Procedures
Pyloric stenosis is more common in whites of northern European ancestry, less common in Black people and rare in Asians. Premature birth. Pyloric stenosis is more common in babies born prematurely than in full-term babies. Family history. Studies found higher rates of this disorder among certain families.
Nutrition
They might suggest:
- Pain relievers. Over-the-counter medicines such as acetaminophen ( Tylenol ), ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin ), or naproxen ( Aleve) might ease your pain.
- Cortisone. This is a steroid that your doctor injects into your spinal column. ...
- Physical therapy or exercise. ...
Can you be too premature to develop pyloric stenosis?
n ursing diagnosis for pyloric stenosis:_ Imbalanced nutrition: less than body requirements related to inability to retain food. Deficient fluid volume related to frequent vomiting. Impaired oral mucous membrane related to NPO status. Risk for impaired skin integrity related to fluid and nutritional deficit.
What is the recovery time for cervical stenosis surgery?
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain, pressure, or tightness
- Fatigue
- Feeling lightheaded or dizzy
- Difficulty when exercising or completing day-to-day activities
What is the nursing diagnosis for Pyloric stenosis?
What is the prognosis for severe aortic stenosis?

Can pyloric stenosis be treated without surgery?
Nonsurgical treatment for infantile hypertrophic pyloric stenosis with atropine sulfate, either intravenous or oral, is an alternative in the rare case that general anesthesia or surgery is contraindicated.
What is the drug of choice for pyloric stenosis?
Medication Summary Atropine has been studied as a potential for conservative management of pyloric stenosis. It is either administered intravenously or orally with the goal of treatment being cessation of projectile vomiting.
Does pyloric stenosis require immediate surgery?
Pyloric stenosis is an urgent condition that needs immediate treatment.
Does pyloric stenosis go away?
Pyloric stenosis can lead to forceful vomiting, dehydration and weight loss. Babies with pyloric stenosis may seem to be hungry all the time. Surgery cures pyloric stenosis.
Can pyloric stenosis be treated with medicine?
Treatment. The first form of treatment for pyloric stenosis is to identify and correct any changes in body chemistry using blood tests and intravenous fluids. Pyloric stenosis is always treated with surgery, which almost always cures the condition permanently.
Can antibiotics cause pyloric stenosis?
Doctors have known that using the antibiotic erythromycin can increase the risk of pyloric stenosis in infants. The new findings confirmed that link, and also found that the antibiotic azithromycin (Zithromax) is associated with a higher risk of pyloric stenosis when given to infants under 6 weeks old.
How long is the hospital stay for pyloric stenosis?
Your child will need anesthesia. His or her surgeon will make a small cut (incision) above your baby's navel. Then the surgeon will fix the pyloric muscle. Your baby will stay in the hospital for 2 to 3 days.
What if pyloric stenosis goes untreated?
If left untreated, hypertrophic pyloric stenosis can cause: Dehydration. Electrolyte imbalance. Lethargy.
How long does pyloric stenosis surgery take?
A pyloromyotomy can be done using a small telescope and two miniature instruments through several small bandaid sized incisions, or it can be done through a very small incision on the abdomen. The operation usually takes about an hour.
Is pyloric stenosis painful?
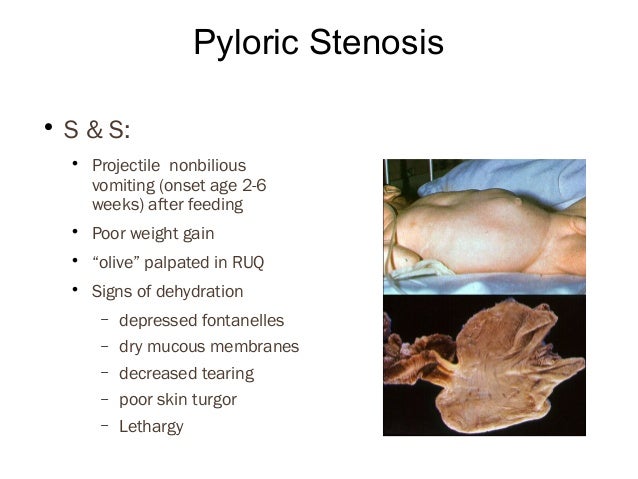
Symptoms and Causes Infants with pyloric stenosis may eat well but have these symptoms: Frequent projectile vomiting (forceful vomiting), usually within a half hour to an hour after eating. Abdominal (belly) pain.
At what age is pyloric stenosis diagnosed?
Pyloric stenosis usually affects babies between 2 and 8 weeks of age, but can occur anytime from birth to 6 months. It is one of the most common problems requiring surgery in newborns. It affects 2-3 infants out of 1,000.
Is pyloric stenosis a birth defect?
Pyloric stenosis is a birth defect. This means that your child is born with it. This condition may run in some families. It's a multifactorial trait.
What is a pyloric stenosis?
What is Pyloric Stenosis? Pyloric stenosis is a problem that affects babies between birth and 6 months of age and causes forceful vomiting that can lead to dehydration. It is the second most common problem requiring surgery in newborns.
How to tell if a baby has pyloric stenosis?
The most common symptoms noted in a baby with pyloric stenosis is forceful, projectile vomiting. This kind of vomiting is different from a "wet burp" that a baby may have at the end of a feeding. Large amounts of breast milk or formula are vomited, and may go several feet across a room. The baby is usually quite hungry and eats or nurses eagerly. The milk is sometimes curdled in appearance, because as the milk remains in the stomach and does not move forward to the small intestine, the stomach acid "curdles" it.
Which part of the stomach is responsible for preventing food from moving from the stomach to the intestine?
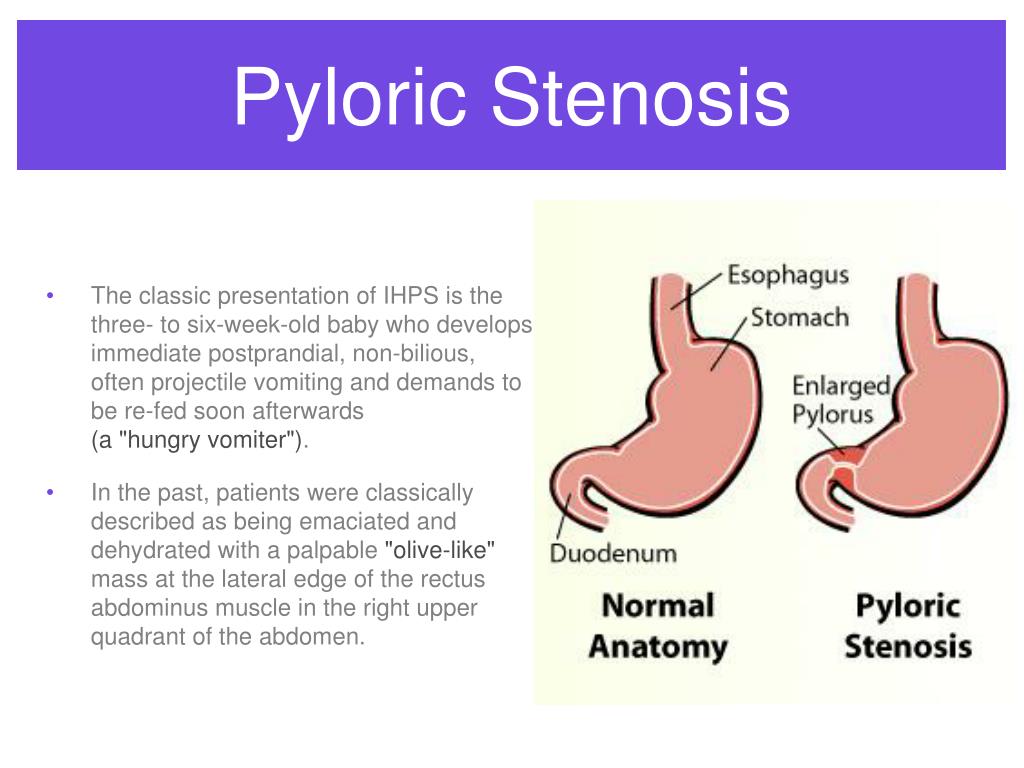
The lower portion of the stomach that connects to the small intestine is known as the pylorus. In pyloric stenosis, the muscles in this part of the stomach enlarge, narrowing the opening of the pylorus and eventually preventing food from moving from the stomach to the intestine.
Do Caucasian babies have pyloric stenosis?
Caucasian babies seem to develop pyloric stenosis more frequently than babies of other races . Boys develop pyloric stenosis more often than girls. Pyloric stenosis may be inherited; several members of a family may have had this problem in infancy.
Is pyloric stenosis more common in males than females?
For example, pyloric stenosis is four times more common in males than females. Once a child has been born with pyloric stenosis, the chance for it to happen again depends on the gender of the child already born with the condition, as well as the gender of the next child.
Is pyloric stenosis a multifactorial trait?
Pyloric stenosis is considered a multifactorial trait. Multifactorial inheritance means that many factors are involved in causing a birth defect. The factors are usually both genetic and environmental. Often one gender (either males or females) is affected more frequently than the other in multifactorial traits.
How to perform pyloric stenosis surgery?
During pyloric stenosis surgery, the team will: Give your child general anesthesia. Your child will be asleep during the surgery and not feel any pain. Make a small incision (cut) on the left side of the abdomen, higher than the belly button. Perform a pyloromyotomy, making an incision in the thickened pylorus.
What happens to the pylorus in pyloric stenosis?
It’s located at the end of the stomach, where the stomach meets the small intestine. The pylorus contracts (closes) when food and liquid need to get digested in the stomach.
What is the term for the thickening of the pylorus?
Pyloric stenosis is a thickening or narrowing of the pylorus, a muscle in the stomach. This problem happens to newborns. The full name of the condition is hypertrophic pyloric stenosis (HPS). Hypertrophy means thickening. Pyloric stenosis causes projectile vomiting and can lead to dehydration in babies. Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic ...
How long does it take for pyloric stenosis to show?
Pyloric stenosis symptoms usually start when the baby is 2 to 8 weeks old. But it can take up to five months for the symptoms to become apparent. If you notice symptoms, talk to your healthcare provider.
What is the term for a condition that affects an infant's pylorus, a muscle?
Pyloric Stenosis (HPS) Pyloric stenosis is a condition that affects an infant's pylorus, a muscle at the end of the stomach. When the pylorus thickens, food can’t pass through. Pyloric stenosis symptoms include forceful vomiting, which may cause dehydration. Surgery can repair the problem.
Why do babies with pyloric stenosis have dehydration?
Infants with pyloric stenosis often have dehydration because they vomit so much. Your provider will make sure your baby is properly hydrated before performing surgery. Your baby will probably need fluids through an IV which will be given at the hospital.
What causes a child to have a pyloric obstruction?
In rare cases, older children can get a pyloric obstruction — something blocking the passage through the pylorus. Usually, a peptic ulcer is the cause in older children. Or perhaps a child has a rare disorder such as eosinophilic gastroenteritis, which inflames the stomach.
Which is more likely to get pyloric stenosis?
Gender: Boys are more likely to get pyloric stenosis than girls. Premature birth: Babies born before the 37th week of pregnancy have a higher chance of having it. Smoking during pregnancy: Babies of moms who smoke are more than twice as likely to get pyloric stenosis.
Where does the pylorus go?
How It Happens. The pylorus is a valve that sits between the stomach and small intestine. It stays closed to hold food in the stomach, then it opens to let food move into the intestine, where it’s digested. In babies with pyloric stenosis, the pylorus gets thicker, and food moves into the small intestine more slowly.
What is the condition where the valve between the stomach and small intestine gets thick and narrow?
Pyloric stenosis is a rare condition that makes the valve between a newborn's stomach and small intestine get thick and narrow. This makes it harder for food to go from the baby's stomach into the intestine. It affects about three out of every 1,000 babies born in the United States.
Why does pylorus get bigger?
Doctors don't know exactly why the pylorus gets bigger, but it might be partly caused by changes in a gene. It's often passed down through families. If one or both parents have pyloric stenosis, their baby has up to a 20% greater chance of getting it. Gender: Boys are more likely to get pyloric stenosis than girls.
What does an enlarged pylorus feel like?
The doctor will also check your child's weight and growth. Then they’ll feel your baby's belly for any lumps: An enlarged pylorus feels like an olive. Your baby’s doctor may want to get a closer look with one of these: Ultrasound: This uses sound waves to make images of the inside of your baby’s stomach.
How to treat a baby with a blockage?
Then surgery (called pyloromyotomy) will be done to open up the blockage. Your baby will get medicine to make them sleep, so the surgery won’t hurt.
How to treat pyloric stenosis?
The first form of treatment for pyloric stenosis is to identify and correct any changes in body chemistry using blood tests and intravenous fluids . Pyloric stenosis is always treated with surgery, which almost always cures the condition permanently. The operation, called a pyloromyotomy, divides the thickened outer muscle, while leaving the internal layers of the pylorus intact. This opens a wider channel to allow the contents of the stomach to pass more easily into the intestines.
What is the procedure for pyloric stenosis?
A minimally invasive approach to abdominal surgery, called laparoscopy is generally the first choice of surgery for pyloric stenosis. To perform laparoscopic surgery, the surgeon inserts a rigid tube (called a trocar) into the abdominal cavity through a small incision (cut). The tube allows the surgeon to place a small camera into ...
How long does a baby have to be in hospital after a pyloromyotomy?
The hospital stay following a pyloromyotomy is typically one or two days, and the decision to discharge a patient is based on how well the child is recovering: specifically, if the baby is able to drink breast milk or formula without vomiting and has pain that can be controlled by medications taken by mouth. It is normal for a baby to vomit small amounts during the first day or two after surgery, but this should gradually improve. If your baby continues to vomit after you return home, call your doctor, because this may indicate continued blockage that is preventing the stomach from emptying normally.
How long does it take for a baby to recover from pyloric stenosis?
After surgery, your baby may be fed special fluids for one or two feedings and then breast milk or formula within 24 hours.
What is the name of the forceful vomiting that is usually clear?
Vomiting is forceful (projectile vomiting) and the vomit itself is usually clear or has the appearance of partially digested (curdled) milk.
How many trocars are needed for pyloromyotomy?
Laparoscopic pyloromyotomy generally involves the use of two or three trocars, and therefore usually requires two or three small incisions. If the surgeon decides that a laparoscopic operation is not the best way to treat the problems that are found in the operating room, then the operation will be changed (converted) to use an older surgical technique. Conversion to a nonlaparoscopic operation (called an “open procedure”) is rare and requires a larger incision, which may take longer to heal.
Can a patient move his or her bowels?
The patient cannot move his or her bowels. Some medications cause constipation, so the surgical team may prescribe stool softeners or mild laxatives to help with bowel movements. If these treatments are ineffective, there may be a more serious problem.
What causes pyloric stenosis?
The causes of pyloric stenosis are unknown, but genetic and environmental factors might play a role. Pyloric stenosis usually isn't present at birth and probably develops afterward.
How many descendants of a male have pyloric stenosis?
Family history. Studies found higher rates of this disorder among certain families. Pyloric stenosis develops in about 20% of male descendants and 10% of female descendants of mothers who had the condition.
How long does it take for pyloric stenosis to appear?
Signs of pyloric stenosis usually appear within three to five weeks after birth. Pyloric stenosis is rare in babies older than 3 months. Signs include: Vomiting after feeding. The baby may vomit forcefully, ejecting breast milk or formula up to several feet away (projectile vomiting).
What happens to the pylorus muscles in a baby?
In pyloric stenosis, the pylorus muscles thicken, blocking food from entering the baby's small intestine.
What is the valve that holds food in the stomach until it is ready for the next stage in the digestive process?
Pylorus. Pylorus . The pylorus is a muscular valve that holds food in the stomach until it is ready for the next stage in the digestive process. Pyloric stenosis. Open pop-up dialog box. Close. Pyloric stenosis. Pyloric stenosis.
Can pyloric stenosis cause weight loss?
Pyloric stenosis can lead to forceful vomiting, dehydration and weight loss. Babies with pyloric stenosis may seem to be hungry all the time.
Can smoking cause pyloric stenosis?
Smoking during pregnancy. This behavior can nearly double the risk of pyloric stenosis. Early antibiotic use. Babies given certain antibiotics in the first weeks of life — erythromycin to treat whooping cough, for example — have an increased risk of pyloric stenosis.
How do you know if you have pyloric stenosis?
There is no known reason for enlargement of the pylorus. The main symptom of pyloric stenosis is vomiting undigested breast milk or formula soon after a feeding. Vomiting usually begins at four weeks of age but can happen as early as two weeks after birth. Once vomiting begins it becomes more frequent, and severe, and is often described as "forceful" or "projectile". Infants with pyloric stenosis may become fussy and, since they cannot keep down all their feedings, are hungry between feedings and are not able to gain weight normally. If the vomiting continues infants may become ill from dehydration.
What is the procedure called when a child is injected with fluids?
The operation is called a "pyloromyotomy" where the surgeon cuts through the muscle fibers of enlarged pyloric muscle in order to widen the opening into the intestine. Prior to the operation, your child will be admitted to the hospital for intravenous fluids. Feedings will be held temporarily and restarted after the operation.
Is pyloric stenosis more common in boys than girls?
Pyloric stenosis is one of the most common conditions requiring surgery in infants. It is more common in boys than girls and usually affects children who are born at full term. It rarely occurs in premature infants.
Can pyloric stenosis cause dehydration?
If the vomiting continues infants may become ill from dehydration. Pyloric stenosis is one of the most common conditions requiring surgery in infants.
Why does pyloric stenosis occur?
This is usually a consequence of a congenital defect. In most cases in adults, pyloric stenosis occurs as a result of chronic ulcers or fibrosis near the gastric outlet. ( 1) Symptoms occur due to inability of the food to pass easily from the stomach into the intestines.
What is a rare disorder in adults that is caused by abnormal thickening of pyloric s?
Pyloric stenosis is a rare disorder in adults that is caused due to abnormal thickening of pyloric sphincter muscle, thereby narrowing the gastric outlet.
What Is Pyloric Stenosis?
Symptoms
Diagnosis
Treatment
Specialist to consult
Recovery