common disorder with a significant mortality rate. Successful endovascular treatment of acute DVT is most likely to be achieved in patients with recently formed thrombus, (<10-14 days) with acute iliofemoral DVT. Endovascular treatment options include: Catheter-d …
What is the name of the blood thinner that is used to treat blood clots?
When this occurs, it is called an embolus. To treat blood clots and prevent the damage they cause, doctors use anticoagulants, which are commonly called blood thinners, to decrease the clotting power of the blood and prevent growth of a clot.
What is the term for a blood clot in the vein?
Thrombosis is the medical term for an abnormal blood clot in an artery or vein. The body’s ability to form blood clots its natural defense against bleeding. Clots are formed through a series of chemical reactions between special blood cells (platelets) and proteins (clotting factors) in blood. The platelets and factors work together to regulate the clotting process to start and stop clotting as the body needs it. Sometimes the process does not work correctly, and a clot forms in blood vessels, blocking blood flow to the surrounding tissues. There are two main types of clots. How they effect the body depends on the type and location of the clot.
How is heparin given?
Heparin. Heparin is a strong, fast-acting anticoagulant (blood thinner). It is usually given in the hospital by IV (a small needle inserted in a vein), but it can also be given by an injection under the skin.
How do platelets and factors work together?
The platelets and factors work together to regulate the clotting process to start and stop clotting as the body needs it. Sometimes the process does not work correctly, and a clot forms in blood vessels, blocking blood flow to the surrounding tissues. There are two main types of clots.
Why do you need blood tests for warfarin?
As with patients who take heparin, patients taking warfarin need to have their blood tested to see how well the drug is working and to be monitored for safety. This blood test measures how long it takes blood to clot, and is also called a prothrombin time, protime, INR, or clotting time.
How to reduce the risk of bleeding from warfarin?
Limit alcohol intake. Drinking a light or moderate amount of alcohol (1-2 glasses of wine or 1-2 beers per day) usually does not influence the INR and will not increase the risk for bleeding. However, drinking a large amount can affect the way warfarin works and increase your risk for bleeding.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of heparin?
The advantages of heparin are its low cost and fast action ( blood can be anticoagulated quickly). The disadvantages of heparin include the need for frequent blood tests to check the levels of anticoagulation and hospitalization to get an IV drug. Patients should expect to be in the hospital 5-10 days to treat a new clot.
How to treat DVT?
DVT is most commonly treated with anticoagulants, also called blood thinners. These drugs don't break up existing blood clots, but they can prevent clots from getting bigger and reduce your risk of developing more clots. Blood thinners may be taken by mouth or given by IV or an injection under the skin.
How to prevent blood clots in legs?
If you've been on bed rest because of surgery or other factors, the sooner you get moving, the lower the chance that blood clots will develop. Wear compression stockings . Wear these to help prevent blood clots in the legs if your doctor recommends them.
What blood thinners are used for DVT?
The most commonly used injectable blood thinners for DVT are enoxaparin (Lovenox) and fondaparinux (Arixtra). After taking an injectable blood thinner for a few days, your doctor may switch you to a pill. Examples of blood thinners that you swallow include warfarin (Jantoven) and dabigatran (Pradaxa).
What blood test is used to diagnose a blood clot?
Tests used to diagnose or rule out a blood clot include: D-dimer blood test. D dimer is a type of protein produced by blood clots. Almost all people with severe DVT have increased blood levels of D dimer. A normal result on a D-dimer test often can help rule out PE. Duplex ultrasound.
What to do if you can't take medicine to thin your blood?
If you can't take medicines to thin your blood, you might have a filter inserted into a large vein — the vena cava — in your abdomen. A vena cava filter prevents clots that break loose from lodging in your lungs. Compression stockings. These special knee socks reduce the chances that your blood will pool and clot.
What is the procedure to check for clots in the foot?
The test is invasive, so it's rarely performed. Other tests, such as ultrasound, often are done first. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan.
How to diagnose DVT?
Diagnosis. To diagnose DVT, your doctor will ask you about your symptoms. You'll also have a physical exam so that your doctor can check for areas of swelling, tenderness or changes in skin color. The tests you have depend on whether your doctor thinks you are at a low or a high risk of DVT. Tests used to diagnose or rule out a blood clot include: ...
What is the treatment for a blood clot?
Treatment may include: Blood-thinning medicines (anticoagulants) Thin tubes (catheters) to widen the affected vessels. A wire mesh tube (stent) that holds a blood vessel open and stops it from closing. Medicines to interfere with or dissolve blood clots. Your healthcare provider may advise other treatments.
What is thrombosis in the heart?
What is thrombosis? Thrombosis occurs when blood clots block your blood vessels. There are 2 main types of thrombosis: Venous thrombosis is when the blood clot blocks a vein. Veins carry blood from the body back into the heart. Arterial thrombosis is when the blood clot blocks an artery. Arteries carry oxygen-rich blood away from the heart to ...
What are the risk factors for venous thrombosis?
Risk factors for venous thrombosis may include: A family history of a blood clot in a vein deep in the body, called a deep vein thrombosis (DVT) A history of DVT. Hormone therapy or birth control pills. Pregnancy. Injury to a vein, such as from surgery, a broken bone, or other trauma.
What is the condition where blood clots block veins?
Thrombosis occurs when blood clots block veins or arteries. Symptoms include pain and swelling in one leg, chest pain, or numbness on one side of the body. Complications of thrombosis can be life-threatening, such as a stroke or heart attack. Treatment includes medicines that thin the blood or prevent clots, and using stents or catheters ...
How do you know if you have thrombosis?
Symptoms may include: Pain in one leg (usually the calf or inner thigh) Swelling in the leg or arm. Chest pain. Numbness or weakness on one side of the body. Sudden change in your mental state. The symptoms of thrombosis may look like other blood disorders or health problems.
How to treat a clot in the blood?
Treatment includes medicines that thin the blood or prevent clots, and using stents or catheters to open blocked vessels. Prevention includes being active, quitting smoking, losing weight, and managing other health conditions.
What tests are done to see if blood clots?
Blood tests. These may include tests to see how well your blood can clot. Venography. For this test, a dye is injected into your veins. Then X-rays are taken to show blood flow and look for clots. The dye makes your veins easier to see on the X-rays. MRI, MRA or CT.
What is thrombosis in the body?
When something clogs them up, things can get pretty dangerous. Thrombosis is the term used for the development of blood clots within deep veins in your body.
Where does thrombosis occur?
Thrombosis is caused by blood clots forming in deep veins, most often in the legs. Blood clots can form whenever there is any condition that prevents blood from circulating or clotting normally. For example, they can happen to people who tend to lack physical movement after an accident, injury, surgery, or during bed rest.
What is the dangerous condition that occurs when a clot breaks up and travels through the body?
Pulmonary Embolism: a dangerous situation that occurs when a clot breaks up and travels through the body. Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT): commonly occurs in the legs and is caused by blood clotting or sedentary lifestyles. Learning Outcomes. Study this lesson and build upon your ability to:
What is the term for blood clots in the legs?
It often occurs in the legs and, more specifically, is called deep vein thrombosis (DVT). It is most often caused by blood clotting disorders, but it can also happen if you stay sedentary for too long.
What are the risks of thrombosis?
Additional risk factors include: If thrombosis occurs, treatments may include the use of blood thinners, clot busters, filters, or compression stockings. Thrombosis can be dangerous if the clot breaks up and travels throughout the body; the most dangerous scenario from this is pulmonary embolism.
Why are blood clots dangerous?
Blood clots are dangerous because they can break apart, travel throughout the body, and cause blockages in the heart, brain, or lungs (leading to heart attack, stroke, or pulmonary embolism, respectively). You must c C reate an account to continue watching. Register to view this lesson.
What are the symptoms of pulmonary embolism?
This can include sudden difficulty breathing, chest pain that gradually intensifies or gets worse when breathing in, dizziness, lightheadedness, increased heart rate, and coughing up blood. All symptoms require physician attention, but a pulmonary embolism requires immediate medical attention.
Arterial thrombosis
This involves a thrombus developing in an artery. Arteries are blood vessels that carry oxygenated blood away from the heart to other areas of the body.
Venous thrombosis
This involves a thrombus developing in a vein. Veins are blood vessels that carry deoxygenated blood back to the heart. A venous thromboembolism (VTE) is a broader term that describes blood clots in veins. There are two subtypes: deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE).
Treatment side effects
People taking anticoagulation medications have an increased risk of excessive bleeding. Signs of this issue include:
Prevention in at-risk individuals
A doctor can perform a VTE risk assessment, and they should do this whenever a person is admitted to a hospital.
Long-term complications
In some cases, thrombosis resolves on its own, as the body breaks down and removes the thrombus. However, around 33–50% of people with DVT develop post-thrombotic syndrome. This stems from damage to the valves within the veins, which help direct blood flow.
Subsequent blood clots
Most people who develop thrombosis go on to have further or recurrent blood clots. However, the likelihood of this happening depends on the factors that caused the initial clot.
What is the best treatment for DVT?
Blood Thinners. These drugs, also called anticoagulants, are the most common treatment for DVT. They can keep a clot from growing or breaking off, and they prevent new clots from forming. But they can't thin your blood, despite their name. And they won’t get rid of an existing clot.
What does a DVT do for you?
What will treating a DVT, a blood clot deep in a vein, do for you? It will keep the clot from growing. It lowers the risk of long-lasting complications, such as leg pain and swelling . Treatment prevents future blood clots, too.
What to do if your vein is narrow?
If your vein seems narrow, they may widen it and help prevent future blockages by doing a balloon angioplasty or placing a stent. Medical Procedures. When taking blood thinners or clot-busting isn't possible or doesn't work well, your doctor may want to try a more involved procedure. Inferior vena cava (IVC) filter.
How long do you have to take blood thinners after a DVT?
After a DVT, you'll take blood thinners for at least 3 to 6 months. Your doctor will tell you exactly how long to take these medications. It might be different based on which drug you use. You may need to take oral blood thinners for a longer time if the reason for your clot is still present in your body.
Where do blood clots move?
Blood clots that move from place to place (mobile thrombus) DVT in your inferior vena cava and iliac veins. These are the veins that run from your heart to your lower body and pelvis. There are two types of IVC filters. One stays in your body permanently.
How often do you need to take heparin?
You may have to keep taking shots once you’re home, once or twice daily . When you get heparin by IV, you'll need blood tests, too.
Is it better to take blood thinners or X-rays?
But it's riskier than taking blood thinners. You have a higher chance of bleeding problems and stroke. You'll go to the hospital to get it done. Using an X-ray as a guide, a specialist will put a thin tube called a catheter into your vein and work the tip of it into your DVT.
What is the treatment for DVT?
Once you receive a diagnosis of DVT, you’ll likely be prescribed medications known as anticoagulants, or blood thinners. These work to keep the clot from growing and to prevent further clots.
What is the best supplement for preventing blood clots?
Omega-3 fatty acids. Omega-3 fatty acids may help lower blood pressure and reduce cholesterol, triglycerides, and inflammation. All of these play a role in preventing blood clots. You can find omega-3s in fish or fish oil supplements.
What is a DVT?
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a medical condition that happens when a blood clot forms in a vein. A deep vein blood clot can occur anywhere in the body, but most often forms in the calf or thigh. Treating DVT is important because of the risk of a life-threatening complication known as pulmonary embolism. This occurs when the blood clot breaks ...
How long do you have to take warfarin?
They’ll give you detailed instructions for taking additional doses at home. You may have to take the anticoagulant medication for three to six months, sometimes longer. Make sure to follow your doctor’s instructions carefully. Taking too much of an anticoagulant medication like warfarin can thin the blood too much and lead to bleeding problems.
Why is it important to make changes to your lifestyle to prevent DVT?
Along with managing your symptoms , it’s important to make changes to your lifestyle in order to prevent DVT happening again. Certain people are at a higher risk of developing DVT, including: people who are having surgery in the lower extremities. heavy smokers.
What is the best medicine for stroke?
Acetyl salicylic acid, which is derived from salicylate and is commonly known as aspirin, is used to prevent stroke. Ginger is a common ingredient in many recipes. It can also be made into a tea. Ginger has many other health benefits as well.
How to get blood out of your leg?
Wear graduated compression stockings. These specially fitted stockings are tight at the feet and become gradually looser up on the leg, creating gentle pressure that keeps blood from pooling and clotting. Elevate the affected leg. Make sure your foot is higher than your hip. Take walks.
What is the name of the blood thinner that is used to treat blood clots?
When this occurs, it is called an embolus. To treat blood clots and prevent the damage they cause, doctors use anticoagulants, which are commonly called blood thinners, to decrease the clotting power of the blood and prevent growth of a clot.
What is the term for a blood clot in the vein?
Thrombosis is the medical term for an abnormal blood clot in an artery or vein. The body’s ability to form blood clots its natural defense against bleeding. Clots are formed through a series of chemical reactions between special blood cells (platelets) and proteins (clotting factors) in blood. The platelets and factors work together to regulate the clotting process to start and stop clotting as the body needs it. Sometimes the process does not work correctly, and a clot forms in blood vessels, blocking blood flow to the surrounding tissues. There are two main types of clots. How they effect the body depends on the type and location of the clot.
How is heparin given?
Heparin. Heparin is a strong, fast-acting anticoagulant (blood thinner). It is usually given in the hospital by IV (a small needle inserted in a vein), but it can also be given by an injection under the skin.
How do platelets and factors work together?
The platelets and factors work together to regulate the clotting process to start and stop clotting as the body needs it. Sometimes the process does not work correctly, and a clot forms in blood vessels, blocking blood flow to the surrounding tissues. There are two main types of clots.
Why do you need blood tests for warfarin?
As with patients who take heparin, patients taking warfarin need to have their blood tested to see how well the drug is working and to be monitored for safety. This blood test measures how long it takes blood to clot, and is also called a prothrombin time, protime, INR, or clotting time.
How to reduce the risk of bleeding from warfarin?
Limit alcohol intake. Drinking a light or moderate amount of alcohol (1-2 glasses of wine or 1-2 beers per day) usually does not influence the INR and will not increase the risk for bleeding. However, drinking a large amount can affect the way warfarin works and increase your risk for bleeding.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of heparin?
The advantages of heparin are its low cost and fast action ( blood can be anticoagulated quickly). The disadvantages of heparin include the need for frequent blood tests to check the levels of anticoagulation and hospitalization to get an IV drug. Patients should expect to be in the hospital 5-10 days to treat a new clot.

Diagnosis
Treatment
- There are three main goals to DVTtreatment. 1. Prevent the clot from getting bigger. 2. Prevent the clot from breaking loose and traveling to the lungs. 3. Reduce the chances of another DVT. DVTtreatment options include: 1. Blood thinners. These medicines, also called anticoagulants, help prevent blood clots from getting bigger. Blood thinners redu...
Clinical Trials
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiestesting new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
- After DVTtreatment, follow these tips to manage the condition and prevent complications or more blood clots: 1. Ask about your diet.Foods high in vitamin K, such as spinach, kale, other leafy greens and Brussels sprouts, can interfere with the blood thinner warfarin. 2. Take medications as directed.Your provider will tell you how long you need treatment. If you're taking certain blood thi…
Preparing For Your Appointment
- DVTis considered a medical emergency. It's important to get treated quickly. If there's time before your appointment, here's some information to help you get ready.