What is the immediate treatment for pulmonary embolism?
Massive PE is a medical emergency requiring immediate treatment with thrombolytics, anticoagulants, and/or surgery; nonmassive PE may be treated in an outpatient setting.Jul 13, 2018
How do you get rid of a pulmonary embolism?
Surgical and other procedures. Clot removal. If you have a very large, life-threatening clot in your lung, your doctor may suggest removing it via a thin, flexible tube (catheter) threaded through your blood vessels.Jun 13, 2020
Is embolism pulmonary curable?
Symptoms of a pulmonary embolism include sudden shortness of breath, pain in and around the chest and coughing. Caused by a blood clot, a pulmonary embolism is a serious but very treatable condition if done immediately.Feb 26, 2019
How long does it take to resolve a pulmonary embolism?
A DVT or pulmonary embolism can take weeks or months to totally dissolve. Even a surface clot, which is a very minor issue, can take weeks to go away. If you have a DVT or pulmonary embolism, you typically get more and more relief as the clot gets smaller.Mar 16, 2020
What are the warning signs of a pulmonary embolism?
What are the Symptoms of Pulmonary Embolism?Shortness of breath.Chest pain that may become worse when breathing in.Cough, which may contain blood.Leg pain or swelling.Pain in your back.Excessive sweating.Lightheadedness, dizziness or passing out.Blueish lips or nails.Oct 23, 2020
What are the odds of surviving a pulmonary embolism?
However, reported survival after venous thromboembolism varies widely, with "short-term" survival ranging from 95% to 97% for deep vein thrombosis8,9 and from 77% to 94% for pulmonary embolism,4,6,8,9 while "long-term" survival ranges from 61% to 75% for both deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism.
How long is hospital stay for blood clot in lungs?
How long is hospitalization? The time a person spends in the hospital depends on how severe the clot is and whether the person's body is dissolving the clot on its own. Some people may not need to stay in the hospital at all, while others may require 1 week or more.Mar 5, 2021
Can a CT scan detect a blood clot in the lungs?
How Do CT Scans Detect Pulmonary Embolism? If a doctor suspects you may have a pulmonary embolism (PE), a CT scan is the gold standard of imaging techniques. This painless scan uses intravenous (IV) contrast, a type of dye, to help the doctor identify if you have a blood clot — or multiple blood clots — in your lungs.Jul 27, 2021
What are the main causes of pulmonary embolism?
Pulmonary embolism is caused by a blocked artery in the lungs. The most common cause of such a blockage is a blood clot that forms in a deep vein in the leg and travels to the lungs, where it gets lodged in a smaller lung artery. Almost all blood clots that cause pulmonary embolism are formed in the deep leg veins.
Does a pulmonary embolism require hospitalization?
If a DVT is not treated, it can move or break off and travel to the lungs. A blood clot in the lungs is called a pulmonary embolism or PE. This requires immediate medical attention since it can cause death.
Is pulmonary embolism fatal?
A pulmonary embolism (PE) can cause a lack of blood flow that leads to lung tissue damage. It can cause low blood oxygen levels that can damage other organs in the body, too. A PE, particularly a large PE or many clots, can quickly cause serious life-threatening problems and, even death.
How to treat pulmonary embolism?
How Pulmonary Embolism Is Treated. Treatment is aimed at keeping the blood clot from getting bigger and preventing new clots from forming. Prompt treatment is essential to prevent serious complications or death. Blood thinners or anticoagulants are the most common treatment for a blood clot in the lung. While hospitalized an injection is used, but ...
How long after pulmonary embolism can you breathe?
If you continue to have breathing difficulty 6 months after a pulmonary embolism you should talk to your doctor and get tested for CTEPH. Your physician may complete a "hypercoagulability" evaluation on you at some point after your diagnosis. This could include blood tests looking for a genetic cause of your DVT.
Why are compression socks important?
It is also important for people taking blood thinners to be careful not to over-exert themselves during exercise. Compression socks are a helpful tool for preventing PE occurrences. Because pulmonary embolism often starts in the legs, the increased pressure on the leg muscles forces blood to move, discouraging clots.
What is a clot dissolver?
Clot dissolvers called thrombolytics are a medication reserved for life-threatening situations because they can cause sudden and severe bleeding. For a very large, life-threatening clot, doctors may suggest removing it via a thin, flexible tube (catheter) threaded through your blood vessels.
Where is the vena cava filter?
The filter is surgically inserted inside a large vein called the vena cava. The filter catches blood clots from the legs before they travel to the lungs, which prevents pulmonary embolism. However, the filter doesn't stop new blood clots from forming.
How long do you have to take blood thinners?
Patients will normally have to take medications regularly for an indefinite amount of time, usually at least 3 months.
Can blood thinners dissolve blood clots?
It is important to note that blood thinners won’t dissolve the blood clot. In most cases, the hope is your body will eventually dissolve the clot on its own. If it doesn’t, more drastic measures may need to be taken.
What is the best imaging technique for pulmonary embolism?
CTA has become the method of choice for imaging the pulmonary vasculature when pulmonary embolism is suspected in routine clinical practice. Scintigraphy can be considered the preferred alternative chest imaging technique for patients with contraindication to CTA.
What is PE in medical terms?
Introduction. Pulmonary embolism (PE) is an acute and potentially fatal condition in which embolic material, usually a thrombus originating from one of the deep veins of the legs or pelvis, blocks one or more pulmonary arteries, causing impaired blood flow and increased pressure to the right cardiac ventricle.
What is the diagnostic yield of individual clinical symptoms, signs and common laboratory tests?
Although the diagnostic yield of individual clinical symptoms, signs and common laboratory tests is limited, the combination of these variables, either by empirical assessment or by a prediction rule, can be used to stratify patients by risk of pulmonary embolism (low, intermediate or high).
What is the AIMAR task force?
In October 2011 the Interdisciplinary Association for Research in Lung Disease (AIMAR) established a Task Force for diagnosis and treatment of PE with multidisciplinary representation including 3 pulmonologists, 3 internists, 2 emergency care physicians, 1 cardiologist, 1 radiologist and 1 nuclear medicine physician.
Why is it important to identify patients with PE?
First, accurate and fast identification of patients with PE is critical because PE is a potentially fatal condition and anticoagulation is associated with the risk of major bleeding. A false diagnosis thus exposes patients to unnecessary risk of death from PE or of bleeding which can also be fatal.
Is pulmonary embolism a major health problem?
Although early treatment is highly effective, PE is underdiagnosed and, therefore, the disease remains a major health problem. Since symptoms and signs are non specific and the consequences ...
Is pulmonary embolism the same as deep vein thrombosis?
Pulmonary embolism and deep vein thrombosis are considered to be two manifestations of the same condition, venous thromboembolism, which is the third most common cardiovascular disorder in industrialized countries [1,2].
Why is it important to have a pharmacist for PE?
Pharmacists play an important role in the management of PE. Patient- specific drug selection and dosing are important to maximize therapy and minimize adverse events. Patient risk factors, comorbidities, and organ function are factors in selecting the appropriate agent at the appropriate dose for the appropriate duration. Drug-drug and drug-nutrient interactions are also important in selecting medications and doses. Owing to the risk of bleeding and other drug misadventures, patient and caregiver education that stresses correct administration, storage, adherence, and when to call a healthcare provider are crucial to preventing complications and identifying recurrences. The community or ambulatory pharmacist may be first-line in triaging these occurrences.
What is a PE in medical terms?
ABSTRACT: Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a clot in the lung artery, most often due to deep vein thrombosis. It can be difficult to detect and may result in death. The severity of PE and the patient’s presentation drive treatment selection and the care plan. Massive PE is a medical emergency requiring immediate treatment with thrombolytics, ...
What are the risk factors for VTE?
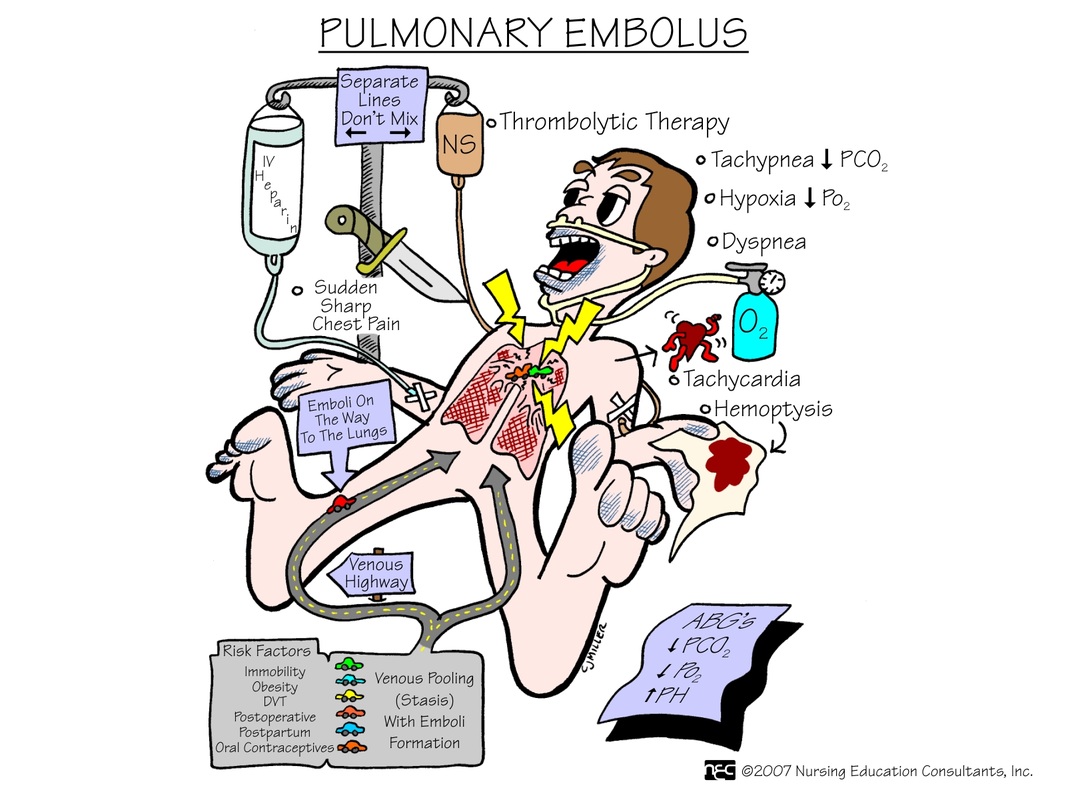
Patient age and history of VTE are risk factors for the development of VTE, with PE commonly resulting from DVT. A clot in a deep vein can dislodge and travel, entering the right side of the heart and continuing to the pulmonary artery. If the clot blocks blood flow in the pulmonary artery or one of its branches, it is a PE, which can lead to death if not treated. 1,8,9 Additional risk factors, typically referred to as Virchow’s Triad, include blood stasis, vascular injury, and hypercoagulability. 1 Malignancy, heart failure, pregnancy, postpartum status, obesity, age, smoking, respiratory failure, intensive care, coagulopathy, and hormone replacement therapy/oral contraceptives are also risk factors. 6,10,11
What are the symptoms of ischemic angina?
Over 90% of patients present with dyspnea, tachypnea, or chest pain that mimics ischemic angina. 1,10 Patients may also have tachycardia. 1 Others may present with coughing (20%), syncope (14%), or hemoptysis (7%). Only 5% to 7% of patients will present with “classic” symptoms of PE reported as a triad of shortness of breath, chest pain , and hemoptysis. 10
Can PE cause death?
If untreated, PE can result in death. Goals of initial treatment include clot resolution; long-term and extended treatment aim to decrease the risk of recurrence. Additional goals include decreased risk of consequences of PE, such as death, pulmonary hypertension, and impaired functional outcomes. Treatment selection is patient-specific ...
How to reduce the risk of pulmonary embolism?
Be sure you discuss and understand your follow- up care with your doctor. Follow your doctor’s recommendations to reduce the risk of another pulmonary embolism. Keep all appointments with your doctor and the laboratory so your response to prescribed treatments can be monitored.
What are the symptoms of a pulmonary embolism?
Symptoms of a pulmonary embolism include sudden shortness of breath, pain in and around the chest and coughing. Caused by a blood clot, a pulmonary embolism is a serious but very treatable condition if done immediately. Appointments & Access. Contact Us.
What is the term for a blood clot in the lung?
A pulmonary embolism is a blood clot in the lung that occurs when a clot in another part of the body (often the leg or arm) moves through the bloodstream and becomes lodged in the blood vessels of the lung. This restricts blood flow to the lungs, lowers oxygen levels in the lungs and increases blood pressure in the pulmonary arteries.
What is a pool of blood in the arm?
Pulmonary embolism may occur: When blood collects (or “pools”) in a certain part of the body (usually an arm or leg). Pooling of blood usually occurs after long periods of inactivity, such as after surgery or bed rest. When veins have been injured, such as from a fracture or surgery (especially in the pelvis, hip, knee or leg).
What is it called when a clot develops in a vein?
If a clot develops in a vein and it stays there, it’s called a thrombus. If the clot detaches from the wall of the vein and travels to another part of your body, it’s called an embolus. If PEs are not treated quickly, they can cause heart or lung damage and even death. Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center.
What tests are done to identify blood clots?
Blood tests (including the D-dimer test). Pulmonary angiogram. Ultrasound of the leg -- helps to identify blood clots in patients who cannot have an X-ray due to dye allergies or who are too sick to leave their hospital room. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the legs or lungs.
How is heparin given?
Heparin is a liquid medication and is given either through an intravenous (IV) line that delivers medication directly into the vein, or by subcutaneous (under the skin) injections given in the hospital. Low molecular-weight heparin is injected beneath or under the skin (subcutaneously).

Epidemiology
Etiology, Risk Factors, and Pathophysiology
- Treatment of pulmonary embolism is aimed at keeping the blood clot from getting bigger and preventing new clots from forming. Prompt treatment is essential to prevent serious complications or death.
Signs and Symptoms
Diagnosis
Management and Classification
Nonpharmacologic Options
Pharmacologic Options
Pharmacist’S Role
Conclusion