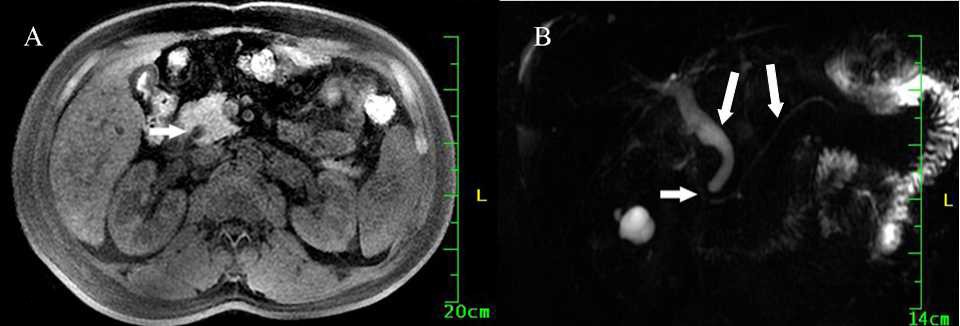
Background and Aim: Endoscopic papillary balloon dilation (EPBD) has been advocated as an alternative therapy to endoscopic sphincterotomy for bile duct stones. However, Accepted for publication 22 September 2007. studies have shown that EPBD may increase the risk for pancreatitis.
Is bile duct cancer a death sentence?
What should be done with a dilated bile duct? Abstract Current methods for imaging the biliary tree include ultrasound, CT, MRI, endoscopic retrograde cholangiography, and endoscopic ultrasound (EUS).
What medications treat a bile duct obstruction?
is a trend of duct dilatation post - cholecystectomy. In a study of 234 patients undergoing cholecystectomy, the CBD increased after surgery from a diameter of 5.9 mm to 6.1mm at an average 393 days post - cholecystectomy CBD diameter ma. y increase 1-2 mm post surgery but some patients may have a more profound CLINICAL APPROACH TO DILATED BILE DUCT
What to do if you have bile duct cancer?
Jul 25, 2012 · A bile duct dilatation of more than 7 mm in 30% of the patients was observed, while no patients had bile duct dilatation of more than 10 mm. All of the bile duct dilatation patients were asymptomatic while clinical characteristics that …
Can bile duct cancer be cured?
Abstract. Background and study aims: Although abdominal ultrasonography (US) is a good initial screening method for detection of biliary tract disease, we sometimes encounter patients who only have findings of dilatation of the common bile duct (CBD) on US, without specific biliary symptoms or jaundice. This study aimed to evaluate the causes and clinical significance of …

What does mildly dilated bile duct mean?
HG Dilated bile ducts are usually caused by an obstruction of the biliary tree, which can be due to stones, tumors (usually of either the papilla of Vater or the pancreas), benign strictures (due to chronic pancreatitis or primary sclerosing cholangitis), benign stenosis of the papilla (ie, papillary stenosis), or a ...
What happens if you have a dilated bile duct?
The size of the common bile duct, if dilated, may suggest a blockage downstream. This is a specific finding that is looked for when a patient gets an ultrasound for a suspected liver or Gallbladder disease. When a patient has their gallbladder removed, the common bile duct dilates over some time.Mar 10, 2011
How serious is a dilated common bile duct?
Coexisting CBD and intrahepatic bile duct dilation, age, and jaundice were found to be indicators of pathologic lesions. Dilation of both the CBD and pancreatic duct was suggestive of pancreatic disease, especially pancreatic malignancy in the setting of obstructive jaundice.
What can cause the bile duct to be dilated?
Choledocholithiasis. Choledocholithiasis is the most common cause of bile duct dilatation in patients with gallstones. Approximately 85% of obstructing bile duct stones are found in the distal duct near the head of the pancreas. This region of the duct is often difficult to visualize with ultrasound.
What is mildly dilated CBD?
Opinions vary slightly on the maximum calibre of a normal CBD, but 6mm is one accepted upper limit of normal with a further 1mm diameter allowed for each decade over 60 years. It normally gets slightly dilated after cholecystectomy, with upper limit (95% prediction interval) being about 10 mm after a few months.
Does a dilated bile duct cause pain?
This can stop the body from absorbing some fats and vitamins properly. People with bile duct obstruction also often experience: itching. abdominal pain, usually in the upper right side.Jun 11, 2018
What are the two types of bile ducts?
The two types of bile ducts in the liver are intrahepatic and extrahepatic ducts. Intrahepatic ducts: Intrahepatic ducts are a system of smaller tubes within the liver that collect and transport bile to the extrahepatic ducts.
What is the treatment for gallstones?
Some of the treatment options include a cholecystectomy and an ERCP. A cholecystectomy is the removal of the gallbladder if there are gallstones. An ERCP may be sufficient to remove small stones from the common bile duct or to place a stent inside the duct to restore bile flow.
What is a biliary obstruction?
A biliary obstruction is a blockage of the bile ducts. The bile ducts carry bile from the liver and gallbladder through the pancreas to the duodenum, which is a part of the small intestine. Bile is a dark-green or yellowish-brown fluid secreted by the liver to digest fats. After you eat, the gallbladder releases bile to help in digestion ...
What happens to the gallbladder after eating?
After you eat, the gallbladder releases bile to help in digestion and fat absorption. Bile also helps clear the liver of waste products. Obstruction of any of these bile ducts is referred to as a biliary obstruction. Many of the conditions related to biliary obstructions can be treated successfully.
What causes gallstones in the liver?
inflammation of the bile ducts. trauma. a biliary stricture, which is an abnormal narrowing of the duct. cysts. enlarged lymph nodes. pancreatitis . an injury related to gallbladder or liver surgery. tumors that have reached the liver, gallbladder, pancreas, or bile ducts.
What are the conditions that can be diagnosed with blood tests?
Blood tests can usually rule out certain conditions, such as: cholecystitis, which is an inflammation of the gallbladder. cholangitis, which is an inflammation of the common bile duct. an increased level of conjugated bilirubin, which is a waste product of the liver. an increased level of liver enzymes.
What is a biliary radionuclide scan?
Biliary radionuclide scan (HIDA scan) A hepatobiliary iminodiacetic acid scan, or HIDA scan, is also referred to as a biliary radionuclide scan. It uses radioactive material to provide valuable information about the gallbladder and any possible obstructions.
What causes bile duct dilation?
Choledocholithiasis. Choledocholithiasis is the most common cause of bile duct dilatation in patients with gallstones. Approximately 85% of obstructing bile duct stones are found in the distal duct near the head of the pancreas. This region of the duct is often difficult to visualize with ultrasound.
What are the findings of bile duct ultrasound?
Ultrasound findings reflect the pathology of the bile ducts, namely diffuse intrahepatic bile duct dilatation, truncation and increased periductal echogenicity, and infectious complications, such as pyogenic cholangitis, liver abscesses, stones, pancreatitis and cholangiocarcinoma.49 Occasionally, flukes or aggregates of eggs are visualized as non-shadowing echogenic foci or casts within the bile ducts ( Figure 8.6 ). 50 Ultrasound is less useful in therapy follow-up and in the differentiation between resolved and active infection, as the pathological changes of the bile ducts can persist for years even after the symptoms have resolved.
How long does it take for a stent to rest?
1. Stent restenosis: The rate of restenosis is usually 20%–30% after 3 months. It is mainly related to tumor growth toward the distal and proximal end of the stent and in the stent, and partly related to bile plug and clastic deposition.
What causes ascending cholangitis?
Recurrent attacks of ascending cholangitis caused by bile duct strictures and dilation, intrahepatic and extrahepatic stone formation (in the absence of cholelithiasis), and enteric bacterial infection characterize the syndrome of recurrent pyogenic cholangitis, also known as oriental cholangiohepatitis, intrahepatic pigment stone disease, and biliary obstruction syndrome of the Chinese. First described in Chinese patients in Hong Kong, it is now recognized as a serious health problem in China, Taiwan, Japan, Korea, Singapore, Vietnam, Malaysia, and the Philippines. 125 This disorder is the main cause of acute abdominal pain in Hong Kong emergency rooms. 126 Sporadic cases have been reported in Europe and South Africa and Australia. In the United States and Canada, the disease is largely, but not exclusively, limited to Asian immigrants. 123, 127 The cause of this disease is unknown. The two most popular theories are infection and malnutrition. The former postulates that inflammatory and fibrosing changes are secondary to chronic infestation of the biliary tree with endemic parasites, such as C. sinensis and A. lumbricoides. Interference to bile flow caused by adult flukes or eggs causes stagnation, which leads to secondary bacterial infection, pigment stone formation, and pyogenic cholangitis. 128 Demonstration of ova, or fragments of parasites, within stones provides support to this theory. However, patients with recurrent cholangitis have only a slightly higher rate of infestation by C. sinensis than the general population in endemic areas where numerous individuals are infected with liver flukes without ever developing cholangitis. In other areas where parasitic infection is much less common, such as Taiwan, the incidence of recurrent cholangitis and hepatolithiasis is high. The second theory postulates that recurrent infectious gastroenteritis in malnourished people causes frequent episodes of portal bacteremia. As mentioned before, bilirubin glucuronide is deconjugated by β-glucuronidase produced by bacteria. Unconjugated bilirubin precipitates as calcium bilirubinate, which initiates the formation of brown stones. A protein-poor diet is thought to be associated with a deficiency of natural inhibitors of the enzyme in the bile. This theory explains the much higher incidence of disease in patients from a low socioeconomic class. However, it does not explain why this disorder is uncommon in other geographic areas, where the population also suffers from chronic malnourishment.
What is PSC in a child?
Primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) has features of bile duct dilatation, with or without intraductal calculi, cirrhosis, and portal hypertension.66 Most children have intrahepatic and extrahepatic involvement, although the disease may be limited to either site. 88 PSC may affect only isolated areas of the intrahepatic bile ducts, unlike Caroli's disease, in which the large central intrahepatic ducts are typically affected. 66
Why is regular follow up important?
Regular followup can make patients communicate with doctors regularly, which can comfort and help them mentally and spiritually. Moreover, small recurrence and metastasis can be detected early and treated in time to improve the curative effect. Through regular followup and evaluation of curative effect, we can summarize experience and lessons, optimize treatment plan, improve treatment measures and improve medical staff’s understanding of the disease. The main followups include:
Why is my bile duct enlarged?
Here’s a look at some of the other causes of enlarged bile ducts: Inflammation. Inflammation of the bile duct can occur due to infection , which then leads to enlargement. Porta hepatis.
What is the function of bile ducts?
Bile ducts have a major function when it comes to our well-being. Having an enlarged bile duct can lead to uncomfortable pain as well as a host of other symptoms. Bile is a liquid produced by our liver. It is a yellowish-brownish or dark-green substance that the bile duct normally carries from the liver and gallbladder through the pancreas to ...
What is a lymph node enlargement?
An enlargement of the lymph node on the surface of the liver where the vein and artery enter and hepatic duct leaves. Cysts. Can be common in the bile duct and cause enlargement. Surgery. Postoperative stricture (narrowing) in the region of the bile duct. Cancer.
Can bile duct cancer be treated with chemotherapy?
Sadly, bile duct cancers are resistant to many types of chemotherapy, so clinical trials are the best way to try this type of treatment. Patients with bile duct strictures may be able to have endoscopic therapy, which can be done on an inpatient or outpatient basis.
What is the name of the cancer that spreads slowly?
Cancer. Malignant cancer of the bile duct is called cholangiocarcinoma and grows slowly. It eventually spreads throughout the liver. A tumor at the head of the pancreas can also lead to enlargement of the bile duct.
What are the symptoms of stricture?
Jaundice. Dark urine, pale feces. Nausea and vomiting. When it comes to strictures, about 15 percent of bile duct problems are found during the time of surgery, but 85 percent are discovered following the operation. Discharge of bile is usually detected through the drainage tube along with deepening jaundice.
What is the procedure to remove cancer from the liver?
The operation could also include removal of lymph nodes to check for cancer. Partial hepatectomy— When cancer is near the liver, the surgeon may remove a part of it.
