Is there a cure for secondary amenorrhea?
May 31, 2016 · Common medical treatments for secondary amenorrhea include: 3. Birth control pills or other types of hormonal medication. Certain oral contraceptives may help restart the menstrual cycle. Medications to help relieve the symptoms of PCOS. Clomiphene citrate (CC) therapy is often prescribed to help trigger ovulation. 4; Estrogen replacement therapy (ERT).
How can I prevent secondary amenorrhea?
Symptoms of individuals with secondary amenorrhea vary depending on the underlying cause of the condition. Some of those underlying causes are frequently associated with infertility , and if not resolved, assisted reproductive therapy may be suggested.
What are the common causes of secondary amenorrhea?
Sep 18, 2012 · The treatment for secondary amenorrhea varies depending on the underlying cause of your condition. Hormonal imbalances can …
What is the most common amenorrhea treatment?
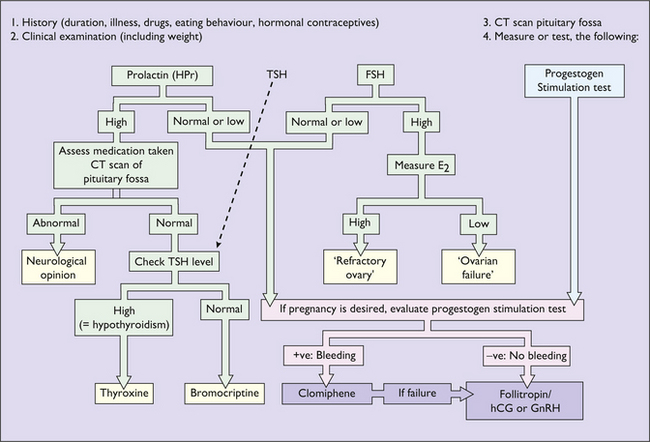
Jul 19, 2021 · Elevated serum prolactin suggests prolactinoma. If prolactin is normal, the next step is to perform a progestin challenge. First, the patient is given oral progesterone (typically medroxyprogesterone, 10mg PO qDay x10 days). After stopping the progesterone, the patient would be expected to have a withdrawal bleed.

How can I get my periods back after secondary amenorrhea?
What medications treat amenorrhea?
| Drug name | Rating | Rx/OTC |
|---|---|---|
| View information about Provera Provera | 7.4 | Rx |
| Generic name: medroxyprogesterone systemic Drug class: hormones/antineoplastics, contraceptives, progestins For consumers: dosage, interactions, side effects For professionals: Prescribing Information | ||
How long does secondary amenorrhea last?
Can you fix secondary amenorrhea naturally?
- Losing weight through dieting and exercise (if excess weight is the cause).
- Gaining weight through an individualized diet plan (if extreme weight loss is the cause).
- Stress management techniques.
- Changing exercise levels.
What is the fastest way to cure amenorrhea?
What is the first line treatment for amenorrhea?
Is secondary amenorrhea serious?
What happens if amenorrhea is not treated?
Can I get pregnant with secondary amenorrhea?
What vitamins should I take to get my period back?
What vitamins should I take for amenorrhea?
What should I eat to recover from amenorrhea?
What is secondary amenorrhea?
Secondary amenorrhea is the absence of regular menstrual periods for at least 3 months or the absence of irregular menstrual periods for 6 months o...
What is the difference between primary and secondary amenorrhea?
The main difference between primary and secondary amenorrhea is that with primary amenorrhea, the individual has not yet had their first menstrual...
What causes secondary amenorrhea?
Secondary amenorrhea can be caused by various conditions that affect the menstrual cycle, including pregnancy, anovulation, estrogen deficiencies,...
How common is secondary amenorrhea?
Secondary amenorrhea occurs in approximately 2% to 5% of women.
What are the signs and symptoms of secondary amenorrhea?
Signs and symptoms of secondary amenorrhea usually depend on the underlying cause of the condition. If pregnancy is causing secondary amenorrhea, e...
Can secondary amenorrhea cause infertility?
Secondary amenorrhea itself cannot cause infertility; however, some of its underlying causes are frequently associated with infertility. All causes...
How is secondary amenorrhea diagnosed?
Diagnosis begins with an assessment of the individual’s medical history and a physical examination. History should cover a full menstrual history,...
How is secondary amenorrhea treated?
To treat secondary amenorrhea, it is important to diagnose and treat its underlying cause. Most cases of PCOS are treated with progesterone-contain...
What are the most important facts to know about secondary amenorrhea?
Secondary amenorrhea refers to the absence of regular menstrual periods for 3 months or more or irregular periods for 6 months or more. Secondary a...
What causes secondary amenorrhea?
Secondary amenorrhea can be caused by various conditions, including pregnancy, anovulation, estrogen deficiencies, reproductive tract obstructions, as well as dramatic lifestyle changes. Symptoms of individuals with secondary amenorrhea vary depending on the underlying cause of the condition. Some of those underlying causes are frequently ...
What is primary amenorrhea?
Primary amenorrhea is typically defined as the complete absence of menstruation by the age of 15. In contrast, with secondary amenorrhea, the individual has menstruated in the past, but their menstrual periods have stopped occurring.
How long does amenorrhea last?
Secondary amenorrhea is the absence of regular menstrual periods for at least 3 months or the absence of irregular menstrual periods for 6 months or more.
What is the difference between primary and secondary amenorrhea?
The main difference between primary and secondary amenorrhea is that with primary amenorrhea, the individual has not yet had their first menstrual period and is older than the typical age at which menstruation begins. Primary amenorrhea is typically defined as the complete absence of menstruation by the age of 15.
What causes a woman to not ovulate?
Anovulation refers to the lack of ovulation, or the inability to release an egg during the menstrual cycle. This results in a hormonal imbalance of estrogens and progesterones, preventing the inner layer of the uterus (i.e., endometrium) from thickening and shedding as it otherwise would during menstruation. There are various causes of anovulation, including polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), in which the ovaries are enlarged and have small cysts; hypothyroidism, characterized by low levels of thyroid hormones; and hyperprolactinemia, characterized by high levels of prolactin that can be caused by a pituitary tumor. In addition, certain medications, such as antidepressants, may lead to anovulation. Notably, hormonal birth control pills prevent ovulation by decreasing the release of follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH). These hormonal changes suppress the thickening of the endometrium and can lead to secondary amenorrhea .
Can endometrium be thin?
Without adequate estrogen levels, the endometrium will be atrophic -- very thin -- and may not be able to shed. Estrogen deficiency can result from perimenopause, the lifestage prior to menopause, during which levels of sex hormones are lower than usual.
Can extreme athletic training cause amenorrhea?
Any dramatic lifestyle changes can affect hormone levels and may subsequently cause secondary amenorrhea. Too much stress or extreme athletic training, as well as severe eating disorders, may lead to delayed menstruations.
What is secondary amenorrhea?
Secondary amenorrhea occurs when you’ve had at least one menstrual period and you stop menstruating for three months or longer. Secondary amenorrhea is different from primary amenorrhea. It usually occurs if you haven’t had your first menstrual period by age 16.
What causes amenorrhea in women?
A hormonal imbalance is the most common cause of secondary amenorrhea. A hormonal imbalance can occur as a result of: 1 tumors on the pituitary gland 2 an overactive thyroid gland 3 low estrogen levels 4 high testosterone levels
What causes a person to have a swollen ear?
A variety of factors can contribute to this condition, including: 1 birth control use 2 certain medications that treat cancer, psychosis, or schizophrenia 3 hormone shots 4 medical conditions such as hypothyroidism 5 being overweight or underweight
What hormones are released during the menstrual cycle?
During a normal menstrual cycle, estrogen levels rise. Estrogen is a hormone responsible for sexual and reproductive development in women. High estrogen levels cause the lining of the uterus to grow and thicken. As the lining of the womb thickens, your body releases an egg into one of the ovaries.
Why does estrogen drop?
High estrogen levels cause the lining of the uterus to grow and thicken. As the lining of the womb thickens, your body releases an egg into one of the ovaries. The egg will break apart if a man’s sperm doesn’t fertilize it. This causes estrogen levels to drop.
Why does estrogen drop during menstruation?
As the lining of the womb thickens, your body releases an egg into one of the ovaries. The egg will break apart if a man’s sperm doesn’t fertilize it. This causes estrogen levels to drop. During your menstrual period you shed the thickened uterine lining and extra blood through the vagina.
Can birth control cause amenorrhea?
Hormonal birth control can also contribute to secondary amenorrhea. Depo-Provera, a hormonal birth control shot, and hormonal birth control pills, may cause you to miss menstrual periods. Certain medical treatments and medications, such as chemotherapy and antipsychotic drugs, can also trigger amenorrhea.
What is the treatment for amenorrhea?
Surgery (in rare cases). In addition, your healthcare provider may recommend some treatments to help with the side effects of amenorrhea: Estrogen therapy to relieve hot flashes and vaginal dryness.
What causes secondary amenorrhea?
Common causes of secondary amenorrhea include: Pregnancy (which is the most common cause of secondary amenorrhea). Breastfeeding. Menopause. Some birth control methods, such as Depo Provera, intrauterine devices (IUDs) and certain birth control pills. Chemotherapy and radiation therapy for cancer.
What is it called when you miss your period?
Amenorrhea. Amenorrhea is missing one or more periods. If you are older than 15 and haven’t gotten your first period (primary amenorrhea) or you’ve missed a period for a few months (secondary amenorrhea), talk to your healthcare provider. Amenorrhea is often the sign of a treatable condition. With treatment, your regular menstrual cycle will ...
Can amenorrhea be permanent?
It can be temporary or permanent. Amenorrhea can result from a change in function or a problem with some part of the female reproductive system. There are times when you’re not supposed to get your period, such as before puberty, during pregnancy and after menopause.
How long does amenorrhea last?
If amenorrhea lasts for more than three months, it should be investigated.
Which gland controls the ovaries?
Hypothalamus, which controls the pituitary gland. Pituitary gland , called “the master gland,” which produces the hormones that instruct the ovaries to ovulate. Ovaries, which produce the egg for ovulation and the hormones estrogen and progesterone. Uterus, which responds to the hormones and prepares the lining.
What causes amenorrhea in women?
Common causes of primary amenorrhea include: Chromosomal or genetic problem with the ovaries (the female sex organs that hold the eggs). Hormonal issues stemming from problems with the hypothalamus or the pituitary gland. Structural problem with the reproductive organs, such as missing parts of the reproductive system.
How to get rid of amenorrhea?
Lifestyle and home remedies. Some lifestyle factors — such as too much exercise or too little food — can cause amenorrhea, so strive for balance in work, recreation and rest. Assess areas of stress and conflict in your life. If you can't decrease stress on your own, ask for help from family, friends or your doctor.
What to do if you have never had a period?
If you have never had a period, your doctor may suggest an ultrasound test to check for any abnormalities in your reproductive organs. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). MRI uses radio waves with a strong magnetic field to produce exceptionally detailed images of soft tissues within the body. Your doctor may order an MRI to check for ...
What does it mean when your prolactin levels are low?
Prolactin test. Low levels of the hormone prolactin may be a sign of a pituitary gland tumor. Male hormone test. If you're experiencing increased facial hair and a lowered voice, your doctor may want to check the level of male hormones in your blood.
What is the purpose of a hysteroscopy?
If other testing reveals no specific cause, your doctor may recommend a hysteroscopy — a test in which a thin, lighted camera is passed through your vagina and cervix to look at the inside of your uterus.
How to reduce stress during menstruation?
Be aware of changes in your menstrual cycle and check with your doctor if you have concerns. Keep a record of when your periods occur .
How to keep track of your period?
Be aware of changes in your menstrual cycle and check with your doctor if you have concerns. Keep a record of when your periods occur. Note the date your period starts, how long it lasts and any troublesome symptoms you experience.
What is the purpose of MRI?
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). MRI uses radio waves with a strong magnetic field to produce exceptionally detailed images of soft tissues within the body. Your doctor may order an MRI to check for a pituitary tumor.
What is secondary amenorrhea?
Secondary amenorrhea is a symptom that can be caused by many pathological states. The diagnostic evaluation should lead to the correct diagnosis if the problem is approached in a logical stepwise manner.
Can amenorrhea be demonstrated on a physical exam?
Some patients will not demonstrate any obvious etiology for their amenorrhea on history and physical exam. These patients can be worked up in a logical manner using a stepwise approach.
How long does amenorrhea last?
Secondary amenorrhea is the absence of menstrual periods for 6 months in a woman who had previously been regular, or for 12 months in a woman who had irregular periods.
How long after estrogen-progestin is done should you draw FSH?
This should not be drawn for about 2 weeks after the estrogen-progestin regimen is completed so that the hormone levels are not affected by the medications.
Can prolactin be measured annually?
Patients with normal prolactin levels and normal imaging studies have hypothalamic amenorrhea of uncertain cause. If amenorrhea and lack of withdrawal bleeding persists, prolactin levels should be measured annually since a small microadenoma could be “hiding”.
Secondary amenorrhea
Amenorrhea is defined by the absence of a menstrual period for more than 3 months. Secondary amenorrhea is defined when you’ve had regular periods but, your period stops for six months or longer.
What is the normal menstrual cycle?
Every month women’s body is prepared for pregnancy by a complex system of hormones.
Symptoms And Signs
The first symptom and sign is your missed menstrual cycle. Other symptoms you may experience according to an underlying condition such as:
Diagnosis and Tests
Once you miss your period more than three months or longer, your healthcare provider will ask for:
Treatments
Treatment depends on your underlying cause, if your period stopped because of pregnancy or menopause, there is no need to treat it.
Outlook
Your period will return once you treat the underlying cause. Amenorrhea is not life-threatening but it is the condition which you may live with lifelong.
What is the diagnosis of amenorrhea?
If a patient with amenorrhea has breast development and minimal or no pubic hair, the usual diagnosis is androgen insensitivity syndrome (i.e., patient is phenotypically female but genetically male with undescended testes). A karyotype analysis is needed to determine proper treatment. If testes are present, they should be removed because of the high risk of malignant transformation after puberty. 1
What causes primary amenorrhea?
Constitutional delay of growth and puberty commonly causes primary amenorrhea in patients with no sexual development. If the patient has normal pubertal development and a uterus, the most common etiology is congenital outflow tract obstruction with a transverse vaginal septum or imperforate hymen.
What causes normogonadotropic amenorrhea?
Two common causes of normogonadotropic amenorrhea are outflow tract obstruction and hyperandrogenic chronic anovulation. The most common cause of outflow obstruction in secondary amenorrhea is Asherman’s syndrome (intrauterine synechiae and scarring, usually from curettage or infection). 3 Hysterosalpingography, hysteroscopy, or sonohysterography can help diagnose Asherman’s syndrome. Other causes of outflow tract obstruction include cervical stenosis and obstructive fibroids or polyps.
Can ovarian failure cause menopause?
Ovarian failure can cause menopause or can occur prematurely. On average, menopause occurs at 50 years of age and is caused by ovarian follicle depletion. Premature ovarian failure is characterized by amenorrhea, hypoestrogenism, and increased gonadotropin levels occurring before 40 years of age and is not always irreversible 27 (0.1 percent of women are affected by 30 years of age and one percent by 40 years of age). 28 Approximately 50 percent of women with premature ovarian failure have intermittent ovarian functioning 29 with a 5 to 10 percent chance of achieving natural conception.