Why is recovery from pituitary surgery so damn slow?
Pituitary Macroadenoma Treatments Surgery Surgery is the best form of treatment and the only way to achieve a cure. Your surgeon will gain access to your pituitary gland using the transsphenoidal approach—so named because the route …
What is the prognosis of pituitary microadenomas?
The goal of treatment is complete cure. When this is not attainable, reducing tumor mass, restoring hormone function, and restoring normal vision …
How are pituitary microadenomas treated?
Apr 08, 2022 · The goal of treatment is complete cure. When this is not attainable, reducing tumor mass, restoring hormone function, and restoring normal …
What to do if you have a damaged pituitary gland?
Medicines to Treat Pituitary Tumors Common treatment approaches Sometimes a combination of treatments is used. For example, surgery may be done to remove some of the tumor, while drugs can be used to relieve symptoms and sometimes shrink the remaining tumor. Common treatment plans differ by tumor type.

How serious is a pituitary Macroadenoma?
Most pituitary adenomas are slow-growing and benign, which means they are not cancer and do not spread to other parts of the body. However, as they grow big they can put pressure on nearby structures, such as the nerves that connect the eyes to the brain, and cause symptoms.Mar 22, 2017
What causes pituitary Macroadenoma?
It is not known exactly what causes a pituitary macroadenoma. Some people inherit gene mutations that increase their risk of developing these tumors. Other cases are sporadic, meaning there is no family history. Gene mutations may still be involved in sporadic cases.
How do you get rid of pituitary Macroadenoma?
The two main surgical techniques for treating pituitary tumors are:Endoscopic transnasal transsphenoidal approach. This usually enables your doctor to remove the tumor through your nose and sinuses without an external incision. ... Transcranial approach (craniotomy).Oct 30, 2021
Is Macroadenoma serious?
Functional pituitary macroadenomas can cause a wide range of symptoms depending on the type of hormone it produces, potentially affecting growth, weight, sexual intimacy and more. Second, if the tumor presses on a normal part of the pituitary gland or surrounding nerves like the optic nerve, symptoms may also develop.
What is the best treatment for Macroadenoma?
The most frequently employed medications include bromocriptine, cabergoline, and, previously, pergolide. Quinagolide is an alternative with fewer adverse effects than bromocriptine. Prolactin-secreting macroadenomas are so responsive to medical therapy that surgery and radiation often are not used in treatment.Aug 11, 2021
What happens if a pituitary tumor goes untreated?
Most pituitary tumors are curable, but if left untreated, they can lead to serious complications such as complete vision loss.
Do Microadenomas need to be removed?
Surgical Care For prolactin-secreting microadenomas, surgical removal is followed by recurrence in 10-50% of patients. Therefore, medical therapy is preferred. Secretory tumors are best removed by the transsphenoidal approach.Aug 30, 2021
How long is pituitary surgery recovery?
It can take up to 6 weeks to fully recover. The cuts the doctor made (incisions) may be sore for about 5 days after surgery. You may also have numbness and shooting pains near your wound, or swelling and bruising around your eyes. As your wound starts to heal, it may start to itch.
What foods to avoid if you have a pituitary tumor?
Foods like Apricot and Beetroot should be eaten when undergoing Fluorouracil treatment for Pituitary Neuroendocrine Tumors. On the same lines, avoid foods like Cauliflower and Green Bean with treatment of Fluorouracil for Pituitary Neuroendocrine Tumors.Apr 14, 2021
How long can you live with pituitary adenoma?
The 5-year survival rate tells you what percent of people live at least 5 years after the tumor is found. Percent means how many out of 100. The 5-year survival rate for people with a pituitary gland tumor is 97%. Survival rates depend on the type of tumor, the person's age, and other factors.
Do Microadenomas grow?
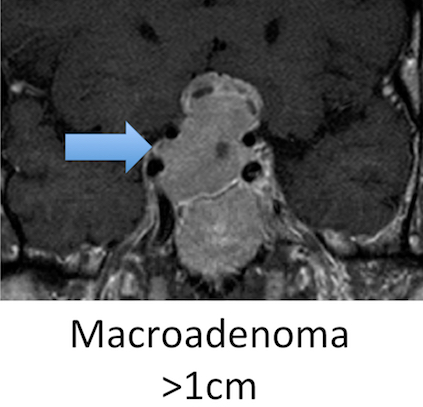
A microadenoma is less than one centimeter in size; a macroadenoma is one centimeter or greater in size. Aggressiveness. Nearly all pituitary adenomas are benign (noncancerous) and slow growing. An atypical pituitary adenoma, the rarer type, grows more quickly and is more likely to recur.
Can pituitary tumors cause death?
Vision problems occur when the tumor “pinches” the nerves that run between the eyes and the brain. Sudden loss of vision, loss of consciousness, and even death can result from sudden bleeding into the tumor. Macroadenomas and pituitary carcinomas can also press on and destroy the normal parts of the pituitary gland.Nov 2, 2017
How is pituitary cancer treated?
Corticotropin-secreting pituitary tumors are treated using surgery and radiation therapy (however, they are rather radioresistant). Medical therapy is reserved for patients whose therapy fails, those who decline other therapy, and those who cannot be treated otherwise.
Why was pergolide withdrawn from the market?
Pergolide was withdrawn from the US market March 29, 2007, because of heart valve damage resulting in cardiac valve regurgitation. It is important not to stop pergolide abruptly. Health care professionals should assess patients’ need for dopamine agonist (DA) therapy and consider alternative treatment.
Is octreotide a continuous infusion?
Octreotide is the treatment of choice. A long-acting formulation administered monthly is now available. Somatostatin must be administered as a continuous infusion, while shorter-acting octreotide is administered tid-qid. Growth hormone receptor antagonists have been another addition to the treatment of acromegaly.
Can acromegaly be treated with radiation?
That acromegaly can be treated with surgery alone is very unlikely. However, debulking the tumor is very important. Radiation therapy results in 50% reduction in growth hormone levels within 2 years, followed by an additional 25% in the following 2 years. Thereafter, the growth hormone levels decline more slowly.
What kind of doctor treats pituitary tumors?
Pituitary tumors often require care from a team of doctors. Doctors on your team may include: Neurosurgeon: a doctor who uses surgery to treat brain and pituitary tumors. Endocrinologist: a doctor who treats diseases in glands that make hormones. Neurologist: a doctor who diagnoses and treats brain and nervous system diseases.
What do people with cancer need?
People with cancer need support and information, no matter what stage of illness they may be in. Knowing all of your options and finding the resources you need will help you make informed decisions about your care.
Why are clinical trials important?
Clinical trials are one way to get state-of-the art cancer treatment. In some cases they may be the only way to get access to newer treatments. They are also the best way for doctors to learn better methods to treat cancer. Still, they're not right for everyone.
Is pituitary adenomas cancer?
Nearly all pituitary tumors are adenomas and not cancer (benign). Treatment of a pituitary adenoma depends on whether or not it makes excess hormones and, if it does, which hormone it makes. Treatment also depends on whether it's a microadenoma (smaller than 1 centimeter across) or a macroadenoma (1 centimeter across or larger).
What is a medical oncologist?
Medical oncologist: a doctor who uses chemotherapy and other medicines to treat cancers and other tumors. Many other specialists might be part of your treatment team as well, including physician assistants, nurse practitioners, nurses, psychologists, social workers, rehabilitation specialists, and other health professionals.
Can you continue cancer treatment?
Whether or not you continue treatment, there are still things you can do to help maintain or improve your quality of life.
What is complementary medicine?
Complementary methods refer to treatments that are used along with your regular medical care. Alternative treatments are used instead of a doctor’s medical treatment.
What is a pituitary adenomas?
Not applicable. Abstract. Pituitary adenomas are tumors that arise in the anterior pituitary gland. They are the third most common cause of central nervous system (CNS) tumors among adults. Most adenomas are benign and exert their effect via excess hormone secretion or mass effect.
What is the first line of treatment for prolactinoma?
Dopamine agonists are the first-line treatment for prolactinoma. Dop amine agonists bind to D2 receptors found on the surfaces of normal and tumorous lactotrophs. This binding alters the downstream signaling in lactotrophs and decreases prolactin secretion [17,32].
Where is the pituitary gland located?
The pituitary gland is located at the base of the brain, coming off the inferior hypothalamus, and weighs no more than half a gram. The pituitary gland is often referred to as the “master gland” and is the most important endocrine gland in the body because it regulates vital hormone secretion [1].
How many lobes are there in the pituitary gland?
Anatomically, the pituitary gland is divided into three lobes: anterior, intermediate, and posterior. The anterior lobe is composed of several endocrine cells, such as lactotropes, somatotropes, and corticotropes, which synthesize and secrete specific hormones.
