Medication
Treatment options include:
- No treatment/"watchful waiting." If the nodules are not cancerous, you and your doctor may decide that you don’t need to be treated at this time. ...
- Radioactive iodine. Your doctor may use radioactive iodine to treat hyperfunctioning thyroid nodules and goiters with several nodules. ...
- Surgery. ...
Procedures
Thyroid Nodules are usually Benign and Not Cancerous The good news is that most people with thyroid nodules do not and will not get thyroid cancer. The bad news is that a thyroid nodule is not normal and may be associated with other conditions of your thyroid gland.
Therapy
Treatment
- A transverse neck crease incision of approximately 2inches is placed over cyst.
- Subplatysmal flap elevation and cyst with surrounding tissue is dissected up to hyoid bone, avoiding rupture of the cyst.
- Strap muscles are divided.
Self-care
The following are common types of thyroid nodules:
- Colloid nodules develop from a lack of iodine, which is a mineral essential to the production of thyroid hormones. ...
- Hyperfunctioning thyroid nodules produce thyroid hormone, which may cause hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid).
- Multinodular goiter occurs when the thyroid gland forms multiple nodules, which grow over time. ...
Nutrition
How are thyroid nodules treated?
Are complex thyroid nodules usually cancerous?
What are the treatment options for thyroid cysts?
What causes thyroid nodules to grow?

What if a thyroid nodule is malignant?
Thyroid Cancers. Five to 10 percent of thyroid nodules are malignant, or cancerous, although most cause no symptoms. Rarely, they may cause neck swelling, pain, swallowing problems, shortness of breath, or changes in the sound of your voice as they grow. There are several types of thyroid cancer.
Do cancerous thyroid nodules need to be removed?
Larger or aggressive cancerous nodules require removal of the whole thyroid and sometimes subsequent radioactive iodine therapy. Fluid-filled nodules (thyroid cysts): It is usually fine to leave cysts untreated, especially if they are causing no problems.
Is malignant thyroid cancer curable?
Thyroid cancer, a type of endocrine cancer, is generally highly treatable with an excellent cure rate.
What is the most common treatment for thyroid cancer?
Most cancers are treated with removal of the thyroid gland (thyroidectomy), although small tumors that have not spread outside the thyroid gland may be treated by just removing the side of the thyroid containing the tumor (lobectomy).
How fast do cancerous thyroid nodules grow?
Malignant thyroid nodules are more likely to grow at least 2 mm per year and increase in volume compared with benign thyroid nodules, according to findings published in The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
What if thyroid biopsy is positive?
A positive marker indicates the need for a total thyroidectomy instead of a lobectomy, and negative markers may support a decision to forgo surgery for a follicular lesion of undetermined significance. Further studies are needed to determine the utility of these tests for indeterminate nodules.
What were your first signs of thyroid cancer?
Signs and Symptoms of Thyroid CancerA lump in the neck, sometimes growing quickly.Swelling in the neck.Pain in the front of the neck, sometimes going up to the ears.Hoarseness or other voice changes that do not go away.Trouble swallowing.Trouble breathing.A constant cough that is not due to a cold.
What is survival rate of thyroid cancer?
Survival rates can give you an idea of what percentage of people with the same type and stage of cancer are still alive a certain amount of time (usually 5 years) after they were diagnosed....Follicular thyroid cancer.SEER Stage5-Year Relative Survival RateRegional98%Distant63%All SEER stages combined98%1 more row•Mar 1, 2022
What is the first stage of thyroid cancer?
Stage I: This stage describes a small tumor (T1) with no spread to lymph nodes (N0) and no distant metastasis (M0). Stage II: This stage describes a larger localized tumor (T2 or T3) with no spread to lymph nodes (N0) and no metastasis (M0).
Do you need chemo or radiation for thyroid cancer?
Chemotherapy is a drug treatment that uses chemicals to kill cancer cells. There are many different chemotherapy drugs that can be used alone or in combination. Some come in pill form, but most are given through a vein. Chemotherapy may help control fast-growing thyroid cancers, such as anaplastic thyroid cancer.
Do you need chemotherapy for thyroid cancer?
Chemotherapy is seldom helpful for most types of thyroid cancer, but fortunately it is not needed in most cases. It is often combined with external beam radiation therapy for anaplastic thyroid cancer and is sometimes used for other advanced cancers that no longer respond to other treatments.
Does oncologist treat thyroid cancer?
Endocrinologists are the primary treating MD for thyroid cancer. Oncologists can assist the endocrinologist when targeted chemotherapies are needed for the rare aggressive thyroid cancers.
What is a thyroid nodule?
The thyroid nodule is large (producing a visible mass in the neck) The thyroid nodule is producing symptoms on the breathing tube or swallowing tube. The thyroid nodule is producing excessive thyroid hormone. Thyroid nodules which have Indeterminate or suspicious for cancer FNAs. Multinodular goiters producing symptoms.
How to tell if thyroid nodules are benign?
Sometimes clearly benign thyroid nodules are managed with surgery. Some potential indications for removing benign thyroid nodules include: 1 The thyroid nodule is large (producing a visible mass in the neck) 2 The thyroid nodule is producing symptoms on the breathing tube or swallowing tube 3 The thyroid nodule is producing excessive thyroid hormone 4 Thyroid nodules which have Indeterminate or suspicious for cancer FNAs. 5 Multinodular goiters producing symptoms
What is the procedure to treat multinodular goiters?
In some circumstances, clearly benign thyroid nodules which are symptomatic, can be managed with a process called radio frequency ablation (also called RFA). If RFA is used to treat a clearly benign thyroid nodule, either general anesthesia or at times, local anesthesia can be utilized.
How long does it take to observe a thyroid nodule?
Observation usually implies repeating thyroid blood tests, ultrasound, and physical examination in approximately one year.
Why should thyroid surgery be performed?
Only expert thyroid cancer surgeons should be performing thyroid surgery because the risk to the patients including the nerves to the voice box and glands that control calcium are significantly higher in those that do not do these types of surgery routinely and frequently .
Can thyroid nodules be treated?
If the thyroid nodule should increase in size or establish symptoms, repeat biopsy or another intervention may be indicated. Thyroid nodules that don’t change over a period of years may never require any treatment whatsoever . Thyroid Hormone Therapy.
Why is thyroid hormone therapy needed after surgery?
Nearby lymph nodes are usually removed as well. Because the thyroid gland is removed , thyroid hormone therapy is needed after surgery. For MTC, thyroid hormone therapy is meant to provide enough hormone to keep the patient healthy, but it does not reduce the risk that the cancer will come back.
What is the treatment for cancer that shows up on a radioiodine scan?
If the cancer shows up on a radioiodine scan (meaning the cells are taking up iodine), radioactive iodine (RAI) therapy may be used, either alone or with surgery. If the cancer does not show up on the radioiodine scan but is found by other imaging tests (such as an MRI or PET scan), external radiation may be used.
How long after thyroidectomy can I take levothyroxine?
If RAI treatment is planned, the start of thyroid hormone therapy may be delayed until the treatment is finished (usually about 6 to 12 weeks after surgery).
What is the first surgery to remove cancer?
If cancer is confirmed, a completion thyroidectomy is done. A thyroidectomy may be done as the first surgery if there are signs the cancer has spread or if the patient wants to avoid having more surgery later. As with papillary cancer, some lymph nodes usually are removed and tested for cancer.
What is RAI therapy?
RAI therapy is often given for more advanced cancers such as T3 or T4 tumors, or cancers that have spread to lymph nodes or distant areas. The goal is to destroy any remaining thyroid tissue and to try to treat any cancer remaining in the body.
Why do you need to remove lymph nodes?
Because removing the lymph nodes allows them to be checked for cancer, this surgery also makes it easier to accurately stag e the cancer. If cancer has spread to other neck lymph nodes, a modified radical neck dissection (a more extensive removal of lymph nodes from the neck) is often done. Treatment after surgery depends on the stage of the cancer:
What is the best treatment for cancer?
For cancers that have spread, chemotherapy alone can be used. If the cancer cells have changes in certain genes, treatment with targeted drugs might be helpful: 1 Dabrafenib (Tafinlar) and trametinib (Mekinist) can be used to treat cancers with certain BRAF gene changes. 2 Selpercatinib (Retevmo) can be used to treat cancers with certain RET gene changes. 3 Larotrectinib (Vitrakvi) or entrectinib (Rozlytrek) can be used to treat cancers with NTRK gene changes.
Why do you need to see an endocrinologist for thyroid nodules?
Common reasons you can be referred to the endocrinology department for evaluation of thyroid nodules include: The nodule was discovered during an imaging test for an unrelated reason, such as a carotid doppler ultrasound or a CT scan that includes your neck.
What is a thyroid nodule?
Nodules can be solid or contain a variable amount of fluid. If they are completely fluid-filled, they are called thyroid cysts. Thyroid nodules are more common in women compared to men and more likely to occur as you get older.
How to tell if thyroid nodules are cancerous?
You have symptoms such as swelling in the neck or front of the throat, trouble swallowing, or a hoarse voice. A thyroid ultrasound is the best way to evaluate these nodules. We use an ultrasound machine to see if any nodules are present, their size, and whether there are signs that the nodule might be cancerous.
How to tell if you have thyroid cancer?
Although most thyroid nodules are benign, some can harbor thyroid cancer. And some types of thyroid cancer are more aggressive than others. You should be more proactive in seeing an endocrinologist if you have any of the following symptoms: 1 A lump in your neck that appears to be growing 2 Swelling or pain in the neck 3 Hoarse voice 4 Persistent cough 5 Trouble breathing or swallowing
What to do if thyroid is producing too much thyroid hormone?
If your thyroid is producing too much thyroid hormone (hyperthyroidism), we can do a radioactive iodine uptake and scan. This study involves swallowing a pill and taking a picture the next day to tell us whether the nodule is making too much thyroid hormone.
How to treat hot nodules?
We can treat hot nodules either with radioactive iodine therapy, which is a single dose of oral medication that destroys the over-active thyroid cells in the nodule, or by surgically removing the side with the nodule. Another option is medication, but it must be taken long-term, so is not preferred.
What is the procedure to take tissue samples of a small portion of a nodule?
If a nodule is large or looks suspicious, we will do a fine needle aspiration biopsy, which involves using thin needles to take tissue samples of a tiny portion of the nodule that is evaluated in the lab for cancer cells.
What causes thyroid nodules?
Certain factors increase your risk of thyroid cancer, such as a family history of thyroid or other endocrine cancers and having a history of radiation exposure from medical therapy or from nuclear fallout. Iodine deficiency. Lack of iodine in your diet can sometimes cause your thyroid gland to develop thyroid nodules.
What causes enlarged nodules in the thyroid gland?
Hashimoto's disease, a thyroid disorder, can cause thyroid inflammation and result in enlarged nodules. This often is associated with hypothyroidism. Multinodular goiter. The term goiter is used to describe any enlargement of the thyroid gland, which can be caused by iodine deficiency or a thyroid disorder.
How do you know if you have a thyroid nodule?
You often won't know you have a thyroid nodule until your doctor discovers it during a routine medical exam. Or your doctor may uncover it during a scan that was done for another health reason. Some thyroid nodules, however, may become large enough to be visible or make it difficult to swallow or breathe. Treatment options depend on the type of ...
Where is the thyroid gland located?
Thyroid gland. Your thyroid gland is located at the base of your neck, just below the Adam's apple. Thyroid nodules are solid or fluid-filled lumps that form within your thyroid, a small gland located at the base of your neck, just above your breastbone. Most thyroid nodules aren't serious and don't cause symptoms.
What is a cyst in the thyroid?
Thyroid cyst. Fluid-filled cavities (cyst s) in the thyroid most commonly result from degenerating thyroid adenomas. Often, solid components are mixed with fluid in thyroid cysts. Cysts are usually noncancerous, but they occasionally contain cancerous solid components. Chronic inflammation of the thyroid.
Can iodine cause thyroid nodules?
Iodine deficiency. Lack of iodine in your diet can sometimes cause your thyroid gland to develop thyroid nodules. But iodine deficiency is uncommon in the United States, where iodine is routinely added to table salt and other foods.
Is thyroid adenoma cancerous?
An overgrowth of normal thyroid tissue is sometimes referred to as a thyroid adenoma. It's unclear why this occurs, but it's not cancerous and isn't considered serious unless it causes bothersome symptoms from its size. Some thyroid adenomas lead to hyperthyroidism. Thyroid cyst.
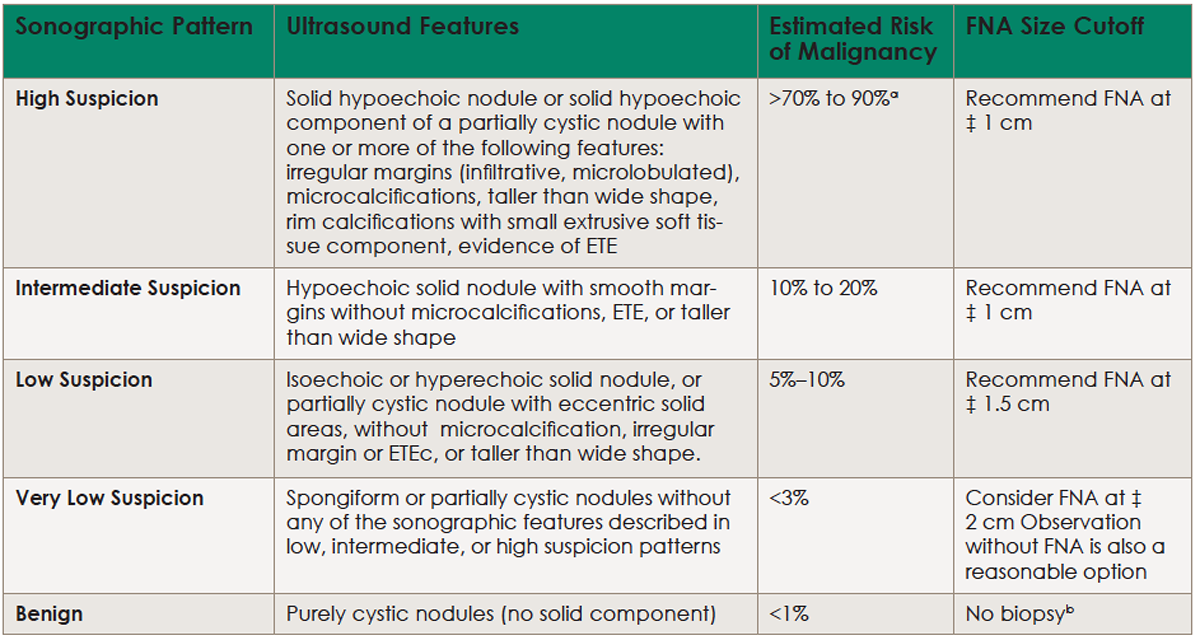
The Current System: Summarizing the ACR-TIRAD
Currently, most clinics rely on the American College of Radiology's Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data System (ACR-TIRAD) to decide if an FNA is warranted.
Location is of critical importance
A recent study published in Thyroid looked at the risk of malignant nodules based on location in the thyroid⁴. Their specific aim was to determine if the location of a nodule made it more or less likely to be malignant. The thyroid was divided into four locations: isthmus, upper, middle, or lower portions of the thyroid lobe.
Nodules in the isthmus are at greater risk
The regression model revealed that location was an independent predictor of malignancy. Meaning that when all other variables were held constant, such as the ACR-TIRAD score, where the nodules were found was significant. Nodules in the lower lobe were least at risk, a result confirmed by two earlier studies using smaller sample sizes³˒⁵.
Should location be added to the ARC-TIRAD score?
Because nodule location appears to be associated with malignancy risk, including location as a measure in the ACR-TIRAD assessment may elevate the accuracy of this tool. Unfortunately, the authors did not report the findings of a multivariate model based solely on these two variables. However, Dr. Jasim told EndocrineWeb the following:
Is thyroid nodule benign or malignant?
Fine needle aspiration (FNA) is the most reliable clinical tool for determining whether a nodule is benign or malignant.
Can thyroid cancer be cured?
Thyroid cancers are slow growing indolent cancer. Thyroid cancer can be cured if appropriately treated. Our Thyroid Cancer Clinic at the University of Rochester Medical Center is run in collaboration with experienced endocrine surgeon, head and neck surgeons (ENT), pathology and nuclear medicine.