
Medication
The first sign you may get is inflammation. Grade 1 can generally reverse within a few weeks to months. On average, Grade 1 May take around 2-3 months to reverse your fatty liver completely. Remember, you can only reverse your damaged liver if you follow the correct diet and corrective measures.
Procedures
To conclude, we should say that no one of us can say the number of years, for which an individual with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease will survive or experience complications. However, if a person chooses to bring lifestyle changes early, he or she may expect to avoid liver failure or liver damage.
Self-care
Your Guide to Anti-Aging Foods That Also Reverse Fatty Liver
- Red Grapes. Resveratrol is a polyphenol prevalent in a variety of plants. ...
- Green Tea. Green tea is a popular beverage that has been used for centuries in traditional Chinese medicine. ...
- Tofu. ...
- Sweet Potato. ...
- Salmon. ...
- Mushrooms. ...
- Avocado. ...
- Pomegranate. ...
- Sun-Dried Tomatoes. ...
- Kale. ...
Nutrition
What does a diet plan for fatty liver disease look like?
- 3 oz. grilled salmon
- 1 cup cooked broccoli
- 1 cup cooked quinoa
- 1 cup mixed berries
See more
How long do you live with NAFLD?
What is the life expectancy of non alcoholic liver disease?
What foods help prevent and reverse fatty liver disease?
What is the best diet to treat fatty liver disease?
See more

What is the best medicine for non-alcoholic fatty liver?
Currently, insulin sensitizers (thiazolidinediones) and antioxidants (vitamin E) seem to be the most promising agents for treating NAFLD/NASH, and lipid-lowering drugs, pentoxifylline, angiotensin receptor blockers, and n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids also have promise.
How long can you live with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease?
Survival and mortality The median survival was 24.2 (range 0.2-26.1) years in the NAFLD group and 19.5 (range 0.2-24.2) years in the AFLD group (p = 0.0007). Median follow-up time for the non-alcoholic group was 9.9 years (range 0.2-26 years) and 9.2 years (0.2-25 years) for the alcoholic group.
Can non-alcoholic fatty liver disease be treated?
Treatment for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) There's currently no specific medication for NAFLD, but making healthy lifestyle choices can help. Treatment also may be recommended for associated conditions (high blood pressure, diabetes and cholesterol) or complications.
What is the fastest way to cure a non-alcoholic fatty liver?
Research suggests that losing weight is the single best thing you can do to control or reverse NAFLD. A good goal is to lose 10% of your total body weight, but even a loss of 3% to 5% can improve your liver health. Talk with your doctor about the best way for you to lose weight safely and effectively.
What are the 3 signs of a fatty liver?
SymptomsAbdominal swelling (ascites)Enlarged blood vessels just beneath the skin's surface.Enlarged spleen.Red palms.Yellowing of the skin and eyes (jaundice)
Is a fatty liver a death sentence?
Researchers Surprised to Find Fatty Liver Disease Poses No Excess Risk for Death.
What causes non alcoholic fatty liver disease?
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease tends to develop in people who are overweight or obese or have diabetes, high cholesterol or high triglycerides. Rapid weight loss and poor eating habits also may lead to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
How do you remove fat from your liver?
Lifestyle and home remediesLose weight. If you're overweight or obese, reduce the number of calories you eat each day and increase your physical activity in order to lose weight. ... Choose a healthy diet. ... Exercise and be more active. ... Control your diabetes. ... Lower your cholesterol. ... Protect your liver.
How long does it take for non alcoholic fatty liver to turn into cirrhosis?
It used to be thought that progression from early stage NAFLD to cirrhosis took decades, but recent studies have shown that some people progress rapidly within 2 years.
Can a non alcoholic fatty liver be reversed?
If you have NASH, no medication is available to reverse the fat buildup in your liver. In some cases, the liver damage stops or even reverses itself. But in others, the disease continues to progress. If you have NASH, it's important to control any conditions that may contribute to fatty liver disease.
What foods to avoid if you have a fatty liver?
6 types of foods to avoid if you have fatty liver diseaseAlcohol. Alcohol can be a major cause of fatty liver disease as well as other liver diseases.Added sugar. Stay away from sugary foods such as candy, cookies, sodas, and fruit juices. ... Fried foods. ... Added salt. ... White bread, rice, and pasta. ... Red meat.
Does a fatty liver make your stomach big?
We conclude that fat infiltration of the liver is well correlated with amount of abdominal fat. Fatty liver tends to be more strongly associated with VF compared to SF. In other words, if a non-obese patient exhibits fatty liver, the patient may in fact have visceral obesity.
How to reverse liver fat?
These may include: Losing weight. Lowering your cholesterol and triglycerides. Controlling your diabetes. Avoiding alcohol . If you have NASH, no medication is available to reverse the fat buildup in your liver.
What is fatty liver disease?
Health care providers divide fatty liver disease into two types. If you just have fat but no damage to your liver, the disease is called nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). If you have fat in your liver plus signs of inflammation and liver cell damage, the disease is called nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH).
What does it mean when you have fatty liver?
Fatty liver disease means that you have fat inside your liver that can, over time, affect liver function and cause liver injury. People who drink too much alcohol may also have fat in their liver, but that condition is different from fatty liver disease.
What is a biopsy of the liver?
A liver biopsy involves getting a tissue sample of your liver with a needle. The needle removes a small piece of liver tissue that can be looked at under a microscope. Here’s how your health care provider makes the diagnosis: If you have fat but no inflammation or tissue damage, the diagnosis is NAFLD.
How to diagnose fatty liver?
It’s usually diagnosed when you have routine blood tests to check your liver. Your health care provider may suspect fatty liver disease with abnormal test results, especially if you are obese. Imaging studies of your liver may show fat deposits. Some imaging tests, including special ultrasound and MRI scans can help diagnose ...
Can you have fatty liver without causing any symptoms?
Fatty liver disease is sometimes called a silent liver disease. This is because it can happen without causing any symptoms. Most people with NAFLD live with fat in their liver without developing liver damage. A few people who have fat in their liver develop NASH.
Can fatty liver disease harm your liver?
If you are living with fatty liver disease, learn as much as you can about your condition and work closely with your medical team. Since many medications can harm your liver, always let all your health care providers know about any medications you are taking.
What is the medical name for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease?
Medications for Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Other names: Fatty Liver; Idiopathic Fatty Liver; NAFLD; NASH; Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis; Steatohepatitis; Steatosis. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) describes a range of conditions that affect people who drink little or no alcohol.
Is there a lack of accepted safety for use under medical supervision?
Has a high potential for abuse. Has a currently accepted medical use in treatment in the United States or a currently accepted medical use with severe restrictions. Abuse may lead to severe psychological or physical dependence.
What is the most common form of liver cancer?
Liver cancer begins in the cells of the liver. The most common form of liver cancer begins in cells called hepatocytes and is called hepatocellular carcinoma. The main complication of NAFLD and NASH is cirrhosis, which is late-stage scarring in the liver. Cirrhosis occurs in response to liver injury, such as the inflammation in NASH.
What is the name of the disease where the body doesn't take up sugar?
Insulin resistance, in which your cells don't take up sugar in response to the hormone insulin. High blood sugar (hyperglycemia), indicating prediabetes or type 2 diabetes. High levels of fats, particularly triglycerides, in the blood. These combined health problems appear to promote the deposit of fat in the liver.
What is the most common form of NAFLD?
NAFLD is increasingly common around the world, especially in Western nations. In the United States, it is the most common form of chronic liver disease, affecting about one-quarter of the population. Some individuals with NAFLD can develop nonalcoholic ...
What is the name of the vein that carries blood from the intestine to the liver?
Esophage al varices. Esophage al varices. Esop hageal varices are enlarged veins in the esophagus. They're often due to obstructed blood flow through the portal vein, which carries blood from the intestine, pancreas and spleen to the liver.
Where is the liver located?
About the size of a football, it's located mainly in the upper right portion of your abdomen, beneath the diaphragm and above your stomach.
What is the complication of NAFLD?
The main complication of NAFLD and NASH is cirrhosis, which is late-stage scarring in the liver. Cirrhosis occurs in response to liver injury, such as the inflammation in NASH. As the liver tries to halt inflammation, it produces areas of scarring (fibrosis).
Abstract
Alcoholic liver disease (ALD) and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) are serious health problems worldwide. These two diseases have similar pathological spectra, ranging from simple steatosis to hepatitis to cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma.
INTRODUCTION
Alcoholic liver disease (ALD) and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) are serious health issues whose incidences are on the rise with each passing decade. Alcohol is responsible for approximately 4% of all deaths annually and 5% of all disabilities worldwide [ 1 ].
ALD TREATMENT
For the last 50 years, abstinence has remained the primary therapy for ALD treatment. However, serious symptoms develop with the abrupt cessation of alcohol. Treating the alcohol withdrawal syndrome is thus extremely important and requires administration of fluid, calories, vitamins and minerals.
NAFLD TREATMENT
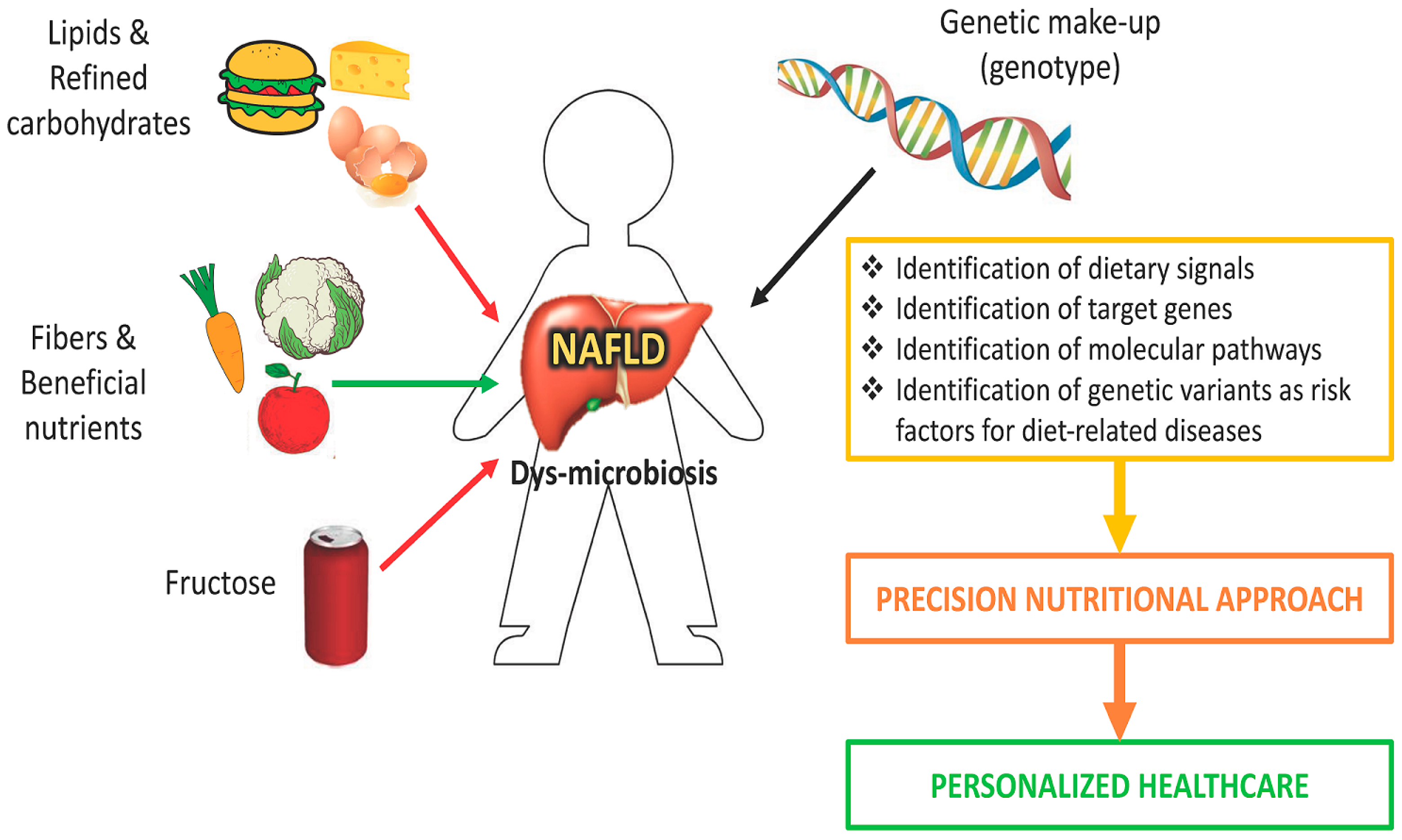
Like ALD there is no effective treatment to date for NAFLD. In the absence of a proven effective therapy, we must follow a multi-disciplinary approach in NAFLD treatment, where a combination of drugs and factors are taken into consideration to counter multiple pathological risk factors involved in NAFLD.
CONCLUSION
Both ALD and NAFLD are chronic liver diseases with similar spectrums from simple steatosis to cirrhosis with basic differences only in their etiology. Despite understanding much of the pathophysiology of both diseases, there is still no effective treatment for either disease.
Contributor Information
Sukhpreet Singh, Research Service, Veterans Affairs Nebraska-Western Iowa Health Care System, Omaha, NE 68105, United States.
What is the most common chronic liver disease?
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease ( NAFLD) has become the most frequently encountered chronic liver disease. NAFLD is associated with increased liver-related morbidity and mortality, but also contributes to cardiovascular disease, diabetes and non-liver-related malignancy.
What is the most severe subtype of NAFLD?
Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) is considered the more severe subtype of NAFLD that drives most of these adverse outcomes. Lifestyle modification and associated weight loss can improve NASH but are not always sufficient and sustained results are difficult to obtain.
Diagnosis
Treatment
Clinical Trials
Alternative Medicine
Specialist to consult
Preparing For Your Appointment