Nutrition
Why tuberculosis is so hard to cure. When microbes divide, you usually get more of the same: A cell splits up and creates two identical copies of itself. But a new study shows that's not true for mycobacteria, which cause tuberculosis (TB) in humans—and that may explain why the disease is so difficult to treat.
Why is tuberculosis (TB) so hard to treat?
Tuberculosis: Post-Exposure Testing and Management
- Urgent message: Patients who present after exposure to tuberculosis test the clinician’s ability to assimilate broad and generalized information, including a unique set of historical, clinical, and laboratory data required ...
- Testing Options. ...
- Special Considerations. ...
- Window Period Prophylaxis. ...
- Current Treatment for LTBI. ...
- Conclusion. ...
What to do if exposed to TB?
Tuberculosis (TB) can be completely cured with the right treatment. Your doctor and health care team will be there to help you every step of the way. The key to a successful recovery is following the treatment as prescribed and communicating any questions and concerns with your doctor.
Can tuberculosis be completely cured?
TB that is resistant to drugs is harder and more expensive to treat. TB disease can be treated by taking several drugs for 6 to 9 months. There are 10 drugs currently approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for treating TB. Of the approved drugs, the first-line anti-TB agents that form the core of treatment regimens are ...
How can you cure tuberculosis?

Is Mycobacterium tuberculosis curable?
Tuberculosis (TB) is caused by bacteria (Mycobacterium tuberculosis) that most often affect the lungs. Tuberculosis is curable and preventable.
What drug is used for Mycobacterium tuberculosis?
Kanamycin, Capreomycin and Amikacin are injectable second-line. Bedaquiline and Delamanid are new drugs. Ethambutol, Pyrazinamide, Thioamides, Cycloserine, Para-aminosalicylic acid, Streptomycin, and Clofazimine are possibly effective. Kanamycin, Capreomycin and Amikacin are injectable second-line.
How long does it take to treat Mycobacterium tuberculosis?
RIPE regimens for treating TB disease have an intensive phase of 2 months, followed by a continuation phase of either 4 or 7 months (total of 6 to 9 months for treatment).
What is the most common treatment for tuberculosis?
The most common medications used to treat tuberculosis include:Isoniazid.Rifampin (Rifadin, Rimactane)Ethambutol (Myambutol)Pyrazinamide.
What is the first-line treatment for tuberculosis?
Of the approved drugs, isoniazid (INH), rifampin (RIF), ethambutol (EMB), and pyrazinamide (PZA) are considered first-line anti-TB drugs and form the core of standard treatment regimens (Figure 6.4) (Table 6.2).
Which one of the following is a first-line drug for TB treatment?
Pyrazinamide (PZA) is an important first-line antituberculosis (anti-TB) drug that is used in short-course chemotherapy and is one of the cornerstone drugs in the treatment of MDR-TB [23].
What are the 3 stages of tuberculosis?
There are 3 stages of TB—exposure, latent, and active disease. A TB skin test or a TB blood test can diagnose the disease. Treatment exactly as recommended is necessary to cure the disease and prevent its spread to other people.
How is Mycobacterium tuberculosis diagnosed?
The Mantoux tuberculin skin test (TST) or the TB blood test can be used to test for M. tuberculosis infection. Additional tests are required to confirm TB disease. The Mantoux tuberculin skin test is performed by injecting a small amount of fluid called tuberculin into the skin in the lower part of the arm.
What is the first stage of tuberculosis?
TB infection happens in 4 stages: the initial macrophage response, the growth stage, the immune control stage, and the lung cavitation stage. These four stages happen over roughly one month.
Where does TB bacteria come from?
1 in the journal Nature Genetics indicates that TB mycobacteria originated at least 70,000 years ago in Africa. The researchers compared the genetic evolutionary trees of mycobacteria and humans side-by-side.
How long does it take to treat TB?
TB disease can be treated by taking several drugs for 6 to 9 months. There are 10 drugs currently approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for treating TB. Of the approved drugs, the first-line anti-TB agents that form the core of treatment regimens are: isoniazid (INH) rifampin (RIF)
What is it called when TB bacteria multiply?
When TB bacteria become active (multiplying in the body) and the immune system can’t stop the bacteria from growing, this is called TB disease. TB disease will make a person sick. People with TB disease may spread the bacteria to people with whom they spend many hours.
What is XDR TB?
Extensively drug-resistant TB (XDR TB) is a rare type of MDR TB that is resistant to isoniazid and rifampin, plus any fluoroquinolone and at least one of three injectable second-line drugs (i.e., amikacin, kanamycin, or capreomycin). Treating and curing drug-resistant TB is complicated.
Can TB be treated?
It is very important that people who have TB disease are treated, finish the medicine, and take the drugs exactly as prescribed. If they stop taking the drugs too soon, they can become sick again; if they do not take the drugs correctly, the TB bacteria that are still alive may become resistant to those drugs.
What is MTB treatment?
Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB) remains a worldwide health care challenge despite the relatively recent evolution of effective antituberculous medications and combination drug therapy.
Is MTB a global health problem?
Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB) remains a worldwide health care challenge despite the relatively recent evolution of effective antituberculous medications and combination drug therapy. In many parts of the world, the continued high prevalence of MTB disease is caused in part by the lack of availabi ….
What is the best treatment for TB?
The most common treatment for active TB is isoniazid INH in combination with three other drugs—rifampin, pyrazinamide and ethambutol. You may begin to feel better only a few weeks after starting to take the drugs but treating TB takes much longer than other bacterial infections.
How long does it take to treat TB?
The treatment for this type of TB takes much longer, 20 to 30 months to complete, and you may experience more side effects.
What are the side effects of TB?
While you are in treatment for active TB disease, you will need regular checkups to make sure your treatment is working. Everyone is different, but there are side effects associated with taking the medications, including: 1 Upset stomach, nausea and vomiting or loss of appetite 2 Tingling or numbness in the hands or feet 3 Itchy skin, rashes or bruising 4 Changes in your eyesight or blurred visions 5 Yellowish skin or eyes 6 Dark-colored urine 7 Weakness, fatigue or fever that for three or more days
What are the symptoms of TB?
Yellowish skin or eyes. Dark-colored urine. Weakness, fatigue or fever that for three or more days. It is important to tell your doctor or TB nurse immediately if you begin having any unusual symptoms while taking medicine for either preventive therapy or for active TB disease.
Can TB cause liver damage?
TB drugs can be toxic to your liver, and your side effects may be a warning sign of liver damage . If you are having trouble with tingling and numbness, your doctor may prescribe a vitamin B6 supplement while you are in treatment. It may also be possible to change TB medications if your side effects are serious.
Can you get TB from taking too much medicine?
You must finish your medicine and take the drugs exactly as prescribed. If you stop taking the drugs too soon you can become sick again and potentially spread the disease to others. Additionally, by taking the drugs incorrectly, TB germs that are still alive may become drug-resistant, making it harder for you to get better next time.
Is TB a serious disease?
TB is a serious disease, and can be fatal if not treated properly. It is important to remember that all medications have risks and benefits. Learn more from CDC’s Dear Colleague letter. Not everyone infected with TB bacteria becomes sick. As a result, two TB-related conditions exist: latent TB infection and TB disease.
Can rifampin be used for TB?
Treatment. impurities in rifampin and rifapentine, two important anti-tuberculosis (TB) medications. People with TB disease or latent TB infection taking rifampin or rifapentine should continue taking their current medication, and should talk with their healthcare provider about any concerns.
When do you suspect tuberculosis? What should you expect to find?
In non-endemic areas of the world such as the US, tuberculosis (TB) should be suspected in the setting of a recent close contact with a person with infectious TB or other risk factors for developing TB (see below). Clinical findings depend on the organ system (s) involved.
How did the patient develop tuberculosis? What was the primary source from which the infection spread?
Mycobacterium tuberculosis, the causative organism for TB, is spread via aerosolized nuclei from individuals with TB disease (pulmonary or rarely upper airway, e.g. laryngeal TB). Close contact with such individuals, especially in a closed, crowded space without good air circulation is the primary source of infection. Infrequently, bovine TB (M.
Which individuals are of greater risk of developing tuberculosis?
Close and recent (generally within the last 12 months) contact with an individual with infectious TB. Individuals (especially children) may be diagnosed as part of a contact investigation, or may be sentinels for close contact with infectious TB. Today’s top picks on the Haymarket Medical Network Continue Reading
What laboratory studies should you order and what should you expect to find?
Positive tuberculin skin test (TST) is supportive. TST should be placed and interpreted by an experienced person. Size of induration (rather than redness) should be recorded in mm (rather than positive or negative). Interpretation of the TST is dependent on the risk of infection and developing active TB.
What imaging studies will be helpful in making or excluding active tuberculosis?
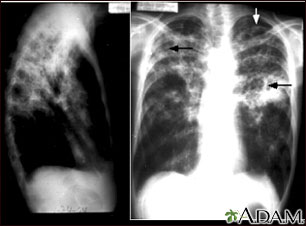
Chest X-ray ($) is quite helpful for diagnosing pulmonary TB. Intrathoracic adenopathy (e.g. hilar adenopathy), cavitary lesion (s), and miliary shadowing are suspicious for TB. In addition, patterns consistent with various forms of pneumonia can also be seen. Calcification is suggestive of a long standing process or likely latent TB infection.
What consult service or services would be helpful for making the diagnosis and assisting with treatment?
If you decide the patient has tuberculosis, what therapies should you initiate immediately?
What other additional laboratory findings may be ordered?
Though non-specific, markers of inflammation (e.g. erythrocyte sedimentation rate [ESR], C-reactive protein [CRP]) are elevated in the majority of patients with active TB. CRP therefore has a high negative predictive value.