Medication
Finding cancer at an early stage improves the chance of curing the cancer. In people with protoporphyria, doctors may recommend protecting the liver by avoiding alcohol and getting hepatitis A and hepatitis B vaccines. If protoporphyria leads to liver failure, you may need a liver transplant.
Procedures
The American Porphyria Foundation (APF) can help you find a specialist in your area. Good nutrition is another important part of taking care of yourself when you have porphyria. Your doctor or dietitian will help you get the right balance of carbohydrates and nutrients in your meals.
Self-care
Episodes of acute porphyria, which rarely happen before puberty, can be set off by taking some kinds of drugs, including: Barbiturates Sulfa antibiotics Birth control pills Seizure medicines
Nutrition
Porphyria cannot be prevented. However, symptoms can be reduced by avoiding or eliminating triggers. Factors that should be eliminated include: Preventing erythropoietic symptoms focuses on reducing light exposure by:
What are the treatment options for protoporphyria?
How can I take care of myself if I have porphyria?
What drugs can set off porphyria?
Can erythropoietic porphyria be prevented?

How long can you live with porphyria?
Patients with porphyria generally have a normal life expectancy. However, those with acute hepatic porphyria are at increased risk of developing high blood pressure, chronic kidney disease, and hepatocellular carcinoma (liver cancer), which may reduce their lifespan.
Can you get rid of porphyria?
Although porphyria can't be cured, certain lifestyle changes to avoid triggering symptoms may help you manage it. Treatment for symptoms depends on the type of porphyria you have.
What causes porphyria?
These disorders are usually inherited, meaning they are caused by gene mutations link passed from parents to children. If you have porphyria, cells fail to change chemicals in your body—called porphyrins and porphyrin precursors—into heme, the substance that gives blood its red color.
What is the survival rate of porphyria?
Results: The 20-year survival was 42.9% (95% confidence interval [CI], 36.9-48.7) for patients with PCT compared with 60.5% (95% CI, 58.6-62.4) for matched control individuals.
What foods should be avoided with porphyria?
People with porphyria are advised to maintain a diet with an average or higher-than-average intake of carbohydrates, which can lessen disease activity—but they are also advised to avoid refined sugars, corn syrup and heavily processed foods.
What organs are affected by porphyria?
Porphyria occurs when the body cannot convert compounds called 'porphyrins' into heme. While all tissues have heme, those that use it the most are the red blood cells, liver and bone marrow. Porphyria can affect the skin, nervous system and gastrointestinal system. More women than men are affected by porphyria.
What does porphyria pain feel like?
Pain symptoms Severe abdominal pain is the most common symptom of acute porphyrias. Pain in other parts of the body, such as the chest, legs, or back, also may occur. Patients with acute porphyrias may experience muscle pain, sometimes accompanied by tingling, numbness, weakness, or paralysis.
When should you suspect porphyria?
The diagnosis of acute porphyria should be suspected, especially in women who present symptoms linked to their menstrual cycles more than once in the ED. Once suspected, the diagnosis of porphyria can be rapidly established by measuring urinary PBG.
What are the 8 types of porphyria?
The specific names of the eight types of porphyrias are:Delta-aminolevulinate-dehydratase deficiency porphyria.Acute intermittent porphyria.Hereditary coproporphyria.Variegate porphyria.Congenital erythropoietic porphyria.Porphyria cutanea tarda.Hepatoerythropoitic porphyria.Erythropoietic protoporphyria.
Is porphyria an autoimmune disease?
The aetiology of porphyria cutanea tarda (PCT) has not been elucidated, but the possibility of an autoimmune mechanism has been proposed. We report a case of an unknown clinical combination of PCT with autoimmune hypothyroidism, alopecia universalis and vitiligo with thyroid and parietal cell circulating antibodies.
Does porphyria worsen?
Early diagnosis and treatment of AIP are critical And symptoms may get worse over time. Untreated attacks can cause serious damage to your nervous system —including paralysis, and even death. That's why early diagnosis and treatment of AIP (acute intermittent porphyria) is so important.
What is the test for porphyria?
Lab tests are required to make a definitive diagnosis of porphyria and to determine which form of the disease you have. Different tests are performed depending on the type of porphyria your doctor suspects. Tests include a combination of blood, urine or stool testing.
How long does panhematin last?
Three to four mg/kg of Panhematin ® given once daily for four days early in an attack produces a highly beneficial effect in most patients. Commonly noted are decreases in pulse rate, blood pressure, abdominal pain, as well as decreased levels of urinary porphobilinogen (PBG). These effects can occur within a day.
What is GIVLAARI used for?
GIVLAARI is a treatment used to reduce acute hepatic porphyria (AHP) attacks in adults. There are 4 types of AHP: acute intermittent porphyria (AIP), variegate porphyria (VP), hereditary coproporphyria (HCP), and ALA-dehydratase deficient porphyria (ADP). GIVLAARI is given once a month as a subcutaneous injection (under the skin) by a healthcare professional.
Is there a cure for porphyria?
The American Porphyria Foundation (APF) promotes comprehensive care necessary for treating individuals with Porphyria. Although there is no cure for Porphyria, there is treatment available for each type of the disease.
Is heme therapy a treatment for mild attacks?
Intravenous glucose therapy is a treatment option for mild attacks. When heme therapy was introduced as a treatment, it was recommended that it be initiated only after several days of glucose therapy was unsuccessful.
What are the treatment options for acute porphyria?
Treatment options may include blood transfusions, surgery to remove the spleen, and liver and bone marrow transplantation.
How to treat acute porphyria?
Treatment for acute porphyria involves intravenous (IV) heme or glucose infusions (adding heme or glucose directly into a vein). These therapies decrease the number of porphyrins or porphyrin precursors produced in the liver. Other drugs are under investigation and may be available through clinical trials.
What is the classification of erythropoietic protoporphyria?
Erythropoietic protoporphyria. Doctors classify porphyrias in several different ways. Besides defining by each specific type, doctors also classify porphyria in two broad categories: Acute porphyrias - Onset is rapid. Symptoms last a short time, but they may come back from time to time.
What are the symptoms of porphyrias?
These symptoms generally occur suddenly and usually last a short period of time. Symptoms of acute porphyrias include: Pain in the abdomen, chest, arms, legs, or back.
How do you know if you have porphyria?
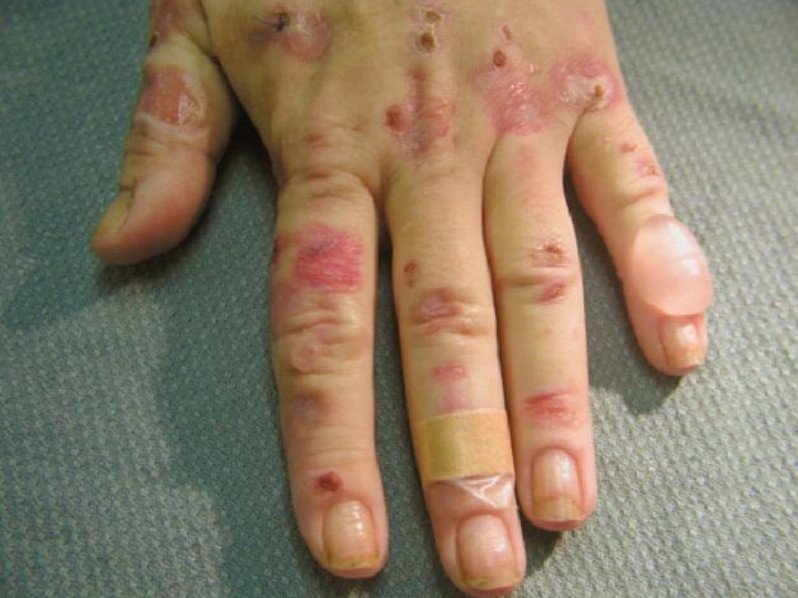
People living with cutaneous types of porphyria, which affects the skin, often experience symptoms including: Oversensitivity to sunlight. Itching. Swelling of skin exposed to sunlight. Abrasions, blisters on the skin, skin erosions. Scarring of sun exposed areas of the skin leading to fragile skin.
Where does porphyrin build up?
If there is a low level of any one of the enzymes needed to make heme, these porphyrin and porphyrin precursors build up in the liver, skin, and other body tissues. When they build up, people may develop symptoms of one of the types of porphyria. Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center.
Do acute porphyrias come back?
Symptoms last a short time, but they may come back from time to time. Most often, acute porphyrias affect the nervous system. Cutaneous porphyrias - Only the skin is affected. Doctors also classify porphyria by which body system becomes overactive:
What is a hepatoerythropoietic porphyria?
Hepatoerythropoietic porphyria (HEP) is the autosomal recessive form of familial porphyria vutanea tarda (f-PCT) and presents with similar symptoms. Skin sensitivity to light often leads to severe blistering, sometimes with mutilation or loss of fingers or facial features. Skin symptoms usually begin in infancy.
What is a porphyria?
What are porphyrias? Porphyrias are a group of rare inherited blood disorders. People with these disorders have problems making a substance called heme in their bodies. Heme is made of body chemicals called porphyrin, which are bound to iron.
What is the most common symptom of congenital erythropoietic porphyria?
The most common symptom is hypersensitivity of the skin to sunlight and some forms of artificial light. Blistering and lesions can often occur from exposure.
What is the most common symptom of variegate porphyria?
Sun sensitivity including blistering skin is the most common skin symptom of Variegate porphyria (VP). Acute attacks of VP often begin with abdominal pain. VP is more common in South Africa in people of Dutch ancestry with up to 3 in 1,000 people in the white population affected. Reports suggest.
What is the treatment for hepatic disease?
Treatments for hepatic disease include: beta-blockers, such as Atenolol, to manage blood pressure. approved givosiran in November 2019 for the treatment of adults with acute hepatic porphyria. The treatment was determined to have decreased the rate at which the liver produces toxic byproducts, leading to less attacks.
What are the two types of porphyria?
There are several types of porphyria, which are classified into two categories: hepatic. erythropoie tic. Hepatic forms of the disorder are caused by problems in the liver. They’re associated with symptoms such as abdominal pain and problems with the central nervous system.
Is porphyria a genetic disease?
Porphyria is a genetic disease. According to the National Institutes of Health (NIH), most types of porphyria are inherited from an abnormal gene, called a gene mutation, from one parent.
What is the treatment for porphyria?
Porphyria Treatment. When you have an outbreak of acute porphyria symptoms, you may need to stay in the hospital. You'll get medicine for pain, nausea, and vomiting. Your doctor may prescribe givosiran ( Givlaari), which helps reduce the toxins linked to the attacks.
How to treat porphyria cutanea tarda?
If you have porphyria cutanea tarda, your treatment might include: Regular removal of your blood to lower the amount of iron in your liver. This is called phlebotomy. Low doses of the antimalarial drug chloroquine or hydroxychloroquine. Your doctor may suggest that you avoid anything that triggers an outbreak.
How long does it take for a porphyria to heal?
Acute porphyria symptoms start quickly and last for a few days or weeks. Severe attacks of acute porphyria can sometimes cause nerve damage and muscle weakness that can take months to get better. Since cutaneous porphyria symptoms start when your skin is in sunlight, staying out of the sun will heal your skin and help prevent permanent damage.
How long does porphyria last?
The symptoms of acute porphyria can develop quickly and last for days or weeks. You might have an imbalance of salt in your body along with this type of porphyria.
When to do a porphyria test?
The best time for you to do these tests is when you have an outbreak of symptoms or around that time. Sometimes you'll get multiple tests to help your doctor figure out which specific type of porphyria you have. Your doctor may also suggest you get a genetic test.
Can you get a porphyria before puberty?
These triggers can be things like: Episodes of acute porphyria, which rarely happen before puberty, can be set off by taking some kinds of drugs, including: Other things that might trigger acute porphyria are:
Is porphyria rare?
It may take time to find the right doctors, because porphyria is so rare. The American Porphyria Foundation (APF) can help you find a specialist in your area. Good nutrition is another important part of taking care of yourself when you have porphyria.
How long does a porphyria last?
Acute porphyrias include forms of the disease that typically cause nervous system symptoms, which appear quickly and can be severe. Symptoms may last days to weeks and usually improve slowly after the attack. Acute intermittent porphyria is the common form of acute porphyria.
What are the symptoms of porphyria?
Signs and symptoms of acute porphyria may include: Severe abdominal pain. Pain in your chest, legs or back. Constipation or diarrhea. Nausea and vomiting. Muscle pain, tingling, numbness, weakness or paralysis. Red or brown urine. Mental changes, such as anxiety, confusion, hallucinations, disorientation or paranoia. Breathing problems.
What is the function of porphyrins?
Porphyrins are essential for the function of hemoglobin — a protein in your red blood cells that links to porphyrin, binds iron, and carries oxygen to your organs and tissues. High levels of porphyrins can cause significant problems. There are two general categories of porphyria: acute, which mainly affects the nervous system, and cutaneous, ...
Can high levels of porphyrin cause skin problems?
High levels of porphyrins can cause significant problems. There are two general categories of porphyria: acute, which mainly affects the nervous system, and cutaneous, which mainly affects the skin. Some types of porphyria have both nervous system symptoms and skin symptoms. Signs and symptoms of porphyria vary, ...
Can you have latent porphyria and never have symptoms?
Just because you inherit a gene or genes that can cause porphyria doesn't mean that you'll have signs and symptoms. You might have what's called latent porphyria, and never have symptoms. This is the case for most carriers of the abnormal genes.
Can you prevent porphyria?
Although there's no way to prevent porphyria, if you have the disease , avoid triggers to help prevent symptoms. Because porphyria is usually an inherited disorder, your siblings and other family members may want to consider genetic testing to determine if they have the disease, and get genetic counseling if needed.
Does a cutaneous porphyria affect the nervous system?
Cutaneous porphyrias include forms of the disease that cause skin symptoms as a result of sensitivity to sunlight, but these forms don't usually affect your nervous system. Porphyria cutanea tarda (PCT) is the most common type of all the porphyrias.
How long does porphyria last?
Symptoms of acute porphyria can be mild or severe, lasting days or weeks. Times when symptoms occur are called attacks. Without early treatment, symptoms of an attack may become more severe and even life-threatening. Symptoms may include
What are the symptoms of porphyria cutanea tarda?
In people with porphyria cutanea tarda, congenital erythropoietic porphyria, or hepatoerythropoietic porphyria, areas of skin exposed to sunlight may develop symptoms such as. blisters. fragile skin that is easily wounded and slow to heal. infection of blisters or wounds. scarring or changes in skin color.
What are the symptoms of cutaneous porphyria?
People with cutaneous porphyria may develop skin symptoms—such as blistering or pain —after their skin is exposed to sunlight.
How many people have porphyrias?
Porphyrias are rare diseases. Studies suggest that all types of porphyrias combined affect fewer than 200,000 people in the United States. 1. The most common type of acute porphyria is acute intermittent porphyria.
When does cutaneous porphyria occur?
Among types of cutaneous porphyria, porphyria cutanea tarda most often develops in people older than age 40, usually men. 2 For other types of cutaneous porphyria, symptoms often appear in early childhood.
Where do porphyrins build up?
Depending on the type of porphyria you have, porphyrins or porphyrin precursors may build up in the liver or the bone marrow. Bone marrow is the spongy tissue inside most of your bones.
Can porphyria cause liver problems?
Several types of porphyrias can cause liver problems. Acute porphyria increases the chance of developing liver cancer. NIH external link. . Porphyria cutanea tarda can damage the liver and increase the chance of developing cirrhosis and liver cancer.
How to help with porphyria?
Ask healthcare providers how you can learn to relax. Be careful with medicines: Certain medicines can trigger an acute porphyria attack, so ask your healthcare provider about the medicines you take.
Why is porphyria bad?
Porphyria prevents your body from creating enough enzymes to control the process, and porphyrin builds up. High levels of porphyrin can cause problems throughout your body, depending on where it builds up. Low levels of heme can also cause organ damage, because your blood cannot bring the organs enough oxygen.
What causes a porphyria attack?
The following can trigger an acute porphyria attack: Certain medicines. Sun exposure. Cigarettes and alcohol. Hormone changes, especially during pregnancy or a monthly period. Physical or mental stress. Dehydration, fasting, or crash dieting.
How long does a porphyria attack last?
Abdominal pain is the most common symptom of an acute porphyria attack. The pain is usually located in the lower abdomen, and may last for hours to days. You may also have any of the following: Pain, especially in your arms, legs, back, chest, neck, or head. Constipation or diarrhea.
What is the best medicine for high blood pressure?
These may include certain medicines to treat high blood pressure, seizures, pain, nausea, or vomiting. You may also need any of the following: Hemin: Hemin, also called hematin, is an enzyme made from RBC. It works by telling the body to slow down the production of the building blocks that make heme.
Can you refuse treatment?
You always have the right to refuse treatment. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Can you smoke if you have porphyria?
Do not smoke cigarettes or drink alcohol: Cigarettes and alcohol can make your acute porphyria worse. They may also damage the liver and further worsen your problems. Talk to your healthcare provider if you have trouble quitting smoking or drinking.
