Explore
13 rows · The therapy of infection due to Pneumocystis carinii has evolved in two areas over the past 20 ...
What is the initial treatment of aspiration pneumonia?
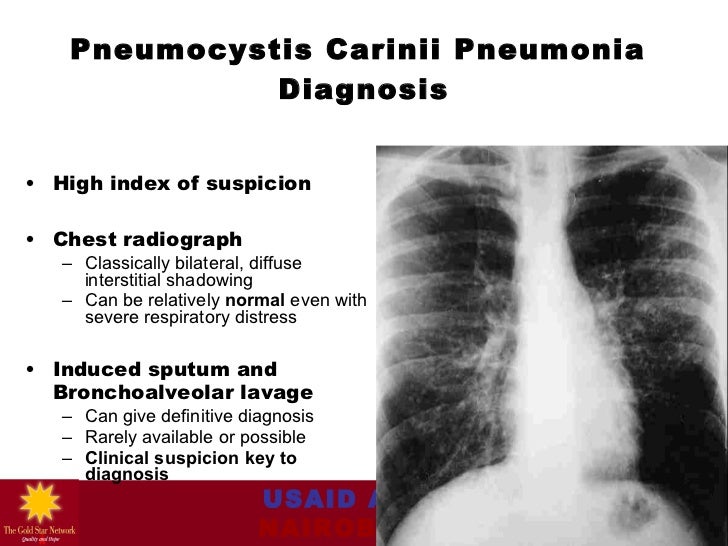
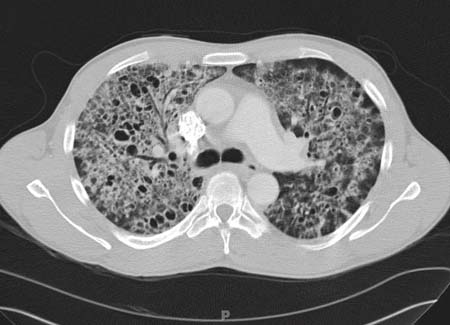
Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia (PCP) is seen in people with a defect in cell-mediated immunity. Today the most common cause for this is the Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS). There have been some remarkable advances recently in the development of new drug regimens to combat this otherwise fatal infection. Although cotrimoxazole (trimethoprim …
What are the treatment options for fungal pneumonia?
In patients who fail to respond to co-trimoxazole or who are intolerant to it, second line treatment is iv pentamidine in those with severe disease and oral dapsone with trimethoprim, oral clindamycin with primaquine or iv pentamidine in those with mild or moderately severe disease.
Is Mycoplasma pneumonia treatable?
The recommended dose of pentamidine isethionate for the treatment of PCP is 4 mg/kg/day, im. or i.v. A few studies have shown good response to aerosolized pentamidine. Trials of investigational agents have excluded patients with severely compromised respiratory status; eflornithine, dapsone in combination with trimethoprim, and trimetrexate have been used.
Is pneumonia curable in the elderly?
The most common form of treatment is trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole (TMP/SMX), which is also known as co-trimoxazole and by several different brand names, including Bactrim, Septra, and Cotrim. This medicine is given by mouth or through a vein for 3 weeks. TMP/SMX can cause side effects such as rash and fever.

What is the treatment of choice in Pneumocystis carinii?
The drug of choice for treatment and prophylaxis is trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, but alternatives are often needed because of adverse effects or, less commonly, treatment failure. Adjunctive corticosteroid therapy improves survival in moderate to severe cases.Oct 15, 1999
Which drugs are most effective at treating Pneumocystis carinii infections?
Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole. TMP-SMX is the agent of choice for the treatment of Pneumocystis pneumonia and extrapulmonary disease in all hosts who tolerate this combination agent (11, 26, 48, 59).
What is the recommended first line treatment for pneumocystis pneumonia?
First-line therapy for Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia (PCP) is trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole.Oct 26, 2009
What is the recommended medication for the treatment of choice for Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia?
The treatment of choice is TMP-SMX, with second-line agents including pentamidine, dapsone (often in combination with pyrimethamine), or atovaquone. However, there are a few reports of successful caspofungin administration in PJP.Apr 24, 2019
What causes pneumocystis carinii?
Pneumocystis pneumonia (PCP) is a serious infection that causes inflammation and fluid buildup in your lungs. It's brought on by a fungus called Pneumocystis jirovecii that spreads through the air. This fungus is very common. Most people's immune systems have fought it off by the time they're 3 or 4 years old.Dec 4, 2021
What is Pneumocystis carinii infection?
Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia is a fungal infection of the lungs. The disease used to be called Pneumocystis carini or PCP pneumonia. AIDS (acquired immune deficiency syndrome) is caused by HIV (human immunodeficiency virus), and is a syndrome that leaves the body vulnerable to a host of life-threatening illnesses.
Is Pneumocystis carinii primary or secondary immunodeficiency?
Pneumocystis carinii is an important opportun- istic pathogen in patients with poor T lym- phocyte function as a result of either primary or secondary immunodeficiency.
Which is usually the most important consideration in the decision to initiate antiretroviral therapy?
[17,18] Regardless of CD4 cell count, the decision to initiate ART should always include consideration of any co-morbid conditions, the willingness and readiness of the patient to initiate therapy, and the availability of resources.
Which one of the following medications provides sufficient prophylaxis for both Pneumocystis pneumonia and toxoplasma encephalitis?
Recommended Regimens for Primary Prophylaxis [17] Note that all recommended regimens for Toxoplasma encephalitis prophylaxis are also effective for Pneumocystis pneumonia prophylaxis. Preferred Therapy: Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole is the preferred agent for Toxoplasma encephalitis prophylaxis in individuals with HIV.
Why was Pneumocystis carinii renamed?
The common AIDS-related opportunistic infection Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia has been renamed Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia to more accurately identify the fungus that causes the infection.Oct 1, 2003
When should I take Bactrim prophylaxis?
Patients with less than 200 CD4+ T-cells/uL should receive PCP prophylaxis. Patients with constitutional symptoms such as thrush or unexplained fever greater than 100 F for greater than or equal to 2 weeks should also receive prophylaxis, regardless of their CD4+ T-cell count.
Is Pneumocystis carinii a fungus or protozoa?
Pneumocystis jirovecii (previously classified as Pneumocystis carinii) was previously classified as a protozoa. Currently, it is considered a fungus based on nucleic acid and biochemical analysis. Reference: Frenkel JK.
What is the best medicine for PCP?
The medicine most commonly used to prevent PCP is called trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole (TMP/SMX), which is also known as co-trimoxazole and by several different brand names, including Bactrim, Septra, and Cotrim. Other medicines are available for people who cannot take TMP/SMX.
What is the cause of pneumonia?
pneumonia. Pneumocystis pneumonia (PCP) is a serious infection caused by the fungus Pneumocystis jirovecii. Most people who get PCP have a medical condition that weakens their immune system, like HIV/AIDS, or take medicines (such as corticosteroids) that lower the body’s ability to fight germs and sickness.
How often is clindamycin given?
Clindamycin was given intravenously (600mg four times daily) or by mouth (300-450mg four times daily, usually after initial intravenous treatment) and primaquine by mouth (15mg daily). Rash developed in half the patients. Leucopenia, nausea and diarrhoea occurred in fewer than 1%.
Is trimetrexate a drug?
Trimetrexate, an antineoplastic drug related to methotrexate, and eflornithine, which suppresses cell growth, have been given to patients who have not responded to, or could not tolerate, co-trimoxazole or pentamidine. Neither is licensed in the UK. View this table: View inline. View popup.
Can P. carinii cause pneumonia?
P. carinii pneumonia also occurs in up to 85% ...