How can photodermatitis be prevented?
How do you treat Photoallergic dermatitis? Your allergist can prescribe creams — or, in some cases, oral medication — to relieve the itching and help the damaged skin to heal. Antihistamines and ointments can also help. Avoid scratching the affected area to prevent infection. How long does a rash from sunscreen last?
Can photodermatitis be acute or chronic?
· In other cases of photodermatitis, phototherapy can also be used to desensitize the skin and help control the symptoms. For people who are extremely sensitive to the sun, doctors may suggest azathioprine in order to suppress the immune system. You can also use glucocorticoids on a short term basis to help control further eruptions as well.
Should I see a doctor for photodermatitis?
With certain types of photodermatitis, doctors may use phototherapy (controlled exposure to light for treatment purposes) to desensitize the skin or to help control symptoms. Drug Therapies For extremely sun sensitive people, doctors may prescribe azathioprine to suppress the …
What is skin type 1 photodermatitis?
· Photochemotherapy (PUVA, psoralene + UV-A) has become established as the method of choice for severe forms of solar urticaria because this procedure can achieve longer remissions (2 to 3 weeks) compared to radiation without psoralene (a few days).

How do you treat Photoallergic dermatitis?
The main form of treatment for photosensitive dermatitis will typically include prevention methods, such as using sun protection, avoiding contact with any known allergens, and stopping any photosensitizing drugs if possible.
How do I get rid of photosensitivity rash?
Skin symptoms usually can be treated with a corticosteroid cream. Solar urticaria — For mild hives, you can try a nonprescription oral antihistamine to relieve itching, or an anti-itch skin cream containing cortisone.
How do you get rid of plant dermatitis?
Apply wet compresses, calamine lotion, or hydrocortisone cream to the skin to reduce itching and blistering.Follow the directions on any creams and lotions. Do not apply to broken skin, such as open blisters.Oatmeal baths may relieve itching.
Why am I suddenly allergic to the sun?
The most common form of sun allergy is polymorphic light eruption, also known as sun poisoning. Some people have a hereditary type of sun allergy. Others develop signs and symptoms only when triggered by another factor — such as a medication or skin exposure to plants such as wild parsnip or limes.
What is the best antihistamine for sun allergy?
Taking oral antihistamines can help relieve the rash and other photosensitivity symptoms caused by a sun allergy. The best antihistamine is the one that works well for you and fits your needs. Typically, this includes less drowsy antihistamines such as levocetirizine, loratadine, fexofenadine, and cetirizine.
Can photosensitivity be cured?
The mainstays of treatment of drug-induced photosensitivity include identification and avoidance of the causative agent, the use of sun protection, and the institution of measures for symptomatic relief. Topical corticosteroids and cool compresses may alleviate drug-induced photosensitivity.
Is Photodermatitis curable?
The symptoms of phytophotodermatitis can be worrisome, but the condition usually goes away on its own over time. More serious cases may be treated by a dermatologist.
What are the 5 poisonous plants that cause contact dermatitis?
Poison Ivy, Poison Oak, and 7 Other Plants That Can Give You a...Poison Ivy: The Best-Known Itchy Plant. ... Poison Oak: Not Related to Oak Trees. ... Poison Sumac: Same Itch as Poison Ivy and Oak. ... Wood Nettle: Beware the Stinging Hairs. ... Stinging Nettle: Close Relative of Wood Nettle. ... Baby's Breath: Irritating When Dried.More items...•
How long does it take for phytophotodermatitis to appear?
Research suggests that the symptoms of phytophotodermatitis usually begin 24 hours after exposure and peak after 48–72 hours. The symptoms, which can be mild or severe, include: large areas of blistering. itching.
What vitamins cause sun sensitivity?
Nutrition and Supplements If you do not get enough of some nutrients, your skin can become sensitive to sunlight. Pellagra, for example, is caused by a niacin deficiency and leads to photosensitivity. Other nutrients, particularly antioxidants and flavonoids, may help protect skin against sun damage in healthy people.
Can vitamin D supplements cause sun sensitivity?
There are three sources of vitamin D: synthesis by the skin following exposure to sunlight, certain foods (often through vitamin D fortification), and vitamin D supplements....Position Statement on Vitamin D (Revised: February 2014.Table 3. IOM Recommendation on Vitamin D0- 12 mo:400 IU/d71+ yrs:800 IU/d1 more row
What is a natural remedy for sun allergy?
Lifestyle and home remediesAvoid sun exposure. Most sun allergy symptoms improve in less than a day or two if you keep the affected skin out of the sun.Stop using medications that make you sensitive to light. ... Apply skin moisturizers. ... Use soothing skin remedies.
How to check for photodermatitis?
Your doctor may examine your condition by performing certain tests of blood and urine to check for any related diseases. Your medical history may also be needed in order to find out if the person was exposed to any chemical, drug or UV rays. Allergy tests may be helpful in identifying the trigger behind the problem. For cases where patients have blisters or weepy eruptions, applying cool and wet dressing may be helpful. In other cases of photodermatitis, phototherapy can also be used to desensitize the skin and help control the symptoms.
How long does photodermatitis last?
If the underlying cause is not treated properly then the reaction of photodermatitis can last for years after as well.
How to treat sun sensitivity?
For people who are extremely sensitive to the sun, doctors may suggest azathioprine in order to suppress the immune system. You can also use glucocorticoids on a short term basis to help control further eruptions as well. For cases where phototherapy cannot be used, hydroxychloroquine, nicotinamide, thalidomide, beta-carotene or nicotinamide are best alternatives to the problem. In most cases, the reactions to photosensitivity go away after a while and cause no permanent damage. But for symptoms which indicate an underlying cause when the exposure to UV rays was severe, the problem can become serious. In some cases, the reaction may also continue for years after.
What are some alternative treatments for rhodiola?
Other supplements and nutrition multivitamins, B-complex vitamins, Vitamin D and Omega-3 fatty acids can all be used as an alternative treatment to the problem.
Which skin type is most sensitive to UV rays?
Individuals with light skin or red and blond hair and green or blue eyes are most sensitive and have a higher risk of getting this condition. People who are exposed to the UV rays for more than 30 minutes at a time and people with the porphyria condition also have a very high risk of getting photodermatitis.
Can phototherapy cause erythema?
Using phototherapy as a method of treatment can also cause erythema which is the reddening of the skin due to exposure to the light. However, the occurrence usually resolves in a few hours. Other side effects of this treatment are headaches, diarrhea, premature aging of the skin among others. Medications like glucocorticoids can have side effects like increasing blood sugar level thereby causing long term diabetes, suppressing calcium uptake by bones thereby triggering osteoporosis, can cause gastritis and ulcers, increase triglycerides and cholesterol level in blood, suppressed immune system and inflammation. Azathioprine can have side effects like nausea and vomiting, diarrhoea and burning sensation and pain during urination.
What is photodermatitis?
5 Pictures. Photodermatitis is an acute or chronic inflammation; also known as sun poisoning, sun allergy or sun burn. It is a unique form of contact allergic dermatitis in the sense that the allergen that causes it does not produce the clinical manifestations, until such time that the skin is being exposed to sunlight to be activated ...
What conditions can cause photodermatitis?
These include systemic lupus erythematosus, solar urticarial, pellagra; these conditions may induce the occurrence of photodermatitis or be worsened by an exposure to UV rays of the sun.
What does it look like after sun exposure?
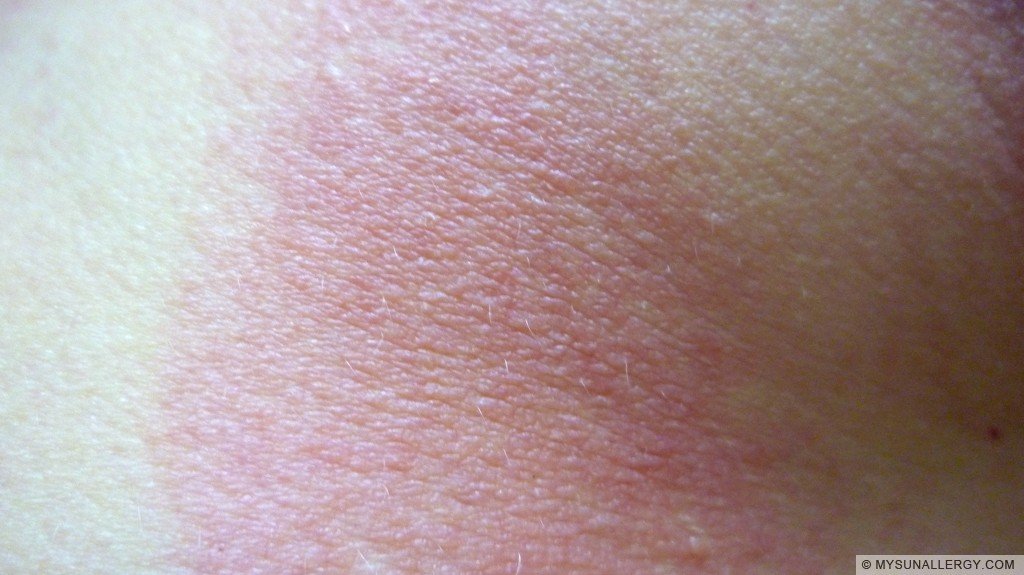
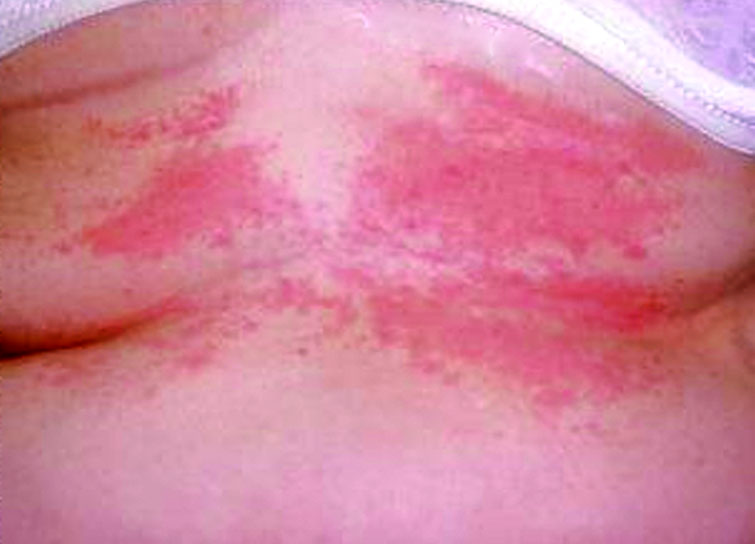
The main symptom of photodermatitis is the red itchy rash found on the skin, which looks like blisters, with peeling of the skin. These can be seen on areas where topical or chemical creams are being applied. The general signs and symptoms are as follows:
What are the long term effects of UV light?
Chills, headache, fever, and nausea may occur. Long-term effects include chronic skin thickening and scarring and an increased risk of skin cancer , if the cause is hereditary in characteristics.
How to tell if you have eczema from cream?
These can be seen on areas where topical or chemical creams are being applied. The general signs and symptoms are as follows: Itchy, scaly, blisters, or raised areas. Lesions that appears like an eczema. Hyperpigmented discoloration of the skin. Outbreaks in areas of skin which are overexposed to UV light.
What are some examples of photosensitizers?
The examples here are pellagra, xeroderma pigmentosum and variegate porphyria; the photosensitizer is being formed and deposited in the skin.
Can medications cause sun sensitivity?
Every person varies in terms of reactions to allergens with its vulnerability to sun light. It is believed that a lot of medications and conditions can trigger sun sensitivity. These conditions may include photosensitivity which is genetic or metabolic in nature or an exposure to some plants that the patient is sensitive with.
What causes photodermatitis?
Photodermatitis can have several causes, including: Genetic or metabolic factors (inherited diseases or conditions, such as pellagra, caused by lack of niacin and vitamin B-3) In reaction to UV rays, certain chemicals and drugs can cause sunburn, an eczema-like reaction, or hives.
How do you know if you have photodermatitis?
Signs and Symptoms. Signs of photodermatitis include: Itchy bumps, blisters, or raised areas. Lesions that resemble eczema. Hyperpigmentation (dark patches on your skin) Outbreaks in areas of skin exposed to light. Pain, redness, and swelling. Chills, headache, fever, and nausea.
What are some medications that help with acne?
Coal tar derivatives and psoralens, used topically for psoriasis. Retinoids, such as tretinoin and medications containing retinoic acid, used for acne. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
What are the diseases caused by UV rays?
Reactions to chemicals and medications. In reaction to UV rays, certain chemicals and drugs can cause sunburn, an eczema-like reaction, or hives.
Why is my skin sensitive to the sun?
Pellagra, for example, is caused by a niacin deficiency and leads to photosensitivity. Other nutrients , particularly antioxidants and flavonoids, may help protect skin against sun damage in healthy people. Antioxidants help protect skin from damage. Recent studies suggest that antioxidants, especially beta-carotene, may help lessen the symptoms of photodermatitis.
Do steroids help with photodermatitis?
People who need steroids to treat photodermatitis must be monitored closely. In addition, anyone with a history of photodermatitis or photoreactivity should keep track of the frequency and duration of symptoms. This information can help determine appropriate treatment.
Can you stop sun sensitivity medication?
Beware of using any product that causes sun sensitivity. (If you are already taking a prescription medication, however, DO NOT stop taking it without consulting your health care provider.)
What is primary photodermatosis?
Photodermatoses are differentiated into primary and secondary types (Box). Primary photodermatoses are induced by photosensitizing substances. They are referred to as idiopathic primary photodermatoses if the etiology is unknown (1, 2). Box.
What is photodermatosis caused by?
Results. Photodermatoses are caused by an abnormal reaction to sunlight, usually to its ultraviolet component. They are divided into phototoxic and photoallergic reactions to known photosensitizers and idiopathic photodermatoses, in which the photosensitizer is unknown.
What is the differential diagnosis of papular eczema?
With the papular or papulovesicular type, differential diagnosis indicates photoallergic eczema, ictus or prurigo simplex. The underlying cause of plaque-type lesions may be delayed onset solar urticaria, erythema multiforme and even lupus erythematosus (LE), particularly the tumid type. However, a latency of 1 to 3 weeks after sun exposure and a long healing time is typical for LE. A dermatological maxim states that “a patient gets PMLE on holiday but brings LE home.” Although PMLE is the most important differential diagnosis for cutaneous LE, it virtually never changes into LE, even if nonspecific positive antinuclear antibodies are present (2, 6).
How to prevent PMLE?
Total body radiation using UV-A and/or UV-B is suitable. Preventative radiation should only be administered under specialist medical supervision and not in a solarium in order to ensure minimal UV exposure. Topical application of broad-spectrum sunscreen is useful. This predominantly benefits UV-B-induced polymorphous light eruption. With an extremely low UV-A threshold, PMLE episodes cannot be prevented even with very potent UV-A filters. General sun protection measures such as covering with clothes and appropriate, sensible behavior are also useful. An interesting new approach to preventative external therapy involves topical application of suitable antioxidants, because pathophysiologically the inflammation reactions are most likely mediated by free radicals generated in the skin. Photochemotherapy is exceptionally effective but should, however, be reserved for extremely light-sensitive patients (7).
What is solar urticaria?
Solar urticaria. Induction of erythema and wheals after radiation with UV-A
How to prevent eczema from dermatitis?
Avoiding the radiation that triggers the dermatitis has the highest priority. Due to the large action spectrum, the use of particularly intensive sun protection is important . In extreme cases artificial lighting at work can also contribute to continued persistence of the eczema. Shifting leisure activities to the evening and night, wearing light-blocking clothing, and full-coverage, tinted make-up preparations can also help.
How to treat polymorphous light eruption?
The first is simple as avoiding further sun exposure leads to rapid and spontaneous remission. It can be accelerated by external application of glucocorticoids . Antihistamines may alleviate the pruritus but their value should not be overestimated. The same applies to topical antihistamines.
What is the best medicine for photodermatitis?
Treatment of Photodermatitis. Medications: Doctors migh prescribe any of the following medicines: – Glucocorticoids that target skin eruptions. – Nicotinamide or thalidomide used for those who cannot use phototherapy. – Azathioprine to treat sensitivity towards UV rays to treat photodermatitis.
Which conditions cause photodermatitis?
Immunological Diseases: Conditions such as solar urticarial, pellagra and systemic lupus erythematosus are capable of causing and worsening photodermatitis. Exposure to ultraviolet rays of the sun is known to aggravate the condition even further.
What is the condition that causes sunburn?
Photodermatitis is a condition that refers to the inflammation of the skin and is also known as sun allergy, sun burn or sun poisoning. The primary factor that triggers this problem is the Sun itself, i.e. the allergens that react against the skin are only able to manifest themselves when the skin is exposed to the sunlight.
What are the different types of photodermatitis?
Types of Photodermatitis. Genetic or Metabolic Photodermatoses: In this type, the phoyosensitizer is formed and deposited on the skin. Examples include variegate porphyria, pellagra and xeroderma pigmentosum. These conditions are commonly prevalent in the individual’s family, which indicates towards a genetically induced problem.
What color eyes are prone to photodermatitis?
Irrespective of their racial or ethnic background, people with fair or light skin, blonde or red hair and blue or green eyes are highly prone to suffer from a condition of photodermatitis
What is idiopathic photodermatosis?
Idiopathic Photodermatoses: The photosensitization reaction remains unknown for this type of dermatitis. They include actini prurigo, polymorphic light eruptions, chronic actini dermatitis and solar urticaria.
What vitamins are needed for photodermatitis?
Nutrition: Food that is eaten must be a balanced diet to ensure that they contain adequate amount of vitamins that help to treat and prevent photodermatitis. Antioxidant vitamins A, C, E, D and B – complex, magnesium, calcium, zinc, selenium, omega 3 fatty acids and alpha lipoic acid must be taken in correct amounts to treat such a condition.
What is a photo patch test?
Photopatch testing. This test shows whether your sun allergy is caused by a sensitizing substance applied to your skin before you go into the sun. In the test, identical patches of common sun allergy triggers are applied directly to your skin, typically on your back. A day later, one of the areas receives a measured dose ...
How to diagnose sun allergy?
In many cases, doctors can diagnose sun allergy simply by looking at the skin. But if the diagnosis isn't clear-cut, you may need tests to help identify what's going on. These tests may include: 1 Ultraviolet (UV) light testing. Also called phototesting, this exam is used to see how your skin reacts to different wavelengths of ultraviolet light from a special type of lamp. Determining which particular kind of UV light causes a reaction can help pinpoint which sun allergy you have. 2 Photopatch testing. This test shows whether your sun allergy is caused by a sensitizing substance applied to your skin before you go into the sun. In the test, identical patches of common sun allergy triggers are applied directly to your skin, typically on your back. A day later, one of the areas receives a measured dose of ultraviolet rays from a sun lamp. If a reaction occurs only on the light-exposed area, it likely is linked to the substance being tested. 3 Blood tests and skin samples. These tests usually aren't needed. However, your doctor may order one of these tests if he or she suspects your symptoms might be caused by an underlying condition, such as lupus, instead of a sun allergy. With these tests, a blood sample or a skin sample (biopsy) is taken for further examination in a laboratory.
What is UV light testing?
Also called phototesting, this exam is used to see how your skin reacts to different wavelengths of ultraviolet light from a special type of lamp. Determining which particular kind of UV light causes a reaction can help pinpoint which sun allergy you have. Photopatch testing.
How to stop being sensitive to the sun?
Stop using medications that make you sensitive to light. If you're taking medications for other conditions, talk with your doctor about whether you can stop taking them if they are making your skin more sensitive to the sun.
Can you take corticosteroid cream over the counter?
Creams containing corticosteroid s are available over-the-counter and in stronger prescription forms. For a severe allergic skin reaction, your doctor may prescribe a short course of corticosteroid pills, such as prednisone.
What is the goal of photodermatitis treatment?
The main goal of treatment is to identify the photosensitising agent and if possible to avoid touching it. Photodermatitis is a self-limited problem that resolves spontaneously once the offending agent is removed or avoided.
What is photocontact dermatitis?
Photocontact dermatitis is a toxic or allergic reaction that may occur when certain chemicals are applied to the skin and subsequently exposed to the sun.
What is a phototoxic reaction?
A phototoxic reaction generally appears similar to a bad sunburn. A photoallergic reaction generally presents as eczema (also called dermatitis) confined to the areas in contact with the responsible chemical and exposed to the sun. Photocontact dermatitis. Photocontact dermatitis. Photocontact dermatitis.
What is the difference between phototoxic and photoallergic?
Phototoxic reactions result from direct damage to tissue caused by light activation of the photosensitising agent. Photoallergic reactions are a cell-mediated immune response in which the antigen is the light-activated photosensitising agent.
Which plant family causes phytophotodermatitis?
Other plant families that cause phytophotodermatitis are Rutaceae, Moraceae and Leguminosae. The main photosensitising substances found in these plants are called furocoumarins and consist of psoralens and 5-methoxypsoralens, 8-methoxypsoralens, angelicin, bergaptol and xanthotal. Plant family.
What is the dark mark on the skin?
Skin lesions may leave behind a dark mark on the skin ( postinflammatory hyperpigmentation ).
What is the best sunscreen for allergies?
If allergic to a sunscreen agent, choose one without the responsible chemical or select a low irritant formula that relies on metal oxides such as zinc oxide or titanium dioxide .
How to prevent phytophotodermatitis?
The inflammatory skin reaction associated with phytophotodermatitis may be prevented by: Identifying the plants that are skin allergens or irritants and take steps to avoid contact with them. Washing hands with plain soap and water following cooking, spending time outdoors, or contact with plants.
What are the risks of phytodermatitis?
However, several factors may increase the risk of experiencing phytophotodermatitis. These include: exposure to certain plants and plant-based products. using perfumes or oils that contain certain plant chemicals.
What is the term for a person who is exposed to sunlight?
Phytophotodermatitis occurs when someone is exposed to plant chemicals and subsequently exposed to sunlight. Symptoms typically arise after direct contact with the plant, such as by touching. Many plants and vegetables contain chemical compounds that cause sensitivity to sunlight.
How long does it take for phytophotodermatitis to appear?
Meadow grass is one plant that may cause this skin reaction. The symptoms of phytophotodermatitis usually begin 24 hours. Trusted Source. after exposure and peak between 48-72 hours. Symptoms can be mild or severe and include:
How long does it take for phytodermatitis to show symptoms?
Research suggests that the symptoms of phytophotodermatitis usually begin 24 hours after exposure and peak after 48–72 hours. The symptoms, which can be mild or severe, include:
What does it mean when you have blisters on your skin?
The patches of blisters are usually irregularly shaped. The patterns represent the areas of the skin that were exposed to the chemical. For example, blisters in the pattern of drips may result from exposure to fruit juice. Streaks may indicate that a person brushed their skin against a plant.
How to prevent hyperpigmentation?
Reducing sun exposure: Spending less time in the sun, especially when UV rays are at their strongest, may help prevent hyperpigmentation from becoming even darker. Also, a person should always wear sunscreen when they cannot avoid sun exposure.
What Is Photodermatitis?
Signs and Symptoms
- The associated signs and symptoms will be remarkable after undue sun exposure with the relative sensitivity of the skin to the UV rays of the sun. The main symptom of photodermatitis is the red itchy rash found on the skin, which looks like blisters, with peeling of the skin. These can be seen on areas where topical or chemical creams are being applied. The general signs and symptoms …
Causes of Photodermatitis
- Every person varies in terms of reactions to allergens with its vulnerability to sun light. It is believed that a lot of medications and conditions can trigger sun sensitivity. These conditions may include photosensitivity which is genetic or metabolic in nature or an exposure to some plants that the patient is sensitive with. The causes for Photodermatitis can be classified as follows:
Treatment
- Methods of prevention
The best treatment for the disease is the observation of preventive measures from having the disease condition to occur. The person has to limit sun exposure, especially the midday sunlight as this can trigger the situation. If there are certain medications being prescribed, it is best to as… - Treatment guide
The application of cool, wet dressings are found helpful to relieve blisters or any skin eruptions due to UV exposure. Phototherapy is recommended by some attending physicians to patients in order to desensitize the skin or to minimize the symptoms.
Pictures
- References 1. Signs and Symptoms, What Causes It?, Who is Most At Risk?, What to Expect at Your Provider’s Office, Treatment Options, Prognosis/Possible Complications at http://pennstatehershey.adam.com/content.aspx?productId=107&pid=33&gid=000155 2. Photodermatitis : Signs and Symptoms, Complementary and Alternative Therapies, Herbs, Home…