What should I do if I've been overexposed to radiation?
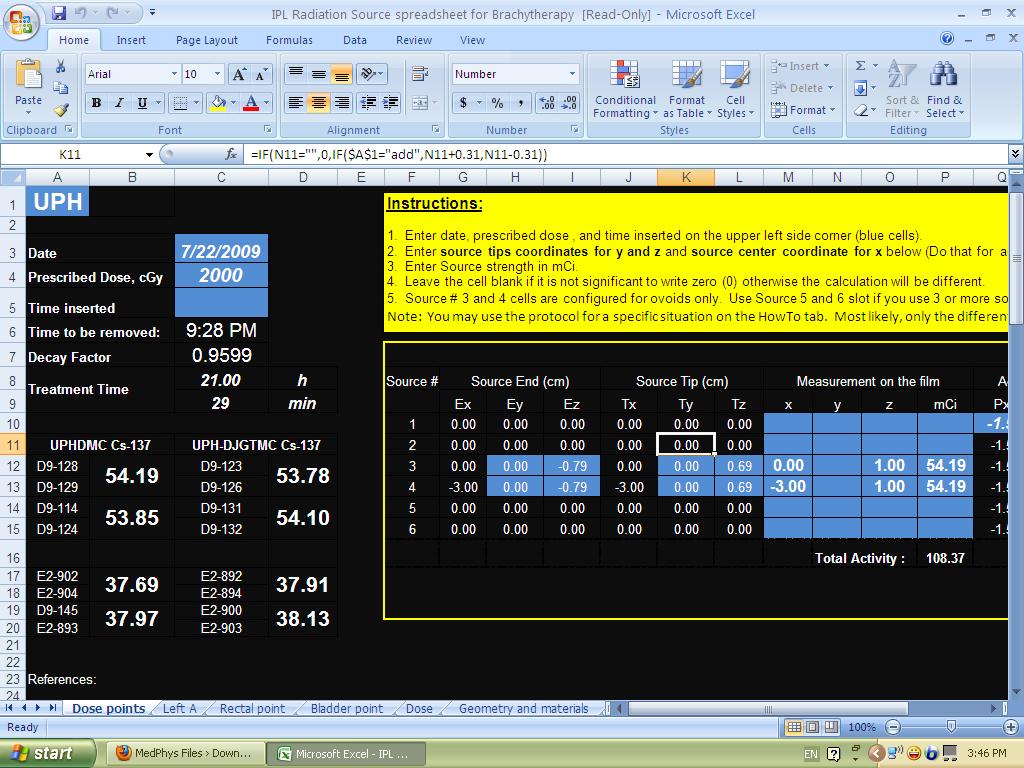
Jul 08, 2016 · The radiation dose that is prescribed by the oncologist is the dose to the point of treatment. However, since radiation is absorbed by the skin and deeper tissues before reaching the point of treatment, the dose at the surface of the skin needs to be higher than the prescribed dose to allow for this attenuation.
What are the treatment options for radiation poisoning?
Nov 07, 2020 · Radiation is the energy released from atoms as either a wave or a tiny particle of matter. Radiation sickness is caused by exposure to a high dose of radiation, such as a high dose of radiation received during an industrial accident. Sources of high-dose radiation. Possible sources of high-dose radiation include the following:
How common is overexposure to radiation?
Mar 19, 2015 · A case of radiation overexposure was defined as presenting at least one of the following criteria: (i) unintended global overexposure of 1 Gy or more, (ii) unintended local skin overexposure of 3 Gy or more, (iii) unintended local organ overexposure (e.g. brain, thyroid, prostate) of 5 Gy or more, or (iv) description of clinical presentation ...
How to reduce the effects of radiation exposure naturally?
May 03, 2017 ·

Is there any treatment for radiation exposure?
There is no cure, but barriers can prevent exposure and some medications may remove some radiation from the body. Anyone who believes they have been exposed to radiation should seek medical attention as soon as possible.
What happens if you are overexposed to radiation?
Exposure to very high levels of radiation, such as being close to an atomic blast, can cause acute health effects such as skin burns and acute radiation syndrome (“radiation sickness"). It can also result in long-term health effects such as cancer and cardiovascular disease.Apr 14, 2021
How do you treat radiation damage?
To treat side effects from radiation during cancer treatment, your doctor may prescribe antinausea medications, oral rinses for your mouth, and hydrocortisone cream for your skin. There is one drug, amifostine, that may be used to protect against radiation damage.Jan 5, 2015
How do you block radiation?
Shielding: Barriers of lead, concrete, or water provide protection from penetrating radiation such as gamma rays and neutrons. This is why certain radioactive materials are stored under water or in concrete or lead-lined rooms, and why dentists place a lead blanket on patients receiving x-rays of their teeth.
Can you survive radiation poisoning?
Radiation damages your stomach and intestines, blood vessels, and bone marrow, which makes blood cells. Damage to bone marrow lowers the number of disease-fighting white blood cells in your body. As a result, most people who die from radiation sickness are killed by infections or internal bleeding.Oct 19, 2020
What is the radiation sickness?
Acute Radiation Syndrome (ARS) (sometimes known as radiation toxicity or radiation sickness) is an acute illness caused by irradiation of the entire body (or most of the body) by a high dose of penetrating radiation in a very short period of time (usually a matter of minutes).
Why is iodine important for thyroid function?
Iodine is essential for proper thyroid function. If you're exposed to significant radiation, your thyroid will absorb radioactive iodine (radioiodine) just as it would other forms of iodine. The radioiodine is eventually cleared from the body in urine.
What is the device that measures radiation?
Dosimeter . A device called a dosimeter can measure the absorbed dose of radiation but only if it was exposed to the same radiation event as the affected person. Survey meter. A device such as a Geiger counter can be used to survey people to determine the body location of radioactive particles. Type of radiation.
How does decontamination work?
Decontamination involves removing external radioactive particles. Removing clothing and shoes eliminates about 90 percent of external contamination. Gently washing with water and soap removes additional radiation particles from the skin. Decontamination prevents radioactive materials from spreading more.
When a person has experienced known or probable exposure to a high dose of radiation from an accident or attack, what
When a person has experienced known or probable exposure to a high dose of radiation from an accident or attack, medical personnel take a number of steps to determine the absorbed radiation dose. This information is essential for determining how severe the illness is likely to be, which treatments to use and whether a person is likely to survive.
What is the treatment for bone marrow damage?
Treatment for damaged bone marrow. A protein called granulocyte colony-stimulating factor, which promotes the growth of white blood cells, may counter the effect of radiation sickness on bone marrow. Treatment with this protein-based medication, which includes filgrastim (Neupogen), sargramostim (Leukine) and pegfilgrastim (Neulasta), ...
How long does it take for a person to die from radiation?
Depending on the severity of illness, death can occur within two days or two weeks. People with a lethal radiation dose will receive medications to control pain, nausea, vomiting and diarrhea.
What is DTPA treatment?
Diethylenetriamine pentaacetic acid (DTPA). This substance binds to metals. DTPA binds to particles of the radioactive elements plutonium, americium and curium.
Overexposure in Diagnostics
The development of CT scans and nuclear imaging technologies has revolutionized the way that illnesses are diagnosed. These tests can detect much more than a standard X-ray machine, and have saved thousands of lives.
Overexposure in Treatments
Radiation treatments provide their most dramatic results when they are purposely used to destroy tissue. While the treatments can be targeted to kill cancer cells or eliminate other abnormal tissues, these treatments can be lifesaving.
Preventing Overexposure
Radiation treatments and imaging always have the potential for side effects, but this possibility can be minimized with responsible patient care. For example, a CT scan can deliver approximately 450 times the amount of radiation than an X-ray does, making it a test which should be used sparingly if possible.
What are the drawbacks of living in a high tech society?
One of the drawbacks of living in a high tech society is that our population is being exposed to increasing amounts of radiation. In the medical field, radiation is a part of more diagnostic tests and treatments than ever before. The improper administration of radiation or accidental irradiation of patients can cause serious immediate injuries as well as have long term consequences on the patients’ health. When radi ation is administered improperly or patients receive incorrect doses, the patients and their families have the right to receive compensation for the cost of treating any ensuing injuries or conditions that may result along with the pain and suffering caused by the error.
How does radiation affect MRI?
Most of us are unaware of how integral radiation has become to diagnostic testing and the treatment of illnesses. While everyone is aware of the use of radiation during X rays, it is less common knowledge that MRI tests are performed while using ionized radiation in order to produce the images generated in the scans. Every imaging test utilizes radiation to some degree and it is estimated that the average person today will be exposed to seven times as much radiation during his or her life than in previous generations.
Is radiation therapy good for cancer?
Radiation therapy is also very popular in the treatment of various forms of cancers. Unfortunately, the misapplication of radiation may result in the worsening of the cancer or the development of new cancer cells— especially in cases where the radiation is administered to the wrong area of the body.
What are the symptoms of radiation poisoning?
Short term symptoms of overexposure to radiation begin with nausea, headaches, fever, vomiting and visible burns to the skin . These symptoms can then develop into dizziness, fatigue, hair loss, lowered blood pressure, bloody stool and the development of cancer as the patient suffers from radiation poisoning.
What are the causes of radiation overexposure?
The main causes of radiation overexposure include the following. Defective equipment that administers incorrect doses of radiation either during radiation therapy or diagnostic testing. Failure of technicians to follow required safety protocol to ensure that the patient is protected from radiation during diagnostic tests.
What is radiation induced illness?
Then, when they finally spotted and treated the cancer, they negligently performed the operation. The patient ended up suffering fibrosis and other issues because of the way they administered the radiation. Radiation-induced illness is definitely a form of negligence as well as medical malpractice and that is exactly what the plaintiff claimed in the subsequent lawsuit. Its mere existence suggests something improper was done and the defendants realized as much when they opted to settle instead of pressing their case at trial. The plaintiff obtained $300,000 in this radiation malpractice case out of Illinois.
What are the effects of radiation?
Common signs of low-level radiation exposure include fatigue, headaches, nausea, scalp tenderness, scalp discoloration, and dry/itchy skin. [ 1] In extreme cases, continued low-level exposure to radiation may also cause brain damage, memory concerns, mood changes and reduced listening capacities, psychomotor abilities, and information processing times. Exposure to low levels of radiation over a long time may increase the likelihood of developing leukemia and lymphoma in the future. [ 2]
Does radiation cause lymphoma?
Exposure to low levels of radiation over a long time may increase the likelihood of developing leukemia and lymphoma in the future. [ 2] Low level exposure to radiation also affects the circulatory system by reducing lymphocytes – a type of white blood cell.
What are the effects of radiation on the reproductive system?
The reproductive system is also vulnerable to radiation, and long-term exposure can lead to sterility, birth defects, and still-births. [ 3] Exposure to high levels of radiation can cause acute radiation syndrome, or mild radiation sickness. [ 4] .
Does bee pollen help with radiation?
Initial evidence suggests that bee pollen may significantly lower the negative side effects of radiation exposure. Bee pollen has antioxidant properties, which allows it to scavenge the free radicals in the body that are generated by radiation. Studies on rat brain cells found the application of bee pollen plus beta-carotene halted the effects of ionizing radiation. [ 20, 21] Because exposure to radiation lowers many of your body's natural vital substances like white and red blood cells and antibodies, bee pollen is a natural way of boosting these vital functions. [ 20]
What are the best natural remedies for radiation?
Below are 13 of the best natural remedies for exposure to radiation. 1. Nascent Iodine.
What is the radioactive isotope of cesium?
In addition to radioactive iodine, the body may be exposed to a radioactive isotope of cesium known as cesium-137, formed as a byproduct of nuclear fission. Potassium iodide can prevent the accumulation of cesium-137 and weaken the damage caused by radiation exposure. [ 5]
What is the best form of potassium to use for radiation exposure?
According to the CDC, potassium iodide can play a major role in protecting the body and thyroid gland after internal contamination, as in the example of the Japanese nuclear reactor explosion. Potassium iodide is the best form of potassium to use for radiation exposure. 3. Calcium and Magnesium.
What is radiotherapy in cancer?
Radiotherapy involves a series of stages , beginning with clear identification of the size, shape, and position of the tumour (or other region of tissue) to be treated, followed by planning of how best to direct the radiation at the treatment site while minimising damage to healthy surrounding tissue. The resulting plan is then used ...
Where does myeloma occur?
Myeloma is a cancer that develops in the plasma cells found in bone marrow. These malignant myeloma cells produce abnormal proteins that can have a number of serious health consequences, including weakened bones and an increased risk of fractures. This typically occurs in the most active bone marrow, which includes the marrow in the spine, pelvic bones, and hips, and because numerous sites can be affected, the disease is often referred to a 'multiple myeloma'.
What is radiation dose?
The radiation dose that is prescribed by the oncologist is the dose to the point of treatment. However, since radiation is absorbed by the skin and deeper tissues before reaching the point of treatment, the dose at the surface of the skin needs to be higher than the prescribed dose to allow for this attenuation.
What is radiation sickness?
Overview. Radiation sickness is damage to your body caused by a large dose of radiation often received over a short period of time (acute). The amount of radiation absorbed by the body — the absorbed dose — determines how sick you'll be. Radiation sickness is also called acute radiation syndrome or radiation poisoning.
Is radiation sickness fatal?
Although radiation sickness is serious and often fatal, it's rare. Since the atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, Japan, during World War II, most cases of radiation sickness have occurred after nuclear industrial accidents, such as the 1986 explosion and fire that damaged the nuclear power plant at Chernobyl, Ukraine.
What to do in a radiation emergency?
In the event of a radiation emergency, stay tuned to your radio or television to hear what protective actions local, state and federal authorities recommend. Recommended actions will depend on the situation, but you will be told to either stay in place or evacuate your area.
What to do if you are evacuated?
If you're advised to evacuate, follow the instructions provided by your local authorities. Try to stay calm and move quickly and in an orderly manner. In addition, travel lightly, but take supplies, including: Flashlight. Portable radio.
How long does it take for a person to show signs of exposure?
If you've had a mild exposure, it may take hours to weeks before any signs and symptoms begin. But with severe exposure, signs and symptoms can begin minutes to days after exposure. Possible symptoms include: Nausea and vomiting. Diarrhea.
Abstract
The aim of this review paper is to examine medical overexposure accidents related to new technologies in radiation therapy during the period 2000–2009.
Introduction
The discovery of the X-ray at the end of nineteenth century spurred the use of radiation in medicine for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. Consequently, new diagnostic and therapeutic techniques developed rapidly and contributed to improvements in healthcare.
Definition of radiation therapy accidents
There are several definitions of accidental exposure. According to the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA), International Basic Safety Standards [ 3 ], an accidental medical exposure is defined as:
Material and methods
Reported radiation therapy overexposures from 2000 to 2009 were searched in English (mainly) and Japanese using the following sources:
Results
Initially, a total of 30 RT treatment centers with overexposure cases were reviewed using 47 overexposure accident reports. Seven accidents were reported in two different sources, and five accidents were reported in three different sources. Six cases were excluded according to the criteria of the review.
Case study by type of error
In April 2006, the new stereotactic unit in the clinic was commissioned by the physicist. This unit operated with micro-multi leaf collimators (MLCs), which create clinically usable fields of small size (6 × 6 mm), or conical standard collimators. Data collected for micro-MLC and standard collimators are handled separately.
Discussion
This review included major RT overexposure accident reports related to new RT technologies from national and international organizations in radiation management and the review of the largest international and national accident registry, ROSIS, US-NRC for the period 2000–2009.
What are the effects of radiation?
Short-Term Health Effects of Radiation Exposure and Contamination 1 Acute Radiation Syndrome#N#Radiation sickness, known as acute radiation syndrome (ARS). 2 Cutaneous Radiation Injury (CRI)#N#Happens when exposure to a large dose of radiation causes injury to the skin.
What is the cause of radioactive contamination?
Radioactive contamination and radiation exposure could occur if radioactive materials are released into the environment as the result of an accident, an event in nature, or an act of terrorism. Such a release could expose people and contaminate their surroundings and personal property. Learn more.
Can radiation cause cancer?
People who receive high doses of radiation could have a greater risk of developing cancer later in life, depending on the level of radiation exposure. Prenatal Radiation Exposure.

Overexposure in Diagnostics
- When a person has experienced known or probable exposure to a high dose of radiation from an accident or attack, medical personnel take a number of steps to determine the absorbed radiation dose. This information is essential for determining how severe the illness is likely to be, which treatments to use and whether a person is likely to survive. Information important for determinin…
Overexposure in Treatments
Preventing Overexposure
The Increased Use of Radiation in The Diagnosis and Treatment of Illness
- The development of CT scans and nuclear imaging technologies has revolutionized the way that illnesses are diagnosed. These tests can detect much more than a standard X-ray machine, and have saved thousands of lives. While the creation of these tests was obviously beneficial for the vast majority of patients, overuse of CT tests and miscalibrated machines have injured hundred…
Injuries Caused by Radiation Over-Exposure
- Radiation treatments provide their most dramatic results when they are purposely used to destroy tissue. While the treatments can be targeted to kill cancer cells or eliminate other abnormal tissues, these treatments can be lifesaving. However, when the patient’s radiation treatments go awry, or when the patient receives much more radiation than was intended, the same treatment …
Causes of Overexposure
- Radiation treatments and imaging always have the potential for side effects, but this possibility can be minimized with responsible patient care. For example, a CT scan can deliver approximately 450 times the amount of radiation than an X-ray does, making it a test which should be used sparingly if possible. Patients should discuss the possible side effects of repeated scans or ima…
Radiation Over-Exposure Malpractice Awards
- Most of us are unaware of how integral radiation has become to diagnostic testing and the treatment of illnesses. While everyone is aware of the use of radiation during X rays, it is less common knowledge that MRI tests are performed while using ionized radiation in order to produce the images generated in the scans. Every imaging test utilizes radiation to some degre…
Our Team Can Help You If You Have Been Exposed to Radiation
- Short term symptoms of overexposure to radiation begin with nausea, headaches, fever, vomiting and visible burns to the skin. These symptoms can then develop into dizziness, fatigue, hair loss, lowered blood pressure, bloody stool and the development of cancer as the patient suffers from radiation poisoning. Radiation poisoning is extremely painful and must be detected and treated …