What are the causes and treatments for a high level of microalbumin?
Elevated microalbumin levels in the urine indicate that your kidneys are leaking protein. There are many conditions that can cause this, and for all of these it is really important to speak to your doctor about this result. The most common causes of elevated protein in the urine is diabetes or high blood pressure (hypertension).
How to cure or prevent microalbuminuria?
Treatment
- Lifestyle Interventions. Lifestyle interventions are an important part of treatment. ...
- Medications. In general, if you have medical conditions that may be worsening your kidney function (like diabetes), it’s helpful to get those under better control.
- Treatment Goals. ...
- Microalbuminuria and Cardiovascular Disease. ...
- A Word From Verywell. ...
How do you treat microalbuminuria?
This may be done in several ways:
- 24-hour urine test. Your doctor may ask you to collect all of your urine in a special container over a 24-hour period and submit it for analysis.
- Timed urine test. Your doctor may ask you to provide a urine sample first thing in the morning or after a four-hour period of not urinating.
- Random urine test. A random urine test can be taken at any time. ...
When to treat microalbuminuria?
Know what the results mean.
- The normal result is less than 30 mg
- 30 to 300 mg is indicative of early kidney disease
- More than 300 mg is indicative of more advanced kidney disease Appropriate discussion with your healthcare provider about the test result is necessary to make prompt treatment and management. ...

Why do you need a microalbumin test?
Why it's done. Your doctor may recommend a urine microalbumin test to detect early signs of kidney damage. Treatment may prevent or delay more-advanced kidney disease. How often you need microalbumin tests depends on any underlying conditions and your risk of kidney damage. For example:
Why is my microalbumin level higher than normal?
Several factors can cause higher than expected urinary microalbumin results, such as: Blood in your urine (hematuria) Certain medications . Fever. Recent vigorous exercise.
Can you have a microalbumin test if you have high blood pressure?
High blood pressure. If you have high blood pressure, your doctor may recommend microalbumin tests more regularly. Discuss with your doctor how often to repeat this test. If your urinary microalbumin level is elevated, your doctor may recommend treatment and more-frequent testing.
Can you eat before a microalbumin test?
The microalbumin test is a simple urine test. You can eat and drink normally before the test. The amount of urine your doctor may want to test may vary — you may only need to provide a random sample, or your doctor may ask you to collect 24 hours' worth of urine.
How is microalbuminuria diagnosed?
Microalbuminuria is diagnosed based on laboratory urine tests that might be performed along with a standard medical exam. Usually, you won’t need to do anything special to prepare for the test.
What causes microalbuminuria?
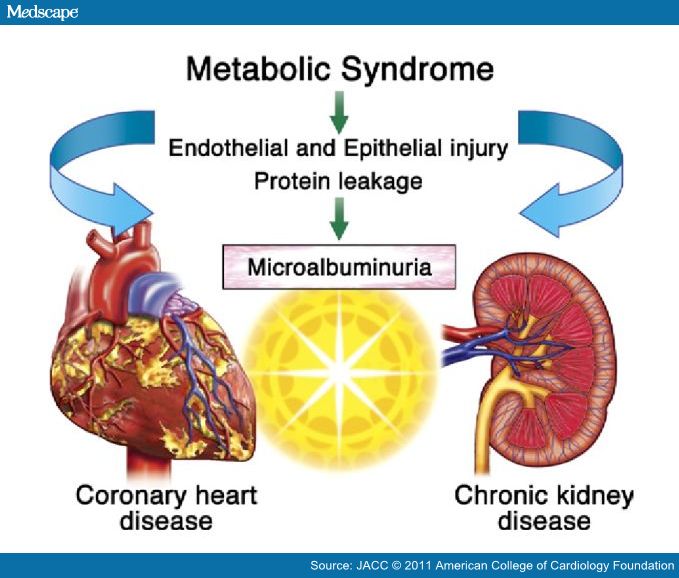
Microalbuminuria is caused by kidney damage. Some medical conditions that can lead to kidney damage include: 1 High blood pressure 2 Type I and type II diabetes 3 Obesity and metabolic syndrome 4 Genetic inherited kidney diseases 4
What is the difference between microalbuminuria and albuminuria?
At this point, the condition might be called albuminuria or macroalbuminuria instead. In other words, microalbuminuria indicates less severe disease than albuminuria.
How much albumin is excreted per day?
Technically, microalbuminuria is defined as urinary excretion of albumin between 30 and 300 milligrams of albumin per day. You also might see it defined as between 20 and 200 micrograms per minute. 2
Does microalbuminuria increase risk?
Not everyone with microalbuminuria will have those issues, but it does somewhat increase your risk. 5 However, some of the treatments to reduce albuminuria may also help reduce this risk. That’s another good reason to look at your whole health overall with your healthcare provider to see how you can act in terms of prevention.
Can microalbuminuria be detected in the kidney?
Microalbuminuria is often the first detectable sign of early kidney disease . People who are at risk of kidney disease may need to have regular urine tests for microalbuminuria. This might apply to you if you have high blood pressure, type 1 or type 2 diabetes, 6 heart disease, obesity or metabolic syndrome, other medical conditions that increase the risk of kidney disease (like lupus), and/or a family history of kidney disease.
Can microalbuminuria cause kidney disease?
Usually, microalbuminuria does not cause any symptoms. However, it can be one of the earliest ways to detect kidney disease. 2 Kidney damage may become significant (and not easily reversed) before a person notices any symptoms. This is part of why it is important for people at risk of kidney disease to have the test repeatedly so that treatment can begin if necessary.
Why do you need a microalbumin test?
Microalbuminuria test indications. Your doctor may recommend a urine microalbumin test to detect early signs of kidney damage. Treatment may prevent or delay more advanced kidney disease. How often you need microalbumin tests depends on any underlying conditions and your risk of kidney damage.
What are the risk factors for microalbuminuria?
These include body mass index (BMI), waist circumference, triglyceride, sex and metabolic syndrome in children and adolescents 10).
What is it called when you have a lot of albumin in your urine?
Once there are larger amounts of albumin in the urine it is called macroalbuminuria and it could indicate more severe kidney disease.
What is the ratio of microalbumin to creatinine?
Microalbuminuria means that you have an excess of albumin in the urine and is diagnosed when urinary albumin excretion is between 30 and 300 mg/day, or when the microalbumin/creatinine ratio is between 30–300 μg/mg in random urine 1). In most healthy people, the kidneys prevent albumin and other proteins from entering the urine.
How can diabetics prevent kidney disease?
Diabetic kidney disease can be prevented by keeping blood glucose in your target range. Research has shown that tight blood glucose control reduces the risk of microalbuminuria by one third. In people who already had microalbuminuria, the risk of progressing to macroalbuminuria was cut in half. Other studies have suggested that tight control can reverse microalbuminuria.
What is 300 mg/g of albumin?
Traditionally, 30–300 mg/g has been called microalbuminuria and greater than 300 mg/g has been called macroalbuminuria. However, the 300 mg/g cut-off merely represents a rough correlation with the lower limit of sensitivity of the traditional urine dipstick for albumin.
Is 300 mg of microalbumin normal?
Less than 30 mg is normal. Thirty to 300 mg may indicate early kidney disease ( microalbuminuria) More than 300 mg indicates more advanced kidney disease ( macroalbuminuria) Discuss your test result with your doctor and what it means for your health. If your urinary microalbumin level is higher than normal, your doctor may recommend repeating ...
How does Ayurveda help with microalbuminuria?
In microalbuminuria treatment, Ayurveda aims to revive kidneys’ health so that kidneys can do their functions naturally. Once the kidneys get healthy, they begin to work well, and thus the albumin urine level gets normalized naturally. Consequently, an albuminuria patient gets rid of this problem naturally for longer.
What is microalbuminuria?
Microalbuminuria is defined as leakage of minor or moderate albumin in urine than normal. It’s the small or initial form of Albuminuria and thus less severe than Albuminuria as well. This problem indicates that your kidneys are not working well. It may also be a risk factor for cardiovascular disease. In microalbuminuria, generally, the urinary ...
How microalbuminuria occurs?
Microalbuminuria is primarily a sign of kidney damage. However, it may also take place for a temporary period, which is not problematic. Various factors may cause damage to kidneys; those are:
What causes microalbuminuria in the kidneys?
Microalbuminuria occurs when there is nominal damage in your kidneys that won’t be visible easily. But it affects kidney functionality and causes a small protein to leak into urine. So, any factor (be it internal or external) can be kept in the list of causative factors for microalbuminuria.
How much albumin is excreted in a day?
In microalbuminuria, generally, the urinary albumin excretion ranges between 30 to 300 milligrams of albumin per day. Sometimes, it may also be seen as about 20-200 micrograms per minute. Urinary albumin value less than the mentioned value is not considered microalbuminuria. Albumin is a type of protein mainly present in your bloodstream.
Does Ayurvedic medicine cure albuminuria?
Ayurvedic microalbuminuria treatment uses herbal formulations, ancient cures, diet changes, and some lifestyle interventions; it offers a permanent cure with no after-use side effects.
Can microalbuminuria cause kidney problems?
In general, Microalbuminuria causes no symptoms. But it can be the earliest way to find a kidney problem. If you are detected with microalbuminuria, it means there is slight or minor damage in your kidneys, causing a small amount of protein to leak into urine, which is slightly higher than the normal protein level in urine.
Why do you need a microalbumin test?
A microalbumin urine test helps because it can find kidney problems before they get too far. Your kidneys filter your blood. They keep the good stuff your body needs and send the waste out through your pee. Your doctor will suggest one when you have: Type 1 diabetes.
What causes microalbumin in urine?
Diabetes and Kidney Disease. Diabetes is the No. 1 cause of kidney failure (and the leading cause of microalbumin in the urine) in the United States. When you have diabetes, the level of sugar (or “glucose”) in your blood is too high. Over time, that extra sugar damages the small blood vessels in your kidneys.
What Is a Microalbumin Urine Test?
A microalbumin urine test checks for small (or "micro") amounts of albumin in your urine -- at levels so small a regular urine test might not find them. It can be a sign of kidney disease.
Why is my urine high in microalbumin?
Finding microalbumin in your urine also may mean you are at a higher risk for heart disease. Higher levels of microalbumin may also be caused by blood in your urine, a urinary tract infection, and an acid-base imbalance in your blood.
How often should you have albumin in your urine?
People with diabetes should have a urine test for albumin when first diagnosed and then at least once a year after that. If you have high blood pressure, talk with your healthcare provider about how often you should be tested.
What does it mean when you have a small amount of albumin in your urine?
A moderate amount of albumin could mean early stages of kidney disease , and it's likely your healthcare provider will need to adjust your treatment. Finding microalbumin in your urine also may mean you are ...
Why does albumin leak into urine?
Albumin is a protein needed for tissue growth and healing. It can leak into your urine when your kidneys aren't working as they should. The test can find out if diabetes has damaged your kidneys.
What is the difference between albuminuria and proteinuria?
Proteinuria is a sign of abnormal excretion of protein by the kidney but is a nonspecific term including any or all proteins excreted. In contrast, albuminuria specifically refers to an abnormal excretion rate of albumin. Microalbuminuria refers to an abnormally increased excretion rate of albumin in the urine in the range of 30-299 mg/g creatinine. It is a marker of endothelial dysfunction and increased risk for cardiovascular morbidity and mortality especially, but not exclusively, in high-risk populations such as diabetics and hypertensives. Testing for microalbuminuria is now made easy by in-office dipstick tests (semiquantitative) and widely available laboratory testing (quantitative). Physicians should screen all diabetics for albuminuria and strongly consider screening hypertensives to identify those at higher risk for cardiovascular disease. Appropriate intervention, including use of drugs that block the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, may be appropriate in such cases as suggested by the American Diabetes Association and the Seventh Report of Joint National Committee on the Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure.
Is microalbuminuria a marker of endothelial dysfunction?
It is a marker of endothelial dysfunction and increased risk for cardiovascular morbidity and mortality especially, but not exclusively, in high-risk populations such as diabetics and hypertensives. Testing for microalbuminuria is now made easy by in-office dipstick tests (semiquantitative) and widely available laboratory testing (quantitative).
How to treat hypoalbuminemia?
You can often treat hypoalbuminemia by raising your albumin levels back to normal. Treatment may vary if a specific condition is causing your hypoalbuminemia.
How much albumin is needed to keep fluid from leaking out of blood vessels?
Depending on your age, your body needs anywhere between 3.5 and 5.9 grams per deciliter (g/dL). Without enough albumin, your body can’t keep fluid from leaking out of your blood vessels. Not having enough albumin can also make it harder to move important substances throughout your body.
What happens if you don't have enough albumin?
Hypoalbuminemia happens when you don’t have enough of the protein albumin in your bloodstream. Albumin is a protein that’s made in your liver. It’s an important protein in the plasma of your blood. Depending on your age, your body needs anywhere between 3.5 and 5.9 grams per deciliter (g/dL). Without enough albumin, your body can’t keep fluid ...
What are the complications of hypoalbuminemia?
Hypoalbuminemia can you put you at risk of developing other conditions, including: pneumonia. pleural effusion, which happens when fluid builds up around your lungs. ascites, which happens when fluid builds up in your abdominal area. atrophy, which is significant weakening of the muscles.
Can hypoalbuminemia be fatal?
Untreated hypoalbuminemia can significantly heighten your risk of fatal injuries or conditions in these cases.
Is hypoalbuminemia a risk factor?
Hypoalbuminemia is also considered a risk factor for some conditions. Developing it while you have certain underlying conditions, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, can put you at risk of developing additional complications.
Can hypoalbuminemia stunt growth?
See your doctor if you begin to feel exhausted or have trouble breathing without warning. Hypoalbuminemia can also stunt a child’s growth. If you notice that your child isn’t growing at a rate normal for their age, talk to your doctor about whether they should test your child for hypoalbuminemia.

Overview
Why It's Done
- Try losing extra weight
- Exercise regularly
- Stop smoking
- Foamy, frothy or bubbly- looking urine
- Needing to urinate more often
- Hiccups
- Fatigue (feeling tired)
- Trouble sleeping
- Nausea and vomiting
- Dry, itchy skin
See a doctor immediately if you notice:
- Swelling in your hands, feet, abdomen or face
- Shortness of breath
How You Prepare
What You Can Expect
- A urine microalbumin test is a test to detect very small levels of a blood protein (albumin) in your urine. A microalbumin test is used to detect early signs of kidney damage in people who are at risk of developing kidney disease. Healthy kidneys filter waste from your blood and hang on to the healthy components, including proteins such as albumin. Kidney damage can cause proteins to l…
Results
- Your doctor may recommend a urine microalbumin test to detect early signs of kidney damage. Treatment may prevent or delay more-advanced kidney disease. How often you need microalbumin tests depends on any underlying conditions and your risk of kidney damage. For example: 1. Type 1 diabetes.If you have type 1 diabetes, your doctor may recommend a microal…