
What is the cause of osteoradionecrosis?
Osteoradionecrosis (ORN) is caused when radiation therapy damages the blood vessels that supply the jawbone with nutrients and oxygen. Without an adequate blood supply, the bone can no longer heal itself when faced with infection or trauma, and it dies.
Can osteoradionecrosis affect the maxilla?
Although rare, osteoradionecrosis can also affect the upper jaw (maxilla). This condition impacts approximately 3-10% of patients and can occur even years after radiation therapy has ended.
Why is the lower jaw at risk for osteoradionecrosis?
The lower jaw is particularly at risk due to its already limited blood supply.
What is hyperbaric oxygen therapy?
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy, which involves breathing pure oxygen in a pressurized chamber. This treatment is helpful in delivering more oxygen to damaged tissue, which improves blood supply and promotes healing.
What to do after radiation treatment?
During and After Radiation Therapy. Always practice good oral hygiene, including before, during, and after treatment. Keeping your mouth, teeth, and gums healthy will aid in preventing infection or dental care-related traumas (e.g., tooth extractions) that may lead to development of ORN.
Do you need radiation therapy before or after a dental extraction?
If extractions are needed, it may be necessary to get hyperbaric oxygen treatments before and after extraction in order to reduce the risk of developing ORN.
What is the procedure to restore blood flow?
Reconstructive surgery to restore blood flow, replace sections of jawbone that were removed, or graft soft tissue to replace muscle or tissue that was removed. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy, which involves breathing pure oxygen in a pressurized chamber.
When was osteoradionecrosis first reported?
Etiology and pathophysiology of osteoradionecrosis. Regaud published the first report on ORN of the jaw after radiotherapy in 1922, and Ewing reported in 1926 on the bone changes associated with radiation therapy and described this disease state as “radiation osteitis” [1, 16].
What causes radiation osteitis?
In 1938, Watson and Scarborough described this radiation osteitis as caused by radiation, trauma and infection. Trauma to the soft tissues overlying bone in the oral cavity induced bacteria to enter into the underlying demineralized bone and lead to osteomyelitis [1, 17].
What is ORN in dentistry?
Abstract. Osteoradionecrosis ( ORN) of the jaw is a significant complication of radiotherapy for oral cavity cancer. In addition to antibiotic medication, treatment options such as hyperbaric oxygen therapy, surgical approaches, and combined therapy with pentoxifylline and tocopherol have been recently introduced.
What is ORN in radiotherapy?
Osteoradionecrosis ( ORN) of the jaw is one of the main complications of radiotherapy, and results in alteration of the shape and function of the oral cavity and jaw that causes substantial deterioration in patient quality of life (Figure 1).
What are the complications of radiotherapy?
Oral and maxillofacial complications of radiotherapy. Radiation-induced damage to the oral and maxillofacial region is the result of the deleterious effects of therapeutic radiation on the oral mucosa and the adjacent salivary glands, maxilla, mandible, teeth, and masticatory musculatures.
What percentage of patients have osteoradionecrosis?
This condition occurs in three to ten percent of patients. Osteoradionecrosis develops as irradiation diminishes the bone’s ability to withstand trauma and avoid infection, and it can be facilitated by poor nutrition and hygiene. This process may be spontaneous or result from trauma, leading to non-healing soft tissue and bone lesions, ...
Does hyperbaric oxygen therapy help osteoradionecrosis?
It has been in the field of treating osteoradionecrosis that hyperbaric oxygen therapy has seen some of its most dramatic successes. When osteoradionecrosis develops, tissue destruction devolves into the breakdown of overlying tissues and symptomatic destruction of bone. During this process, the response to antibiotics can be poor.
Why is osteoradionecrosis a spontaneous process?
Osteoradionecrosis develops as irradiation diminishes the bone’s ability to withstand trauma and avoid infection, and it can be facilitated by poor nutrition and hygiene. This process may be spontaneous or result from trauma, leading to non-healing soft tissue and bone lesions, followed by bone necrosis.
How does radiation affect bone tissue?
Essentially, the radiation destroys some of the very small blood vessels within the bone. These blood vessels carry both nutrients and oxygen to the living bone. A reduction in these vessels correlates to a reduction in the bone’s ability to heal itself.
What is the treatment for ORN?
Such a problem when complicated by ORN, can cause massive destruction of the jawbones. Treatment for ORN may include hyperbaric oxygen treatments in which the bone is subjected to saturation with oxygen in a pressure chamber, not unlike those used to treat divers for the bends.
When was hyperbaric oxygen therapy first used?
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBO) was first proposed as a treatment for cancer and other conditions in the 1960s. At the time, research studies did not achieve any reproducible results, which engendered much skepticism among medical personnel.
How long does osteoradionecrosis last?
Osteoradionecrosis is non-healing, exposed bone in a previously radiated area of the body, usually the lower jaw in head and neck cancer patients treated with radiation, present for at least 6 months.
Can radiation cause ORN?
Patients treated with head and neck radiation are at increased risk for the development of ORN of the jaw if they have had surgical manipulation of the jaw (e.g. extraction of an infected tooth), particularly after radiation treatments.
What to do if you have a toothache from radiation?
Call your radiation oncologist if you have been treated with head and neck radiation and you develop a toothache that your dentist feels should be treated with an extensive dental procedure ( root canal) or tooth extraction.
Can a patient with osteoradionecrosis respond to hbo?
The osteoradionecrosis is more severe, the patient is unlikely to respond to HBO and he or she still has a good amount of healthy bone to maintain a stable jaw.
What is the term for a bone that has died from radiation?
What is osteoradionecrosis (ORN)? Osteoradionecrosis (ORN) is a condition in which bone has died due to exposure to radiation. It is a side effect of radiation treatments for cancer in the head or neck. ORN can develop months or years after radiation treatment for cancer.
How does radiation affect bone health?
How does radiation treatment affect bone health? The radiation damages the blood supply to the bone and this makes it harder to heal from surgery (such as removal of a tooth), trauma or infection. Without a properly working blood supply, the bone and surrounding tissue: Cannot resist infection.
Can radiation damage bone?
The radiation damages the blood supply to the bone and this makes it harder to heal from surgery (such as removal of a tooth), trauma or infection. Without a properly working blood supply, the bone and surrounding tissue: Cannot resist infection. Cannot heal properly and an expanding area begins to die. The jaw is particularly at risk ...
What is the treatment for ORN?
Medical therapy in treatment of ORN is primarily supportive, involving nutritional support along with superficial debridement and oral saline irrigation for local wounds. Antibiotics are indicated only for definite secondary infection.
How soon before radiation therapy can you get your teeth extracted?
Teeth that cannot be salvaged with conservative endodontic therapy should be extracted. Ideally, extractions should be performed 3 weeks prior to beginning radiation therapy.
What is the term for the loss of bone tissue after exposure to radiation?
Osteoradionecrosis (ORN) is a condition in which bone tissue dies as a result of radiation exposure. Normally, bone tissue is able to regenerate. However, repeated exposure to radiation (such as with X-rays) results in the loss of the bone's regenerative capacity. Osteoradionecrosis can occur spontaneously, but may be the result of an injury such as tooth extraction or oral surgery. This condition often occurs in the lower jawbone (mandible), a site which is exposed to radiation in cases of radiation therapy for head and neck cancers.
What is the primary prerequisite for developing ORN?
The primary prerequisite for developing ORN is radiation exposure, which damages important structures present in the irradiated area. The inner lining of the blood vessels supplying the area become inflamed, a condition known as endarteritis. This prevents adequate blood flow to the tissues by increasing the chances of blood clot formation, an effect which may lead to poor wound healing.
How long before radiation therapy for head and neck cancer?
Dental extractions should be scheduled three weeks before the radiation therapy to prevent tissue injury, which could induce the development of ORN. Patients should also be educated on the importance of proper dental hygiene.
What is osteoradionecrosis?
Osteoradionecrosis is the result of an avascular, aseptic necrosis. Much of the pioneering studies on hyperbaric oxygen for osteoradionecrosis were done by Robert Marx, DDS who developed a staging system and treatment protocols for osteoradionecrosis.
Can radiation cause osteoradionecrosis?
However, a small percentage of patients treated with radiation for head and neck cancers will develop osteoradionecrosis (ORN) of the jaw. Patients treated with more than 6000 centigrays (cGy) of radiation have an approximately 9% incidence of developing mandibular osteoradionecrosis.
Can hyperbaric oxygen be used for osteoradionecrosis?
Many of these patients will go on to heal spontaneously and without complications, but some will develop osteomyelitis and even fractures of the mandible leading to eventual soft tissue necrosis. Hyperbaric oxygen treatment has become a mainstay treatment for osteoradionecrosis.
Who developed the scale for osteoradionecrosis?
Much of the pioneering studies on hyperbaric oxygen for osteoradionecrosis were done by Robert Marx, DDS who developed a staging system and treatment protocols for osteoradionecrosis. Marx's scale classifies mandibular necrosis and is used to describe the severity of the osteoradionecrosis. Scale of Osteoradionecrosis.
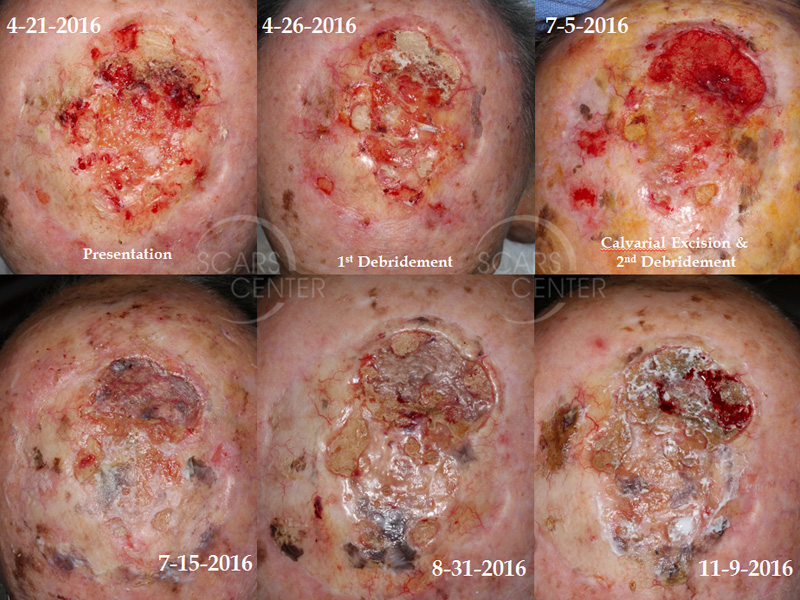
Treatment
- When osteoradionecrosis develops, tissue destruction devolves into breakdown of overlying tissues and symptomatic destruction of bone. During this process, the response to antibiotics can be poor. In many cases, the situation can be improved with the use of HBO therapy. Hyperbaric oxygen has been shown to be more effective than penicillin. Patients being treated with penicilli…
Diagnosis
- Your doctor will try to find the cause of osteoradionecrosis. This usually includes doing a physical exam, including a complete head and neck exam. Your doctor may also review your medical records to find out the total dose of radiation you received and the area that was treated.You may also need the following tests: 1. x-ray of the whole jaw 2. CT scan 3. MRI 4. biopsy of the area to …
History
- Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBO) was first proposed as a treatment for cancer and other conditions in the 1960s. At the time, research studies did not achieve any reproducible results, which engendered much skepticism among medical personnel. This skepticism even extended to HBOs use in treating clinical conditions that it had previously been shown to help. It was not unti…
Causes
- Osteoradionecrosis is caused by radiation therapy to the bone. It may develop years after radiation therapy for head and neck cancers. The risk of developing osteoradionecrosis increases when the dose of radiation received is greater than 60 grays. It is also higher if the bone treated with radiation is exposed.There is also a higher risk of developing osteoradionecrosis if a dental …
Operation
- Multiplace chambers are large tanks able to accommodate anywhere from two to fourteen people. These chambers are commonly built to reach pressures up to 6 atmospheres and have a chamber lock entry system that allows medical personnel to pass through without altering the pressure of the inner chamber. This system allows patients to be directly cared for by staff withi…
Safety
- Due to the high concentration of oxygen in both mono and multiplace chambers, fire hazards restrict the use of certain electronic equipment, but some monitors and ventilators with solid-state circuitry can be used within the chamber, allowing intensive care of critically ill patients.
Symptoms
- Symptoms can vary depending on the grade or extent of the osteoradionecrosis and include: 1. pain 2. swelling 3. a sore, or ulcer, in the mouth or on the jaw 4. difficulty opening the jaw, or trismus 5. an abnormal opening, or fistula, between the jaw and the surface of the body 6. less feeling in the mouth or jaw, or even a complete loss of sensation in the area 7. infection 8. teeth …
Advantages
- Monoplace chambers cost less to operate than multiplace chambers and are relatively portable. Monoplace chambers are also far less expensive than their larger counterparts, a fact that has allowed hospitals to institute HBO programs more cost effectively. The internal environment of a monoplace chamber is maintained at 100% oxygen, so the patient does not need to wear a mask.
Risks
- All patients who require extraction of teeth in a previously irradiated field should be considered at risk of developing osteoradionecrosis. The traumatic fracture of a maxillary bone or the mandible post treatment in an accident can also result in severe consequences. Such a problem when complicated by ORN, can cause massive destruction of the jawbones. Treatment for ORN may i…
Mechanism
- Essentially, the radiation destroys some of the very small blood vessels within the bone. These blood vessels carry both nutrients and oxygen to the living bone. A reduction in these vessels correlates to a reduction in the bones ability to heal itself.