
Medication
Jun 02, 2014 · Treatment of thrombocytopenia Inherited thrombocytopenia. Patients with inherited thrombocytopenia and their families should be educated about their... Immune thrombocytopenia (ITP). According to the Medscape reference librar y [ 12 ], the incidence rates for ITP are as... Thrombotic ...
Procedures
Other treatments include: Blood transfusion to temporarily increase platelet levels in your blood. Platelets are transfused only if the platelet... Splenectomy or removal of the spleen. Steroids (prednisone or dexamethasone), immunoglobulins (antibody proteins), and other medications that …
Self-care
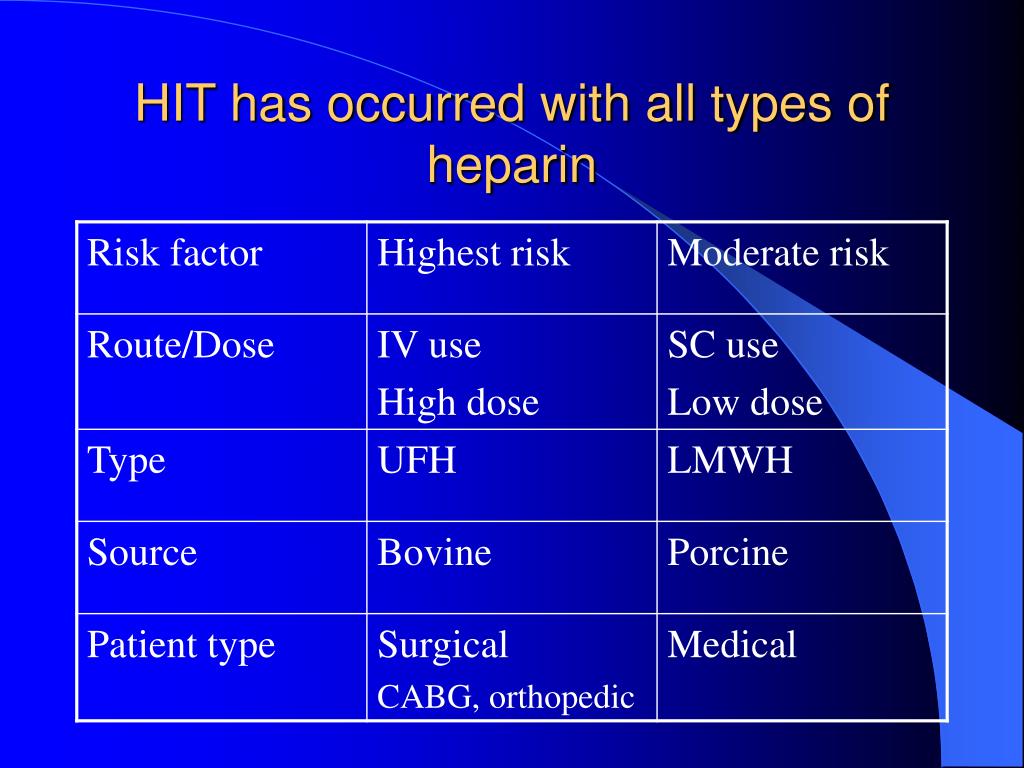
Mar 24, 2022 · Heparin is a medicine commonly used to prevent blood clots. However, your immune system can trigger the medicine to cause blood clots and thrombocytopenia. This condition is called heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT).
Nutrition
Apr 19, 2022 · Certain medications can reduce the number of platelets in your blood. Sometimes a drug confuses the immune system and causes it to destroy platelets. Examples include heparin, quinine, sulfa-containing antibiotics and anticonvulsants.
What are home remedies for thrombocytopenia?
Mar 24, 2022 · Medicines often are used as the first treatment for both children and adults. Corticosteroids, such as prednisone and dexamethasone, are commonly used to treat ITP. These medicines help increase your platelet count. However, steroids have many side effects. Some people relapse (get worse) when treatment ends.
What doctor treats thrombocytopenia?
Jan 17, 2022 · For persistent ITP, your doctor may recommend periodic injections of the monoclonal antibody rituximab ( Rituxan ). Splenectomy (surgical removal of the spleen). This may be necessary if ITP that has not improved with other treatment. If the spleen is removed, thrombocytopenia goes away in more than half of ITP patients.
How to correct thrombocytopenia?
Your doctor will likely suggest these treatments for ITP first: Corticosteroids. Dexamethasone or prednisone is typically prescribed to raise your platelet count. You take it once a day in the form...
Can thrombocytopenia be cured?
What happens if you have thrombocytopenia?
If you have thrombocytopenia, you don't have enough platelets in your blood. Platelets help your blood clot, which stops bleeding. For most people, it's not a big problem. But if you have a severe form, you can bleed spontaneously in your eyes, gums, or bladder or bleed too much when you're injured.Nov 20, 2020
What are 3 causes of thrombocytopenia?
Factors that can decrease platelet production include:Leukemia and other cancers.Some types of anemia.Viral infections, such as hepatitis C or HIV.Chemotherapy drugs and radiation therapy.Heavy alcohol consumption.
When does thrombocytopenia need treatment?
When the platelet count falls below 100,000 per μl, a person may develop spontaneous bleeds. This form of thrombocytopenia usually requires immediate treatment that focuses on managing the cause of thrombocytopenia.Jan 16, 2022
Which drug is use for thrombocytopenia?
Drugs used to treat ThrombocytopeniaDrug nameRatingRx/OTCView information about eltrombopag eltrombopag5.0RxGeneric name: eltrombopag systemic Brand name: Promacta Drug class: platelet-stimulating agents For consumers: dosage, interactions, side effects For professionals: AHFS DI Monograph37 more rows
Can thrombocytopenia be cured?
People with mild thrombocytopenia might not need treatment. For people who do need treatment for thrombocytopenia, treatment depends on its cause and how severe it is. If your thrombocytopenia is caused by an underlying condition or a medication, addressing that cause might cure it.
What foods to avoid if you have low platelets?
What Not to EatAlcohol: Wine, liquor, and regular or nonalcoholic beer can lower platelet counts. ... Refined grains, sugar, and foods or drinks with added sugar: These may cause fatigue and reduce platelet count.More items...•Dec 6, 2021
Which drug is a likely cause of thrombocytopenia?
A systematic review of individual patient data found that the most commonly reported drugs with a definite or probable causal relation to thrombocytopenia were quinine, quinidine, trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole, vancomycin, penicillin, rifampin, carbamazepine, ceftriaxone, ibuprofen, mirtazapine, oxaliplatin, and ...Nov 30, 2018
What happens if ITP is not treated?
Without treatment to correct platelet counts, bleeding can become severe and life threatening. Many adults with mild ITP don't need treatment. They can be observed by their doctor and monitored with blood tests. Others might go into remission.
Which antibiotics cause low platelets?
Some prescribed medications can also cause thrombocytopenia, including:amiodarone.ampicillin and other antibiotics.cimetidine.piperacillin.seizure medications, such as carbamazepine.sulfonamides, such as trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole.vancomycin.
What are the symptoms of thrombocytopenia?
What are the symptoms of thrombocytopenia?Bleeding gums.Blood in stool (black, tarry-looking), urine (hematuria) or vomit.Heavy menstrual periods.Petechiae (tiny red or purple dots on the lower legs that resemble a rash).Purpura (purple, red or brown bruises) or bruising easily.Rectal bleeding.Nov 23, 2020
What is the treatment for thrombocytopenia?
Treatment for thrombocytopenia depends on its cause and severity. The main goal of treatment is to prevent death and disability caused by bleeding. If your condition is mild, you may not need treatment. A fully normal platelet count isn't necessary to prevent bleeding, even with severe cuts or accidents.
What is a blood transfusion?
Blood or platelet transfusions are used to treat people who have active bleeding or are at a high risk of bleeding. During this procedure, a needle is used to insert an intravenous (IV) line into one of your blood vessels. Through this line, you receive healthy blood or platelets.
Is it normal to have a low platelet count?
A fully normal platelet count isn't necessary to prevent bleeding , even with severe cuts or accidents. Thrombocytopenia often improves when its underlying cause is treated. People who inherit the condition usually don't need treatment. If a reaction to a medicine is causing a low platelet count, your doctor may prescribe another medicine.
Can you take another medicine for low platelet count?
If a reaction to a medicine is causing a low platelet count, your doctor may prescribe another medicine. Most people recover after the initial medicine has been stopped. For heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT), stopping the heparin isn't enough. Often, you'll need another medicine to prevent blood clotting.
Can steroids slow platelet destruction?
Steroids may slow platelet destruction. These medicines can be given through a vein or by mouth. One example of this type of medicine is prednisone. The steroids used to treat thrombocytopenia are different from illegal steroids taken by some athletes to enhance performance.
Observation
If thrombocytopenia is mild and is not causing any symptoms, it may not require any treatment. Continued monitoring of platelet counts and reporting any symptoms of bleeding or bruising may be the only intervention that is required. 1
Medication Avoidance
If thrombocytopenia is due to a reaction after taking a medication, stopping that medication may be the only treatment required. It may also be necessary to avoid or use with caution other medications that affect platelet function.
Prescription Medications
Depending upon the underlying cause leading to the development of thrombocytopenia, multiple prescription medication treatments may be prescribed.
Platelet Transfusion
Giving an infusion of donated platelets may be necessary for instances of severe thrombocytopenia and bleeding or with a need for emergent surgery. A unit of platelets can increase platelet counts by 30,000 to 60,000 per deciliter of blood.
Surgical Options
If nonsurgical treatments such as steroids, immune globulin infusions, and antibody infusions are not effective in increasing platelet counts, a splenectomy may be needed. During a splenectomy, a surgeon removes the spleen from the body.
Lifestyle Changes
Sometimes low platelet counts can be associated with low vitamin B12 or folate levels. Increasing these nutrients in the diet may improve platelet counts. 1
A Word From Verywell
Having low platelet counts may come with a lot of worry about the potential risk of bleeding. However, having low platelet counts doesn’t always come with problems.
How to prevent thrombocytopenia?
If you’re at risk for thrombocytopenia, these steps may help prevent it: Avoid medicines that thin blood and increase bleeding risk, such as aspirin, naprosyn and ibuprofen. Take care with contact sports and activities that can cause injuries, bruising and bleeding. Minimize contact with toxic chemicals.
What is thrombocytopenia in blood?
What is thrombocytopenia? Thrombocytopenia (THROM-bo-sigh-toe-PEE-ne-ah) occurs when your blood platelet count is low. Platelets are also called thrombocytes. This type of blood cell clumps together to form blood clots to help stop bleeding at the site of a cut or wound. Another name for a blood clot is thrombus.
What are the three main classes of thrombocytopenia?
The three main classes of thrombocytopenia are: Platelet destruction such as with an auto-antibody that attaches to the platelet surface. Platelet sequestration such as in someone with a large spleen or with liver disease. Decreased platelet production as occurs in certain bone marrow diseases.
How long does a platelet last in blood?
Platelets are transfused only if the platelet count is extremely low. (Transfused platelets only last about three days in the circulation.) Splenectomy or removal of the spleen.
How to tell if your platelet count is low?
Often, one of the first signs is a cut or nosebleed that won’t stop bleeding. Other signs of low platelet count include: Bleeding gums. Blood in stool (black, tarry-looking), urine (hematuria) or vomit. Heavy menstrual periods. Petechiae (tiny red or purple dots on the lower legs that resemble a rash).
What is the name of the tissue that makes blood clots?
Another name for a blood clot is thrombus. Bone marrow is the soft, spongy tissue inside bones that makes all blood cells including platelets. People who have thrombocytopenia don’t have enough platelets to form a blood clot. If you get a cut or other injury, you may bleed too much and the bleeding can be hard to stop.
What causes ITP?
Autoimmune disease which causes ITP. ITP is sometimes associated with other autoimmune conditions such as lupus. Bone marrow diseases , including aplastic anemia, leukemia, certain lymphomas and myelodysplastic syndromes. Cancer treatments like chemotherapy and radiation therapy.
What are the symptoms of thrombocytopenia?
Thrombocytopenia signs and symptoms may include: Easy or excessive bruising (purpura) Superficial bleeding into the skin that appears as a rash of pinpoint-sized reddish-purple spots (petechiae), usually on the lower legs. Prolonged bleeding from cuts.
How to tell if you have thrombocytopenia?
Thrombocytopenia signs and symptoms may include: 1 Easy or excessive bruising (purpura) 2 Superficial bleeding into the skin that appears as a rash of pinpoint-sized reddish-purple spots (petechiae), usually on the lower legs 3 Prolonged bleeding from cuts 4 Bleeding from your gums or nose 5 Blood in urine or stools 6 Unusually heavy menstrual flows 7 Fatigue 8 Enlarged spleen
How many platelets are in thrombocytopenia?
Thrombocytopenia means you have fewer than 150,000 platelets per microliter of circulating blood. Because each platelet lives only about 10 days, your body normally renews your platelet supply continually by producing new platelets in your bone marrow.
Why do platelets stop bleeding?
Platelets stop bleeding by clumping and forming plugs in blood vessel injuries. Thrombocytopenia might occur as a result of a bone marrow disorder such as leukemia or an immune system problem. Or it can be a side effect of taking certain medications. It affects both children and adults.
What causes a shortage of platelets in the bloodstream?
Increased breakdown of platelets. Some conditions can cause your body to use up or destroy platelets faster than they're produced, leading to a shortage of platelets in your bloodstream. Examples of such conditions include: Pregnancy. Thrombocytopenia caused by pregnancy is usually mild and improves soon after childbirth.
What medications can reduce platelets?
Sometimes a drug confuses the immune system and causes it to destroy platelets. Examples include heparin, quinine, sulfa-containing antibiotics and anticonvulsants.
What is the rare condition that occurs when small blood clots suddenly form throughout your body, using up large numbers
This is a rare condition that occurs when small blood clots suddenly form throughout your body, using up large numbers of platelets. Hemolytic uremic syndrome. This rare disorder causes a sharp drop in platelets, destruction of red blood cells and impairs kidney function. Medications.
Why does thrombocytopenia occur?
In general, thrombocytopenia develops for one or more of the following reasons: The body's bone marrow fails to produce enough platelets. This can happen because: A cancer gets into the bone marrow and destroys megakaryocytes. These are the cells that produce platelets. Aplastic anemia affects platelet production.
When to call a doctor for thrombocytopenia?
Be sure to call if you notice abnormal bruises or if you experience significant bleeding from your nose, mouth, vagina, rectum or urinary tract.
What is a TTP?
Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP). This is a rare disease. Blood clots form in the smallest arteries throughout the body. Platelets are consumed by this process. People with TTP also have anemia (low red blood cell count), fever, kidney malfunction and neurological symptoms.
What is the best treatment for persistent ITP?
For persistent ITP, your doctor may recommend periodic injections of the monoclonal antibody rituximab ( Rituxan ). Splenectomy (surgical removal of the spleen). This may be necessary if ITP that has not improved with other treatment. If the spleen is removed, thrombocytopenia goes away in more than half of ITP patients.
How long does it take for thrombocytopenia to heal?
This is often the standard strategy in children with acute ITP. Most children recover without treatment within 6 weeks.
What are the symptoms of thrombocytopenia?
People with severe thrombocytopenia may have abnormal bleeding almost anywhere in the body. Symptoms can include: Reddish or purplish spots in the skin (called petechiae), often concentrated in the lower legs. Excessive bruising, even from minor trauma. Blood in the urine or stool.
What is the procedure to remove a small piece of bone marrow?
If that happens, you have drug-induced thrombocytopenia. Your doctor may recommend a bone marrow biopsy. In this procedure, a long needle is used to remove a small piece of bone marrow. The marrow is examined in a laboratory.
What to expect if you have thrombocytopenia?
What to Expect. Getting Support. If you have thrombocytopenia, you don’t have enough platelets in your blood. Platelets help your blood clot, which stops bleeding. For most people, it’s not a big problem.
What is the best treatment for ITP?
Your doctor will likely suggest these treatments for ITP first: Corticosteroids. Dexamethasone or prednisone is typically prescribed to raise your platelet count.
How often is Eltrombopag taken?
Eltrombopag is a once-daily pill, romiplostim is taken by shot once a week, and avatrombopag (Doptelet) is taken once a day and then the dose is adjusted to your platelet count. They get your bone marrow to make more platelets. Side effects include nausea, vomiting, headache, and a higher chance of getting blood clots.
What is the normal platelet count?
A healthy person usually has a platelet count of 150,000 to 400,000. You have thrombocytopenia if your number falls under 150,000. If you're wondering what the long name means, here's how it breaks down: "Thrombocytes" are your platelets, and "penia" means you don't have enough of something.
What causes low platelets?
Thrombocytopenia has many causes. One of the most common causes of low platelets is a condition called immune thrombocytopenia (ITP). You may hear it called by its old name, idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura.
How long does it take for a platelet to increase?
You take it once a day in the form of a pill or tablet. An increased or normalized platelet count is generally seen within 2 weeks of therapy, particularly with high-dose dexamethasone.
What are the risks of ITP?
Medicines Linked to ITP. Some medicines can increase your risk of ITP, such as: Certain drugs for heart problems, seizures, and infections. Heparin, a blood thinner used to prevent blood clots. Work with your doctor to figure out if a drug is causing your platelet count to drop.

Observation
Medication Avoidance
Prescription Medications
Platelet Transfusion
Specialist to consult
Surgical Options
- The following can be used to determine whether you have thrombocytopenia: 1. Blood test.A complete blood count determines the number of blood cells, including platelets, in a sample of your blood. 2. Physical exam, including a complete medical history.Your doctor will look for sign…
Lifestyle Changes
A Word from Verywell