Hypotension occurring during chronic hemodialysis is a major clinical problem with consequent ischemia of the heart, brain and gut [1]. Reduced cardiac preload due to hypovolemia may be further diminished in the presence of diastolic dysfunction [2]. An increase in sympathetic tone may add functional problems [3].
Full Answer
How can hypotension be corrected in patients on dialysis?
Therapeutic interventions to correct hypotension, if necessary, should be oriented to the pathophysiology rather than to symptoms alone. In chronic hemodialysis patients, risk factors of hypotension include shifts in extracellular volume, osmolarity, and electrolytes, dialysis-induced temperature changes, and altered vasoregulation [ 3 ].
What causes hypotension during hemodialysis?
Hypotension during hemodialysis results from an impairment of arteriolar tone and left ventricular function We conclude that dialysis-related hypotension in our patient group did not result from an inability to maintain blood volume or from decreased cardiac filling.
How is low blood pressure treated at a dialysis clinic?
Clinic Treatment for Low Blood Pressure. Clinics prevent or treat low blood pressure during a treatment in a number of ways: Many clinics use sodium modeling. They program the machine to use more sodium (salt) in the dialysate at the start of a treatment when you have more fluid, and less at the end when little is left.
How common is chronic hypotension in patients on dialysis?
Chronic hypotension, defined by a systolic blood pressure < 100 mmHg in the interdialytic period, affects 5-10% of hemodialysis patients, and is more prevalent among patients on long-term hemodialysis. This complication requires a substantial amount of medical and nursing care before and during dialysis to control its symptoms.

New study to predict low blood pressure during dialysis
10 Dialysis Side Effects and How To Prevent Them - DaVita
What is hypotension during hemodialysis?
Hypotension during hemodialysis results from an impairment of arteriolar tone and left ventricular function
Does dialysis cause hypotension?
We conclude that dialysis-related hypotension in our patient group did not result from an inability to maintain blood volume or from decreased cardiac filling. Hypotension appeared to result from the inability to adequately increase arteriolar tone and a reduction in left ventricular function. Both …
Why does blood pressure drop after a procedure?
The cause may be the same: a decrease in the volume of fluid in the bloodstream. This reduced volume (called hypovolemia) is due to the fluid removed ruing the treatment.
How do you know if your blood pressure is low?
Symptoms of low blood pressure can vary. Some of the more common signs are dizziness, nausea, headaches, muscle cramps, and, in more severe cases, non-responsiveness, chest pain, and loss of consciousness. You may have a drop in blood pressure at the very start of a treatment, or you may suffer a sudden drop later in the procedure.
Why is it important to monitor fluid intake?
Monitor Fluid Intake: It is very important to keep your fluid intake between treatments at levels prescribed by your doctor. Adding too much fluid between treatments means that more fluid must be removed during each treatment to reach your dry weight. Removing more fluid increases the rate at which the fluid is pulled out of your bloodstream, (the ultrafiltration rate or UFR), which can increase your risk for hypovolemia and hypotension during treatment.
How many blood pressure readings are needed for a cuff?
You think to yourself, “here we go again,” as you prepare for another treatment that will include more than 10 or 12 blood pressure readings over the next few hours.
Is low blood pressure a problem for dialysis patients?
Low blood pressure, hypotension, is rather common for dialysis patients. Although some patients rarely have the problem, others need constant attention to this life-threatening condition. I would like to share some information about hypotension with my fellow patients for two reasons. First, it is vital to understand the condition, its causes, ...
Does electrolyte raise blood pressure?
The added fluid and electrolyte will raise your blood pressure and reduce the symptoms of hypotension. In most cases, these measures are enough to correct the problem; in some cases a trip to the hospital may be needed.
Can high blood pressure cause renal failure?
In many patients, it is high blood pressure that prompted renal failure in the first place. For you, high blood pressure is still a concern, but it is the risk of low blood pressure during treatment that drives the frequent pressure measures. Low blood pressure, hypotension, is rather common for dialysis patients.
What is the job of dialysis?
One of the main jobs of dialysis is to remove excess water from your body. Seems pretty simple, right? Like wringing out a wet towel? Of course, your body is more complex than a towel—and taking over a task that healthy kidneys did isn’t really so easy.
Why does my dialysis machine keep pushing?
And this is why you may feel awful. If your blood becomes too “dry,” your blood pressure drops. This happens if you go below your dry weight, or even if you are above your dry weight, but the extra fluid is not in your bloodstream.
How long does in center hemo last?
It’s not necessarily you. Healthy kidneys work 24/7. But most U.S. patients get in-center hemo three days a week for 3 to 4 hours perm treatment. It’s because the treatment is intermittent and short that the fluid limits are so strict. In fact, one study found that in-center hemo patients had significantly more sudden cardiac deaths on Mondays and Tuesdays—after the 2-day gap. 8 Most forms of dialysis have some fluid limits, and in-center hemo has the strictest ones. If you choose in-center hemo, you must choose to follow your fluid limits to feel your best.
Why do they use sodium modeling?
They program the machine to use more sodium (salt) in the dialysate at the start of a treatment when you have more fluid, and less at the end when little is left. The sodium helps pull fluid from the swollen tissues into the blood, so it can be dialyzed off.
How does salt affect kidney function?
Kidneys control how much water and salt you retain or lose as urine. Salt pulls water from one compartment to another until they’re equal. In fact, salty foods make you thirsty so you’ll drink more fluid and get back into balance. Water doesn’t just slosh around between compartments.
What happens if you drink too much water on dialysis?
In the short term, if too much water is removed from your blood in a 3-4 hour treatment, your body will become dehydrated (dried out). Besides low blood pressure, you may have painful muscle cramps, nausea and vomiting, feel dizzy, or pass out. These symptoms can be so severe that you dread coming to dialysis.
Does saline help with blood pressure?
Normal saline has the same amount of salt as your blood. It replaces blood volume, which improves your blood pressure. In some centers, hypertonic saline may be given. Hypertonic saline has more salt than your blood. It can help pull fluid from your tissues into your blood, which raises your blood pressure.
What is dialysis hypotension?
dialysis hypotension. mortality. Dialysis-induced hypotension (DIH) is a very, or even the most frequent complication in renal replacement therapy. It is usually associated with such symptoms as muscle cramps, abdominal and chest pain, nausea and vomiting, dyspnea, light-headedness, weakness, anxiety, vertigo, paleness, ...
Why is dialysis hypotension important?
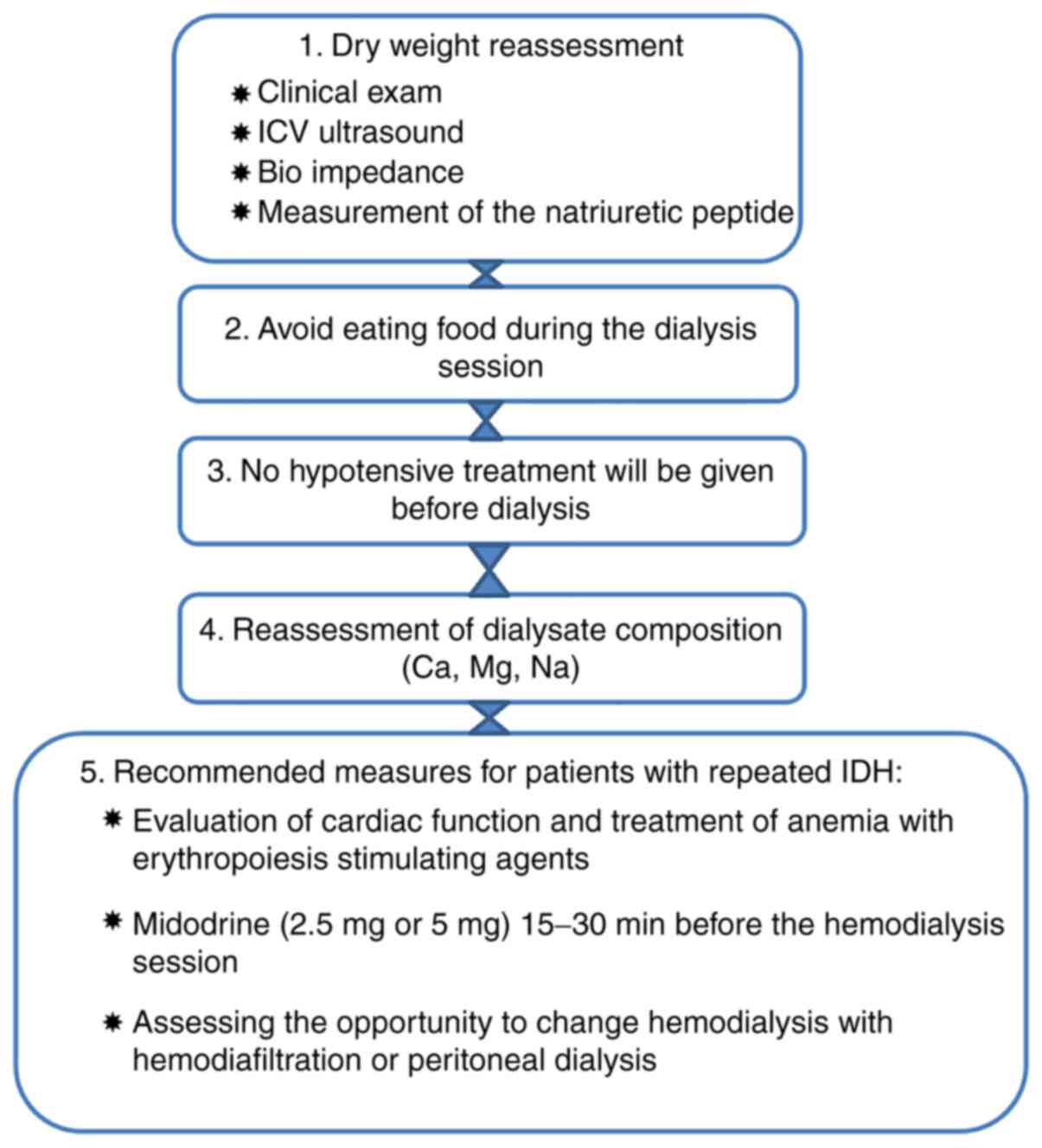
Dialysis hypotension is a very important, multifactorial clinical problem with tendency to increased incidence owing to more elderly and diabetic patients on dialysis. The main role in its prevention play: patients education to avoid excessive interdialytic weight gain, accurate setting of ‘dry weight’, adequate dosing of antihypertensive drugs, dialysis modification (more frequent dialysis, sodium and ultrafiltration profiling, cool dialysate), midodrine treatment, and perfect patients supervision by dialysis staff.
What is the best drug for dih?
A well-known and generally accepted drug used for acute and persistent form of DIH management is midodrine. Midodrine hydrochloride – prodrug – that undergoes plasma enzymatic hydrolysis, is a selective peripheral α1-adrenergic agonist, which increases tonicity of blood vessels, as well as stimulates venous blood flow.
How does isotermic dialysis work?
Some devices the so called ‘isotermic dialysis artificial kidneys’ with blood temperature monitor are able to reduce hypotensive episodes via extrapolation of patient's core temperature estimated from blood temperature and to keep it stable by modifying dialysate temperature.
Is dialytic hypotension a coexisting illness?
Coexisting illnesses, especially cardiovascular diseases, particularly common in older and diabetic patients have an essential meaning in the episodes of dialytic hypotension. Efficient treatment of DIH is difficult owing to no generally accepted guidelines – is still a great challenge to the nephrologist.
Does midodrine help with blood pressure?
Numerous studies indicate that midodrine is able to blunt the blood pressure drop during dialysis.25 Other drugs, commonly used to treat dialytic hypotension, which have similar, but non-selective, α 1/ β1 agonistic effects are caffeine, ephedrine, and etilefrine.
Is it rare to overdose on antihypertensive?
In elderly, demented patients, the overdosage of antihypertensive drugs is also not rare. Coexisting severe cardiovascular diseases, especially common in older patients, can have an essential meaning in tend to episodes of DIH.
