Explore
Whether acetylcholinesterase inhibitors, which delay the progression of Alzheimer's dementia, are relevant in small vessel disease remains unclear. Potential prophylactic and treatment strategies might be those that target brain microvascular endothelium and the blood brain barrier, microvascular function and neuroinflammation.
What is the prognosis for small vessel disease?
Sep 25, 2018 · Intravenous tissue plasminogen activator (t-PA) is the gold standard of treatment of acute ischemic stroke, but the role of t-PA in patients with lacunar infarction has been debated due to the different pathomechanisms compared with common stroke related to large-vessel changes and increasing risks of hemorrhage in patients with WMH or CMB.
How is small vessel ischemia treated?
Treatment of Small Vessel Disease The treatment for small vessel disease involves medications to control the narrowing of your small blood vessels that could lead to a heart attack and to relieve pain. Treatment options include: Lifestyle changes Avoid smoking Eat a heart-healthy diet Exercise under the directions of your doctor.
What is the overall treatment for ischemia?
Common causes of CSVD include arteriosclerosis, cerebral amyloid angiopathy (CAA), genetic small vessel angiopathy, inflammation and immune-mediated small vessel diseases, and venous collagenosis. There is no causal treatment and management is mainly based on combating known risk factors for cardiovascular disease (CVD). Keywords:
How do we best treat patients with ischemic heart disease?
Dec 04, 2017 · Small vessel disease treatment Primary treatment options for small vessel disease involve medications that relieve pain, treat risk factors, and control associated symptoms. These medications will...

What causes small vessel ischemic disease in the brain?
Microvascular ischemic brain disease describes conditions that affect the small blood vessels in the brain. These conditions include stroke, cerebral hemorrhage, and dementia. Age, high blood pressure, and diabetes are among the primary risk factors for microvascular ischemic brain disease.Feb 21, 2019
Can small vessel ischemic disease be reversed?
Studies with rats found the treatment can reverse changes in blood vessels in the brain associated with the condition, called cerebral small vessel disease. Treatment also prevents damage to brain cells caused by these blood vessel changes, raising hope that it could offer a therapy for dementia.Jul 4, 2018
What does small vessel ischemic disease mean on my MRI?
Background. Cerebral small vessel disease (SVD) is a frequent finding on CT and MRI scans of elderly people and is related to vascular risk factors and cognitive and motor impairment, ultimately leading to dementia or parkinsonism in some.Feb 28, 2011
What are the symptoms of small vessel disease of the brain?
The main clinical manifestations of CSVD include stroke, cognitive decline, dementia, psychiatric disorders, abnormal gait, and urinary incontinence. Currently, there are no specific preventive or therapeutic measures to improve this condition.
How is brain ischemia treated?
In order to treat cerebral ischemia, doctors may prescribe medications for ischemic stroke. Alteplase is an medication used to acute ischemic stroke. If this medication is administered within four and a half hours, the treatment with tpa improves the probability for a promising outcome over a placebo treatment.
What are the first symptoms most likely to be seen in vascular dementia?
Vascular dementia signs and symptoms include:Confusion.Trouble paying attention and concentrating.Reduced ability to organize thoughts or actions.Decline in ability to analyze a situation, develop an effective plan and communicate that plan to others.Slowed thinking.Difficulty with organization.More items...•Jul 29, 2021
Is small vessel disease of the brain serious?
Cerebral small vessel diseases (cSVDs) are a common cause of stroke and an important contributor to age-related cognitive decline and risk for dementia.Nov 22, 2019
Does small vessel disease lead to dementia?
Background and Purpose— Cerebral small vessel disease (SVD) is the most common cause of vascular cognitive impairment, with a significant proportion of cases going on to develop dementia.Sep 12, 2019
Is brain ischemia serious?
The symptoms of brain ischemia can range from mild to severe. They can last from a few seconds to a few minutes. If the ischemia is brief and resolves before permanent damage (infarction) can occur, then the event is often referred to as a transient ischemic attack (TIA).Feb 21, 2021
At what age does small vessel disease start?
Family history of the disease, especially in women. High blood pressure. Inactive lifestyle. Increasing age: older than 45 in men and older than 55 in women.Nov 9, 2021
Do statins help small vessel disease?
Statins have been recommended by several guidelines as the primary prevention medication for cardiovascular diseases. However, the benefits of statin therapy for cerebral small vessel disease (CSVD), particularly in adults ≥75 years of age, have not been fully evaluated.Aug 17, 2020
How does small vessel disease affect your eyes?
Other eye problems experienced by people with COL4A1-related brain small-vessel disease include clouding of the lens of the eye (cataract ) and the presence of arteries that twist and turn abnormally within the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye (arterial retinal tortuosity).
What is small vessel ischemic disease?
Small vessel ischemic disease entails a situation where injuries to arterioles and capillaries are predominant, resulting in reduced and interrupted brain perfusion. The brain is primarily affected by this disease, but the disease has been associated with other vital organs in a few cases.
What are the symptoms of a stroke?
When small vessel ischemic disease results in stroke (a stroke is an emergency that requires prompt treatment to stop disease progression and increase chances of reversing the condition), symptoms presented include: Sudden confusion.
What happens when blood flow to the brain is cut off?
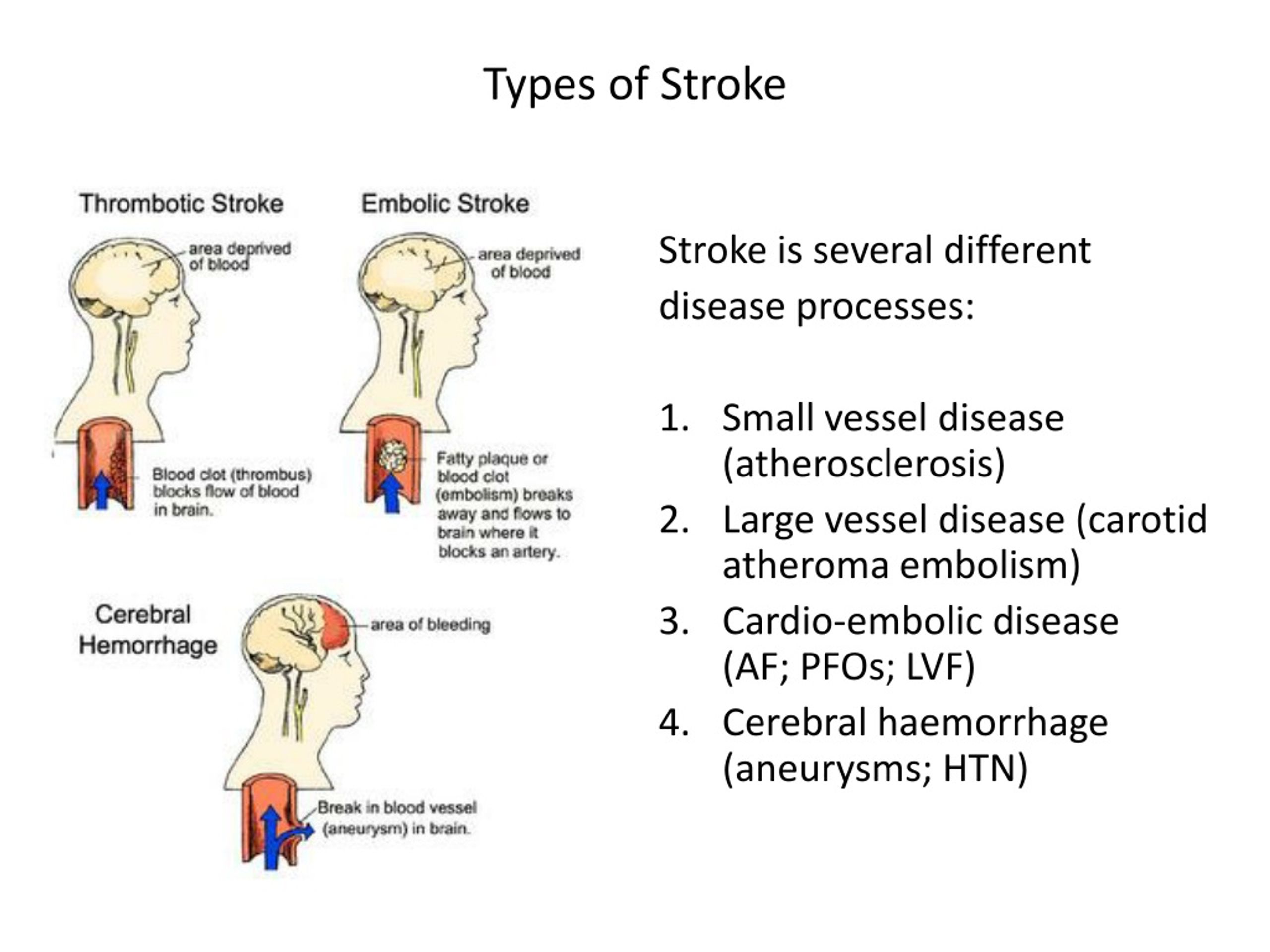
When blood flow to the brain is cut-off or reduced, certain parts of the brain may not receive enough oxygen, leading to brain tissue damage and subsequently an ischemic stroke. Secondly, a factor that can result in small vessel ischemic disease is that blood vessels can become hard and brittle. A hardened artery can develop bulges called ...
What is a small vessel?
Small vessel disease (SVD), also called coronary microvascular disease or small artery disease, is a condition in which the walls of the small arteries in the heart (the tiny branches off the larger coronary arteries), are damaged and don’t dilate properly. Your small vessels need to expand to provide oxygen-rich blood ...
What are non-modifiable risk factors?
Non-modifiable risk factors: These factors are irreversible and cannot be changed. The more of these risk factors you have, the greater your chance of developing small vessel disease: Family history/Genetics. Female gender. Modifiable risk factors: These factors can be modified, treated or controlled through medications or lifestyle changes.
How to tell if you have a symtom?
Some of the symptoms include the following: Chest pain, fullness, discomfort or pressure. Discomfort or pain in one or both arms, the back, neck, jaw, or stomach. Lightheadedness/Fainting. Fatigue. Rapid heart rate (tachycardia) of over 100 beats per minute. Heart palpitations.
What are the causes of high blood pressure?
High blood pressure. High cholesterol. Little to no physical activity. Obesity or having a body mass index “BMI” of 30 or greater. Extreme emotional stress. Diabetes (when your blood glucose, also called blood sugar, is too high).
Does aspirin help with heart attack?
Aspirin will treat pain, inflammation, and reduce risk of a heart attack. Vasodilators will help the muscle in the walls of the blood vessels to relax, allowing the vessel to dilate. ACE inhibitors will help blood vessels relax and open up, leading to a lower blood pressure.
What is small vessel disease?
Small vessel disease is a condition in which the walls of the small arteries in your heart — the tiny branches off the larger coronary arteries — are damaged and don’t dilate properly. Your small vessels need to expand to provide oxygen-rich blood to your heart.
How long does chest pain last?
Typical chest pain from this condition can last anywhere from 11–30 minutes or more.
What causes a heart attack and heart failure?
high cholesterol. obesity. diabetes mellitus. If left untreated, small vessel disease will force your heart to work harder to pump blood to your body. This could trigger coronary artery constriction/spasms, a heart attack, heart failure, or death.
What is microvascular ischemic disease?
Microvascular ischemic disease: What to know. Microvascular ischemic disease describes conditions that affect the small blood vessels in the brain. These conditions include stroke, cerebral hemorrhage, and dementia. Age and high blood pressure are among the main risk factors for microvascular ischemic disease.
What happens if you don't get enough oxygen?
Without enough blood flow, certain areas of brain tissue may not receive enough oxygen, which can result in tissue damage or an ischemic stroke. The blood vessels can also become hard and brittle.
What is the white matter in the brain?
Conditions that affect these blood vessels can damage white matter in the brain. White matter contains nerve fibers that send signals between different parts of the brain. Microvascular ischemic disease is a “silent” disease, which means that most people who have it do not experience noticeable symptoms. However, doctors can look ...
Treatment
- The goals of treatment for small vessel disease are to control the narrowing of the small blood vessels that can lead to a heart attack and to relieve pain. Medications for small vessel disease may include: 1. Nitroglycerin (Nitrostat, Nitro-Dur).Nitroglycerin tablets, sprays and patches can …
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Alternative Medicine
Preparing For Your Appointment
Causes
- The exact etiology of small vessel ischemic disease has not been comprehended yet; however, many factors have been closely associated with changes and damages to the brain’s blood vessels. The first factor is the pilingup of plaque, scar tissues, or fatty tissues inside these small arterioles; this can wholly or partially restrict blood flow to and in the brain. When blood flow to t…
Risk Factors
- One of the critical risk factors of small vessel ischemic disease (SVID) is age. According to a published review in 2009, just 5% of people at least 50 years are affected by SVID, but nearly 98% of individuals over the age of 90. Some other risk factors of SVID include: 1. High blood cholesterol 2. Hypertension 3. Personal history of stroke and other cardiovascular diseases 4. S…
Symptoms
- Small vessel ischemic disease can present itself in mild, moderate, or severe forms. Most older adults, particularly those with a mild form of the disease, are asymptomatic; that is, they show no symptoms of the disease even when there are visible damage areas (through MRI scan) in the brain; hence, the name is a silent disease. According to recent research on small vessel ischemi…
Diagnosis
- The first line of laboratory tests used to diagnose small vessel ischemic disease is magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). This imaging test uses strong magnets and high-frequency radio waves to create detailed images of the body’s internal structures, but in this case, the brain. Small vessel ischemic disease can be observed on an MRI in various ways: 1. As small visible strokes (these …
Treatment
- Small vessel ischemic disease affects tiny vessels that transport blood, less than 0.5 mm in diameter. This size makes the condition challenging to identify and treat surgically. Generally, treatments recommended by doctors are treatments to manage risk factors and symptoms. Doctors’ choice of management may depend on the patient’s symptoms and risk factors best su…
Prevention
- To reduce the risk of developing small vessel ischemic in the future and prevent the outcome of strokes, follow these tips: 1. If a person is overweight, they should work with a doctor and a dietitian to bring the weight back to a healthy range. 2. Healthy diet plans should be followed, such as DASH or Mediterranean diet, which are high in nutrition and low in saturated fat, sugar, and s…
Summary
- Small vessel ischemic disease is not a condition to be overlooked as it can be severe, resulting in a stroke, dementia, and even death if not treated. The disease is the cause of 45% of dementia cases and 20% of stroke cases. A reasonable way to prevent these complications is first to avoid small vessel ischemic damage. Follow healthy diets, regular exercises, and follow medication pr…