Why is lipid management important in diabetes?
Reaching adequate blood glucose control is important in decreasing microvascular complications associated with diabetes; however, good lipid management is vital for reducing the incidence of cardiovascular events in patients with diabetes.1–4
Which medications are used in the treatment of lipid abnormalities?
Medical therapy is needed in most patients to reach the current lipid goals. Lipid-reducing drugs include statins, fibric acid derivatives, bile acid sequestrants, nicotinic acid, and cholesterol absorption inhibitors. The choice of drug is dependent on the individual patient lipid abnormality.
Do cholesterol lowering drugs increase the risk of diabetes?
As mentioned above, more data is needed to assess if the newly approved class of cholesterol lowering drugs, PSCK9 inhibitors, increase the rate of developing newly diagnosed diabetes. The FOURIER study did not demonstrate an increase rate of developing diabetes in the subjects taking evolocumab.
Is aggressive lipid control effective in women with Type 2 diabetes?
Over time, studies such as the CARE trial and the Heart Protection Study have shown benefit with aggressive lipid control in the diabetic population. Women with type 2 DM appear to lose the “protection” that is seen in age-controlled nondiabetic women.
How to reduce LDL in diabetics?
Diet and exercise modifications should be recommended to all patients. Studies have shown up to a 30% reduction in LDL in 6 months with lifestyle changes. The role of the nutritionist in the diabetes education team is critical and has a great influence on diet-directed goals for treatment.
How often should you monitor lipid levels?
The method of monitoring the effects of lipid-lowering therapy is not clear. Rather than take a rigid approach to measuring lipid profiles in patients with diabetes, current recommendations suggest that a lipid profile be obtained at the time of diagnosis of diabetes, the initial medical evaluation, and at a minimum every 5 years beyond the initial evaluation. A lipid profile is recommended prior to starting treatment with a statin. The major change in monitoring the effects of lipid lowering therapy is to individualize the testing frequency for LDL cholesterol to the patient rather than set intervals. With statins, lipid levels stabilize within weeks after dose adjustment. Routine monitoring of serum creatine kinase (CK) levels is not recommended in patients on statins. It may be helpful to have a baseline CK level to assess for any change if the patient develops symptoms later on.
How long does it take to reduce LDL?
Diet and exercise modifications should be recommended to all patients. Studies have shown up to a 30% reduction in LDL in 6 months with lifestyle changes. The role of the nutritionist in the diabetes education team is critical and has a great influence on diet-directed goals for treatment.
How many patients were in the Jupiter study?
The JUPITER study assigned 17,802 healthy patients with LDL-C level < 130 mg/dL and a C-reactive protein > 2.0 mg/L to treatment with rosuvastatin 20 mg daily or placebo. The trial was stopped early for benefit after a follow-up of 1.9 years. Treated patients had lower levels of LDL-C and lower levels of C-reactive protein. Patients treated with rosuvastatin had a slightly higher rate of newly diagnosed diabetes despite these beneficial effects.
What is the goal of treatment for diabetes?
The goal of treatment is to decrease this risk . Treatments include weight loss in obese patients, exercise, diet modification, and medication review (hormone-based treatments, etc). In patients with diabetes, strict glycemic control is needed, as well as hypertension and smoking cessation.
What causes elevated triglycerides?
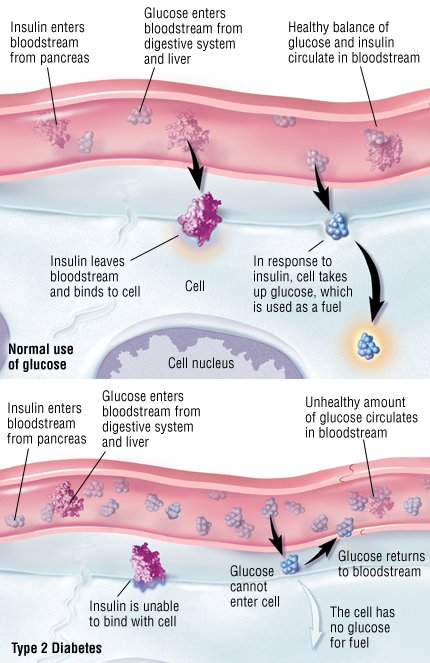
It can also be caused by drugs such as beta blockers, anabolic steroids or benzodiazepines. Most commonly, it is found in insulin resistant states such as type 2 diabetes, obesity and hypertension. Elevated triglycerides are often found in the insulin resistant state.
What are the primary factors that determine the intensity of treatment for diabetes?
Patients with diabetes are evaluated as to treatment and intensity of treatment by two primary factors: age and presence of risk factors for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) or the presence of ASCVD.
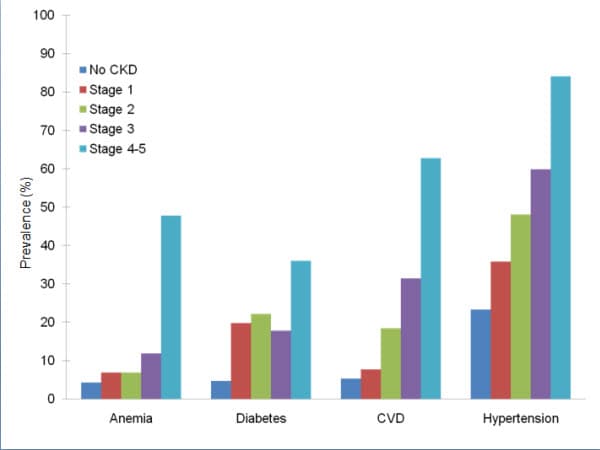
LIPOPROTEIN PATTERN IN DIABETES
The most typical lipoprotein pattern in diabetes, also known as diabetic dyslipidemia or atherogenic dyslipidemia, consists of moderate elevation in triglyceride levels, low HDL cholesterol values, and small dense LDL particles. This lipoprotein pattern is associated with insulin rsistance and is present even before the onset of diabetes.
LIPID TARGETS
Diabetes is considered a CHD equivalent. Therefore, lipid targets for individuals with diabetes are the same as those for individuals with established CHD. 7 The primary target is an LDL cholesterol < 100 mg/dl.
CLINICAL TRIAL EVIDENCE
Subgroup analyses of intervention trials using statins suggest that the relative cardiovascular benefit of statins is similar among diabetic and nondiabetic participants. There are fewer studies using fibrates or niacin.
TREATMENT
Diet, exercise, and weight loss in over-weight individuals are essential in the management of lipid disorders in diabetes. The NCEP and the ADA concur in reducing the intake of saturated and trans -saturated fatty acids to lower LDL cholesterol levels.
PHARMACOLOGICAL LIPID MANAGEMENT
Both the NCEP and the ADA give achievement of the LDL cholesterol target first priority. Both recommend treatment with a statin for all diabetic subjects with an LDL cholesterol > 130 mg/dl.
What is lipid lowering therapy?
Lipid-lowering therapies constitute an essential part in the treatment and prevention of cardiovascular diseases and are consistently shown to reduce adverse cardiovascular outcomes in wide-scale populations.
Why is lipid modification important?
Since the prevalence of metabolic syndrome and diabetes is rising, and lipid-modifying therapies are widely used to reduce the cardiovascular burden in these populations, it is of importance to examine the relationship between lipid-lowering drugs, glycemic control and incident diabetes.
Can lipid lowering drugs cause insulin resistance?
Recently, there is increased awareness of the possibility that lipid-lowering drugs may affect glucose control and insulin resistance. This phenomenon is reported in all classes of lipid-modifying agents, with differential effects of distinct drugs. Since the prevalence of metabolic syndrome and diabetes is rising, ...

Diagnosis of Cholesterol Issues in The Diabetic Patient
Strategy For Treatment
- As noted above, the goals for therapy have changed since the ATP III guidelines first appeared. There is a general consensus over the use of the ACC AHA recommendations for statin and combination therapy. Patients with diabetes are evaluated as to treatment and intensity of treatment by two primary factors: age and presence of risk factors for atherosclerotic cardiovas…
Monitoring Response to Statins and Safety Profile
- The method of monitoring the effects of lipid-lowering therapy is not clear. Rather than take a rigid approach to measuring lipid profiles in patients with diabetes, current recommendations suggest that a lipid profile be obtained at the time of diagnosis of diabetes, the initial medical evaluation, and at a minimum every 5 years beyond the initial evaluation. A lipid profile is recommended pri…
Statin Intolerance
- Cholesterol goals can be met by moving to an alternate statin such as fluvastatin or pravastatin, with careful dose titration when the patient is asymptomatic. There are a number of different options that can be tried to help get the appropriate patient back on a statin if desired. An alternate more potent statin, given daily or weekly, such as ros...
Other Issues
- This is an interesting and evolving area. Some patients achieve very low LDL-C levels on while on therapy. There is little evidence by which to determine the optimal low limit of LDL-C. In the JUPITER trial, patients on rosuvastatin with LDL less than 50 mg/dL had a slightly higher rate of adverse events than those who did not. Though there is not consistent recommendation, consid…