
Medication
Depending on the type of ovarian cancer, different types of drug treatment might be used, including: Chemotherapy for Ovarian Cancer. Hormone Therapy for Ovarian Cancer. Targeted Therapy for Ovarian Cancer.
Procedures
Surgery is the main treatment for ovarian cancer, recommended primarily when the vast majority of the cancer or affected tissue can be removed successfully. Some early-stage ovarian patients may undergo minimally-invasive procedures to remove ovarian tumors and/or preserve fertility.
Self-care
Treatment for ovarian cancer. Treatment for ovarian cancer will depend on: the size and type of ovarian cancer you have; where the cancer is; if it has spread; your general health; The main treatments are surgery and chemotherapy. Other treatments include targeted medicines and hormone treatments. The specialist care team looking after you will:
Can you be fully cured of ovarian cancer?
Chemotherapy for Ovarian Cancer. Chemotherapy (chemo) is the use of drugs to treat cancer. Most often, chemo is a systemic treatment, meaning the drugs enter the bloodstream and reach almost all areas of the body. Chemo can be useful to kill very small amounts of cancer cells that may still be around after surgery, for cancers that have metastasized (spread), or to shrink very …
How do you cure ovarian cancer?
Niraparib (Zejula) may be used in different situations to treat ovarian cancer. In women with or without a BRCA gene mutation: Niraparib might be used as maintenance treatment for ovarian cancer, where the cancer has shrunk with chemotherapy containing cisplatin or carboplatin; In women with a BRCA mutation:
How much does treating ovarian cancer cost?
Surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation may be used to treat ovarian cancer, depending on the disease’s stage. Find out what to expect from ovarian cancer treatment.
When to stop chemotherapy for ovarian cancer?
For women with ovarian cancer, a florescent drug called pafolacianine (Cytalux) will be injected into your body a few hours before surgery and will attach to a …
See more
What is the most effective treatment for ovarian cancer?
Surgery is the main treatment for ovarian cancer, recommended primarily when the vast majority of the cancer or affected tissue can be removed successfully. Some early-stage ovarian patients may undergo minimally-invasive procedures to remove ovarian tumors and/or preserve fertility.
Can you be cured of ovarian cancer?
Approximately 20% of women with advanced-stage ovarian cancer survive beyond 12 years after treatment and are effectively cured. Initial therapy for ovarian cancer comprises surgery and chemotherapy, and is given with the goal of eradicating as many cancer cells as possible.
What is the first treatment for ovarian cancer?
The initial treatment for stage I ovarian cancer is surgery to remove the tumor. Most often the uterus, both fallopian tubes, and both ovaries are removed (a hysterectomy with bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy). The treatment after surgery depends on the sub-stage of the cancer.Jun 10, 2020
Is ovarian cancer curable at stage 1?
Most women with Stage 1 ovarian cancer have an excellent prognosis. Stage 1 patients with grade 1 tumors have a 5-year survival of over 90%, as do patients in stages 1A and 1B....What is the survival rate for Stage 1 ovarian cancer?StageRelative 5-Year Survival RateI90%IA94%IB92%IC85%
Where does ovarian cancer usually spread to first?
Where does ovarian cancer spread first? There is no single trajectory for where ovarian cancer will spread; however, if not caught in early stages, most cases of ovarian cancer will follow a similar path: from the pelvis, to more distant parts of the abdomen and peritoneal cavity, to the lymph nodes, and the liver.Jul 27, 2021
What are the early warning signs of ovarian cancer?
What are the early warning signs of ovarian cancer?Pelvic or abdominal pain or cramping. ... Feeling full quickly after starting to eat or lack of appetite. ... Indigestion or upset stomach.Nausea.Feeling like you have to urinate more frequently or urgently than normal. ... Unexplained exhaustion. ... Bloating and/or constipation.More items...
What stage is ovarian cancer usually diagnosed?
It's typical for women to be diagnosed with ovarian cancer initially at stage 3. At that point, it is challenging to treat and, unfortunately, the disease is frequently fatal. More than 14,000 women die every year from ovarian cancer.Nov 10, 2017
What's the survival rate for ovarian cancer?
Survival rates can give you an idea of what percentage of people with the same type and stage of cancer are still alive a certain amount of time (usually 5 years) after they were diagnosed....Invasive epithelial ovarian cancer.SEER stage5-year relative survival rateRegional75%Distant31%All SEER stages combined49%1 more row•Mar 1, 2022
How fast does ovarian cancer spread?
Does ovarian cancer spread quickly? Ovarian cancer grows quickly and can progress from early stages to advanced within a year. With the most common form, malignant epithelial carcinoma, the cancer cells can grow out of control quickly and spread in weeks or months.Aug 23, 2020
What kind of leg pain is associated with ovarian cancer?
Although leg swelling can be caused by several unrelated health concerns, ovarian cancer is one of several cancer types known to cause edema. About 20 percent of women diagnosed with ovarian cancer develop leg swelling.Mar 4, 2020
Is ovarian cancer painful?
Ovarian cancer is often caught in later, more advanced stages because there are often few symptoms early on in the course of the disease. Unfortunately, late-stage ovarian cancer can cause pain and discomfort. And although treatment often helps alleviate pain, some therapies may actually add to the discomfort.Sep 18, 2020
How long can you have ovarian cancer without knowing?
In most women diagnosed with ovarian cancer, the symptoms surfaced about five months or less before the diagnosis.Jan 28, 2010
What is the treatment for ovarian cancer?
Types of Treatment. Treatment for ovarian cancer usually involves a combination of surgery and chemotherapy. Surgery: Doctors remove cancer tissue in an operation. Chemotherapy: Using special medicines to shrink or kill the cancer.
What is the name of the doctor who treats cancer?
Different treatments may be provided by different doctors on your medical team. Gynecologic oncologists are doctors who have been trained to treat cancers of a woman’s reproductive system. They perform surgery and give chemotherapy (medicine). Surgeons are doctors who perform operations.
How to remove ovarian cancer?
Operations to remove ovarian cancer include: Surgery to remove one ovary. For very early stage cancer that hasn't spread beyond one ovary, surgery may involve removing the affected ovary and its fallopian tube. This procedure may preserve your ability to have children. Surgery to remove both ovaries.
Where is chemo injected?
Chemotherapy drugs can be injected into a vein or taken by mouth. Sometimes the drugs are injected directly into the abdomen (intraperitoneal chemotherapy). Chemotherapy is often used after surgery to kill any cancer cells that might remain. It can also be used before surgery.
What is pelvic exam?
Pelvic examination. Pelvic examination. In a pelvic exam, your physician inserts two gloved fingers inside your vagina. While simultaneously pressing down on your abdomen, he or she can examine your uterus, ovaries and other organs. Tests and procedures used to diagnose ovarian cancer include: Pelvic exam.
What is CA 125?
For example, a cancer antigen (CA) 125 test can detect a protein that's often found on the surface of ovarian cancer cells. These tests can't tell your doctor whether you have cancer, but may give clues about your diagnosis and prognosis. Surgery.
Can palliative care be used for cancer?
Palliative care can be used while undergoing other aggressive treatments, such as surgery and chemotherapy. When palliative care is used along with all of the other appropriate treatments, people with cancer may feel better and live longer.
What is targeted therapy?
Targeted therapy. Targeted therapy uses medications that target the specific vulnerabilities present within your cancer cells. Targeted therapy drugs are usually reserved for treating ovarian cancer that returns after initial treatment or cancer that resists other treatments.
Is ovarian cancer scary?
A diagnosis of ovarian cancer can be overwhelming and scary. In time you'll find ways to cope with your feelings, but in the meantime you might find it helpful to:
What is the best treatment for ovarian cancer?
Surgery is the main treatment for ovarian cancer, recommended primarily when the vast majority of the cancer or affected tissue can be removed successfully. Some early-stage ovarian patients may undergo minimally-invasive procedures to remove ovarian tumors and/or preserve fertility.
What is the procedure to remove ovarian cancer?
Other ovarian cancer surgical procedures may include: Removal of the ovaries or fallopian tubes (unilateral or bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy) Taking a small sample of your omentum, pelvic or abdominal lymph nodes and/or additional biopsies to examine for cancerous cells under a microscope and remove cancerous tissue.
How many women have ovarian cancer?
One in 70 women will be diagnosed with ovarian cancer during her lifetime. Because there are no screening tests for ovarian cancer, and symptoms are often subtle, most ovarian cancer cases are diagnosed at a more advanced stage. Because of the complexities of ovarian cancer subtypes, it is imperative that your treatment is conducted ...
When is chemo given for ovarian cancer?
Chemotherapy for ovarian cancer may be administered at any stage, but it is usually given at the later stages of the disease. In general, chemotherapy drugs are administered after surgery to eliminate remaining cancer cells, or to keep them from returning.
Does DF/BWCC offer a chemo?
In addition to traditional IP chemotherapy, DF/BWCC offers hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC). In contrast to standard IP chemotherapy that is given after surgery, HIPEC involves a single use of heated chemotherapy in the abdomen, which is given at the time of surgery. Heating the chemotherapy improves absorption and directly destroys cancer cells. At the completion of the surgery, the chemotherapy is removed from the abdomen. Recent studies have shown that adding HIPEC to select patients’ treatment improves survival significantly and doesn’t increase side effects or complications. HIPEC is for select patients with advanced stage ovarian cancer and we encourage patients to discuss treatment options with their cancer team.
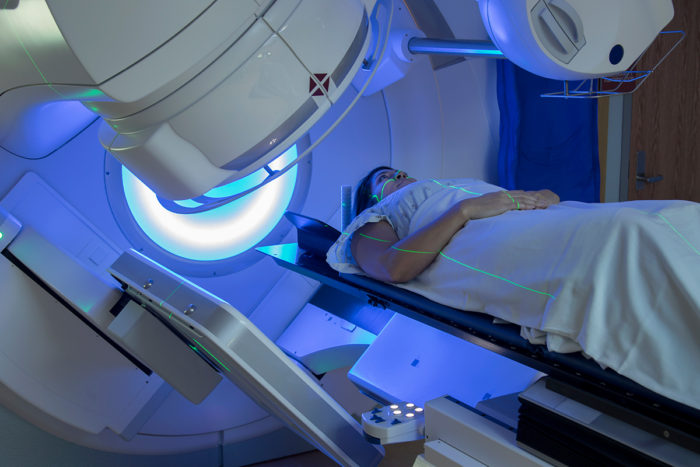
What is radiation therapy?
Radiation therapy is a cancer treatment that uses high-energy X-rays or other types of radiation to eliminate cancer cells or stop cancer growth. Radiation therapy for ovarian cancer is given by our experienced team of radiation oncologists.
Can you get radiation for ovarian cancer?
While most ovarian cancer patients are not treated with radiation therapy, it may be used for patients with certain types of ovarian cancer, those who have isolated and/or minimal recurrence, or to control symptoms such as pain. In rare or recurrent cases, these radiation treatments may be performed:
How to treat invasive ovarian cancer?
Treatment of Invasive Epithelial Ovarian Cancers, by Stage. The first step in treating most stages of ovarian cancer is surgery to remove and stage the cancer. Debulking is also done as needed. (See Surgery for Ovarian Cancer .) Because fallopian tube and primary peritoneal cancers have the same staging system as ovarian cancers they are included ...
What is the treatment for stage 1 ovarian cancer?
Stage I cancers. The initial treatment for stage I ovarian cancer is surgery to remove the tumor. Most often the uterus, both fallopian tubes, and both ovaries are removed (a hysterectomy with bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy). The treatment after surgery depends on the sub-stage of the cancer. Stages IA and IB (T1a or T1b, N0, M0): The treatment ...
What is stage 2 cancer?
This includes a hysterectomy and bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy. The surgeon will try to remove as much of the tumor as possible.
Can stage 4 cancer be treated?
These cancers are very hard to cure with current treatments, but they can still be treated. The goals of treatment are to help patients feel better and live longer.
What is maintenance therapy?
The goal of maintenance therapy is to keep the cancer from coming back after platinum chemotherapy. Drugs that might be used include bevacizumab, niraparib, rucaparib, and olaparib.
Can ovarian cancer come back?
Advanced epithelial ovarian cancer often comes back months or years after the initial treatment.
Does Avastin help with ovarian cancer?
Often, however, their effects are temporary, and the cancer returns or persists. Ovarian cancer can also block the intestinal tract.
What is the best treatment for ovarian cancer?
Getting a combination of drugs instead of just one drug alone seems to work better as a first treatment for ovarian cancer. Usually, the combination includes a type of chemo drug called a platinum compound (usually cisplatin or carboplatin), and another type of chemo drug called a taxane, such as paclitaxel (Taxol ®) or docetaxel (Taxotere ® ).
What is chemo for ovarian cancer?
Chemotherapy for Ovarian Cancer. Chemotherapy (chemo) is the use of drugs to treat cancer. Most often, chemo is a systemic treatment, meaning the drugs enter the bloodstream and reach almost all areas of the body. Chemo can be useful to kill very small amounts of cancer cells that may still be around after surgery, ...
Where does chemo go?
Giving chemo this way gives the most concentrated dose of the drugs directly to the cancer cells in the abdominal cavity. This chemo also gets absorbed into the bloodstream and so can reach cancer cells outside the abdominal cavity.
Do side effects of cancer go away?
These side effects usually go away after treatment is finished. While you are in treatment, tell your cancer care team about any side effects you are having. There are often ways to lessen these side effects. For example, drugs can be given to help prevent or reduce nausea and vomiting.
What is intraperitoneal chemo?
Intraperitoneal (IP) chemotherapy. For women who have stage III ovarian cancer (cancer that has not spread outside the abdomen) and whose cancers were optimally debulked (no tumors larger than 1 cm after surgery), intraperitoneal (IP) chemotherapy might be given in addition to systemic chemo (paclita xel given in a vein).
Can chemo cause menopause?
Chemo can also cause early menopause and infertility (being unable to become pregnant), which may be permanent. This is rarely an issue in the treatment of epithelial ovarian cancer, since most women have both ovaries removed as a part of treatment. Rarely, some chemo drugs can permanently damage bone marrow.
What is the best chemotherapy for cancer?
High dose chemotherapy (the exact drugs used can vary depending on what cancer center is giving the treatment) TIP (paclitaxel/Taxol, ifosfamide, and cisplatin/Platinol) VeIP (vinblastine, ifosfamide, and cisplatin/Platinol) VIP (etoposide/VP-16, ifosfamide, and cisplatin/Platinol)
What is the best treatment for ovarian cancer?
In women with a BRCA mutation: 1 Olaparib can be used to treat advanced ovarian cancer that has gotten smaller in response to first treatment with chemotherapy containing cisplatin or carboplatin. 2 Olaparib and rucaparib can be used to treat advanced ovarian cancer that has previously been treated with 2 or 3 chemotherapy drugs. 3 Olaparib can be used with bevacizumab (see above) as maintenance treatment in women whose cancers have shrunk quite a bit with chemotherapy containing carboplatin or cisplatin.
What is the name of the drug that is used to treat ovarian cancer?
Olaparib (Lynparza) and rucaparib (Rubraca) are used to treat advanced ovarian cancer, typically after chemotherapy has been tried. These drugs can be used in patients with or without mutations in one of the BRCA genes. In women with a BRCA mutation:
What is the name of the drug that attaches to VEGF?
Bevacizumab (Avastin) belongs to a class of drugs called angiogenesis inhibitors. For cancers to grow and spread, they need to make new blood vessels to nourish themselves (called angiogenesis). This drug attaches to a protein called VEGF (that signals new blood vessels to form) and slows or stops cancer growth.
Can you use olaparib with bevacizumab?
In women without a BRCA mutation: If the tumor has a high genomic instability score (a test measuring the amount of abnormal genes in cancer cells), olaparib can be used with bevacizumab as maintenance treatment in women whose cancers have shrunk quite a bit with chemotherapy containing carboplatin or cisplatin.
What is the best treatment for BRCA mutation?
In women with a BRCA mutation: Olaparib can be used to treat advanced ovarian cancer that has gotten smaller in response to first treatment with chemotherapy containing cisplatin or carboplatin. Olaparib and rucaparib can be used to treat advanced ovarian cancer that has previously been treated with 2 or 3 chemotherapy drugs.
What is niraparib used for?
Niraparib might be used as maintenance treatment for ovarian cancer, where the cancer has shrunk with chemotherapy containing cisplatin or carboplatin. In women with a BRCA mutation: Niraparib might be used to treat advanced ovarian cancer after several chemotherapy drugs have been tried.
What are the side effects of PARP inhibitors?
Side effects of these drugs can include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, fatigue, loss of appetite, taste changes, low red blood cell counts (anemia), belly pain, and muscle and joint pain. Rarely, some patients treated with these drugs have developed a blood cancer, such as myelodysplastic syndrome or acute myeloid ...
Diagnosis
Treatment
Clinical Trials
Coping and Support
Specialist to consult
Preparing For Your Appointment
- Treatment for ovarian cancer usually involves a combination of surgery and chemotherapy. 1. Surgery:Doctors remove cancer tissue in an operation. 2. Chemotherapy:Using special medicines to shrink or kill the cancer. The drugs can be pills you take or medicines given in your veins, or sometimes both. Different treatments may be provided by different doctors on your medical tea…
Stage I Cancers
Stage II Cancers
Stage III Cancers
- Tests and procedures used to diagnose ovarian cancer include: 1. Pelvic exam.During a pelvic exam, your doctor inserts gloved fingers into your vagina and simultaneously presses a hand on your abdomen in order to feel (palpate) your pelvic organs. The doctor also visually examines your external genitalia, vagina and cervix. 2. Imaging tests.Tests, such as ultrasound or CT scans of y…
Stage IV Cancers
- Treatment of ovarian cancer usually involves a combination of surgery and chemotherapy. Other treatments may be used in certain situations.
Recurrent Or Persistent Ovarian Cancer
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiestesting new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.
Palliative Treatments
- A diagnosis of ovarian cancer can be overwhelming. In time you'll find ways to cope with your feelings, but in the meantime, you might find it helpful to: 1. Find someone to talk with.You may feel comfortable discussing your feelings with a friend or family member, or you might prefer meeting with a formal support group. Support groups for the families of people with cancer als…