Stylecraze.com
Apr 13, 2017 · Megaloblastic anemia is caused by deficiency or impaired utilization of vitamin B12 and/or folate, whereas nonmegaloblastic macrocytic anemia is caused by various diseases such as myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS), liver dysfunction, alcoholism, hypothyroidism, certain drugs, and by less commonly inherited disorders of DNA synthesis. Macrocytic anemias are treated …
Top10homeremedies.com
Treatment of Anemia With a Low or High MCH Which treatment you need depends on the condition that raised or lowered your MCH level. If you have anemia, supplements can replace what your body lacks.
Rapidhomeremedies.com
Jan 07, 2021 · The most common cause of low MCHC is anemia. Hypochromic microcytic anemia commonly results in low MCHC. This condition means your red blood cells are smaller than usual and have a decreased level ...
What is the treatment for low MCh in blood?
Feb 11, 2022 · Anemia of chronic disease. There's no specific treatment for this type of anemia. Doctors focus on treating the underlying disease. If symptoms become severe, a blood transfusion or injections of a synthetic hormone normally produced by your kidneys (erythropoietin) might help stimulate red blood cell production and ease fatigue. Aplastic anemia.
What causes anemia with a low MCH?
Dec 01, 2021 · The mean corpuscular hemoglobin (MCH) measurement is part of a complete blood count (CBC) test. The MCH represents the average amount of hemoglobin in a cell. Hemoglobin is a protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen and carbon dioxide. A low MCH can indicate conditions like anemia and thalassemia.
What is the treatment for anemias?
What is the most effective treatment for pernicious anemia (PA)? a. oral folate b. injections of B12 c. oral B12 d. alterations in diet
What is hypochromic microcytic anemia (MCHC)?
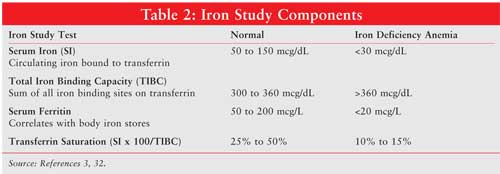
Apr 01, 2022 · Transferrin: Serum Transferrin level is needed for the D/D of the anemia. Percent transferrin saturation (normal % transferrin saturation = 20% to 50%). Calculation of the % transferrin saturation = Serum iron ÷ TIBC x 100 = Transferrin normally 33% is saturated. This is used for the D/D of the anemias.

How do you treat low MCH?
Treatment for low MCH caused by iron deficiency can include adding iron-rich foods to your diet (there are even vegetarian options) and taking iron supplements. In rare cases, such as when symptoms are severe or blood loss has occurred, you may need a blood transfusion.Oct 25, 2017
How do you treat low MCH and MCHC?
Can low MCHC levels be treated?Increase iron in your diet.Take iron supplements.Get more vitamin B6, which is necessary for proper absorption of iron.Add more fiber to your diet, which can help improve the intestinal absorption of iron.More items...
What medications can cause high MCH?
Certain medicines may cause your MCV and MCH levels to go up, including these types:Anticancer.Antiretroviral.Anticonvulsant.Anti-inflammatory.Antidiabetic.Diuretics.
What MCH level is considered anemic?
Registering an MCH level below 27 picograms/cell is most commonly associated with anemia.Dec 1, 2021
How can I increase my MCH levels naturally?
Doctors may recommend that individuals add more iron and vitamin B6 to their diet. Eating vitamin C and fiber, along with foods that contain iron, may also help increase the MCH levels. Supplements for various vitamins are available to purchase online, including vitamin B12, vitamin C, folic acid, and iron.
How can I increase iron in my body?
Choose iron-rich foodsRed meat, pork and poultry.Seafood.Beans.Dark green leafy vegetables, such as spinach.Dried fruit, such as raisins and apricots.Iron-fortified cereals, breads and pastas.Peas.Jan 4, 2022
What happens if MCH count is high?
An anemia with a high MCH is called macrocytic anemia. When you have this condition, your red blood cells are larger than normal. Other causes of macrocytic anemia include: Lack of enough folic acid.Dec 9, 2021
Can you take aspirin if you have anemia?
Be safe with medicines. Do not take non-steroidal anti-inflammatory pain relievers unless your doctor tells you to. These include aspirin, naproxen (Aleve), and ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin).
What level of hemoglobin is dangerously high?
Hemoglobin levels greater than 16.5 g/dL (grams per deciliter) in women and greater than 18.5 g/dL in men suggest polycythemia. In terms of hematocrit, a value greater than 48 in women and 52 in men is indicative of polycythemia.
Why is my MCH low?
The common causes include malnutrition or nutritional and iron deficiencies. Because the body needs iron to make hemoglobin, iron deficiency can lead to anemia and low MCH levels. People may have a higher risk of iron-deficient anemia if they: Bleed a lot during menstruation.Feb 17, 2022
How do you treat high MCV?
Add more red meat and chicken to your diet to increase your vitamin B-12 intake. If you're a vegetarian or vegan, you can add beans and dark, leafy greens for folate. Try fortified breakfast cereals for vitamin B-12. Reduce the amount of alcohol you drink.
What is the meaning of MCH in medical terms?
mean cell hemoglobinMCH: Abbreviation for mean cell hemoglobin, which is the average amount of hemoglobin in the average red cell. The MCH is a calculated value derived from the measurement of hemoglobin and the red cell count.Mar 29, 2021
Why is my MCH low?
The outlook for people with abnormal MCH values depends on the condition that’s causing it. Low MCH values are often caused by iron deficiency anemia. Typically, this condition can be treated with lifestyle changes including consuming foods rich in iron as well as taking iron supplements.
How to calculate MCH?
MCH is calculated by dividing the amount of hemoglobin in a given volume of blood by the number of red blood cells present.
Why is iron important for hemoglobin?
Iron is important for the production of hemoglobin. Your body absorbs a small amount of iron that you eat in order to produce hemoglobin. Some of the general causes of iron deficiency include eating a diet that is low in iron, major surgery or trauma, or blood loss.
What does MCH mean?
What is MCH? MCH stands for “mean corpuscular hemoglobin.”. An MCH value refers to the average quantity of hemoglobin present in a single red blood cell. Hemoglobin is the protein in your red blood cells that transports oxygen to the tissues of your body. Your MCH value is related to two other values, mean corpuscular volume (MCV) ...
Why is my MCH high?
Causes. High MCH value can often be caused by anemia due to a deficiency of B vitamins, particularly B-12 and folate. Both of these vitamins are required by your body in order to make red blood cells. These types of anemia can develop if your diet is low in B vitamins or if your body does not absorb B-12 or folate properly.
What is the difference between MCH and MCHC?
The difference between MCH and MCHC is that the MCHC measurement takes the volume or size of the red blood cell into account while MCH does not.
What are the symptoms of folate deficiency?
bloating and gas. mental symptoms, such as depression or confusion. If you have anemia due to folate deficiency, you could experience the following additional symptoms: diarrhea. decrease in appetite. irritability. a smooth or sensitive tongue.
What is MCH in Blood Test?
MCH in blood test is usually a part of Complete Blood Count (CBC) test. The full form of MCH is “Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin”. Hemoglobin is a protein in Red Blood Cells (RBC) that helps to carry oxygen and reach this oxygen into different parts of our body.
MCH Blood Test Purpose
MCH blood test is usually done as routine blood test just like MCV and MCHC blood tests to assess anemia. Anemia is the medical condition where there is deficiency of hemoglobin in the blood due to either too few red blood cells (RBC), or too little hemoglobin in the body.
MCH Blood Test Importance
Anemia can give abnormal MCH level in MCH Blood Test report. Not only anemia, there are several medical conditions such as liver disease, Hypothyroid, Thalassemia etc. can cause abnormal MCH value in MCH blood test.
MCH Blood Test Process
There is no specific test process to follow. This test is done through simple blood sample. Just like basic hemoglobin test this test also do not require any restrictions in food, drinks or in timing.
MCH Blood Test Low Level
If your MCH Blood test value is below 27 pg then it is considered as low MCH both in man and woman. Most common cause of MCH blood test low value is the anemia due to iron deficiency. The causes of MCH low level are
MCH Blood Test High Level
When the MCH Blood Test value is more than 33 pg then it is considered as high MCH for both man and woman.
MCH Blood Test Low Treatment
Treatment depends upon the cause. So, if you have low MCH due to iron deficiency, then iron rich foods in diet and iron supplements can help. Adding Vitamin C in your diet also helps for iron absorption. If symptoms are severe in low MCH due to blood loss, rarely blood transfusion is needed.
What is macrocytosis in adults?
Abstract. Anemia is one of the most common health problems in the primary care setting. Macrocytosis in adults is defined as a red blood cell (RBC) mean corpuscular volume (MCV) >100 femtoliter (fL). Macrocytic anemias are generally classified into megaloblastic or nonmegaloblastic anemia.
What causes macrocytosis?
Megaloblastic anemia is caused by deficiency or impairment of utilization of vitamin B12 or folate. Nonmegaloblastic anemia may be the result of liver dysfunction, alcoholism, myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS), or hypothyroidism. Common causes of macrocytosis are different by region and setting.
Why do vegetarians have a B12 deficiency?
Vitamin B12 deficiency is caused by insufficient dietary intake, as in the cases of vegetarians or malnutrition, malabsorption due to the absence of intrinsic factor caused by pernicious anemia or following gastric surgery, congenital disorders, such as transcobalamin II deficiency, or exposure to nitrous oxide.
Where is B12 absorbed?
Vitamin B12 binds to intrinsic factor secreted by the gastric parietal cells, and it is absorbed in the terminal ileum. Once absorbed, vitamin B12 acts as a coenzyme in the enzymatic reaction that produces methionine from homocysteine. As a result, folic acid is converted into its active form.
Is oral vitamin B12 effective?
Although it is not an established treatment, recently it has been reported that oral treatment is effective, because 1%‐5% of vitamin B12 absorption in the terminal ileum is by passive diffusion, which does not involve intrinsic factor.10. 4. Pernicious Anemia.
What percentage of red blood cells are reticulocytes?
In general, approximately 1% of red blood cells are counted as reticulocytes. If the absolute reticulocyte count is more than 100 000/μl, acute blood loss or hemolysis is suspected. High levels of indirect bilirubin and LDH, and decreased levels of haptoglobin suggest the presence of hemolytic anemia.
Does B12 affect DNA synthesis?
As a result, the intracellular reaction involving the coenzyme form of folic acid is affected. Thus, not only vitamin B 12 but also folate defici encies impair DNA synthesis.
What does MCH mean in blood?
MCH is short for "mean corpuscular hemoglobin.". It's the average amount in each of your red blood cells of a protein called hemoglobin, which carries oxygen around your body. It's possible you'll learn about MCH when you get a blood test called a CBC (complete blood count). This test measures different parts of your blood, ...
What does MCHC check?
MCHC checks the average amount of hemoglobin in a group of red blood cells. Your doctor may use both measurements to help in a diagnosis of anemia. It's a condition caused by not having enough healthy red blood cells, or the red blood cells you do have don't work as well as they should.
Why is my MCH level so high?
Trouble walking. Weakness. Depression. Trouble thinking clearly. Some conditions, including high cholesterol and high triglycerides, can make your MCH level seem high on a test when they're not really. Your doctor will help you interpret the test results. Treatment of Anemia With a Low or High MCH.
How to do CBC?
To do a CBC, a nurse puts a needle into a vein in your arm. The needle attaches to a test tube, where the blood collects. A lab then analyzes the blood sample.
How to tell if you have low B12?
Signs of low vitamin B12 include: Numbness or tingling in your hands and feet. Trouble walking or staying balanced. Trouble thinking. Tiredness. Weakness. Swollen tongue. An anemia with a high MCH is called macrocytic anemia. When you have this condition, your red blood cells are larger than normal.
What does it mean when your MCH is high?
Fast or abnormal heartbeat. Chest pain. Headache. Cold hands or feet. An anemia with a high MCH level could also be a sign that you don't have enough vitamin B12 or other nutrients. Your body needs vitamin B12 to make healthy blood cells, nerves, and DNA.
What to do if you have a polyp?
If you have a bleeding polyp or tumor, you may need surgery to remove it. If your body doesn't have enough vitamin B12 or folate, your treatment will be to get more of these vitamins. They're in foods like fish, liver, green leafy vegetables, and fortified cereals.
What is MCHC in blood?
What is MCHC? The mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration (MCHC) is the average concentration of hemoglobin in your red blood cells. Hemoglobin is the protein molecule that allows red blood cells to carry oxygen to tissues within your body. Your MCHC can fall into low, normal, and high ranges, even if your red blood cell count is normal.
What does a doctor check for anemia?
Your doctor may check your iron levels and iron-binding capacity, which measures whether your body absorbs iron the way it’s supposed to. All of this can be done from the same blood draw used for your CBC, and these two tests can help your doctor determine the cause of the anemia.
Why is my hemoglobin low?
This type of microcytic anemia can be caused by: lack of iron. inability of your body to absorb iron, which can be caused by conditions like celiac disease, Crohn’s disease, and gastric bypass surgery.
How to get iron out of your body?
Get more vitamin B6, which is necessary for proper absorption of iron. Add more fiber to your diet , which can help improve the intestinal absorption of iron. Take no more than the daily requirement of calcium, as too much can make it difficult for your body to absorb iron.
What is CBC test?
These tests may be included in a complete blood count (CBC). A CBC measures whether you have normal ranges of red and white blood cells. Through the results of the tests they order, your doctor should be able to determine exactly what type of anemia you have, making it easier to find the underlying cause.
Is spinach a good source of iron?
To do this, try to make sure you’re getting enough iron and vitamin B6 in your diet. Keep in mind that the iron in spinach is not as readily absorbed because of its oxalic acid content. This can be improved by consuming it with things like vitamin c/citric acid, beef, poultry, or fish. Foods rich in iron include:
What is the treatment for anemia?
Treatment for this anemia can include blood transfusions to boost levels of red blood cells. You might need a bone marrow transplant if your bone marrow can't make healthy blood cells. Anemias associated with bone marrow disease. Treatment of these various diseases can include medication, chemotherapy or bone marrow transplantation.
What is the treatment for hemolytic anemia?
Sickle cell anemia. Treatment might include oxygen, pain relievers, and oral and intravenous fluids to reduce pain and prevent complications. Doctors might also recommend blood transfusions, folic acid supplements and antibiotics.
What is CBC in anemia?
A CBC is used to count the number of blood cells in a sample of your blood . For anemia, your doctor will be interested in the levels of the red blood cells contained in your blood (hematocrit) and the hemoglobin in your blood. Normal adult hematocrit values vary among medical practices but are generally between 40% and 52% for men and 35% ...
How to treat iron deficiency?
Iron deficiency anemia. Treatment for this form of anemia usually involves taking iron supplements and changing your diet. If the cause of iron deficiency is loss of blood — other than from menstruation — the source of the bleeding must be located and the bleeding stopped. This might involve surgery. Vitamin deficiency anemias.
What is the normal hemoglobin level?
Normal adult hemoglobin values are generally 14 to 18 grams per deciliter for men and 12 to 16 grams per deciliter for women. A test to determine the size and shape of your red blood cells. Some of your red blood cells might also be examined for unusual size, shape and color.
What is the treatment for folic acid deficiency?
This might involve surgery. Vitamin deficiency anemias. Treatment for folic acid and vitamin C deficiency involves dietary supplements and increasing these nutrients in your diet. If your digestive system has trouble absorbing vitamin B-12 from the food you eat, you might need vitamin B-12 shots.
What to do before a doctor appointment?
Before your appointment, make a list of: Your symptoms and when they began. Key personal information, including major stresses, implanted medical devices, exposure to toxins or chemicals, and recent life changes. All medications, vitamins and other supplements you take, including the doses.
What is the MCH in blood?
Mean corpuscular hemoglobin (MCH) in a blood test refers to the average amount of hemoglobin in a person's red blood cells. Hemoglobin is a protein that carries oxygen around the human body. MCH is one of the standard measurements in a complete blood count test. Andrew Brookes/Getty Images.
What does low MCH mean?
Low MCH Levels. Having MCH levels below 27 picograms/cell is most commonly associated with anemia. But in addition to anemia , it may also be a sign of conditions including: Internal or external blood loss resulting from surgery, injury, menstrual bleeding, or bleeding from the gastrointestinal tract.
What are the symptoms of anemia?
Having MCH levels below 27 picograms/cell is most commonly associated with anemia. But in addition to anemia, it may also be a sign of conditions including: 1 Iron deficiency (almost always caused by blood loss) 2 Deficiency of other nutrients, such as vitamin B12 or folic acid 3 Internal or external blood loss resulting from surgery, injury, menstrual bleeding, or bleeding from the gastrointestinal tract 4 Cancer 5 Thalassemia (a common inherited blood disorder caused by genetic mutations in the hemoglobin genes) 6 Kidney disease 7 Autoimmune diseases 4 8 Liver disease 5
Where is blood drawn for CBC?
A small sample of blood is required for a CBC and is typically drawn from a vein in a person's arm using a needle. While this is bearable for many people, others experience physical and/or mental discomfort when it comes to needles or drawing blood.
What is the red blood cell?
These red blood cells transport oxygen to the tissues throughout the human body, and waste (in this case, carbon dioxide) away from the tissues—which then leaves the body when it is exhaled through the lungs. When combined with oxygen, hemoglobin is what gives blood its red color. 1 .
What happens if your MCH is higher than normal?
If a patient's MCH levels appear to be higher or lower than normal, it will result in a discussion with their physician about what this means to their overall health—including potential treatment options , if necessary .
How many picograms are normal for MCH?
If a doctor is using MCH levels to assist with making a diagnosis or simply learning more about a patient's health, they first look to see if it is in the normal range of 27 to 31 picograms/cell. 3 There are specific symptoms and conditions associated with MCH levels that are both lower and higher than normal.
