What are the treatment options for stage zero breast cancer?
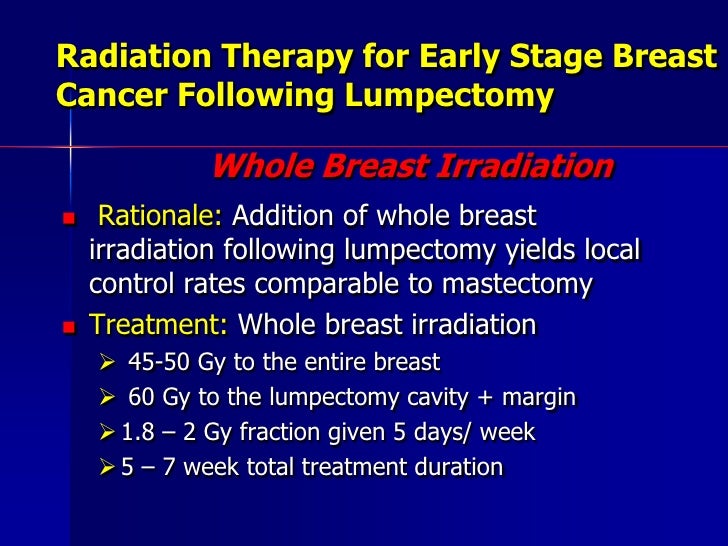
Jun 09, 2021 · Thus far, we have been focused on reducing that risk at all costs and treating DCIS like an early-stage breast cancer: The first step is surgery—usually lumpectomy—followed by radiation treatment for three to four weeks and finally hormone therapy for five years.
How should we treat Stage 0 breast cancer?
Typical DCIS treatments are: Surgery. For smaller DCIS tumors, you might get a lumpectomy, in which the abnormal cells and some breast tissue are removed. Some women decide to have a mastectomy, in...
What is the prognosis for stage 0 breast cancer?
Jun 11, 2021 · Radiation therapy for stage 0 breast cancer may follow a lumpectomy or mastectomy. Treatments are given 5 days a week for several weeks. If the DCIS is hormone receptor-positive (HR+), hormone...
Is stage 0 breast cancer actually cancer?
Aug 02, 2018 · Treatment for stage 0 breast cancer (see the full article for early breast cancer treatment) Stage 0 breast cancer is usually treated with surgery. Radiotherapy can be given in an adjuvant setting in selected cases. Chemotherapy is not generally applied to stage 0 cancer.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/breast-cancer-staging-stage-zero-429887-color-V1-2ab0aa1e60564c1c9f913ad037642990.png)
Does stage 0 breast cancer need treatment?
“DCIS is considered a pre-invasive cancer, but the current standard of care is to treat it like an early-stage invasive breast cancer,” says Apar Gupta, MD, assistant professor of radiation oncology at Columbia University Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons and lead author of the study.Jun 9, 2021
Does Stage 0 cancer require chemo?
Even though Stage 0 breast cancer is considered “non-invasive,” it does require treatment, typically surgery or radiation, or a combination of the two. Chemotherapy is usually not part of the treatment regimen for earlier stages of cancer.
How is Stage 0 cancer treated?
The following are treatment options for stage 0 (non-invasive, or in situ) breast cancer. Your healthcare team will suggest treatments based on your needs and work with you to develop a treatment plan. ... Surgery. Surgery is the main treatment for DCIS. ... Radiation therapy. ... Hormonal therapy. ... Clinical trials.
Is breast cancer curable in the 1 stage?
Stage 1 breast cancer is very treatable with surgery, radiation, chemotherapy, or targeted therapies. It is considered early-stage breast cancer and the prognosis is good.Feb 15, 2022
Is Stage 0 cancer curable?
In situ means "in place." Stage 0 cancers are still located in the place they started. They have not spread to nearby tissues. This stage of cancer is often curable. Surgery can usually remove the entire tumor.
What are the side effects of radiation therapy?
Specific side effects of radiation therapy that affect parts of the bodyHeadaches.Hair loss.Nausea.Vomiting.Extreme tiredness (fatigue)Hearing loss.Skin and scalp changes.Trouble with memory and speech.More items...•Dec 10, 2020
Is Stage 0 cancer serious?
Stage 0 breast cancer can be very slow growing and may never progress to invasive cancer. It can be successfully treated. According to the American Cancer Society, women who've had DCIS are approximately 10 times more likely to develop invasive breast cancer than women who've never had DCIS.
Can you live with stage 0 breast cancer?
Stage zero (stage 0) breast cancer is also known as carcinoma in situ. According to the American Cancer Society, people with a type of breast cancer that has not spread beyond the breast tissue have a 5 year survival rate of 99% .Aug 1, 2019
Does stage 0 breast cancer come back?
According to Breastcancer.org, most recurrences happen within 5 to 10 years after initial diagnosis. The chances of a recurrence are less than 30%.Aug 25, 2017
At what stage of cancer is chemotherapy used?
Systemic drug treatments, such as targeted therapy or chemotherapy, are common for stage 4 cancers. Often, a clinical trial may be an option, offering new treatments to help you fight stage 4 cancer.Feb 11, 2022
Can you live 20 years with breast cancer?
Since the hazard rate associated with inflammatory breast cancer shows a sharp peak within the first 2 years and a rapid reduction in risk in subsequent years, it is highly likely that the great majority of patients alive 20 years after diagnosis are cured.
How soon after diagnosis of breast cancer is surgery?
Overall, the optional time for surgery after diagnosis is less than 90 days. Lumpectomy, mastectomy and lymph node removal are three common surgical procedures to treat breast cancer.Oct 25, 2021
What is stage 0 breast cancer?
Stage 0 breast cancer means you have abnormal cells in the lining of the milk ducts of your breast, but they are contained to the ducts or lobules and haven't invaded the surrounding breast tissues. There are two types of stage 0 breast cancer (DCIS and LCIS), both of which are "in situ" cancers.
What are the different types of breast cancer?
The two types of stage 0 breast cancer are: 1 Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS): Abnormal cells inside a milk duct 2 Lobular carcinoma in situ (LCIS): Abnormal cells inside the milk-producing lobules
Why is stage 0 called stage 0?
Oncologists call it stage 0 because it hasn't broken out of place (has not spread beyond what's called the basement membrane) or invaded other tissues. The two types of stage 0 breast cancer are: Lobular carcinoma in situ (LCIS): Abnormal cells inside the milk-producing lobules.
What is the difference between carcinoma in situ and invasive cancer?
The cells in carcinoma in situ look identical to the cancer cells of invasive cancer. The only difference is the fact that they are "in place" and have not spread. When caught and treated at stage 0, these cases have an excellent prognosis. Verywell / Gary Ferster.
What is the difference between N0 and M0?
N0: Cancer has not spread to the nearby lymph nodes. M0: X-rays (or other imaging tests) have concluded that cancer has not spread to other parts of the body (metastasized) TNM Staging in Breast Cancer. Once the T, N, and M are determined, they are combined, and an overall stage of 0, I, II, III, IV is assigned.
Is it good to catch stage 0 breast cancer early?
The outlook is good for people diagnosed with stage 0 breast cancers. When detected early and treated, the five-year relative survival rate is 99%. The five-year survival rate drops to 93% for stage 2 cancer and 73% for stage 3 diagnoses. That shows you how important it is to catch breast cancer early.
Can a stage 0 breast cancer be treated?
But, they also might not. So far, doctors can't say which direction any particular case will go. While stage 0 breast cancer should be taken seriously, the lower the stage number, the easier the disease is to treat. ( Invasive breast cancers are assigned a stage number from 1 to 4.)
What happens after a mastectomy?
After a mastectomy, you might choose to have breast reconstruction surgery. Radiation therapy usually follows a lumpectomy. The radiation attacks any abnormal cells that might have been missed and lowers the risk of getting another breast cancer.
What is ductal carcinoma in situ?
Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) is when abnormal cells appear in the breast ducts. The words in situ mean “in the original place.”. It’s possible for the cells to turn into invasive cancer, meaning they spread into healthy tissue. That's why you should get treatment right away.
What is LCIS in breast?
That's why you should get treatment right away. Lobular carcinoma in situ (LCIS) is when abnormal cells appear in the lobes of the breast, but nowhere else. You may not feel a tumor, and there may not be any changes in your mammogram. It’s often found during a breast biopsy for something else.
Why do women have double mastectomy?
Some women at high risk for breast cancer choose to have a double mastectomy, the removal of both breasts, because they’re worried about getting an invasive cancer.They might have a strong family history of breast cancer, or they might have genetic mutations called BRCA1 or BRCA2.
How to treat DCIS?
Treatments. Typical DCIS treatments are: Surgery. For smaller DCIS tumors, you might get a lumpectomy, in which the abnormal cells and some breast tissue are removed. Some women decide to have a mastectomy, in which the breast is removed. After a mastectomy, you might choose to have breast reconstruction surgery.
Can LCIS be found during a breast biopsy?
It’s often found during a breast biopsy for something else . Women with LCIS need to see a doctor often for checkups and to discuss if any treatment is needed. LCIS increases the risk of developing a cancer in either breast that can spread.
What is stage 0 breast cancer?
Stage 0 breast cancer. Stage 0 breast cancer, or ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS), is when there are atypical cells in the lining of your milk ducts. But those cells have not spread beyond the wall of the duct to reach surrounding tissue, your bloodstream, or lymph nodes. DCIS is noninvasive and is sometimes called “precancer.”.
How long does radiation therapy last for stage 0 breast cancer?
Radiation therapy for stage 0 breast cancer may follow a lumpectomy or mastectomy. Treatments are given 5 days a week for several weeks. If the DCIS is hormone receptor-positive (HR+), hormone therapy can be used to lower the chances of developing invasive breast cancer later.
What is the difference between mastectomy and lumpectomy?
While mastectomy removes your entire breast, lumpectomy removes only the area of DCIS plus a small margin around it. Lumpectomy is also called breast-conserving surgery or wide local excision. This preserves most of your breast and you may not need reconstruction surgery.
What is LCIS in breast?
Lobular carcinoma in situ (LCIS) Stage 0 breast cancer used to include lobular carcinoma in situ (LCIS). Even though the name contains the word carcinoma, LCIS is no longer categorized as cancer. LCIS involves atypical cells in your lobules, but they don’t spread beyond your lobules. LCIS is sometimes called “lobular neoplasia.”.
Why do you need a mastectomy?
Some of the reasons to consider mastectomy are: you have DCIS in more than one part of your breast. the area is large relative to your breast size. you can’t have radiation therapy. you prefer mastectomy instead of a lumpectomy with radiation therapy.
How to diagnose cancer?
Biopsy is the only way to diagnose cancer. For this, the doctor will use a needle to remove a tissue sample. A pathologist will examine the tissue under a microscope and provide a report to your doctor. The pathology report will say whether there are atypical cells present and, if so, how aggressive they may be.
Can DCIS be treated?
It can be successfully treated. According to the American Cancer Society, women who’ve had DCIS are approximately 10 times more likely to develop invasive breast cancer than women who’ve never had DCIS. looked at more than 100,000 women who had been diagnosed with stage 0 breast cancer.
What is stage 0 breast cancer?
This is a form of Non invasive breast cancer. This is the earliest stage of breast cancer, also known as ‘pre-cancer’. When the cancer has not invaded in the breast tissue, or to lymph nodes, or to any other part of the body, it is identified as stage 0.
What are the most common forms of stage 0 breast cancer?
Stage 0 breast cancer commonly occurs in the following types (For more information, see the full article on types of breast cancer ):
Treatment for stage 0 breast cancer
Stage 0 breast cancer is usually treated with surgery. Radiotherapy can be given in an adjuvant setting in selected cases. Chemotherapy is not generally applied to stage 0 cancer.
How does breast cancer start?
To understand breast cancer the language used to describe it, it’s helpful to first understand breast anatomy. The breast consists of three main kinds of tissue:
Breast cancer staging and biologic factors
There are five stages of breast cancer: stage 0, stage 1 (I), stage 2 (II), stage 3 (III), and stage 4 (IV). Breast cancer staging is complicated, especially given there are multiple different approaches to staging.
What is stage 0 breast cancer?
Stage 0 breast cancer is also referred to as noninvasive breast cancer. It describes a cancer that has not invaded any tissue beyond the area where it started. This is the earliest stage of breast cancer, and it’s called carcinoma in situ.
Symptoms of stage 0 breast cancer
Stage 0 breast cancer, especially DCIS, usually doesn’t have any symptoms. Approximately 80% of these cancers are found by routine screening with a mammogram. If symptoms are present, they may include a breast lump or abnormal nipple discharge.
Diagnosis of stage 0 breast cancer
A stage 0 breast cancer diagnosis usually starts with an abnormality seen on a mammogram. This is followed by a biopsy, which collects cells from the area of suspicion. A pathologist then observes these cells under a microscope and classifies them as cancer based on their appearance.
Treatment of stage 0 breast cancer
The goal of treatment for stage 0 is to cure the cancer. And every person will have a treatment plan that is best for that individual and the specific characteristics of their cancer.
What steps can I take to help prevent recurrence after treatment?
The risk of cancer recurrence varies depending on multiple factors: the stage of breast cancer when diagnosed, characteristics of the tumor, individual risk factors, and treatment of the cancer. One study estimated the risk of recurrence with DCIS as less than 20%.

Overview
Diagnosis
- A mammogram can often detect the abnormal cells of stage 0 breast cancer. If an area of your breast appears concerning, the next step is to have a needle biopsy, which is a procedure that removes cells in the area of concern. The cells are analyzed under a microscope by a pathologist.3
Staging
- The staging system most often used for breast cancer is the American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) TNM system. The TNM Staging System is based on the extent of the tumor (T), the extent of spread to the lymph nodes (N), and the presence of metastasis (M). Numbers or letters after T, N, and M provide details about these classifications. Using this classification syst…
Treatment
- Not all stage 0 breast cancers require treatment. Sometimes active monitoring or a watch-and-wait approach is recommended to see if the carcinoma will remain stable or if it will progress. And sometimes cancer treatments such as surgery, radiation, or hormone therapy are recommended. Numerous factors will affect your treatment plan. Some of these i...
Survival Rates
- The outlook is good for people diagnosed with stage 0 breast cancers. When localized stage 0 breast cancer is detected early and treated, the five-year relative survival rate is 90%, according to the American Cancer Society.5
Follow-Up Care
- After treatment for stage 0 breast cancer, there's a small risk of recurrence or future development of invasive breast cancer.6After complete surgical removal of stage 0 cancer, there is a risk of new breast cancer that's not related to first breast cancer—this risk is similar to the risk for women who have never had breast cancer. Your healthcare provider may recommend more freq…
Coping
- Understanding of what stage 0 breast cancer is (and isn't) is one of the best steps you can take to cope with your diagnosis. It puts your condition in perspective and can help temper worries. Although it's common to feel helpless at first, know that the more you educate yourself about treatment options and the emotional aspect of the diagnosis, the better prepared you'll be to dea…
Summary
A Word from Verywell
- A cancer diagnosis can be overwhelming. But with a stage 0 diagnosis, you're facing the best-case scenario by catching it early. Work closely with your healthcare provider to create a treatment plan that's best for you, and move forward with the knowledge that what you have is treatable and highly curable.