Medication
What is the treatment for syphilis? A single injection of long-acting Benzathine penicillin G can cure the early stages of syphilis. This includes primary, secondary, or early latent syphilis. CDC recommends three doses of long-acting Benzathine penicillin G at weekly intervals for late latent syphilis or latent syphilis of unknown duration.
Self-care
This study found that 99% of women with the double dose of benzathine penicillin G were cured. Historically, multiple doses of benzathine penicillin G (once a week for three weeks) or procaine penicillin 1.2 MU (once daily for 20 days) have been successful for …
Nutrition
Nov 12, 2014 · Randomized clinical trials have shown that oral azithromycin (as a single 1- to 2-g dose) is effective in the treatment of early syphilis, with much of the data derived from studies done in Africa. 11,12,24 The emergence of azithromycin resistance mutations in T pallidum with resultant treatment failure has limited its usefulness in many regions of the United States. …
How long does it take to treat and cure syphilis?
Apr 03, 2020 · Syphilis affects your nervous system: Penicillin given through an IV (intravenous) infusion, with treatment given once a week for two weeks. To treat syphilis with penicillin, you need a shot or IV infusion. Taking penicillin pills cannot cure you. You should not have sex for at least 1 week after treatment and until all symptoms have gone away.
What happens if syphilis is left untreated?
Apr 07, 2005 · Penicillin G is the mainstay of treatment for syphilis. Depending on the stage of infection and other factors, the preparation, dose, and duration of therapy can vary. If penicillin G cannot be used due to a penicillin allergy, other antibiotics may be prescribed. The sexual partners of someone with syphilis should also be treated.
What is the best treatment for syphilis?
The recommended treatment at all stages of this disease is the antibiotic penicillin. If you’ve been infected for less than a year, you may need just one injection of penicillin to be cured.
Can syphilis be cured at any stage?
Penicillin remains the treatment of choice for syphilis, with sustained low blood levels curing virtually all patients having early syphilis and halting disease progression in most patients with symptomatic syphilis. Tetracycline, erythromycin or cephalothin yields similar cure rates for patients with early syphilis who are allergic to penicillin.

What is the best treatment for syphilis?
How long does syphilis take to cure?
The type of treatment you need depends on how long you've had syphilis. Syphilis that has lasted less than 2 years is usually treated with an injection of penicillin into your buttocks, or a 10-14 day course of antibiotic tablets if you can't have penicillin.
Is syphilis 100% curable?
Does syphilis go away?
What are the signs of syphilis in a man?
What happens if syphilis is left untreated?
What syphilis looks like?
Can Amoxicillin 500mg treat syphilis?
How long can you have syphilis without knowing?
How long should I take amoxicillin 500mg for syphilis?
How do you test for syphilis?
What is the best treatment for syphilis?
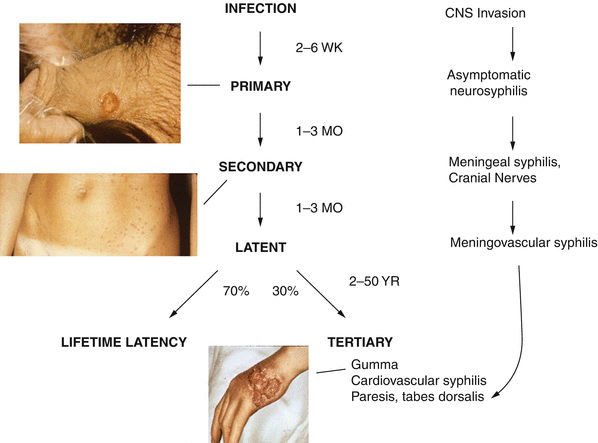
Penicillin G , administered parenterally, is the preferred drug for treating patients in all stages of syphilis. The preparation used (i.e., benzathine, aqueous procaine, or aqueous crystalline), dosage, and length of treatment depend on the stage and clinical manifestations of the disease. Treatment for late latent syphilis (>1 years’ duration) and tertiary syphilis requires a longer duration of therapy because organisms theoretically might be dividing more slowly (the validity of this rationale has not been assessed). Longer treatment duration is required for persons with latent syphilis of unknown duration to ensure that those who did not acquire syphilis within the preceding year are adequately treated.
When should syphilis be treated?
Persons who have had sexual contact with a person who receives a diagnosis of primary, secondary , or early latent syphilis >90 days before the diagnosis should be treated presumptively for early syphilis if serologic test results are not immediately available and the opportunity for follow-up is uncertain. If serologic tests are negative, no treatment is needed. If serologic tests are positive, treatment should be based on clinical and serologic evaluation and syphilis stage.
How to screen for syphilis?
Clinical laboratories sometimes screen syphilis serologic samples by using automated treponemal immunoassays, typically by EIA or CIA (571–573). This reverse sequence algorithm for syphilis testing can identify persons previously treated for syphilis, those with untreated or incompletely treated syphilis, and those with false-positive results that can occur with a low likelihood of infection (574). Persons with a positive treponemal screening test should have a standard quantitative nontreponemal test with titer performed reflexively by the laboratory to guide patient management decisions. If the nontreponemal test is negative, the laboratory should perform a treponemal test different from the one used for initial testing, preferably TP-PA or treponemal assay based on different antigens than the original test, to adjudicate the results of the initial test.
What is the definitive method for diagnosing syphilis?
Darkfield examinations and molecular tests for detecting T. pallidumdirectly from lesion exudate or tissue are the definitive methods for diagnosing early syphilis and congenital syphilis (565). Although no T. pallidumdirect-detection molecular NAATs are commercially available, certain laboratories provide locally developed and validated PCR tests for detecting T. pallidumDNA. A presumptive diagnosis of syphilis requires use of two laboratory serologic tests: a nontreponemal test (i.e., Venereal Disease Research Laboratory [VDRL] or rapid plasma reagin [RPR] test) and a treponemal test (i.e., the T. pallidumpassive particle agglutination [TP-PA] assay, various EIAs, chemiluminescence immunoassays [CIAs] and immunoblots, or rapid treponemal assays) (566–568). At least 18 treponemal-specific tests are cleared for use in the United States. Use of only one type of serologic test (nontreponemal or treponemal) is insufficient for diagnosis and can result in false-negative results among persons tested during primary syphilis and false-positive results among persons without syphilis or previously treated syphilis.
What is latent syphilis?
Latent infections (i.e., those lacking clinical manifestations) are detected by serologic testing. Latent syphilis acquired within the preceding year is referred to as early latent syphilis; all other cases of latent syphilis are classified as late latent syphilis or latent syphilis of unknown duration.
How long before syphilis diagnosis should you treat?
Persons who have had sexual contact with a person who receives a diagnosis of primary, secondary, or early latent syphilis <90 days before the diagnosis should be treated presumptively for early syphilis, even if serologic test results are negative.
Is CSF evaluation necessary for syphilis?
Further testing with CSF evaluation is warrant ed for persons with clinical signs of neuro syphilis (e.g., cranial nerve dysfunction, meningitis, stroke, acute or chronic altered mental status, or loss of vibration sense). All patients with ocular symptoms and reactive syphilis serology need a full ocular examination, including cranial nerve evaluation. If cranial nerve dysfunction is present, a CSF evaluation is needed. Among persons with isolated ocular symptoms (i.e., no cranial nerve dysfunction or other neurologic abnormalities), confirmed ocular abnormalities on examination, and reactive syphilis serology, a CSF examination is unnecessary before treatment. CSF analysis can be helpful in evaluating persons with ocular symptoms and reactive syphilis serology who do not have ocular findings or cranial nerve dysfunction on examination. Among patients with isolated auditory abnormalities and reactive syphilis serology, CSF evaluation is likely to be normal and is unnecessary before treatment (583,584).
How often should I take penicillin for syphilis?
In adults and adolescents with late syphilis or unknown stage of syphilis, the WHO STI guideline recommends benzathine penicillin G 2.4 million units intramuscularly once weekly for three consecutive weeks over no treatment.
How many units of penicillin should I take for syphilis?
In adults and adolescents with late syphilis or unknown stage of syphilis, the WHO STI guideline suggests benzathine penicillin G 2.4 million units intramuscularly once weekly for three consecutive weeks over procaine penicillin 1.2 million units once daily for 20 days.
How often should I take erythromycin for STI?
due to stock-outs), the WHO STI guideline suggests using, with caution, erythromycin 500 mg orally four times daily for 14 days or ceftriaxone 1 g intramuscularly once daily for 10–14 days or azithromycin 2 g once orally.
How many units of penicillin should I give to a pregnant woman with syphilis?
In pregnant women with early syphilis, the WHO STI guideline recommends benzathine penicillin G 2.4 million units once intramuscularly over no treatment.
How many people refused syphilis injections?
There was some research evidence relating to overall acceptability of injections versus medicines taken orally in people with syphilis: approximately 10–20% of people refused injections. The GDG noted that in practice some health-care providers are averse to providing injections, and there are additional staff time and equipment costs with IM administration. The GDG raised concerns about the impending global shortage of benzathine penicillin; a shortage would reduce health equity and it would not be feasible to apply the treatment recommendation.
Is doxycycline better than ceftriaxone?
Remarks:Doxycycline is preferred over ceftriaxone due to its lower cost and oral administration. Doxycycline should not be used in pregnant women (see recommendations 3 and 4 for pregnant women). Azithromycin is an option in special circumstances only when local susceptibility to azithromycin is likely. If the stage of syphilis is unknown, recommendations for people with late syphilis should be followed.
What test can confirm syphilis?
Blood. Blood tests can confirm the presence of antibodies that the body produces to fight infection. The antibodies to the syphilis-causing bacteria remain in your body for years, so the test can be used to determine a current or past infection. Cerebrospinal fluid.
How to prevent HIV infection?
Avoid sexual contact with new partners until the treatment is completed and blood tests indicate the infection has been cured. Notify your sex partners so that they can be tested and get treatment if necessary. Be tested for HIV infection.
What does giving a complete report of your symptoms and sexual history do?
Giving your doctor a complete report of your symptoms and sexual history will help your doctor determine how to best care for you. Here are some of the things your doctor may ask:
Can you cure syphilis with penicillin?
When diagnosed and treated in its early stages, syphilis is easy to cure. The preferred treatment at all stages is penicillin, an antibiotic medication that can kill the organism that causes syphilis. If you're allergic to penicillin, your doctor may suggest another antibiotic or recommend penicillin desensitization.
What to do if you have syphilis?
If you might have syphilis, your doctor will order a blood test. If this blood test is positive, the lab typically performs a second test on your blood to confirm that you have syphilis. If you have syphilis, you need treatment.
How long does it take to get penicillin for syphilis?
Here’s how you may get the antibiotic: Early stage: One shot of penicillin. Late stage: Three shots of penicillin, with one shot given each week for three weeks. Syphilis affects your nervous system: Penicillin given through an IV (intravenous) infusion, with treatment given once a week for two weeks. To treat syphilis with penicillin, you need ...
How long after syphilis treatment can you have sex?
To treat syphilis with penicillin, you need a shot or IV infusion. Taking penicillin pills cannot cure you. You should not have sex for at least 1 week after treatment and until all symptoms have gone away.
Where do you report syphilis?
Your doctor is required by law to report all syphilis infections to the local health department. If you prefer, the health department can help notify your partner (s) that they need to be tested.
Can you take doxycycline for syphilis?
If your doctor decides to treat you with one of these antibiotics, you will need several follow-up appointments. These antibiotics can be less effective at treating syphilis.
Do you need a follow up appointment for syphilis?
Others get re-infected. During your follow-up appointments, you’ll have: A blood test to make sure you no longer have syphilis. Other medical tests if the disease was caught late.
Can you use latex condoms for syphilis?
When you start having sex again, use latex condoms and/or dental dams to prevent getting syphilis again or other sexually transmitted diseases. While the right antibiotic can cure syphilis, it cannot undo damage already done. If syphilis caused hearing loss, you’ll continue to have hearing loss after being treated.
How many injections are needed for syphilis?
Syphilis treatment often requires a single injection. The course of therapy is largely directed by the stage of infection (primary, secondary, latent, tertiary) and other contributing factors. Of note, the primary and secondary stages of syphilis are the most infectious.
How long does it take for antibodies to decrease after syphilis treatment?
Syphilis antibody levels will be elevated after treatment but gradually subside over time. A four-fold decrease in antibodies after one year is considered a treatment success. 7 Most people are advised to undergo retesting six to 12 months after the completion of treatment. 5. Causes and Risk Factors of Syphilis.
How many shots of benzathine penicillin G?
Generally, a single shot of long-acting Benzathine penicillin G will cure a person of primary, secondary, or early latent syphilis. Late latent and tertiary syphilis is treated with three doses given at one-week intervals. 5.
What are some alternatives to penicillin?
For people allergic to penicillin, alternative drugs such as doxycycline, tetracycline, azithromycin, and ceftriaxone may be used. The only exceptions would be neurosyphilis (a late-stage complication affecting the brain and central nervous system) or congenital syphilis (where the infection is passed from mother to child during pregnancy) in which penicillin is the only option.
What to do if your mother is allergic to penicillin?
If a mother is allergic to penicillin, her doctor will need to desensitize her with a series of allergy shots. This would involve exposing the mother to smaller amounts of penicillin and increasing the dosage gradually to build tolerance so that she can eventually be treated with the antibiotic.
How long after syphilis treatment can you be contagious?
While a person is generally not considered contagious 24 hours after completing treatment, some healthcare providers will recommend abstinence until follow-up tests have been completed.
How many people get syphilis each year?
Syphilis, a sexually transmitted infection (STI), is fairly common - affecting more than 120,000 people each year. The mainstay treatment for this STI is penicillin, but other types of antibiotics may be appropriate as well. 1
How long do side effects of syphilis last?
Joint or muscle pain. All of the above, plus nausea and chills. If you do have side effects, they typically only last about 24 hours. Once you’ve completed your treatment, the antibiotics will kill the bacteria that cause syphilis and prevent any additional problems from occurring because of that particular case.
How does syphilis affect the body?
Syphilis can cause blindness or paralysis. It increases your chances of getting and spreading HIV, the virus that causes AIDS. Over time, it can damage your organs and even lead to death.
Can antibiotics cure syphilis?
There are no over-the-counter medications or home remedies that will cure syphilis -- only antibiotics can do that.
Is a syringe curable?
The good news: It’s easily treated and curable in its early stages.
Can you get syphilis again?
And, they’ll advise you to be tested for HIV and avoid all sexual contact until blood tests confirm you’re cured. And remember that getting treatment doesn’t mean you can’t get syphilis again or spread it at a later time.
How to get rid of syphilis?
Syphilis is usually super easy to get rid of in the early stages. Your nurse or doctor will prescribe antibiotics to treat the infection — usually penicillin, unless you’re allergic or can’t take it for other reasons. If you’re having syphilis treatment, it’s really important for your sexual partners to get treated also.
What happens if you don't treat syphilis?
Your sexual partners need to be treated, too. If you don’t treat syphilis, it can lead to very serious health problems. X in a circle.
Does syphilis increase your chances of getting AIDS?
Having syphilis also increases your chances of getting or spreading HIV, the virus that causes AIDS.
Can syphilis be passed to a baby?
Syphilis can be passed to your fetus during pregnancy or to your baby at birth. This is called congenital syphilis, and it’s very dangerous. Congenital syphilis can lead to stillbirth, birth defects, or infant death. You should be tested for syphilis if you’re pregnant to make sure this doesn’t happen.
Can you pass syphilis back and forth?
If you’re having syphilis treatment, it’s really important for your sexual partners to get treated also. Otherwise, you may pass the infection back and forth, or to other people.
Can you pass syphilis to someone?
Even though syphilis is common and has mild symptoms in the beginning, it can become a really big deal if it’s not treated. You can also easily pass it to other people. Syphilis is easily cured in the early stages. But if you don’t treat syphilis early on, it can get worse and do serious harm to your body in the future.
Can you get syphilis again?
Make sure you both take all of the medicine prescribed to you. Even if you finish your treatment and the syphilis is totally gone, it’s still possible to get a new syphilis infection again if you’re exposed in the future. Syphilis isn’t a one-time-only deal. So use condoms and/or dental dams and get tested regularly.
Nontreponemal Tests and Traditional Algorithm
Treponemal Tests and Reverse Sequence Algorithm
Cerebrospinal Fluid Evaluation
Diagnosis
Specialist to consult
Treatment
Clinical Trials
- The majority of patients who have reactive treponemal tests will have reactive tests for the remainder of their lives, regardless of adequate treatment or disease activity. However, 15%–25% of patients treated during the primary stage revert to being serologically nonreactive after 2–3 years (570). Treponemal antibody titers do not predict treatmen...
Coping and Support
- Further testing with CSF evaluation is warranted for persons with clinical signs of neurosyphilis (e.g., cranial nerve dysfunction, meningitis, stroke, acute or chronic altered mental status, or loss of vibration sense). All patients with ocular symptoms and reactive syphilis serology need a full ocular examination, including cranial nerve evaluation. If cranial nerve dysfunction is present, a …
Preparing For Your Appointment
- Tests
Syphilis can be diagnosed by testing samples of: 1. Blood.Blood tests can confirm the presence of antibodies that the body produces to fight infection. The antibodies to the syphilis-causing bacteria remain in your body for years, so the test can be used to determine a current or past inf…