Full Answer
Which emergency medication may cause cerebral hemorrhage?
Mar 30, 2022 · Cerebral hemorrhage can occur from a brain injury or a condition that causes blood vessels to leak or burst. Treatments include medication and possibly surgery to stop the bleeding, relieve pressure in the brain, and manage symptoms, which can include seizures.
What are the chances of surviving a brain bleed?
Aug 10, 2021 · Some patients with smaller cerebellar hemorrhage remain awake and may complain of headache, nausea, vomiting, vertigo, or ataxia. If the hemorrhage is large, patients may present with an altered level of consciousness or even unresponsiveness. Symptoms may change suddenly, correlating with hematoma expansion.
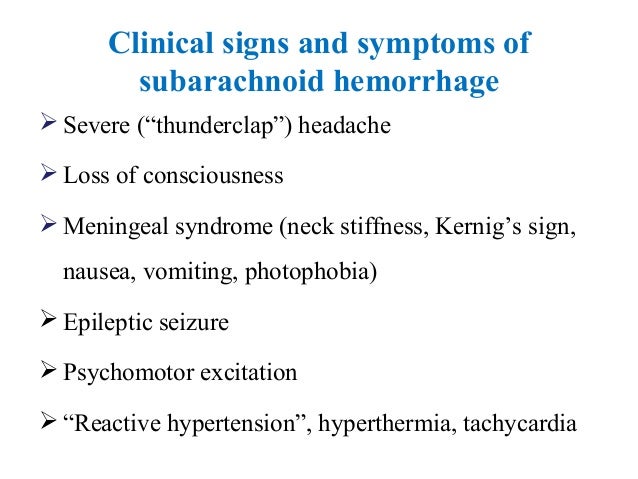
Do you recognize the 12 symptoms of brain hemorrhage?
The clinical presentation of cerebellar hemorrhage can range from symptoms mimicking ischemic stroke to catastrophic neurologic decline. Symptomatology largely depends on the size of the hemorrhage and the degree of perilesional edema. The posterior fossa is a tight compartment with virtually no additional space to accommodate the mass effect.
What are the signs of a brain hemorrhage?
Symptoms depend on location of hemorrhage an include: Headache, nausea, vomiting Alterations in levels of consciousness Weakness/numbness in face, arm or leg (usually on one side) Vision loss Seizures When & How to Seek Medical Care Seek medical care immediately when neurological symptoms occur.

What are the symptoms of cerebellar hemorrhage?
The following symptoms are roughly in descending order of incidence:Headache of abrupt onset.Nausea and vomiting.Inability to walk (reflecting truncal ataxia)Dizziness, vertigo.Dysarthria.Nuchal pain.Loss or alteration of consciousness.
What is cerebellar hemorrhage?
Cerebellar hemorrhage or hematoma is a type of intracranial hemorrhage (ICH) where the bleeding is located in the posterior fossa or cerebellum and accounts for 9% to 10% of all ICH. The posterior fossa is a small space in the skull containing the brainstem and cerebellum.Aug 10, 2021
How is a cerebellar hemorrhage treated?
There are two options for managing the mass effect from the cerebellar hemorrhage: (1) hyperosmolar agents or (2) decompressive surgery.Apr 9, 2022
What causes cerebellar hemorrhage?
Cerebellar hemorrhage can be spontaneous, a result of a stroke or secondary to trauma, and occurs most frequently in middle-aged and older adults. Patients typically have underlying risk factors leading to hemorrhages such as hypertension or small vessel disease.Aug 10, 2021
How long does it take to recover from cerebellar stroke?
Cerebellar Stroke Recovery Time During the first 3 months after a stroke, the brain is in a heightened state of plasticity. It recovers faster during this time, which explains why many patients experience a plateau after the 3 month mark.Jul 29, 2020
How is cerebellar stroke treated?
Treating a cerebellar stroke If your doctor discovers a blood clot, they'll surgically remove the clot or prescribe you medication to dissolve it. They may also recommend medication to: control blood pressure. prevent seizures.
What is cerebellar pathology?
Cerebellar dysfunction causes balance problems and gait disorders along with difficulties in coordination resulting in ataxia, uncoordinated movements, imbalance, speech problems(dysarthria), visual problems (nystagmus) and vertigo as a part of the vestibulocerebellar system.Aug 30, 2021
Is cerebellar stroke ischemic?
A cerebellar stroke happens when blood supply to the cerebellum is stopped. This part of the brain helps with body movement, eye movement, and balance. There are two main types of stroke: ischemic and hemorrhagic . An ischemic stroke is the most common type.
What is cerebellar function?
The cerebellum (which is Latin for “little brain”) is a major structure of the hindbrain that is located near the brainstem. This part of the brain is responsible for coordinating voluntary movements. It is also responsible for a number of functions including motor skills such as balance, coordination, and posture.Jun 16, 2020
Can a person survive a brain hemorrhage?
Many patients who have experienced a brain hemorrhage do survive. However, survival rates are decreased when the bleeding occurs in certain areas of the brain or if the initial bleed was very large. If a patient survives the initial event of an intracranial hemorrhage, recovery may take many months.
How long can you live after a brain hemorrhage?
Conclusion: We found that hemorrhagic stroke is associated with a very high risk for death in the acute and subacute phase. The survival rate after hemorrhagic stroke was 26.7% within a period of five years.
Can you recover from a cerebellar stroke?
Most people who experience a cerebellar stroke improve, but this may take time. Physical therapy is a cornerstone of recovery, particularly when it comes to regaining balance and learning how to walk safely. 7 Over time, tremors and jerking movements may improve.Mar 4, 2021
How do you know if you have an intracerebral hemorrhage?
Symptoms. Intracerebral hemorrhage can be characterized by a smooth progressive onset over minutes to hours, but can also be like ischemic stroke, with sudden onset of symptoms. Symptoms depend on location of hemorrhage an include: Headache, nausea, vomiting. Alterations in levels of consciousness.
How long does it take for a hemorrhage to enlarge?
Hemorrhages often enlarge within first three hours in at least 33% of cases and volume of hemorrhage correlates highly with outcomes (bigger the hemorrhage, worst the outcome). Serial computerized tomography (CT) scans in Case 3. An increase in volume of hemorrhage from 8 to 35 cc was recorded between the first CT scans (upper), ...
What is the procedure to remove a clot from the brain?
Surgical treatments include: A craniotomy involves removing a piece of the skull bone and exposing the brain to remove the clot. It is useful when the clot is close to the surface of the brain or if the clot is associated with an underlying brain lesion.
How long does it take for a CT scan to show a hemorrhage?
An increase in volume of hemorrhage from 8 to 35 cc was recorded between the first CT scans (upper), obtained 50 minutes after onset of symptoms, and the second CT scans (lower), obtained 210 minutes after onset.
What causes a swollen artery in the brain?
Causes. Hypertension: chronic high blood pressure causes changes to the arteries of the brain which can make them much more likely to rupture. Age: more common after age of 55, with buildup of protein in walls of arteries called amyloid angiopathy. Gender: more common in men.
Where is the hemorrhage located?
The hemorrhage is located primarily in the right temporal lobe and causes 1 cm of midline shift. Right: Digital subtraction angiography demonstrating an 8-mm saccular aneurysm arising from the proximal third of the MMA (arrowhead). In addition, there is obvious displacement of surrounding vessels.
Does blood damage the brain?
The blood itself can damage the brain tissue. Furthermore, the extra blood in the brain may increase the pressure within the skull (intracranial pressure (ICP)) to a point that further damages the brain.
How to control cerebral hemorrhage?
The single most important thing you can do is control yours through diet, exercise, and medication. Don’t smoke. Don’t use drugs. Cocaine, for example, can increase the risk of bleeding in the brain.
What causes a brain hemorrhage?
There are several risk factors and causes of brain hemorrhages. The most common include: 1 Head trauma. Injury is the most common cause of bleeding in the brain for those younger than age 50. 2 High blood pressure. This chronic condition can, over a long period of time, weaken blood vessel walls. Untreated high blood pressure is a major preventable cause of brain hemorrhages. 3 Aneurysm. This is a weakening in a blood vessel wall that swells. It can burst and bleed into the brain, leading to a stroke. 4 Blood vessel abnormalities. (Arteriovenous malformations) Weaknesses in the blood vessels in and around the brain may be present at birth and diagnosed only if symptoms develop. 5 Amyloid angiopathy. This is an abnormality of the blood vessel walls that sometimes occurs with aging and high blood pressure. It may cause many small, unnoticed bleeds before causing a large one. 6 Blood or bleeding disorders. Hemophilia and sickle cell anemia can both contribute to decreased levels of blood platelets and clotting. Blood thinners are also a risk factor. 7 Liver disease. This condition is associated with increased bleeding in general. 8 Brain tumors.
What is the term for the mass of blood that collects in the brain?
This is known as cerebral edema. The pooled blood collects into a mass called a hematoma. These conditions increase pressure on nearby brain tissue, and that reduces vital blood flow and kills brain cells. Bleeding can occur inside the brain, between the brain and the membranes that cover it, between the layers of the brain's covering ...
What is the meaning of "hemorrhage" in Greek?
This bleeding kills braincells. The Greek root for bloodis hemo. Hemorrhage literally means "bloodbursting forth.".
How to prevent bleeding from aneurysms?
Investigate corrective surgery. If you suffer from abnormalities, such as aneurysms, surgery may help to prevent future bleeding. Be careful with Coumadin. If you take this blood-thinning drug, also called warfarin, follow up regularly with your doctor to make sure your blood levels are in the correct range.
What test can reveal internal bleeding?
Once you see a doctor, they can determine which part of the brain is affected based on your symptoms. Doctors may run a variety of imaging tests, such as a CT scan , which can reveal internal bleedingor blood accumulation, or an MRI.
Where does bleeding occur in the brain?
Bleeding can occur inside the brain, between the brain and the membranes that cover it, between the layers of the brain's covering or between the skull and the covering of the brain. What Causes Bleeding in the Brain? There are several risk factors and causes of brain hemorrhages. The most common include:
What is the treatment for a hemorrhage?
Long-term treatment depends on the hemorrhage location and the amount of damage. Treatment may include physical, speech, and occupational therapy. Many people have some level of permanent disability.
How long does it take to recover from a hemorrhage?
These include your age and overall health, the location of the hemorrhage, and the extent of the damage. Some people may take months or years to recover. Most ICH patients have some long-term disability. In some cases, around-the-clock or nursing home care may be necessary.
What is the term for the damage caused by blood leaking into the brain?
Intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) is when blood suddenly bursts into brain tissue, causing damage to your brain. Symptoms usually appear suddenly during ICH. They include headache, weakness, confusion, and paralysis, particularly on one side of your body. The buildup of blood puts pressure on your brain and interferes with its oxygen supply.
How to overcome brain damage?
Depending on your symptoms, treatment may include physical and speech therapy to help restore muscle function or improve communication.
Why do I have a weak spot in my brain?
In younger people, another common cause is abnormally formed blood vessels in the brain. Other causes include: head injury or trauma. ruptured cerebral aneurysm (a weak spot in a blood vessel that bursts) arteriovenous malformation (a grouping of malformed blood vessels in your brain that disrupts normal blood flow)
How to diagnose brain hemorrhage?
To make a brain hemorrhage diagnosis, your doctor will first ask about your brain bleed symptoms. Next, they’ll work to locate the source of the bleeding. To do this, your doctor may order a CT scan, an MRI, or one of the following tests: 1 Angiogram: During an angiogram, a catheter is inserted into an artery and threaded through the circulatory system up to the brain. A dye is then injected through the catheter. This dye makes blood flow easy to see on X-rays. 2 Computed tomography angiography (CTA): During a CTA test, dye is injected directly into the bloodstream. This dye makes it easy to see the arteries in your brain on a CT scan. 3 Cerebrospinal fluid exam: Evidence of blood in this fluid may indicate bleeding. 4 A lumbar puncture, Also known as a spinal tap, a lumbar puncture is another way to make a brain bleed diagnosis.
What is the treatment for brain bleed?
Catheter: A long, thin tube is threaded through blood vessels until it reaches the affected area. Physical, occupational and speech therapy: These brain bleed treatments can help individuals regain brain functions (such as the ability to speak) that may have been affected by brain bleed.
What is the best way to see if you have a brain bleed?
This dye makes it easy to see the arteries in your brain on a CT scan. Cerebrospinal fluid exam: Evidence of blood in this fluid may indicate bleeding. A lumbar puncture, Also known as a spinal tap, a lumbar puncture is another way to make a brain bleed diagnosis.
Why does my brain bleed?
Bleeding in the brain (also called a brain hemorrhage or brain bleed) can happen because of an accident, brain tumor, stroke, or high blood pressure caused by congenital or other health conditions.
What is the best treatment for hematoma?
Surgery: In some cases, traditional surgery may be needed to drain blood from the brain or to repair damaged blood vessels. Draining the fluid that surrounds the brain: This creates room for the hematoma to expand without damaging brain cells. Medication: Drugs are used to control blood pressure, seizures or headaches.
How does a hemorrhage affect the brain?
When a hemorrhage interrupts blood flow around or inside the brain, depriving it of oxygen for more than three or four minutes, the brain cells die.
What is the term for a bleed in the brain?
Brain Bleed, Hemorrhage (Intracranial Hemorrhage ) Brain bleeds – bleeding between the brain tissue and skull or within the brain tissue itself – can cause brain damage and be life-threatening. Some symptoms include headache; nausea and vomiting; or sudden tingling, weakness, numbness or paralysis of face, arm or leg.
What is the name of the bleed that occurs inside the brain?
Bleeding inside the brain tissue. Two types of brain bleeds can occur inside the brain tissue itself – intracerebral hemorrhage (also called cerebral hemorrhage and hemorrhagic stroke) and intraventicular hemorrhage.
What does it mean when your brain bleeds?
To most people, a “brain bleed” simply means any bleed inside your head. However, a doctor – and specifically doctors who treats brain bleeds (neurologists and neurosurgeons) – would say that a “brain bleed” (also known by the medical term intracranial hemorrhage) is too broad of a term. These doctors further describe brain bleeds by their exact ...
Where does intraventricular hemorrhage occur?
Intraventricular hemorrhage: This bleeding occurs in the brain’s ventricles, which are specific areas of the brain (cavities) where cerebrospinal fluid is produced. Brain bleeds can occur in the meninges layers outside the brain tissue or inside the brain tissue itself.
What causes a tumor to bleed?
Brain tumor that presses on brain tissue causing bleeding. Smoking, heavy alcohol use, or use of illegal drugs such as cocaine. Conditions related to pregnancy or childbirth, including eclampsia, postpartum vasculopathy, or neonatal intraventricular hemorrhage.
Why does my brain bleed?
Bleeding in the brain has a number of causes, including: Head trauma, caused by a fall, car accident, sports accident or other type of blow to the head. High blood pressure ( hypertension ), which can damage the blood vessel walls and cause the blood vessel to leak or burst.
Overview
Hemorrhage is loss of blood from a damaged blood vessel. The bleeding can be inside or outside the body, and blood loss can be minor or major.
Possible Causes
Alcohol, drug or tobacco use that is heavy or long-term (bleeding in the brain).
When to Call the Doctor
Seek immediate medical attention if you or someone else is bleeding externally or may be bleeding internally and: