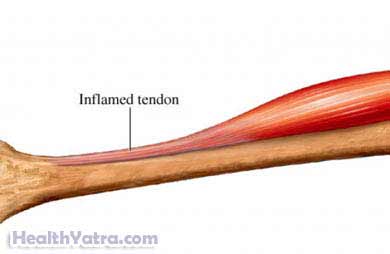
Full Answer
Can tendinopathy go away?
Tendinitis may go away over time. If not, the doctor will recommend treatments to reduce pain and inflammation and preserve mobility. Severe symptoms may require specialized treatment from a rheumatologist, an orthopaedic surgeon or a physical therapist.
Does tendonitis ever go away?
Tendonitis is acute (short-term) inflammation in the tendons. It may go away in just a few days with rest and physical therapy. Tendonitis results from micro-tears in the tendon when it’s overloaded by sudden or heavy force. There is no inflammation in tendonosis, but rather the actual tissue in the tendons is degrading.
What is the best treatment for tendonitis?
Treatment for tendinitis includes: RICE method: this is the best home treatment for mild injury. Rest: avoid activates that cause or aggravate the injury. Ice: helps decrease pain, swelling, and redness. If done immediately after the injury, it may prevent some inflammation. Use an ice pack or ice wrapped in a towel.
How to cure tendon pain?
approach — rest, ice, compression, elevation:
- Rest. Avoid activities that cause pain, swelling or discomfort. ...
- Ice. Even if you're seeking medical help, ice the area immediately. ...
- Compression. To help stop swelling, compress the area with an elastic bandage until the swelling stops. ...
- Elevation. ...
How long does a tendinopathy take to heal?
How long does it take to recover from tendinopathy? Recovery time for tendinitis can take as little as two days (if it's an acute injury) and as long as six weeks. Tendinosis usually takes about two to six months.
What is the best treatment for tendinosis?
Treatment and self-care recommendations for tendinosis include:Rest. ... Adjust ergonomics and biomechanics. ... Use appropriate support. ... Stretch and keep moving, though conservatively. ... Apply ice. ... Eccentric strengthening. ... Massage. ... Nutrition.
Will tendinopathy heal on its own?
In a vast majority of cases tendinopathy will not improve without this vital load stimulus. 5) Modifying load is important in settling tendon pain. This often involves reducing (at least in the short-term) abusive tendon load that involves energy storage and compression.
Can chronic tendinopathy be cured?
Early treatment is necessary because untreated tendinosis can rupture the tendons and lead to further degeneration of tendon tissue. Tendinosis can be cured but may take 3 to 6 months to heal. Physical therapy and other treatment measures may speed up the healing process.
What is severe tendinopathy?
Tendinopathy is a broad term encompassing painful conditions occurring in and around tendons in response to overuse. Recent basic science research suggests little or no inflammation is present in these conditions.
What happens in tendinopathy?
Tendinopathy (often called tendinitis or tendinosis) is the most common tendon disorder [86, 99]. It is characterized by activity-related pain, focal tendon tenderness, and decreased strength and movement in the affected area. The histological features of tendinopathy are further described in the current study.
What happens if tendinopathy goes untreated?
Untreated tendonitis can develop into chronic tendinosis and cause permanent degradation of your tendons. In some cases, it can even lead to tendon rupture, which requires surgery to fix. So if you suspect tendonitis, stop doing the activities that cause the most pain.
Is tendinopathy permanent?
Tendonitis: Tendonitis occurs when overuse causes tendon wear and inflammation. This is an acute injury, meaning the pain is immediate, but it's easily treated and damage is not permanent.
What does tendinopathy look like?
Symptoms. You typically have pain around a joint, especially if you continue to use it a lot in hobbies, sports, or on the job. It may feel weak, look swollen and red, and feel warm to the touch. In rare cases when infection causes tendinosis, you also could have a rash, fever, or unusual discharge.
Is massage good for tendinopathy?
For people suffering from tendonitis, it can help with pain relief and speed up the recovery process. Since tendonitis can take weeks to heal, using a massage therapy program to both relax and strengthen the inflamed tendon can give the sufferer a better chance of a full and speedy recovery.
How is tendinopathy diagnosed?
The diagnosis of tendinopathy is primarily based on patient history and physical examination6. The major clinical feature is longstanding pain1. The findings from the physical examination include tenderness of the affected part of the tendon(s), pain with tendon loading, and, occasionally, palpable nodular thickening7.
Does heat help with tendinopathy?
Heat may be more helpful for chronic tendon pain, often called tendinopathy or tendinosis. Heat can increase blood flow, which may help promote healing of the tendon. Heat also relaxes muscles, which can relieve pain.
What type of massage is used for tendinopathy?
There are several techniques that a physical therapist might use to treat tendinopathy, but two common ones include: deep transverse friction massage, a type of connective tissue massage that can help to stimulate cell activity and generate new collagen fibers.
What causes tendinopathy and tendonitis?
What causes tendinopathy? Both tendinopathy and tendonitis are often caused by overuse of or sudden stress on a tendon. Aging and lack of muscle tone can also play a role in the development of tendinopathy. Doctors previously thought that tendinopathy was an eventual result of tendonitis.
What is the difference between tendinopathy and tendonitis?
While the two have almost identical symptoms, they’re different conditions. Tendinopathy is a degeneration of the collagen protein that forms the tendon. Tendonitis, on the other hand, is just inflammation of the tendon.
What causes pain in the rotator cuff?
They connect your muscles to your bones. Tendinopathy, also called tendinosis, refers to the breakdown of collagen in a tendon. This causes burning pain in addition to reduced flexibility and range of motion. While tendinopathy can affect any tendon, it’s more common in the: Achilles tendon. rotator cuff tendons.
How to treat a tendon injury?
You can also try the RICE method, which is often very effective for tendon injuries: 1 R est. Try to stay off the affected body part as much as you can. 2 I ce. Wrap an ice pack in a light towel and hold it to the affected area for 20 minutes. You can do this up to eight times a day. 3 C ompress. Wrap the area in an elastic bandage, making sure it’s not too tight. 4 E levate. Keep the affected area raised on a pillow or other device. This can help to reduce any swelling.
How long does it take to heal a tendon?
They’ll probably recommend you do some physical therapy during the recovery process, which can take up to 12 weeks.
Which tendon is most affected by tendinopathy?
While tendinopathy can affect any tendon, it’s more common in the: Achilles tendon. rotator cuff tendons . patellar tendon. hamstring tendons. Read on to learn more about tendinopathy, including how it compares to tendonitis and how it’s treated.
What is the treatment for a tendon tear?
Treatment consists of activity modification, relative rest, ice, stretching, and strengthening.
What are the most common places to get tendinopathy?
In athletes, common locations for tendinopathy include the Achilles and patella tendons. In the general population, the Achilles and lateral epicondyle are the most commonly affected. There are many terms used to characterize chronic tendon disorders.
What is tendon degeneration?
Tendinopathy is a general term that describes tendon degeneration characterized by a combination of pain, swelling, and impaired performance. Common sites include the rotator cuff (supraspinatus tendon), wrist extensors (lateral epicondyle) and pronators (medial epicondyle), patellar and quadriceps tendons, and Achilles tendon.
What is a painful tendon?
Tendonitis refers to a painful tendon with histologic signs of inflammation within the tendon. Tendinosis is a localized intrinsic degeneration of unknown etiology, characterized by localized swollen tendon nodes. Several studies have shown that tendon biopsies taken at surgery lack inflammatory cells. [1]
How many muscle tendons are there in the human body?
There are over 600 muscle-tendon units in the human body. Theoretically, tendinopathy can occur in any one of them. However, this monograph will focus on the common sites including: the rotator cuff (supraspinatus tendon) in the shoulder, wrist extensors (lateral epicondyle) and pronators (medial epicondylitis) in the elbow, patellar and quadriceps tendon in the knee, and Achilles tendon in the heel.
What is the best medication for tendinitis?
For tendinitis, your doctor may recommend these medications: Pain relievers. Taking aspirin, naproxen sodium (Aleve) or ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others) may relieve discomfort associated with tendinitis. Topical creams with anti-inflammatory medication — popular in Europe and becoming increasingly available in the United States — also may be ...
How to treat tendinitis at home?
is the acronym to remember — rest, ice, compression and elevation. This treatment can help speed your recovery and help prevent further problems. Rest. Avoid activities that increase the pain or swelling. Don't try to work or play through the pain.
How to reduce swelling in knees?
Wraps or compressive elastic bandages are best. Elevation. If tendinitis affects your knee, raise the affected leg above the level of your heart to reduce swelling. Although rest is a key part of treating tendinitis, prolonged inactivity can cause stiffness in your joints.
What is the procedure to remove scar tissue from a tendon?
Dry needling. This procedure involves making small holes in the tendon with a fine needle to stimulate factors involved in tendon healing. Ultrasonic treatment. This minimally invasive procedure uses a small incision to insert a special device that removes tendon scar tissue with ultrasonic sound waves. Surgery.
How to get rid of swelling in a joint?
For an ice massage, freeze a plastic foam cup full of water so that you can hold the cup while applying the ice directly to the skin. Compression. Because swelling can result in loss of motion in an injured joint, compress the area until the swelling has ceased. Wraps or compressive elastic bandages are best.
How to help a swollen muscle?
Ice. To decrease pain, muscle spasm and swelling, apply ice to the injured area for up to 20 minutes several times a day. Ice packs, ice massage or slush baths with ice and water all can help.
What is the best treatment for pain without side effects?
Topical creams with anti-inflammatory medication — popular in Europe and becoming increasingly available in the United States — also may be effective in relieving pain without the potential side effects of taking anti-inflammatory medications by mouth. Corticosteroids.
What is the last option for tendinopathy?
Surgery is often considered a last option in the treatment of tendinopathy that persists after exhausting all nonoperative options. The most commonly described procedure is open surgical débridement of the involved tendon or peritendinous tissue with repair or augmentation of the tendon as needed. Although there are many publications describing the results of surgery in the treatment of tendinopathy, our literature search identified only four randomized, controlled studies [ 14, 27, 129, 144 ]. Two studies compared surgery to extracorporeal shock wave therapy [ 129, 144] and two compared surgery to exercises [ 14, 27 ].
What is sclerotherapy in tendinopathy?
Polidocanol is not FDA-approved although other sclerosing agents are. The rationale behind using sclerotherapy in tendinopathy is based on the finding that there is a proliferation of small blood vessels in areas of tendinopathy. Nerve fibers appear to travel in close proximity to these areas of neovascularization [ 24, 95, 97 ]. It is possible these nerve fibers are the pain generators in tendinopathy. In theory, injecting a sclerosing agent into the areas of neovascularization could not only sclerose the vessels, but also may eradicate the pain-generating nerve fibers. These injections are performed under Doppler ultrasound guidance ( Fig. 3A-C ).
What is ESWT therapy?
Extracorporeal shock wave therapy (ESWT) has been advocated for treating a number of soft tissue conditions, including plantar fasciitis, lateral epicondylitis, calcific and noncalcific tendonitis of the supraspinatus, and tendinopathy of the Achilles tendon. It is FDA-approved for plantar fasciitis and lateral epicondylitis only. ESWT entails delivering a series of low-energy shock waves directly over the painful area of the tendon. The mechanism by which ESWT would provide pain relief or enhance tendon healing is not clear. Ohtori et al. [ 121] reported the administration of a single session of low-energy shock waves to rat skin resulted in nearly complete degeneration of epidermal sensory nerve fibers. The fibers began to regenerate in 14 days. By applying a second session of shock waves at 14 days, the nerve fiber regeneration was delayed to 42 days [ 175 ]. There is also evidence tenocytes release growth factors in response to ESWT that may promote tendon healing. Chen et al. [ 33] reported administering shock waves to a rat Achilles tendinopathy model resulted in increased tenocyte proliferation and increased expression of transforming growth factor-beta1 and insulin growth factor 1.
What is the term for pain in and around tendons?
Introduction. Traditionally, pain in and around tendons associated with activity has been termed tendonitis. This terminology implies the pain associated with these conditions results from an inflammatory process. Not surprisingly, treatment modalities have mainly been aimed at controlling this inflammation.
Is tendinopathy a debilitating condition?
Tendinopathy is a common and often debilitating condition that can be quite difficult to treat. We performed an extensive review of the literature including 177 clinical trials and systematic reviews of the current treatment options for this condition. Our purpose was to provide a comprehensive and up-to-date review of these treatment options with recommendations based on the best level of evidence available.
