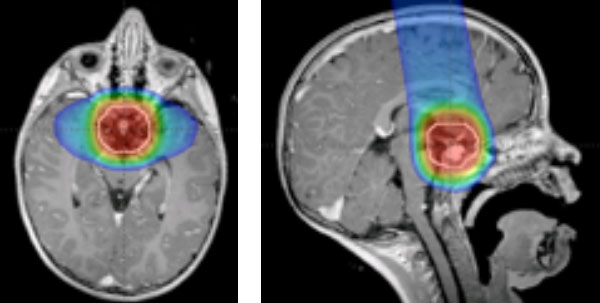
Treatment depends on the exact size and location of the tumor as well as the overall health of the patient and may include surgical removal, chemotherapy, or radiation. Questions or concerns regarding temporal lobe tumors should be discussed with a primary care physician or neurologist
Neurology
Neurology is a branch of medicine dealing with disorders of the nervous system. Neurology deals with the diagnosis and treatment of all categories of conditions and disease involving the central and peripheral nervous systems, including their coverings, blood vessels, and all effector tissue, …
Full Answer
What are the treatment options for malignant tumors?
· Treatment depends on the exact size and location of the tumor as well as the overall health of the patient and may include surgical removal, chemotherapy, or radiation. Questions or concerns regarding temporal lobe tumors should be discussed with a primary care physician or neurologist .
How is a brain tumor treated?
· Cancer treatment options include: Surgery. The goal of surgery is to remove the cancer or as much of the cancer as possible. Chemotherapy. Chemotherapy uses drugs to kill cancer cells. Radiation therapy. Bone marrow transplant. Immunotherapy. Hormone therapy.
What are the treatment options for Malignant meningioma?
Radiation therapy is the use of high-energy x-rays or other particles to destroy tumor cells. Doctors may use radiation therapy to slow or stop the growth of a brain tumor. It is typically given after surgery and possibly along with chemotherapy. A doctor who specializes in giving radiation therapy to treat a tumor is called a radiation oncologist.
What are the different types of targeted therapy for brain tumors?
· Radiation therapy uses high-energy beams, such as X-rays or protons, to kill tumor cells. Radiation therapy can come from a machine outside your body (external beam radiation), or, very rarely, radiation can be placed inside your body close to your brain tumor (brachytherapy).

Can temporal lobe tumors be removed?
Third, MTL tumors, especially those with the pathological characteristics of low-grade lesions, tend to be restricted to the anatomical boundary of the temporal lobe, and complete removal of them is possible in many cases. Last, in many cases, in toto temporal lobe resection is required for seizure control.
How long can you live with a malignant brain tumor?
Survival for all types of cancerous (malignant) brain tumour 40 out of 100 people (40%) survive their cancer for 1 year or more. more than 10 out of 100 people (more than 10%) survive their cancer for 5 years or more.
How do you treat malignant brain tumor?
If you have a malignant brain tumour, you'll usually need surgery to remove as much of it as possible. Radiotherapy and/or chemotherapy may then be used to treat any remaining cancerous tissue.
What are the chances of surviving a malignant brain tumor?
The 5-year survival rate for people in the United States with a cancerous brain or CNS tumor is almost 36%. The 10-year survival rate is almost 31%. Age is a factor in general survival rates after a cancerous brain or CNS tumor is diagnosed. The 5-year survival rate for people younger than age 15 is about 75%.
Can a malignant brain tumor be cured?
Outlook. The outlook for a malignant brain tumour depends on things like where it is in the brain, its size, and what grade it is. It can sometimes be cured if caught early on, but a brain tumour often comes back and sometimes it isn't possible to remove it.
Are malignant brain tumors always fatal?
Survival for patients with benign tumors is usually much better but, in general, survival rates for all types of brain cancers, benign and malignant, are: About 70% in children.
What is the best treatment for brain tumor?
Surgery. Surgery is the usual treatment for most brain tumors. To remove a brain tumor, a neurosurgeon makes an opening in the skull. This operation is called a craniotomy.
What is the success rate of brain tumor surgery?
Here are some basic survival rate statistics, as reported by the American Cancer Society: Oligodendroglioma - 90% for patients 20-44, 82% for patients 45-54 and 69% for patients 55-64. Meningioma - 84% for patients 20-44, 79% for patients 45-54 and 74% for patients 55-64.
Is a brain tumor a death sentence?
Some brain tumours grow very slowly (low grade) and cannot be cured. Depending on your age at diagnosis, the tumour may eventually cause your death. Or you may live a full life and die from something else. It will depend on your tumour type, where it is in the brain, and how it responds to treatment.
How long is recovery after brain tumor removal?
Most patients are pretty active postoperatively and resume their normal activities within a few days, and often return to work around four to six weeks after surgery.
What are the side effects of radiation treatment on the brain?
Radiation to the brain can cause these short-term side effects:Headaches.Hair loss.Nausea.Vomiting.Extreme tiredness (fatigue)Hearing loss.Skin and scalp changes.Trouble with memory and speech.More items...•
Can you fully recover from a brain tumor?
Some people may complete recovery in a few weeks or months, others will have to learn to adjust to permanent changes in their life such as not being able to work or accomplish all the same tasks they did before.
Can malignant tumors invade the temporal bone?
Management of Malignant Tumors that Invade the Temporal Bone. Malignant tumors that invade the temporal bone are rare, and diagnosis and treatment are straightforward with few areas of controversy. Nevertheless, these tumors often pose a surgical challenge, especially when they invade adjacent structures such as the carotid artery and the dura.
Is temporal bone malignant?
Malignant tumors that invade the temporal bone are rare, and diagnosis and treatment are straightforward with few areas of controversy. Nevertheless, these tumors often pose a surgical challenge, especially when they invade adjacent structures such as the carotid artery and the dura. ENToday spoke with experts in managing these uncommon but potentially disfiguring tumors about the current state of the art.
What are the three places that tumors invade the temporal bone?
Tumors that can invade the temporal bone have three possible origins: the skin of the outer ear , the parotid gland , and the ear canal. Those that arise in the outer ear and parotid gland are the most common, whereas those arising in the ear canal are rare. Skin tumors present as a mass or ulcer in the outer ear, while parotid tumors present as a mass in the parotid gland. Tumors of the ear canal may present with signs that mimic chronic otitis media, such as hearing loss, purulence, or a canal mass. Other symptoms that can signal the presence of a tumor that invades the temporal bone are bleeding from the ear and facial paralysis or weakness.
Where do tumors originate?
Tumors that can invade the temporal bone have three possible origins: the skin of the outer ear , the parotid gland, and the ear canal. Those that arise in the outer ear and parotid gland are the most common, whereas those arising in the ear canal are rare.
Is parotid gland tumor rare?
Those that arise in the outer ear and parotid gland are the most common, whereas those arising in the ear canal are rare. Skin tumors present as a mass or ulcer in the outer ear, while parotid tumors present as a mass in the parotid gland. Tumors of the ear canal may present with signs that mimic chronic otitis media, such as hearing loss, ...
What is the difference between a skin tumor and a parotid tumor?
Skin tumors present as a mass or ulcer in the outer ear, while parotid tumors present as a mass in the parotid gland. Tumors of the ear canal may present with signs that mimic chronic otitis media, such as hearing loss, purulence, or a canal mass.
What are the signs of a tumor in the ear canal?
Tumors of the ear canal may present with signs that mimic chronic otitis media, such as hearing loss, purulence, or a canal mass. Other symptoms that can signal the presence of a tumor that invades the temporal bone are bleeding from the ear and facial paralysis or weakness.
What is the best treatment for a tumor?
Chemotherapy, radiation, hormone therapy, and surgery (or combinations of these treatments) are the most common methods offered to patients. Depending on the location, surgery is sometimes the most effective option to remove the tumor and prevent a recurrence.
What is the most appropriate course of treatment for a tumor?
The most appropriate course of treatment is determined by the size, location, and stage of the tumor, as well as the patient’s overall health. Chemotherapy, radiation, hormone therapy, and surgery (or combinations of these treatments) are the most common methods offered to patients.
What are the characteristics of a malignant tumor?
A malignant tumor is a group of diseased cells defined by one of three characteristics: uncontrolled growth, invasion and damage of healthy cells, or metastasizing (spreading) to other organs of the body. They differ from benign tumors, which do not spread or affect other areas of the body.
What are the symptoms of a malignant tumor?
These include excessive sweating (particularly at night), weight loss due to poor appetite, fatigue, anemia, and a host of other common symptoms. If a tumor is suspected, a pathologist can perform a biopsy on ...
Is it possible to predict the prognosis of a tumor?
It is difficult to predict a patient’s prognosis. Most malignant tumors are considered to be fatal; depending on the location, type, size, and stage of the tumor, the patient’s outlook can vary greatly.
Is a malignant tumor fatal?
Most malignant tumors are considered to be fatal; depending on the location, type, size, and stage of the tumor, the patient’s outlook can vary greatly. In most cases, early detection and treatment will help to improve the patient’s prognosis and prolong their life expectancy.
Can a pathologist biopsy a tumor?
These include excessive sweating (particularly at night), weight loss due to poor appetite, fatigue, anemia, and a host of other common symptoms. If a tumor is suspected, a pathologist can perform a biopsy on the cells to determine whether or not it is malignant.
What are the treatments for a tumor?
You may also receive palliative treatments similar to those meant to get rid of the tumor, such as chemotherapy, surgery, or radiation therapy.
What is the only treatment for a low grade brain tumor?
For a low-grade brain tumor, surgery may be the only treatment needed especially if all of the tumor can be removed. If there is visible tumor remaining after surgery, radiation therapy and chemotherapy may be used.
What is a multidisciplinary team in brain cancer?
In brain tumor care, different types of doctors often work together to create a patient’s overall treatment plan that combines different types of treatment. This is called a multidisciplinary team. Your care team may include a variety of other health care professionals, such as physician assistants, nurse practitioners, oncology nurses, social workers, pharmacists, counselors, dietitians, rehabilitation specialists, and others. It is important to have a care team that specializes in caring for people with a brain tumor, which may mean talking with medical professionals beyond your local area to help with diagnosis and treatment planning.
What is the treatment for a tumor after surgery?
If there is visible tumor remaining after surgery, radiation therapy and chemotherapy may be used. For higher-grade tumors, treatment usually begins with surgery, followed by radiation therapy and chemotherapy. Your exact treatment plan will be made by your health care team.
What are the effects of brain tumors?
Physical, emotional, and social effects of a brain tumor. A brain tumor and its treatment cause physical symptoms and side effects, as well as emotional, social, and financial effects. Managing all of these effects is called palliative care or supportive care. It is an important part of your care that is included along with treatments intended ...
What is the procedure called when a brain tumor is removed?
A neurosurgeon is a doctor who specializes in surgery on the brain and spinal column. Surgery to the brain requires the removal of part of the skull, a procedure called a craniotomy. After the surgeon removes the tumor, the patient's own bone will be used to cover the opening in the skull.
What is the name of the doctor who treats brain tumors?
A doctor who specializes in giving radiation therapy to treat a tumor is called a radiation oncologist.
What is the best treatment for brain tumors?
The chemotherapy drug used most often to treat brain tumors is temozolomide (Temodar). Other chemotherapy drugs may be recommended depending on the type of cancer. Chemotherapy side effects depend on the type and dose of drugs you receive. Chemotherapy can cause nausea, vomiting and hair loss.
Can targeted therapy be used for brain tumors?
Targeted therapy drugs are available for certain types of brain tumors, and many more are being studied in clinical trials. Your doctor may have your tumor cells tested to see whether targeted therapy is likely to be an effective treatment for your brain tumor.
What tests are done to determine if you have a brain tumor?
Diagnosis. If it's suspected that you have a brain tumor, your doctor may recommend a number of tests and procedures, including: A neurological exam. A neurological exam may include, among other things, checking your vision, hearing, balance, coordination, strength and reflexes. Difficulty in one or more areas may provide clues about the part ...
What is the best way to diagnose brain tumor?
A neurological exam. A neurological exam may include, among other things, checking your vision, hearing, balance, coordination, strength and reflexes. Difficulty in one or more areas may provide clues about the part of your brain that could be affected by a brain tumor. Imaging tests.
Can a biopsy be done on a brain tumor?
A biopsy can be performed as part of an operation to remove the brain tumor, or a biopsy can be performed using a needle. A stereotactic needle biopsy may be done for brain tumors in hard to reach areas or very sensitive areas within your brain that might be damaged by a more extensive operation.
Can a brain tumor be removed?
Other brain tumors can't be separated from surrounding tissue or they're located near sensitive areas in your brain, making surgery risky. In these situations, your doctor removes as much of the tumor as is safe. Even removing a portion of the brain tumor may help reduce your signs and symptoms.
Is it safe to remove a brain tumor?
In these situations, your doctor removes as much of the tumor as is safe. Even removing a portion of the brain tumor may help reduce your signs and symptoms. Surgery to remove a brain tumor carries risks, such as infection and bleeding. Other risks may depend on the part of your brain where your tumor is located.
What is the treatment for a tumor?
The surgeon will remove the tumor and some of the surrounding tissue. You may have heard of chemotherapy and radiation therapy for the treatment of tumors. Chemotherapy, also known as chemo, is a common cancer treatment that uses drugs to destroy the fast-growing cancer cells.
What are the two types of treatment for malignant tumors?
Let's take a look at two common types of treatment for malignant tumors: surgical and medical treatments. Surgery. Surgery can be a scary situation, but for many individuals with aggressive malignant tumors, it can be a lifesaver.
What is a malignant tumor?
Well, a malignant tumor is a tumor that is invasive, meaning it can invade the surrounding tissues. Malignant tumors contain cells that are cancerous, growing out of control and capable of metastasizing. Metastasize simply means that the cells of the tumor are able to leave the original tumor and travel to other parts of the body.
What is the term for a tumor that is cancerous and growing out of control?
Malignant tumors contain cells that are cancerous, growing out of control and capable of metastasizing. Metastasize simply means that the cells of the tumor are able to leave the original tumor and travel to other parts of the body. In cancerous tumors or malignant tumor s, the cells have lost the ability to stop growing.
Is a tumor malignant or benign?
The tumor can either be malignant or it can be benign, which means it is not cancerous. Okay, so you may be thinking, what is the difference between a malignant tumor and a benign tumor? That is a good question.
What is the difference between a benign tumor and a malignant tumor?
Recall that a benign tumor is non-cancerous and most likely not life threatening, and a malignant tumor is cancerous and can be life threatening. Lastly, we learned a few of the treatment options for malignant tumors. First, tumors can be removed surgically.
Is a benign tumor cancerous?
Recall that a benign tumor is non-cancerous and most likely not life threatening, and a malignant tumor is cancerous and can be life threatening. Lastly, we learned a few of the treatment options for malignant tumors. First, tumors can be removed surgically. They can also be treated with strong medication known as chemotherapy or ...
Overview
A tumor is a mass or group of abnormal cells that form in the body. If you have a tumor, it isn’t necessarily cancer. Many tumors are benign (not cancerous).
Symptoms and Causes
Your body is constantly making new cells to replace old or damaged ones that die off. Sometimes, the cells don’t die off as expected. Or, new cells grow and multiply faster than they should. The cells start to pile up, forming a tumor.
Diagnosis and Tests
Your healthcare provider performs a biopsy to determine whether a tumor is cancer. A biopsy involves removing cell samples from a tumor. A pathologist (a medical doctor who studies diseases) examines the samples in a lab to make a diagnosis.
Management and Treatment
Treatments for a tumor depend on many factors, including the tumor type (malignant or benign) and location.
Prevention
Most tumors occur for no known reason. Still, these steps may lower your risk of developing a tumor:
How to treat malignant meningioma?
The first treatment for a malignant meningioma is surgery, if possible. The goal of surgery is to obtain tissue to determine the tumor type and to remove as much tumor as possible without causing more symptoms for the person. Most people with atypical and anaplastic meningiomas receive further treatments.
Can cancer cause meningiomas?
Genes may be mutated (changed) in many types of cancer, which can increase the growth and spread of cancer cells. The cause of meningiomas is not known. Exposure to radiation, especially in childhood, is the only known environmental risk factor for developing meningiomas.
What are the different grades of meningioma?
What are the grades of meningiomas? 1 Grade I meningiomas are low grade tumors and are the most common. This means the tumor cells grow slowly. 2 Grade II atypical meningiomas are mid-grade tumors. This means the tumors have a higher chance of coming back after being removed. The subtypes include choroid and clear cell meningioma. 3 Grade III anaplastic meningiomas are malignant (cancerous). This means they are fast-growing tumors. The subtypes include papillary and rhabdoid meningioma.
Where does a meningioma begin?
This means it begins in the brain or spinal cord. Overall, meningiomas are the most common type of primary brain tumor. However, higher grade meningiomas are very rare. To get an accurate diagnosis, a piece of tumor tissue will be removed during surgery, if possible.
What is a grade 1 meningioma?
Grade I meningiomas are low grade tumors and are the most common. This means the tumor cells grow slowly. Grade II atypical meningiomas are mid-grade tumors. This means the tumors have a higher chance of coming back after being removed.
What is grade 3 anaplastic meningioma?
This means the tumors have a higher chance of coming back after being removed. The subtypes include choroid and clear cell meningioma. Grade III anaplastic meningiomas are malignant (cancerous). This means they are fast-growing tumors. The subtypes include papillary and rhabdoid meningioma.
What is a meningioma survivor?
Meningioma Survivor Finds Meaning in Rare Cancer Diagnosis. Deborah is a two-time cancer survivor. She shares what it is like to live with a type of rare brain cancer called meningioma to help others.