Nutrition
There are 10 drugs currently approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for treating TB. Of the approved drugs, the first-line anti-TB agents that form the core of treatment regimens are:
How many drugs are currently approved for treating tuberculosis (TB)?
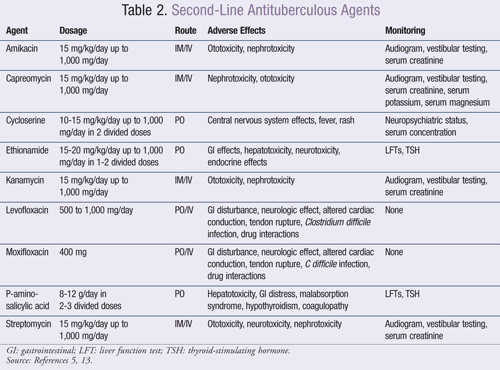
Treatment for Drug-Resistant TB. Extensively drug-resistant TB (XDR TB) is a rare type of MDR TB that is resistant to isoniazid and rifampin, plus any fluoroquinolone and at least one of three injectable second-line drugs (i.e., amikacin, kanamycin, or capreomycin). Treating and curing drug-resistant TB is complicated.
What is the treatment for drug-resistant tuberculosis?
Regimens for treating TB disease have an intensive phase of 2 months, followed by a continuation phase of either 4 or 7 months (total of 6 to 9 months for treatment). Drug Susceptible TB Disease Treatment Regimens. Regimens for treating TB disease have an intensive phase of 2 months, followed by a continuation phase of either 4 or 7 months ...
What is the duration of treatment for tuberculosis (TB)?
MDR TB strains can also grow resistant to second-line drugs, further complicating treatment. MDR TB occurs when a Mycobacterium tuberculosis strain is resistant to isoniazid and rifampin, two of the most powerful first-line drugs. To cure MDR TB, healthcare providers must turn to a combination of second-line drugs, several of which are shown here.
What is MDR tuberculosis (TB)?
Where is the highest rate of TB in the world?
In 2020, the 30 high TB burden countries accounted for 86% of new TB cases. Eight countries account for two thirds of the total, with India leading the count, followed by China, Indonesia, the Philippines, Pakistan, Nigeria, Bangladesh and South Africa.
Where is drug resistant TB most common?
The countries with the largest numbers of MDR/RR-TB cases (47% of the global total) were China, India and the Russian Federation. It is estimated that about 6.2% of these cases were XDR-TB.
What is the most active drug for the treatment of tuberculosis?
The most common treatment for active TB is isoniazid INH in combination with three other drugs—rifampin, pyrazinamide and ethambutol.
Which country has some of the highest number of new MDR TB cases?
88% of estimated MDR-TB cases occur in middle- or high-income countries, and 60% occur in Brazil, China, India, the Russian Federation and South Africa.
Is there a cure for tuberculosis in 2021?
3. There is no cure for TB. This is false; TB is treatable. The most common treatment for a latent TB infection is the antibiotic isoniazid.
Who Anti tuberculosis drug resistance in the World?
Based on World Health Organization reports, 5% of global TB cases are now considered to be extensively drug resistant (XDR), defined as MDR with additional resistance to both fluoroquinolones and at least one second-line injectable drug. XDR-TB had been reported by 105 countries by 2015.
Is TB Treatment Free in USA?
The department will only pay for services relevant to the treatment of tuberculosis. Payment for services above the normal treatment requirements for tuberculosis will be the responsibility of the patient and/or provider.
How is TB treated in the Philippines?
In the Philippines, effective anti-tuberculosis drugs (isoniazid, rifampicin, Pyrazinamide, Ethambutol, and Streptomycin) are available for free-of-charge through national and local government health centers (Philippine Department of Health).
What is the gold treatment for TB?
The usual treatment is: 2 antibiotics (isoniazid and rifampicin) for 6 months. 2 additional antibiotics (pyrazinamide and ethambutol) for the first 2 months of the 6-month treatment period.
Which two countries have seen the most XDR TB cases?
India (27%, 130,000 cases), China (14%, 66,000) and the Russian Federation (9%, 41,000) account for more than 50% of the global burden. Political declaration of the High-Level Meeting of the General Assembly on the fight against tuberculosis.
Why is tuberculosis most common in Africa?
The unprecedented growth of the tuberculosis epidemic in Africa is attributable to several factors, the most important being the HIV epidemic. Although HIV is Africa's leading cause of death, tuberculosis is the most common coexisting condition in people who die from AIDS (see radiograph).
Which 5 countries are least affected by TB?
Canada, the United States of America, Australia & New Zealand also have among the lowest rates. In these countries the incident rate is less than 10 cases per 100,000 population per year. Countries with a very low incident rate tend to have different aims with regard to TB, compared to the high incidence countries.
How common is antibiotic resistant TB?
According to the report, approximately 20% of TB cases globally are estimated to be resistant to at least one of the first- or second-line anti-TB drugs, and 5% are resistant to both isoniazid and rifampicin, the most powerful and commonly used antibiotics in first-line treatment.
What circumstances have led to the spread of drug resistant tuberculosis?
The spread of drug resistance stems from many factors: poor public health infrastructure (e.g., delays in the diagnosis of drug resistance, inconsistencies in TB medication supply), inadequate treatment (e.g., unmonitored therapy, nonadherence, incorrect use of anti-TB agents), inefficient infection control, and the ...
When does TB become drug resistant?
Sometimes drug-resistant TB occurs when bacteria become resistant to the drugs used to treat TB. This means that the drug can no longer kill the TB bacteria. Drug-resistant TB (DR TB) is spread the same way that drug-susceptible TB is spread. TB is spread through the air from one person to another.
When should one suspect the possibility of drug resistant TB?
Up to 90% of all patients who fail treatment, defined as a positive AFB sputum smear or culture after 5 months of therapy, will have MDR-TB strains. Given this, patients who remain smear positive after 3 months of treatment should be investigated for possible drug-resistant TB.
What is the new drug for TB?
Bedaquiline and Delamanid are new drugs. Ethambutol, Pyrazinamide, Thioamides, Cycloserine, Para-aminosalicylic acid, Streptomycin, and Clofazimine are possibly effective. Kanamycin, Capreomycin and Amikacin are injectable second-line. XDR TB occurs when a Mycobacterium tuberculosis strain is resistant to isoniazid and rifampin, ...
How to cure MDR TB?
To cure MDR TB, healthcare providers must turn to a combination of second-line drugs, several of which are shown here. Second-line drugs may have more side effects, the treatment may last much longer, and the cost may be up to 100 times more than first-line therapy. MDR TB strains can also grow resistant to second-line drugs, ...
What drugs target DNA?
Rifamycins, Oxazolidinones and Macrolides act on DNA. Tuberculosis drugs target various aspects of Mycobacterium tuberculosis biology, including inhibition of cell wall synthesis, protein synthesis, or nucleic acid synthesis. For some drugs, the mechanisms of action have not been fully identified.
Who took the photo of Mycobacterium tuberculosis?
The photo of Mycobacterium tuberculosis is from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, CDC/Dr. Ray Butler, Janice Carr. This illustration is in the public domain. Please credit the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID).
Is XDR TB resistant to isoniazid?
NIAID. XDR TB occurs when a Mycobacterium tuberculosis strain is resistant to isoniazid and rifampin, two of the most powerful first-line drugs, as well as key drugs of the second line regimen—any fluoroquinolone and at least one of the three injectable drugs shown above. XDR TB strains may also be resistant to additional drugs, ...
What is XDR TB?
XDR-TB is defined as resistance to at least isoniazid and rifampicin, and to any fluoroquinolone, and to any of the three second-line injectables (ami kacin, capreomycin, and kanamycin).
Is total drug resistance defined as tuberculosis?
Terms such as “totally drug resistant” have not been clearly defined for tuberculosis. While the concept of “total drug resistance” is easily understood in general terms, in practice, in vitro drug susceptibility testing (DST) is technically challenging and limitations on the use of results remain: conventional DST for the drugs ...
Do all countries have to have MDR TB?
Almost all countries must, in addition, ensure appropriate diagnosis and treatment of cases of MDR-TB. [11,12] National regulations for the quality and dispensing of anti-TB drugs, particularly of the second-line drugs, need to be strictly enforced.