Medication
High risk retinoblastoma warrants enucleation and additional 6-9 cycles of high-dose IVC to prevent metastatic disease.[25,43,44] Due to small caliber vessels, use of IAC is typically reserved for patients older than 3 or 4 months.[19] In younger patients, bridge therapy with IVC is administered until weight reaches 6 kg.[14]
Procedures
However, the same primary goals of protecting life and preventing metastatic disease, followed by globe preservation, and finally optimization of vision are commonly shared among retinoblastoma specialists.
Nutrition
Clinical trials are studies to test new treatments and new ways of using existing treatments. While clinical trials give your child a chance to try the latest in retinoblastoma treatments, they can't guarantee a cure. Ask your child's doctor whether your child is eligible to participate in clinical trials.
See more
Over the past few decades, research into retinoblastoma has led to many advances in treatment, which in turn has led to much higher cure rates and fewer side effects. Still, not all children are cured, and even those who are cured might still have long-term side effects from treatment, so more research is needed.
What are the treatment options for high risk retinoblastoma?
What do retinoblastoma specialists have in common?
What is a clinical trial for retinoblastoma?
Can retinoblastoma be cured in children?

What treatments eliminate retinoblastoma?
Treatment of progressive or recurrent intraocular retinoblastoma may include the following:External-beam radiation therapy or plaque radiotherapy.Cryotherapy.Thermotherapy.Systemic chemotherapy or ophthalmic artery infusion chemotherapy.Intravitreal chemotherapy.Surgery (enucleation).More items...•
How long is treatment for retinoblastoma?
If the retinoblastoma is in both eyes, doctors will try to save at least one eye if at all possible so that the child maintains some vision. Many children will get several types of treatment. Treatment might be needed for months or even years.
Who treats retinoblastoma?
David Abramson, Chief of Ophthalmic Oncology at Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center (MSKCC); and MSKCC pediatric oncologist Dr. Ira Dunkel. Together, these three doctors are leading the field in advanced treatment for retinoblastoma.
Can chemotherapy cure retinoblastoma?
Chemoreduction uses chemotherapy to reduce the size of the tumor. This is a treatment approach that is often used for children with retinoblastoma in both eyes in the hope of avoiding enucleation and preserving vision in at least 1 eye.
Can you recover from retinoblastoma?
Overall, more than 9 in 10 children with retinoblastoma are cured. The chances of long-term survival are much better if the tumor has not spread outside the eye.
How long is chemotherapy for retinoblastoma?
Due to their good intraocular penetration, the standard chemotherapeutic agents used are vincristine, etoposide, and carboplatin (VEC protocol). These are administered for at least six cycles at 28 day intervals.
What is the rate of survival of retinoblastoma?
Doctors often use the observed survival rate when they talk about a prognosis. The 5-year observed survival for retinoblastoma in children 0 to 14 years of age is 96%. This means that, on average, 96% of children diagnosed with retinoblastoma are expected to live at least 5 years after their diagnosis.
What happens if retinoblastoma is not treated?
Untreated, retinoblastoma can spread widely: Throughout the retina. Throughout the fluid inside the eye (also called the vitreous). Large tumors may detach from the retina and break into smaller tumors, called vitreous seeds.
Is retinoblastoma benign or malignant?
A benign tumor means the tumor can grow but will not spread. Retinoblastoma is a rare cancer that begins in the part of the eye called the retina. The retina is a thin layer of nerve tissue that coats the back of the eye and enables the eye to see.
Can retinoblastoma cause blindness?
Although rare, retinoblastoma is the most common eye tumor in children. In most cases, it affects youngsters before age 5. It causes 5% of childhood blindness.
What chemo is used for retinoblastoma?
A standard combination is carboplatin, vincristine, and etoposide, although for very small tumors, only carboplatin and vincristine may be enough. Other drugs might be used if these are not effective.
Is retinoblastoma inherited?
Hereditary retinoblastoma is passed from parents to children in an autosomal dominant pattern, which means only one parent needs a single copy of the mutated gene to pass the increased risk of retinoblastoma on to the children. If one parent carries a mutated gene, each child has a 50% chance of inheriting that gene.
What is retinoblastoma eye exam?
Key Points. Retinoblastoma is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the retina. Children with a family history of retinoblastoma should have eye exams to check for retinoblastoma. Retinoblastoma occurs in heritable and nonheritable forms.
What are the symptoms of retinoblastoma?
Signs and symptoms of retinoblastoma include "white pupil" and eyes that appear to be looking in different directions (crossed eyes). Tests that examine the retina are used to diagnose retinoblastoma. Certain factors affect prognosis (chance of recovery) and treatment options.
What is the heritable form of retinoblastoma?
A child is thought to have the heritable (inherited) form of retinoblastoma when there is a certain mutation (change) in the RB1 gene. The mutation in the RB1 gene may be passed from the parent to the child, or it may occur in the egg or sperm before conception or soon after conception.
Why is retinoblastoma not a routine screening?
CT (computerized tomography) scans are usually not used for routine screening in order to avoid exposing the child to ionizing radiation. Heritable retinoblastoma also increases the child's risk of other types of cancer such as lung cancer, bladder cancer, or melanoma in later years.
How old is a child diagnosed with retinoblastoma?
The brain tumor is usually diagnosed between 20 and 36 months of age. Regular screening using MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) may be done for a child thought to have heritable retinoblastoma or for a child with retinoblastoma in one eye and a family history of the disease.
How often do you check for retinoblastoma?
After heritable retinoblastoma has been diagnosed and treated, new tumors may continue to form for a few years. Regular eye exams to check for new tumors are usually done every 2 to 4 months for at least 28 months.
What is the name of the disease where the brain receives light?
Retinoblastoma is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the retina. The retina is made of nerve tissue that lines the inside wall of the back of the eye. It receives light and converts the light into signals that travel down the optic nerve to the brain.
What is the treatment for retinoblastoma?
Radiation therapy uses high-powered energy, such as X-rays and protons, to kill cancer cells. Types of radiation therapy used in treating retinoblastoma include: Local radiation. During local radiation, also called plaque radiotherapy or brachytherapy, the treatment device is temporarily placed near the tumor.
What is the procedure to remove retinoblastoma?
Eye removal surgery for retinoblastoma includes: Surgery to remove the affected eye (enucleation). During surgery to remove the eye, surgeons disconnect the muscles and tissue around the eye and remove the eyeball. A portion of the optic nerve, which extends from the back of the eye into the brain, also is removed.
How to diagnose retinoblastoma in children?
Tests and procedures used to diagnose retinoblastoma include: Eye exam. Your eye doctor will conduct an eye exam to determine what's causing your child's signs and symptoms. For a more thorough exam, the doctor may recommend using anesthetics to keep your child still. Imaging tests.
Why do you put radiation near a tumor?
Placing radiation near the tumor reduces the chance that treatment will affect healthy tissues outside the eye. This type of radiotherapy is typically used for tumors that don't respond to chemotherapy. External beam radiation.
What tests can be done to determine if a child has retinoblastoma?
Imaging tests. Scans and other imaging tests can help your child's doctor determine whether retinoblastoma has grown to affect other structures around the eye. Imaging tests may include ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), among others.
Can you remove your eye to treat retinoblastoma?
When the cancer is too large to be treated by other methods, surgery to remove the eye may be used to treat retinoblastoma. In these situations, eye removal may help prevent the spread of cancer to other parts of the body. Eye removal surgery for retinoblastoma includes:
Can retinoblastoma be treated with laser?
In children with retinoblastoma, chemotherapy may help shrink a tumor so that another treatment, such as cryotherapy or laser therapy, may be used to treat the remaining cancer cells. This may improve the chances that your child won't need surgery to remove the eye.
What kind of doctor treats retinoblastoma?
Children with retinoblastoma are treated by a team of doctors that often includes: 1 A pediatric ophthalmologist: a doctor who treats eye diseases in children 2 An ocular oncologist: a doctor (usually an ophthalmologist) who treats cancers of the eye 3 A pediatric oncologist: a doctor who treats children with cancer 4 A radiation oncologist: a doctor who treats cancer with radiation therapy
Why is it important to treat hereditary retinoblastoma?
To preserve as much vision as possible. To limit the risk of side effects later in life that can be caused by treatment, particularly second cancers in children with hereditary retinoblastoma. The most important factors that help determine treatment are: The size and location of the tumor (s)
What to do when your child has cancer?
Making treatment decisions. Once the cancer is found and the needed tests have been done, the cancer care team will discuss treatment options with you. It’s important to discuss all of the options as well as their possible side effects with your child’s doctors to help you make an informed decision.
How many children with retinoblastoma are cured?
Overall, more than 9 in 10 children with retinoblastoma are cured. The chances of long-term survival are much better if the tumor has not spread outside the eye. Treatment of Retinoblastoma, Based on Extent of the Disease.
What is a radiation oncologist?
A radiation oncologist: a doctor who treats cancer with radiation therapy. The team might also include other doctors, physician assistants (PAs), nurse practitioners (NPs), nurses, therapists, child psychologists, social workers, genetic counselors, and other professionals.
What is the best way to help a child with cancer?
These might include nursing or social work services, financial aid, nutritional advice, rehab, or spiritual help. For children and teens with cancer and their families, other specialists can be an important part of care as well.
Can retinoblastoma be treated with more than one type of treatment?
Sometimes more than one type of treatment may be used. The treatment options are based on the extent ( stage) of the cancer and other factors. The goals of treatment for retinoblastoma are: To get rid of the cancer and save the child’s life. To save the eye if possible.
What are the symptoms of retinoblastoma?
At a glance: Retinoblastoma. Symptoms: Eye swelling or redness, whiteness in the pupil, eyes that point in different directions. Diagnosis: Dilated eye exam, scans or imaging tests of the eye.
What is the name of the cancer that forms in the retina?
Retinoblastoma is a type of cancer that forms in the retina (the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye).
Is retinoblastoma a life threatening disease?
Retinoblastoma is a serious, life-threatening disease. However, with early diagnosis and timely treatment, in most cases, a child’s eyesight and life can be saved. For more information on treating retinoblastoma, please visit the National Cancer Institute website. Last updated: August 12, 2019.
What is the treatment for retinoblastoma?
The role of intravenous chemotherapy (IVC) in bilateral disease. A 4-month-old patient was diagnosed with a (a) Group B retinoblastoma in the right eye, and was treated with 6 cycles of standard-dose IVC, (b) achieving a complete regression of the tumor. Consolidation therapy with TTT was required during the course of the treatment, leaving flat scars (black arrows) and completely regressed tumors. The (c) left eye was diagnosed with Group D retinoblastoma, regressing to a (d) smaller calcified scar in the macular region after treatment
What is the percentage of the globe occupied by retinoblastoma?
Retinoblastoma occupying >50% of the globe OR neovascular glaucoma opaque media from hemorrhage in subretinal space, vitreous, or anterior chamber invasion of postlaminar optic nerve, choroid (>2 mm), sclera, orbit, anterior chamber
How much safety margin is needed for optic nerve tumor?
Typically, a 2 mm safety margin is added to the largest basal diameter for optimal tumor coverage. Tumors within 2 mm of the optic nerve require a notched plaque, with deep notch used for 3 or more clock hours of tumor around the nerve.
Is cryotherapy used for retinoblastoma?
Cryotherapy remains a reliable and regularly used treatment in the management of retinoblastoma. Indications include treatment of small tumors and foci of sub retinal or preretinal seeds. A modality termed 'chemo-cryo' describes the application of cryotherapy to the peripheral ora serrata on the same day as IVC in order to improve drug concentration to the intraocular space.[14] Treatment is performed under indirect ophthalmoscopy, placing the cryotherapy probe on the conjunctiva for peripheral lesions or directly on the sclera following a conjunctival incision for more posteriorly located lesions. A triple-freeze-thaw technique is preferably employed, visualizing the tumor becoming entirely encased in an ice ball and then waiting for a complete thaw prior to applying the following freeze cycle. Presently, cryotherapy is rarely used as standalone therapy, and is more frequently used in combination with some sort of chemotherapy, most commonly IVC but sometimes IAC. Exudative and rhegmatogenous retinal detachment have been reported following extensive cryotherapy.[14,66]
Is retinoblastoma a cancer?
Retinoblastoma, the most common ocular malignancy in childhood, is lethal if left untreated. In high-income countries (HICs), retinoblastoma is considered a curable cancer with a near 100% disease-free survival rate.[1] .
Can antibiotics be used to treat papillary conjunctivitis?
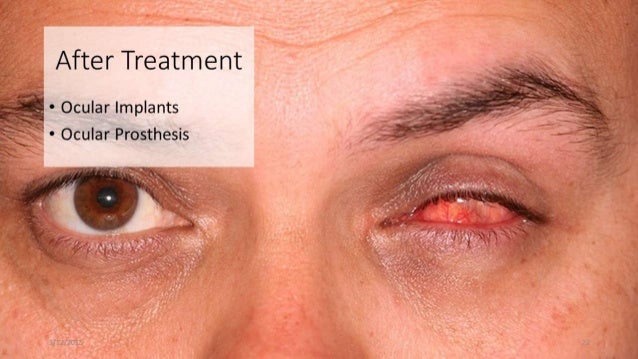
Infection can be managed topically or systemically with antibiotics but implant removal can be necessary in severe cases. Giant papillary conjunctivitis secondary to continuous contact of the prosthesis can be managed with antibiotic-steroid ointments and copious amounts of lubricants.
Can IVC be used for vitreous seed recurrence?
Despite significant improvements in survival, tumor control, and globe salvage in the IVC and IAC eras, several group D and E eyes often required enucleation for vitreous seed recurrence .[14,34] Intravitreal chemotherapy (IvitC), first introduced by Kaneko and Suzuki in 2003, was found useful in combination with IAC for many eyes that otherwise would have been lost. Current indications for IvitC include the presence of refractory or recurrent vitreous seeds following other treatments [Fig. 3]. It is noteworthy to highlight that IvitC is almost never used as primary therapy, but mostly as globe salvage therapy, given the limited efficacy on the primary tumor. Contraindications for IvitC include presence of tumor or vitreous seeds at the planned site of needle entry, tumor invasion of the pars plana, and anterior chamber seeding. Careful clinical examination with the aid of ultrasound biomicroscopy (UBM) can help administer IvitC safely.
What is the best treatment for cancer near the front of the eye?
Cryotherapy: A touch with a super-cooled metal probe freezes and kills cancer cells. This works best on small tumors near the front of the eye. Thermotherapy: A special laser kills cancer cells with heat. Doctors use it by itself on small tumors or along with other treatments for larger tumors.
How do you treat cancer in children?
If the cancer is likely to spread or has already spread, your child will probably take the medications by mouth or through a vein so they can work throughout the body.
Where does eye cancer start?
This is a rare form of eye cancer that usually happens in childhood. It starts in the retina -- the part of the eye that senses light and sends pictures to the brain. Fewer than 300 children in the U.S. are diagnosed with it each year. Usually, it's found before they turn 2.
Can a tumor be removed from a child's eye?
Surgery: If the tumor is very large by the time it’s found, it may not be possible to save the child’s vision. In these cases, the eye may be removed . It’s nearly impossible for a small child to keep still long enough for a thorough exam, much less when something is being done to the child's eye.
Can a tumor in one eye be caused by a gene?
In most cases, the gene damage happens at random and occurs in just one cell. That causes a tumor in one eye. Some children are born with the damaged gene in every cell of their body. These children are likely to have more than one tumor and to have them in both eyes. They also have a greater chance of getting other kinds of cancer.
Is retinoblastoma curable?
Retinoblastoma is almost always curable, especially if it hasn’t spread beyond the eye. Children treated for retinoblastoma need very close follow-up care. Your child will have frequent checkups to watch for signs that the cancer has come back. Frequent checkups are important for other reasons, too.
What is the best treatment for retinoblastoma?
Newer forms of radiation therapy such as intensity modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) and proton beam therapy can better target the tumor and spare nearby normal tissues. These techniques, which are described in Radiation Therapy for Retinoblastoma, may help doctors limit the side effects from radiation therapy.
What is new in retinoblastoma research?
What’s New in Retinoblastoma Research? Over the past few decades, research into retinoblastoma has led to many advances in treatment, which in turn has led to much higher cure rates and fewer side effects. Still, not all children are cured, and even those who are cured might still have long-term side effects from treatment, ...
Why is chemo given after removal of the eye?
Chemo is also given to some children after the removal of the eye (known as adjuvant chemotherapy) to help prevent the recurrence of retinoblastoma outside the eye. Doctors are also studying the use of different chemo drugs, as well as new ways of combining currently used drugs, to try to improve how well chemo works.
What is a SCT in retinoblastoma?
These techniques are described in Chemotherapy for Retinoblastoma. High-dose chemotherapy and stem cell transplant : A stem cell transplant (SCT) lets doctors give higher doses of chemo than could safely be given otherwise. (In the past, this type of treatment was commonly referred to as a bone marrow transplant.)
When was the RB1 gene discovered?
The defective gene responsible for nearly all retinoblastomas ( the RB1 gene) was identified in 1986. This discovery, along with technical advances in finding DNA changes, has made genetic testing for heritable (hereditary) retinoblastoma possible.
Which oncogene is overactive in retinoblastoma cells?
For example, researchers have found that an oncogene known as SYK is overactive in retinoblastoma cells. Drugs that target the protein this gene makes are now being developed. Another gene called MDM4 also seems to be involved in the development of retinoblastoma, and drugs aimed at blocking its effects are being studied.
What is the goal of focal treatment?
The goal is to kill tumor cells more precisely while sparing other parts of the eye.

Diagnosis
Treatment
Clinical Trials
Coping and Support
Specialist to consult
Preparing For Your Appointment
- Tests and procedures used to diagnose retinoblastoma include: 1. Eye exam.Your eye doctor will conduct an eye exam to determine what's causing your child's signs and symptoms. For a more thorough exam, the doctor may recommend using anesthetics to keep your child still. 2. Imaging tests.Scans and other imaging tests can help your child's doctor det...