Table 3
| Ethylene glycol | Methanol | |
| Lethal dose | 1.4–1.6 mL/kg | 1.2 mL/kg (risk of blindness: 10–15 mL) |
| Elimination | Zero or 1st order | Zero order |
| Total body clearance | 70 mL/min | 11 mL/min |
| Renal clearance * | 17–39 mL/min | 1 mL/min |
Full Answer
Is there a cure for methanol poisoning?
Is there a cure for methanol poisoning? There is a cure! The sooner the antidote, fomepizole, is taken, the increased likelihood of a good outcome for the victim. Other treatment options include dialysis and consumption of sodium bicarbonate, folate, and thiamine. This is of course, not medical advice.
How do medications treat methanol poisoning?
Toxic Methanol in Hand Sanitizers: Poisonings Continue
- FDA's List Grows. The FDA first alerted consumers about toxic hand sanitizers in mid-June, when the agency warned against the use of hand sanitizer products with methanol made by Eskbiochem.
- Methanol, Ethanol, Isopropanol. ...
- A Closer Look at the Arizona, New Mexico Cases. ...
Why is ethanol an antidote for methanol poisoning?
When ethanol is given to someone with methanol poisoning, what we are trying is to use the body's preference of ethanol over methanol. In other words, the body will neutralize the ethanol first and then the methanol. When the body is busy working on ethanol, there other excretion routes will reduce the methanol concentration to a safer level.
Why is methanol poisonous than ethanol?
Which one is more toxic ethanol or methanol? But, when you consume methanol, the way your body metabolizes it makes it much more toxic than ethanol. Methanol poisonings were common during the Prohibition Era of the 1920’s and 30’s because methanol was intentionally added to industrially produced ethanol. Why does ethanol treat methanol ...

What is the antidote for methanol?
Although both ethanol and fomepizole are effective, fomepizole is the preferred antidote for methanol poisoning.
How is methanol poisoning managed treated?
The primary treatments are either ethanol or fomepizole, and unlike ethylene glycol toxicity, dialysis is often recommended.
Can you recover from methanol poisoning?
Methanol poisoning can be treated successfully if diagnosed within 10-30 hours of ingestion. If you suspect someone might have methanol poisoning, get them to a hospital which has dialysis equipment as soon as possible.
What is the antidote of methanol and ethylene glycol?
Ethylene glycol (EG) and methanol are responsible for life-threatening poisonings. Fomepizole, a potent alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) inhibitor, is an efficient and safe antidote that prevents or reduces toxic EG and methanol metabolism.
What is the antidote for ethanol poisoning?
Fomepizole has few side effects and is easy to use in practice and it may obviate the need for haemodialysis in some, but not all, patients. Hence, fomepizole has largely replaced ethanol as the toxic alcohol antidote in many countries.
How long does methanol poisoning last?
Clinically, methanol ingestion is associated with an acute inebriation followed by an asymptomatic period lasting 24 to 36 hours. Abdominal pain caused by pancreatitis, seizures, blindness, and coma may develop.
What happens if you get methanol poisoning?
The initial symptoms of methanol intoxication include central nervous system depression, headache, dizziness, nausea, lack of coordination, and confusion. Sufficiently large doses cause unconsciousness and death.
How is methanol poisoning diagnosed?
Definitive diagnosis requires measurement of the serum concentration of methanol by the gold standard test which is gas chromatography and confirmation of an elevated methanol level (> 6mmol/L or 20mg/dL) [6].
What is the antidote for ethylene glycol?
Administration of either intravenous ethanol or fomepizole, both of which competitively inhibit ethylene glycol metabolism by alcohol dehydrogenase and can prevent the production and accumulation of the toxic metabolites, can be used as an antidote.
How do you test for methanol poisoning?
The diagnosis of methanol poisoning is challenging, requiring blood gas analysis and then laboratory-based chromatographic measurement of methanol concentrations. This usually takes hours if at all available in the receiving hospital.
What happens when you inhale methanol?
Symptoms of acute methanol exposure may include headache, weakness, drowsiness, nausea, difficult breathing, drunkenness, eye irritation, blurred vision, loss of consciousness, and possibly death.
How is methanol metabolized in the body?
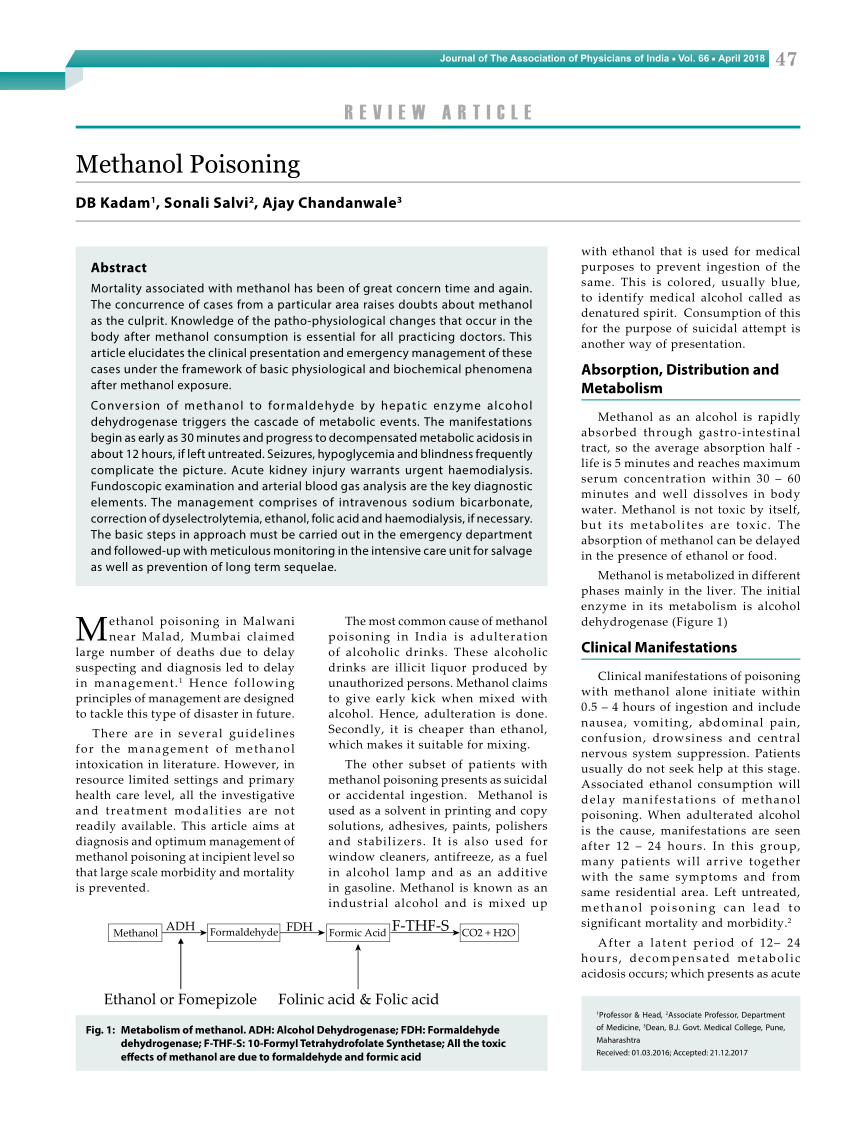
Methanol is primarily metabolized in the liver via alcohol dehydrogenase into formaldehyde. Formaldehyde is subsequently metabolized via aldehyde dehydrogenase into formic acid, which ultimately is metabolized to folic acid, folinic acid, carbon dioxide, and water. A small portion is excreted unchanged by the lungs.
Can hemodialysis remove methanol?
Hemodialysis can easily remove methanol and formic acid. Indications for this procedure include (1) greater than 30mL of methanol ingested, (2) serum methanol level greater than 20 mg/dL, (3) observation of visual complications, and (4) no improvement in acidosis despite repeated sodium bicarbonate infusions.
Is ethanol metabolized by ADH?
Like methanol, ethanol is metabolized by ADH, but the enzyme’s affinity for ethanol is 10-20 times higher than it is for methanol. Fomepizole is also metabolized by ADH; however, its use is limited because of high cost and lack of availability. [ 10, 22, 23] Hemodialysis can easily remove methanol and formic acid.
Does bicarbonate help with methanol poisoning?
Metabolic acidosis in methanol poisoning may necessitate the administration of bicarbonate and assisted ventilation. Bicarbonate potentially may reverse visual deficits. In addition, bicarbonate may help to decrease the amount of active formic acid.
What is methanol poisoning?
Methanol poisoning may result from the ingestion of windshield washer fluid, gasoline additives, duplicating fluids, canned cooking fuels, and a variety of other products found in the home and workplace. Over 1000 pediatric exposures were reported to the AAPCC in 2003.1
How long does methanol last?
Clinically, methanol ingestion is associated with an acute inebriation followed by an asymptomatic period lasting 24 to 36 hours. Abdominal pain caused by pancreatitis, seizures, blindness, and coma may develop. The blindness is due to direct toxicity of formic acid on the retina.
What is ethylene glycol and methanol?
Ethylene glycol and methanol intoxications are characteristically associated with the development of a severe anion gap metabolic acidosis. Metabolism of ethylene glycol by alcohol dehydrogenase generates various acids, including glycolic, oxalic, and formic acids.
How long does it take for methanol to cause an anion gap?
Methanol intoxication is accompanied by the production of formaldehyde and formic acid; production of the latter leads to a profoundly elevated anion gap, which usually develops 12 to 24 hours after ingestion . Although controversial, formic acid seems to be the earliest cause of anion-gap elevation, although lactic and other organic acids may contribute to this disturbance. Additionally, multiple-organ failure results in decreased hepatic lactate utilization. In untreated patients, as methanol is metabolized, an early osmolal gap and normal or slightly elevated anion gap is followed by a decrease in the osmolal gap with an increase in the anion gap. Treatment includes correction of the profound academia with bicarbonate administration, use of fomepizole or ethanol to inhibit the metabolism of methanol, and hemodialysis to correct the profound acidemia and remove the toxic compounds. Methanol is further discussed in Chapter 32.
Is methanol a toxic substance?
Ingestion of greater than 100 mg/kg of methanol should be deemed potentially toxic. Therefore, even a single swallow of windshield washer fluid, with 40% methanol, is to be considered dangerous. Methanol is less inebriating than ethanol or ethylene glycol, so patients may appear well shortly after ingestion.
Can you get a liver biopsy after methanol poisoning?
However, it should be recalled that the patients poisoned by methanol are often chronic ethanol abusers. The liver can be safely procured after methanol poisoning provided that liver function tests are normal with absence of steatosis at the biopsy.
Can methanol cause gastritis?
Gastritis and/or pancreatitis sometimes occur after acute ingestion of methanol. Methanol is slowly metabolized by alcohol dehydrogenase into formaldehyde, which is further metabolized to formic acid. Hypoglycemia may occur as was described for ethanol.
How many cases of methanol poisoning per year?
1,700 cases per year (US) Methanol toxicity is poisoning from methanol, characteristically via ingestion. Symptoms may include a decreased level of consciousness, poor or no coordination, vomiting, abdominal pain, and a specific smell on the breath. Decreased vision may start as early as twelve hours after exposure.
How many people died from methanol poisoning?
There are cases of methanol resistance, such as that of Mike Malloy, whom someone tried and failed to poison by methanol in the early 1930s. In December 2016, 78 people died in Irkutsk, Russia from methanol poisoning after ingesting a counterfeit body lotion that was primarily methanol rather than ethanol as labeled.
How do you know if you are intoxicated by methanol?
The initial symptoms of methanol intoxication include central nervous system depression, headache, dizziness, nausea, lack of coordination, and confusion. Sufficiently large doses cause unconsciousness and death. The initial symptoms of methanol exposure are usually less severe than the symptoms from the ingestion of a similar quantity of ethanol. Once the initial symptoms have passed, a second set of symptoms arises, from 10 to as many as 30 hours after the initial exposure, that may include blurring or complete loss of vision, acidosis, and putaminal hemorrhages, an uncommon but serious complication. These symptoms result from the accumulation of toxic levels of formate in the blood, and may progress to death by respiratory failure. Physical examination may show tachypnea, and eye examination may show dilated pupils with hyperemia of the optic disc and retinal edema .
What is ethanol excreted from?
Methanol is excreted by the kidneys without being converted into the very toxic metabolites formaldehyde and formic acid. Alcohol dehydrogenase instead enzymatically converts ethanol to acetaldehyde, a much less toxic organic molecule.
How much methanol is fatal?
As little as 10 mL of pure methanol when drunk is metabolized into formic acid, which can cause permanent blindness by destruction of the optic nerve. 15 mL is potentially fatal, although the median lethal dose is typically 100 mL (3.4 fl oz) (i.e. 1–2 mL/kg body weight of pure methanol ).
What is hemodialysis used for?
Hemodialysis may also be used in those where there is organ damage or a high degree of acidosis. Other treatments may include sodium bicarbonate, folate, and thiamine. Outbreaks of methanol ingestion have occurred due to contamination of drinking alcohol. This is more common in the developing world.
What is the best treatment for acidosis?
The preferred antidote is fomepizole, with ethanol used if this is not available. Hemodialysis may also be used in those where there is organ damage or a high degree of acidosis.
Drugs used to treat Methanol Poisoning
The following list of medications are in some way related to, or used in the treatment of this condition.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
