Treatment for Ureaplasma Urealyticum is done by prescribing a course of antibiotics that includes azithromycin Azithromycin extended-release suspension is used to treat certain bacterial infections. This medication is used to treat a certain type of skin condition called rosacea.Azithromycin
Doxycycline Monohydrate
What is Ureaplasma in men, and what is the treatment?
- Discharge
- Painful urination
- Burning sensation
- Pelvic or abdominal pain
How do you treat Ureaplasma?
- Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) – not proven
- Chorioamnionitis
- Postpartum and postabortal fever
- Pyelonephritis
- Central nervous system infections
- Septicemia
- Wound infections, especially postoperative wounds
- Joint infections
- Upper and lower respiratory tract infections
- Endocarditis
Does Levaquin treat Ureaplasma?
Levaquin for ureaplasma? didnt work for me. it has a black box warning about tendinitis and ruptured tendons. let me tell you , nothing like opening the door to 7-11 and thinking for a split second your arm is gonna fall off because your elbow feels like it has disintegrated - *edited spelling mistakes for clarity.
Does azithromycin cure UTI?
Azithromycin is an antibiotic used to treat chest infections mainly, also called upper respiratory tract infections. It is not used to treat UTI, unless only under some special cases, And it won’t work if you use it for the purpose of treating UTI most of the time. But, it might be beneficial for the people suffering from UTI in some cases.
See more

Is Ureaplasma serious in men?
Both men and women can develop serious urological and reproductive problems as a result of genital mycoplasma and ureaplasma bacteria. These parasitic bacteria are mollicutes, some of the smallest known organisms that can reproduce.
Does partner need treatment for Ureaplasma?
Both the patient and their partner should be tested and treated at the same time. Sexual partners should abstain from sex or use condoms until both test negative for Ureaplasma infection.
What is the best antibiotic for Ureaplasma?
Doxycycline is the treatment of choice for M. hominis and U. urealyticum. Duration and dose vary by site of infection, and are usually incombination with other antibiotics.
What kills Ureaplasma?
Povidone-iodine killed Ureaplasma urealyticum and Mycoplasma hominis organisms.
How much azithromycin do I take for Ureaplasma?
A single 1-g dose of azithromycin is approved for treatment of urethritis due to Chlamydia trachomatis and works as well clinically as 7 days of doxycycline in persons with urethritis due to Ureaplasma species.
Can a urologist treat Ureaplasma?
At New York Urology Specialists, our urologists are specially trained in the evaluation and treatment of sexually transmitted infections (STI). We understand the challenges that STDs such as chlamydia, herpes, gonorrhea, and ureaplasma create for our patients, their relationships, and their self-esteem.
Is doxycycline or azithromycin better for Ureaplasma?
Conclusions. A single 1-g dose of azithromycin is more effective than multidose doxycycline for the treatment of M. genitalium–associated urethritis in men.
Does Ureaplasma go away after antibiotics?
How is it treated? Ureaplasma can go away on its own without treatment. However, if you have symptoms, or are, or wish to be pregnant (or your partner is, or wishes to be pregnant), it can also treated with a course of antibiotics.
What is the best antibiotic for ureaplasma?
Treatment typically involves a course of antibiotics. The preferred antibiotics for a Ureaplasma infection are azithromycin (Zithromax) or doxycycline (Acticlate, Doryx, Vibra-Tabs). If you don’t respond to treatment, your doctor may prescribe another type of antibiotic called fluoroquinolones.
How long does it take for uraplasma to go away?
Ureaplasma can also be passed from mother to child. The infection usually goes away within a few months. It’s rare among children and sexually inactive adults.
What is the microbiome of uraplasma?
Ureaplasma is often a part of the human microbiome, which consists of trillions of tiny cells that live in and on the human body. These tiny organisms help you digest food, fight infections, and maintain reproductive health.
Can ureaplasma cause urethra infection?
Most people with a U reaplasma infection don’t experience any symptoms. Ureaplasma infection is a possible cause of inflammation in the urethra. This is called urethritis. Both men and women may experience the following symptoms of urethritis:
Can ureaplasma cause bacterial vaginosis?
Ureaplasma is also a possible cause of bacterial vaginosis. Symptoms can include:
Does uraplasma cause preterm delivery?
Ureaplasma does seem to play a role in the risk of preterm delivery. It’s important to understand that Ureaplasma doesn’t cause preterm delivery. It’s only one part of a complex series of events.
Can a doctor test for ureaplasma?
Most doctors don’t normally test for Ureaplasma. If you’re experiencing symptoms and all other problems have been ruled out, doctors can take a sample to send to a lab. They may use any of the following tests to help diagnose Ureaplasma:
What is Ureaplasma Urealyticum?
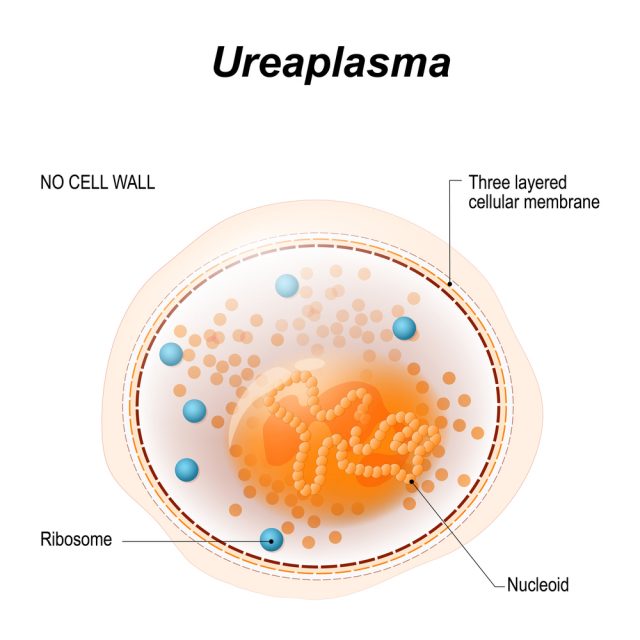
Ureaplasma Urealyticum is a group of bacteria present in the urogenital and reproductive and respiratory tract. They are very tiny and are not even visible through a regular microscope. They are generally harmless but when they increase in numbers, it can result in inflammation of tissues which can lead to infection if not diagnosed in time and treated quickly. Simply walk in to STD Express Clinic and get tested.
What lab test is done to determine if you have ureaplasma?
Following lab tests are generally done to make a diagnosis: Cervical swab. Urine sample. Endometrial swab and/or biopsy.
How does ureaplasma spread?
How Does It Spread. Ureaplasma Urealyticum is usually transmitted through sexual contact. The infection is generally seen in sexually active individuals. It can also be passed from the mother to the child. Individuals with a poor immune system are generally affected.
Is uraplasma a microbiome?
Many people have Ureaplasma as an inherent part of their microbiome. Its presence should not create any major health issues unless you are pregnant.
How long does ureaplasma persist?
In the absence of sexual activity, the organisms tend to persist for years. Multiple studies indicate up to 85 percent of healthy men who attended sexually transmitted disease clinics had ureaplasma in their urethras, PubMed Central reports.
What is uraplasma in men?
What Is Ureaplasma in Men, and What Is the Treatment? Ureaplasma are bacteria in a man’s urogenital tract, according to the New York Urology Specialists. Men may contract the infection at birth from their mothers, and symptoms tend to disappear until they reach puberty.
Can men contract a bacterial infection?
Men may contract the infection at birth from their mothers , and symptoms tend to disappear until they reach puberty. Typically, sexual contact causes infection, and bacterial presence rises with an increase in the number of sexual partners, explains PubMed Central. In the absence of sexual activity, the organisms tend to persist for years.
Can ureaplasma cause burning?
Ureaplasma may be unnoticeable in some men, but in others, symptoms such as urinary frequency, pain, dis charge and burning appear, according to the New York Urology Specialists. Treatment involves the isolation of ureaplasma and administration of antibiotics.
What is the first line of treatment for ureaplasma?
The first line of treatment for Ureaplasma is broad-spectrum antibiotics such as azithromycin and doxycycline which have a good success rate. Some of the treatment protocols used for Ureaplasma include ( link ):
What Antibiotics Treat Ureaplasma?
Hominis) do not require treatment as they rarely cause symptoms. When Ureaplasma urealyticum is associated with symptoms, treatment is advisable.
What is a urologist in New York?
At New York Urology Specialists, our urologists are specially trained in the evaluation and treatment of sexually transmitted infections (STI). We understand the challenges that STDs such as chlamydia, herpes, gonorrhea, and ureaplasma create for our patients, their relationships, and their self-esteem. We help you find an effective treatment for your symptoms that may be caused by STD, UTI or another cause.
How long after treatment for STDs can you repeat PCR?
A PCR assay (DNA test) needs to be done 4 weeks after treatment to ensure the antibiotics have worked and relapse has not occurred.
What is a urologist?
Urologists are doctors specializing in the treatment of infections in men and women caused by sexually transmitted diseases as well as bladder infections (UTI). By the virtue of our experience and skill, we are able to offer an effective treatment option for nearly every man and woman with urinary problems and bladder control problems.
Where to schedule a consultation for ureaplasma?
Schedule a consultation with ureaplasma specialist at New York Urology Specialists.
Does New York Urology offer same day testing?
At New York Urology Specialists, we offer same-day mycoplasma and ureaplasma testing and treatment for men and women.
What antibiotics are used for ureaplasma urealyticum?
The antibiotic treatments we offer are Azithromycin and Doxycycline and they should be taken as instructed.
What is ureaplasma urealyticum?
Ureaplasma urealyticum is a bacterial infection transmitted via unprotected sexual contact. This condition is highly common in the UK and symptoms aren't usually noticeable, which reflects how important it is to get tested for this bacterial infection. Ureaplasma urealyticum itself is a genital mycoplasma that produces the infection within the genital tract. Although this condition is normally spread via sexual contact, it can also be spread by needles, air, saliva or blood.
Is ureaplasma urealyticum contagious?
Despite ureaplasma urealyticum being highly contagious, it is possible to successfully prevent this bacterial infection from occurring. This can be achieved by following the below methods of prevention:
Can you avoid sex with a bacterial infection?
To give yourself the best chance possible at completely curing this bacterial infection it is recommended that you try to avoid sex until your course of treatment is complete. These treatments, when taken correctly, can ensure that you experience the following benefits: Uncomfortable symptoms will be alleviated.
Can ureaplasma be transmitted through nose?
In extremely rare cases it can also be transmitted through nose or eye secret ions. Engaging in unprotected sex can increase your chance of contracting this infection, especially if you do so with multiple partners. Unprotected sexual contact is the most common cause of ureaplasma urealyticum.
Can I buy ureaplasma urealyticum treatment online?
You can order ureaplasma u realyticum treatments here at euroClinix to successfully cure this bacterial infection and alleviate symptoms. The antibiotic treatments we offer are Azithromycin and Doxycycline and they should be taken as instructed. All you need to do is complete a free and confidential online consultation to ensure your suitability for the medication you choose.
How to prevent ureaplasma?
Prevention of ureaplasma. The safest way to avoid the infection is to be without oral sex and sexual intercourse. This may not be realistic advice, so the best way is to use protection during sexual intercourse. There are currently two contraceptive methods in the market, such as condoms and condoms for women.
Why are antibiotics used for ureaplasma?
Bacteria that cause Ureaplasma Infection are slightly different from other bacterial strains because they do not have a cell wall. Antibiotic activity is usually based on the destruction of the bacterial cell walls.
How should I treat it?
The test is performed by taking a sample of the tip of the urethra where bacteria are most often hidden. In some cases, urine tests may also help to provide a proper diagnosis.
Why is it important to test if mycoplasma is gone?
This is because the mycoplasma bacteria belonging to Ureaplasma urealyticum can develop susceptibility to certain antibiotics. Therefore, you should keep an eye on your symptoms and test that everything is as it should be.
What is the class of mycoplasma?
Both infections are classified into the bacteria class of Mycoplasma. The bacterial class is very broad, with few of them causing problems or imbalances in the body. Ureaplasma urealytic and Mycoplasma genitalium are two infections that need treatment. Both infections cause the same symptoms, such as perspiration in urination ...
What is ureaplasma 2021?
07. 2021. Ureaplasma is a bacterial infection in the urinary tract that can easily and efficiently be treated with antibiotics. Infection is caused by Ureaplasma urealyticum. The disease is not classified as a sexually transmitted disease, but because it usually transmits sexually, it often ends up below this class.
Is mycoplasma genitalium a bacterial infection?
However, most of the mycoplasma bacteria are harmless. However, some bacterial infections should be kept an eye for, for example , Ureaplasma urealyticum infections.
What antibiotics are used for ureaplasma urealyticum?
Sensitive antibiotics are needed for treatment; azithromycin and doxycycline are commonly used antibiotics for Ureaplasma urealyticum infection. However, due to the increasing drug resistance of Ureaplasma urealyticum in recent years, if the above two drugs can not be completely cured, herbal medicine Diuretic and Anti-inflammatory Pill can be selected for regular treatment.
How long have the symptoms of urethral syptoms disappeared?
1. The clinical symptoms have disappeared for more than a week, and the white blood cells in the urethral secretions or secretions were less than 4/100 times under the microscope.
How deep should a urethra swab be?
The swab should be deep into the urethra for 2 to 4 cm when male patients take samples, and the swab should be rotated forcefully to obtain cells. Avoid contact with antibiotics, analgesics, or lubricants when collecting specimens.
How high is the detection rate of mycoplasma?
If men get Mycoplasma infection, the highest detection rate of infection of sexual partners can reach 36.8%, so it is necessary for them to check and treat at the same time in order to avoid re-infection.
Should urethritis be treated in hospitals?
2. If patients’ sexual partners also have some symptoms of urethritis, and they should be examined and treated in hospitals, too.
What causes persistent urethritis?
Symptomatic recurrent or persistent urethritis might be caused by treatment failure or reinfection after successful treatment . Among men who have persistent symptoms after treatment without objective signs of urethral inflammation, the value of extending the duration of antimicrobials has not been demonstrated. Treatment failure for chlamydial urethritis has been estimated at 6%–12% ( 755 ). The most common cause of persistent or recurrent NGU is M. genitalium, especially after doxycycline therapy ( 756, 757 ). Treatment failure for M. genitalium is harder to determine because certain men achieve clinical cure (i.e., resolution of symptoms) but can still have detectable M. genitalium in urethral specimens ( 758 ).
What is M. genitalium associated with?
M. genitalium is associated with symptoms of urethritis and urethral inflammation and accounts for 15%–25% of NGU cases in the United States ( 691 – 693, 696, 697, 700 ). Among men with symptoms of urethritis, M. genitalium was detected in 11% of those with urethritis in Australia ( 701 ), 12%–15% in the United Kingdom ( 702 – 704 ), 15% in South Africa ( 696 ), 19% in China ( 705 ), 21% in Korea, 22% in Japan ( 706 ), and 28.7% in the United States (range: 20.4%–38.8%) ( 697 ). Data are inconsistent regarding other Mycoplasma and Ureaplasma species as etiologic agents of urethritis ( 707 ). The majority of men with Ureaplasma infections do not have overt disease unless a high organism load is present.
What is the presumptive gonococcal infection?
Presumed gonococcal infection is established by documenting the presence of WBCs containing GNID in Gram stain or intracellular purple diplococci in MB or GV smears; men should be tested for C. trachomatis and N. gonorrhoeae by NAATs and presumptively treated and managed accordingly for gonococcal infection (see Gonococcal Infections).
Can T. vaginalis cause urethritis?
T. vaginalis can cause urethritis among heterosexual men ; however, the prevalence varies substantially by U.S. geographic region, age, and sexual behavior and within specific populations. Studies among men with and without overt urethritis in developed countries document relatively low rates of T. vaginal is in the Netherlands (0.5%) ( 708 ), Japan (1.3%) ( 706, 709 ), the United States (2.4%) ( 710 ), and the United Kingdom (3.6%) ( 703 ). Studies in other countries have documented higher rates, such as in Croatia (8.2%) ( 711) and Zimbabwe (8.4%) ( 712 ), particularly among symptomatic patients.
Is urethritis an infectious disease?
Urethritis, as characterized by urethral inflammation, can result from either infectious or noninfectious conditions. Symptoms, if present, include dysuria, urethral pruritis, and mucoid, mucopurulent, or purulent discharge. Signs of urethral discharge on examination can also be present among persons without symptoms. Although N. gonorrhoeae and C. trachomatis are well established as clinically important infectious causes of urethritis, M. genitalium has been strongly associated with urethritis and, less commonly, prostatitis ( 691 – 697 ). If POC diagnostic tools (e.g., Gram, methylene blue [MB], or gentian violet [GV] stain microscopy) are unavailable, drug regimens effective against both gonorrhea and chlamydia should be administered. Further testing to determine the specific etiology is recommended for preventing complications, reinfection, and transmission because a specific diagnosis might improve treatment compliance, delivery of risk-reduction interventions, and partner services. Both chlamydia and gonorrhea are reportable to health departments. NAATs are preferred for detecting C. trachomatis and N. gonorrhoeae, and urine is the preferred specimen for males ( 553 ). NAAT-based tests for diagnosing T. vaginalis among men with urethritis have not been cleared by FDA; however, laboratories have performed the CLIA-compliant validation studies ( 698) needed to provide such testing.
Is erythromycin safe for NGU?
To maximize compliance with recommended therapies, medications should be dispensed on-site at the clinic, and, regardless of the number of doses involved in the regimen, the first dose should be directly observed. Erythromycin is no longer recommended for NGU because of its gastrointestinal side effects and dosing frequency. Levofloxacin is no longer recommended for NGU because of its inferior efficacy, especially for M. genitalium.
Can a man with NGU be tested for gonorrhea?
All men who have suspected or confirmed NGU should be tested for chlamydia and gonorrhea by using NAATs. A specific diagnosis can potentially reduce complications, reinfection, and transmission. M. genitalium testing should be performed for men who have persistent or recurrent symptoms after initial empiric treatment. Testing for T. vaginalis should be considered in areas or among populations with high prevalence, in cases where a partner is known to be infected, or for men who have persistent or recurrent symptoms after initial empiric treatment.
