
What is the prognosis for MALT lymphoma?
CASE REPORT—A 36 year old patient was referred from another hospital with a diagnosis of a low grade gastric MALT lymphoma associated with H pylori. The patient was in stage I and while waiting for the biopsies to be reviewed H pylori eradication ...
What is the best treatment for lymphoma cancer?
- Chemotherapy for Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma
- Immunotherapy for Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma
- Targeted Drug Therapy for Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma
- Radiation Therapy for Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma
- High-Dose Chemotherapy and Stem Cell Transplant for Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma
- Surgery for Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma
What type of lymphoma is curable?
- When lymphoma returns after beforehand being dealt with, either in its unique area or in another body zone.
- Repeat can happen not long after treatment or years after the fact.
- Re-organizing might be necessary in case of a repeat.
What are symptoms and treatments for lymphoma?
What Are The Symptoms Of Malignant Lymphoma?
- swelling of the lymph nodes
- night sweats
- weight loss
- Fire
- Itching and rashes on the skin
- Fatigue, weakness
- Shortness of breath
- Cough

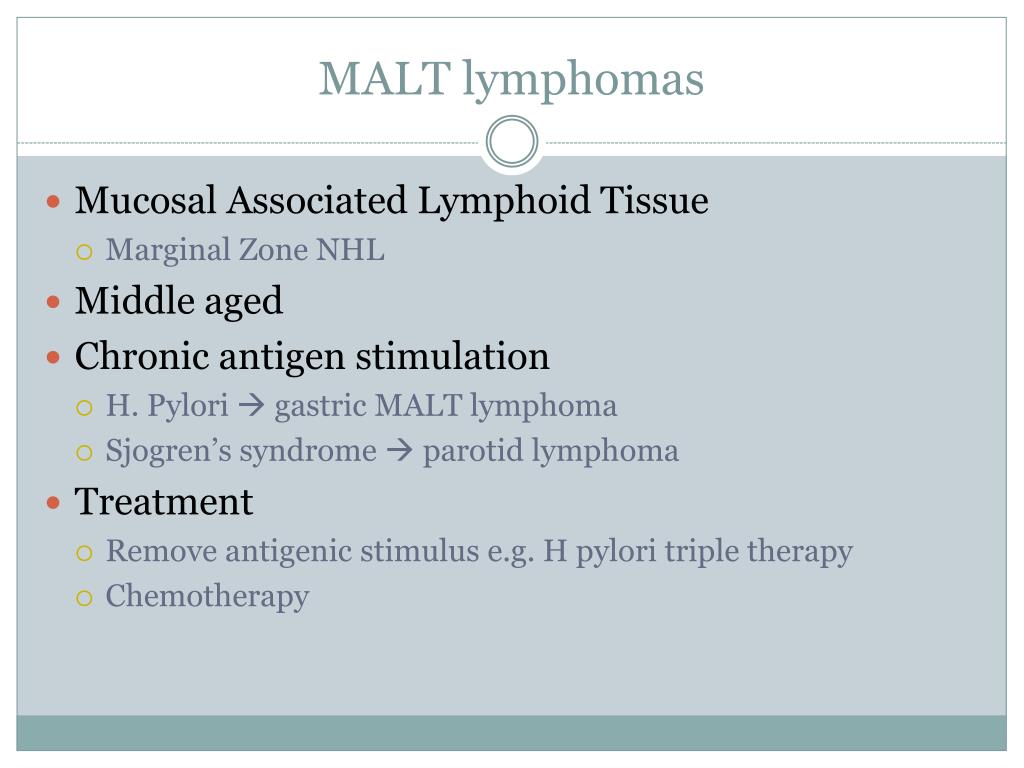
What is the best treatment for MALT lymphoma?
The majority of cases with MALT lymphoma are cured by eradication therapy, but there are cases that need to be treated with rituximab alone or in combination with other drugs.
Is MALT lymphoma a cancer?
What is MALT lymphoma? Lymphoma is a type of blood cancer that develops when white blood cells called lymphocytes grow out of control. Lymphocytes are part of your immune system. They travel around your body in your lymphatic system, helping you fight infections.
How long can you live with MALT lymphoma?
Prognosis: the overall five-year survival and disease-free survival rates are as high as 90% and 75%, respectively. 70-80% of patients reveal complete remission of MALT lymphoma following successful eradication of H. pylori.
Can MALT lymphoma be cured with antibiotics?
Hp eradication with wide-spectrum antibiotics is the conventional first-line treatment for patients with limited-stage gastric MALT lymphoma associated with this bacterial infection (35). The ideal eradication therapy should be safe, effective (eradication rate >90%), simple, and economical.
Why do you get MALT lymphoma?
Most cases of MALT lymphoma of the stomach are linked to a chronic stomach infection caused by the bacteria Helicobacter pylori. This infection causes inflammation of the stomach lining, with symptoms of indigestion and stomach pain. MALT lymphoma of the stomach is treated with antibiotics.
Where does MALT lymphoma spread?
Among the other areas of the body that can be affected by MALT lymphoma are the lungs, thyroid, skin, bowels, salivary glands, and the tissue around the eye. These cases of MALT lymphomas spread to other organs in about 50% of cases.
Can MALT lymphoma spread to the brain?
The clinical course of MALT lymphoma is relatively indolent and, in the majority of cases (50%), the lymphoma arises within the stomach. Primary central nervous system lymphoma (PCNSL), an uncommon variant of extranodal NHL, can affect any part of the neuraxis, including the eyes, brain, leptomeninges, or spinal cord.
Can you live 20 years with lymphoma?
Most people with indolent non-Hodgkin lymphoma will live 20 years after diagnosis. Faster-growing cancers (aggressive lymphomas) have a worse prognosis. They fall into the overall five-year survival rate of 60%.
What type of lymphoma is not curable?
Lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma or Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia. It's found mainly in the bone marrow, lymph nodes, and spleen. This type of lymphoma can't be cured.
What does lymphoma in stomach feel like?
Additional symptoms that may occur in individuals with primary gastric lymphoma include a feeling of stomach fullness after only eating a little food (early satiety), abdominal tenderness, nausea, vomiting, unintended weight loss, a general feeling of poor health (malaise), and indigestion.
What are the symptoms of lymphoma in the stomach?
Symptoms of Lymphoma of the Stomach (Gastric Lymphoma)Upper abdominal pain;Upset stomach or indigestion;Change of bowel habits;Nausea and vomiting;Loss of appetite;Weight loss.
Is lymphoma in stomach treatable?
MALT lymphomas confined to the gastric mucosa and submucosa may be treated in the first instance byHelicobacter eradication; those that fail to respond are usually cured by surgery. Patients with more advanced tumors or DLBCLs are treated by surgery, adjuvant chemotherapy, or radiotherapy.
When is chemo used for gastric malt?
Chemotherapy is used for early-stage gastric MALT lymphomas when antibiotics fail to control the disease, or when the lymphoma recurs after a period of remission.
What are the drugs that treat malignant lymphoma?
Kinase Inhibitors. Kinase inhibitors are drugs that target lymphoma cells and block kinases— proteins that cause cancer cells to grow and flourish. Two kinase inhibitors used to treat MALT non-Hodgkin lymphoma are Imbruvica (ibrutinib) and Calquence (acalabrutinib). These drugs are taken twice a day by mouth.
What is the name of the non-Hodgkin lymphoma that forms in the stomach?
Gastric (MALT) lymphoma is a form of non-Hodgkin lymphoma that arises from tissue that forms the lining of the stomach, the mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT). Because gastric MALT lymphoma usually is caused by Helicobacter pylori ( H. pylori) bacteria, it often can be treated successfully with antibiotics.
What to do if you have a positive H pylori?
Active Monitoring. If patients are H Pylori positive, they are always treated with antibiotics to eradicate the H Pylori infection, which can often lead to regression of the lymphoma. If patients are H Pylori negative, or if eradication of H Pylori does not lead to regression of the lymphoma, but the lymphoma is localized to the stomach, ...
What is the first line of treatment for H. pylori?
For H. pylori -positive gastric MALT lymphoma, the first-line treatment is a protocol called triple therapy , which involves a combination of two antibiotics to fight the infection plus a proton pump inhibitor (PPI) drug to lower the production of gastric acid in the stomach and prevent ulcers. The antibiotics used most often are Amoxil ...
What is Rituxan used for?
(Antigens are molecules that trigger the immune response.) It's given intravenously (IV) or as an injection under the skin, and it can be used alone or in combination with chemotherapy drugs.
Can radiation therapy help with malt lymphoma?
For cases of MALT lymphoma not caused by H.pylori infection or for those that don't respond to antibiotics, radiation therapy can be an effective option. This protocol involves directing relatively low doses of external beam radiation to the tumors in the stomach. In more than 95% of people with gastric MALT lymphoma who undergo radiation, ...
What is malt lymphoma?
The World Health Organization (WHO) has defined mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) lymphoma as "an extranodal lymphoma composed of morphologically heterogenous small B cells, including marginal zone cells, cells resembling monocytoid cells, small lymphocytes, and scattered immunoblasts and centroblast-like cells". [1]#N#Jaffe ES, Harris NL, Stein H, et al, eds. World Health Organization classification of tumors. Pathology and genetics: tumors of haemopoietic and lymphoid tissues. Lyon, France: IARC Press; 2008.#N#Plasma cell differentiation occurs in a proportion of cases. The infiltrate is located in the marginal zone of reactive B-cell follicles and extends into the interfollicular region. Lymphoepithelial lesions develop in epithelial tissues due to infiltration of the epithelium with neoplastic cells. [1]#N#Jaffe ES, Harris NL, Stein H, et al, eds. World Health Organization classification of tumors. Pathology and genetics: tumors of haemopoietic and lymphoid tissues. Lyon, France: IARC Press; 2008.#N#The stomach is the most commonly involved organ, and there is an important association with chronic Helicobacter pylori infection in the majority of gastric MALT lymphoma cases. MALT lymphomas are categorized as indolent or low-grade B-cell lymphomas. Very rarely do they show features of high-grade histology or transformation at the time of initial presentation.
Is malt lymphoma a B cell?
MALT lymphomas are categorized as indolent or low-grade B-cell lymphomas. Very rarely do they show features of high-grade histology or transformation at the time of initial presentation.
Is mucosa associated lymphoid tissue a B cell?
Mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) lymphoma is categorized as indolent or low-grade B-cell lymphoma; however, high-grade histologic transformation can occur. Median age at presentation is 61 years. The stomach is the most frequently involved organ, and in most cases (90%), there is a strong association between gastric MALT lymphoma ...
Is MALT a B cell?
The stomach is the most commonly involved organ, and there is an important association with chronic Helicobacter pylori infection in the majority of gastric MALT lymphoma cases. MALT lymphomas are categorized as indolent or low-grade B-cell lymphomas. Very rarely do they show features of high-grade histology ...
Where does malt lymphoma start?
MALT lymphoma starts in the B cells, so it is a B cell lymphoma. These low grade (indolent) lymphomas are most often diagnosed in the stomach (called gastric MALT). But they can also develop in the lung, thyroid, salivary glands, eye, skin or soft tissues (called non gastric MALT). MALT lymphoma usually grows slowly.
How do you know if you have malt lymphoma?
Symptoms. Your symptoms depend on where the MALT lymphoma starts. Indigestion or heartburn are the most common symptoms of MALT lymphoma that starts in the stomach. Some people also lose weight, feel or are sick, and have pain in the tummy (abdomen).
What is lymph cancer?
Lymphoma is cancer of the lymphatic system. The lymphatic system is a network of thin tubes and lymph nodes that run throughout the body. Lymph nodes are bean shaped glands. The thin tubes are called lymph vessels or lymphatic vessels. Tissue fluid called lymph circulates around the body in these vessels and flows through the lymph nodes.
What causes malt in the stomach?
Treatment for stomach (gastric) MALT. Most cases of MALT lymphoma of the stomach are linked to a chronic stomach infection caused by the bacteria Helicobacter pylori. This infection causes inflammation of the stomach lining, with symptoms of indigestion and stomach pain.
How to treat non gastric malt?
In some people, the MALT has spread to nearby lymph nodes or, less often, to another body organ when it is diagnosed. You might have chemotherapy with immunotherapy (chemoimmunotherapy).
Does malt lymphoma grow?
MALT lymphoma usually grows slowly. Most people have early stage (localised) MALT lymphoma when they are diagnosed. The outlook is good, even when the lymphoma is quite widespread. Read about stages and grades.
Is Malt a low grade lymphoma?
MALT is a low grade lymphoma and treatment usually works well. The type of treatment you have for low grade ( indolent) NHL depends on: the stage of your lymphoma when it is diagnosed. the symptoms you have at the time. your general health and fitness.
What is malt lymphoma?
MALT lymphoma is a rare B-cell non-Hodgkin's lymphoma that typically runs an indolent or slow-growing clinical course . MALT is an acronym:
Where does malt lymphoma originate?
The disease begins when B-cells in lymphoma tissue in these sites mutates. The most commonly MALT lymphoma-related organ or area is the stomach. MALT lymphoma originating here accounts for as many as two of every three MALT lymphomas.
Can Malt lymphoma spread to other parts of the body?
Most patients who are eventually diagnosed with MALT lymphoma present with: Fortunately, these symptoms often bring people to visit a doctor, and as a consequence it is common for the disease to be found in its early stages, before it has had a chance to spread to nearby lymph nodes or to other parts of the body.
Is Malt lymphoma related to Celiac disease?
Furthermore, MALT lymphoma has been associated with a number of other related diseases and health conditions, including Sjogren Syndrome, Celiac Disease, Crohn’s Disease, and Hashimoto Thyroiditis.
What is the treatment for maltoma?
The traditional monotherapy regimens employed for MALTomas have included chlorambucil, cyclophosphamide, or fludarabine. In addition, standard combination regimens such as CHOP have been used successfully. Conjunctival MALTomas have been treated with interferon alfa-2a.
Where do maltomas occur?
Nongastric MALTomas most commonly occur in the head and neck, [ 22, 23, 24] lung, [ 25] and orbit. [ 20, 26] These nongastric MALTomas are not associated with H pylori and are treated by means of standard modalities, including radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and administration of monoclonal antibodies.
Is mucosa associated with lymphoepithelial lesions?
Lymphoepithelial lesions are strongly associated with mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphomas (MALT lymphomas); however, they may appear in other types of lymphomas. High magnification micrograph of a lymphoepithelial lesion of the gastrointestinal tract in the setting of a primary gastrointestinal tract lymphoma.
Is debulking performed for maltoma?
Similarly, debulking is only rarely performed. Surgery management of nongastrointestinal MALToma predominantly involves excisional biopsy of the lungs or orbital soft tissue.
Is maltoma gastric or nongastric?
Management differs, depending on whether the MALToma is gastric or nongastric. Gastric MALTomas are the most common and well-studied MALTomas. These neoplasms are intimately associated with Helicobacter pylori, which is present in more than 90% of pathologic specimens of MALTomas. [ 14] .
What is the goal of lymphoma treatment?
The goal of treatment is to destroy as many cancer cells as possible and bring the disease into remission.
What is the treatment for cancer?
Radiation therapy . Radiation therapy uses high-powered beams of energy, such as X-rays and protons, to kill cancer cells. Bone marrow transplant. A bone marrow transplant, also known as a stem cell transplant, involves using high doses of chemotherapy and radiation to suppress your bone marrow.
What tests can be done to determine if you have lymphoma?
Physical exam. Your doctor checks for swollen lymph nodes, including in your neck, underarm and groin, as well as a swollen spleen or liver. Removing a lymph node for testing. Your doctor may recommend a lymph node biopsy procedure to remove all or part of a lymph node for laboratory testing. Advanced tests can determine if lymphoma cells are ...
How to determine if lymphoma is present?
Advanced tests can determine if lymphoma cells are present and what types of cells are involved. Blood tests. Blood tests to count the number of cells in a sample of your blood can give your doctor clues about your diagnosis. Removing a sample of bone marrow for testing. A bone marrow aspiration and biopsy procedure involves inserting a needle ...
Can lymphoma be treated with supplements?
No supplements have been found to treat lymphoma. But integrative medicine may help you cope with the stress of a cancer diagnosis and the side effects of cancer treatment. Talk to your doctor about your options, such as: Physical activity. Art therapy. Meditation. Music therapy. Relaxation exercises. Acupuncture.
Causes
Symptoms of Malt Lymphoma
- The symptoms of MALT lymphoma depend on the organ that is affected. Often, there are no symptoms when the disease originates outside the stomach. When MALT lymphoma begins in the stomach, you may feel indigestion or you may experience weight loss; black stools are also possible because of bleeding into the stomach. Some people may feel a vague pain in the abdo…
Diagnosis
- To diagnose a MALT lymphoma, the doctor will need to take a biopsy from the tumor. For MALT lymphomas of the stomach, this usually involves an endoscopy. Doctors will also test for the presence of the H. pyloribacteria in the stomach. This can be done via a blood test, stool test, or breath test.
Staging
- Staging of MALT lymphoma requires multiple procedures:3 1. Complete physical examination 2. Blood count 3. Renal and liver test 4. Tests for the enzyme dehydrogenase 5. Tests for a protein called beta-2-microglobulin 6. Imaging tests 7. Bone marrow biopsy The staging of lymphomasinvolves three separate ratings. First, MALT lymphomas are classified based on ho…
Prognosis
- MALT lymphomas are low-grade lymphomas. Oncologists refer to them as “indolent” lymphomas, which means they grow slowly and remain confined to one organ for a relatively long time.5The result is that usually MALT lymphomas have a favorable outcome and will not cause serious illness or death. Overall survival rate for MALT lymphoma is excellent for the majority of patient…
A Word from Verywell
- Like any cancer diagnosis, MALT lymphoma is overwhelming. This slow-growing cancer has a good prognosis, though, and can often be managed or cured. Take time to research the condition and therapies to ensure you’re able to work with your healthcare provider to make the best decisions for your long-term health and quality of life.