
Explore
After a lacunar stroke, some people also require: physical therapy to restore function occupational therapy to improve skills needed for everyday living speech therapy to improve language skills
What kind of therapy is needed After a lacunar stroke?
Kidney and various blood tests may be requested as well. The main decider of lacunar stroke prognosis is the speed at which treatment is initiated. Because the brain is being starved of oxygen-rich blood, the more time that is taken to help relieve this blockage, more brain cells will die.
What is the prognosis for lacunar stroke?
An acute lacunar infarct is efficiently treated with TPA. [30][31] If symptom onset duration is more than 4.5 hours and there is suspicion for intracranial arterial occlusion in the anterior circulation, CTA/MRA is useful for selecting candidates for mechanical thrombectomy between 6 to 24 hours from last known well.
What are the treatment options for acute lacunar infarct?
When symptoms of a lacunar stroke are present, your doctor will immediately call for a CT scan or MRI scan in order to get a detailed image of the brain. A Doppler ultrasound may also be used to measure blood flowing through veins and arteries. Your doctor may also run tests to measure your heart function.
What tests are used to diagnose a lacunar stroke?
Can you recover from a lacunar stroke?
People often begin to recover within hours or days of a lacunar stroke. Lacunar strokes have a better rate of recovery than other strokes that involve larger blood vessels. More than 90 percent of people with a lacunar stroke will recover substantially within the first three months following the stroke.
How long can you live after lacunar stroke?
Overall, the case fatality rates at 30 days (mean, 2.5%) and at 1 year (mean, 2.8%) were similar to those in the general population; however, the mortality rate after lacunar infarctions increased to 27.4% at 5 years, 60% after 10 years, and 75% after 14 years.
What does a lacunar stroke affect?
Strokes can damage brain tissue in the outer part of the brain (the cortex) or deeper structures in the brain underneath the cortex. A stroke in a deep area of the brain (for example, a stroke in the thalamus, the basal ganglia or pons) is called a lacunar stroke.
What is the most common lacunar stroke syndrome?
Pure motor stroke (PMS), also known as pure motor hemiparesis, was first reported by Fisher and Curry in 1965 and it is considered the commonest lacunar syndrome in clinical practice, accounting for between one half and two thirds of cases, depending on the series.
Is a lacunar stroke serious?
Some early research has indicated that lacunar infarct has a better outlook than other types of strokes. But it can still lead to an increased risk of further strokes, dementia, and death from cardiovascular causes.
Is a lacunar stroke a disability?
In this clinical trial of lacunar stroke patients, we found high average functional scores, reflecting relatively mild disability compared with prior studies among all stroke subtypes.
What does a lacunar stroke feel like?
The infarct of this lacunar syndrome is usually in the thalamus. Symptoms consist of persistent or transient numbness and/or tingling on one side of the body (eg, face, arm, leg, trunk). Occasionally, patients complain of pain or burning, or of another unpleasant sensation. Unilateral sensory loss is observed.
What is the cause of lacunar strokes?
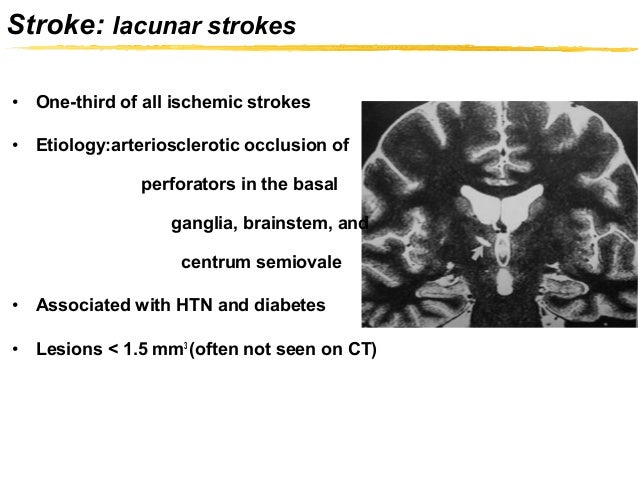
A quarter of all ischaemic strokes (a fifth of all strokes) are lacunar type. Lacunar infarcts are small infarcts (2–20 mm in diameter) in the deep cerebral white matter, basal ganglia, or pons, presumed to result from the occlusion of a single small perforating artery supplying the subcortical areas of the brain.
Can a lacunar stroke affect vision?
It accounts for 7% of cases of lacunar strokes. The sensations affected are pain, temperature, touch, pressure, vision, hearing, and taste.
What part of the brain does a lacunar stroke affect?
A lacunar stroke occurs when an artery to the deep part of the brain, containing structures like the thalamus or basal ganglia, is blocked. These arteries are very small and branch off directly from a larger artery, making them particularly vulnerable to blockages.
What are two risk factors for lacunar stroke?
Results: Significantly increasing the risk of lacunar stroke were hypertension (with an odds ratio of 8.9 [95% confidence intervals 4.2, 18.8]), current smoking (6.6 [2.9, 14.8]), and diabetes (2.3 [1.0, 5.5]), whereas frequent physical exercise was associated with a significantly decreased risk (0.3 [0.1, 0.7]).
Can lacunar infarcts disappear?
Some symptomatic lacunar infarcts also disappear. Although it may be that the brain tissue healed without the formation of a lacune (which implies “real” regression of cSVD), it seems more likely that these lacunar infarcts have progressed into small collapsed lacunes that are indiscernible at conventional MRI.
Why is it important to have a lacunar stroke?
Experiencing a lacunar stroke increases your risk of future strokes. In order to reduce damage and future complications, it’s important that lacunar stroke is detected right away so treatment can begin early on. According to the National Institutes of Health, lacunar stroke accounts for one-fifth of all strokes.
How to know if you have a lacunar stroke?
It’s important to recognize the symptoms of lacunar stroke so that you can receive medical attention right away. Symptoms of a lacunar stroke are similar to those accompanying other stroke types, namely, slurred speech, inability to raise arms, one side of the face appearing droopy, numbness on one side of the body, difficulty walking or moving arms, confusion, memory problems, struggling to speak or understand language, headache, and loss of consciousness.
How many strokes are caused by lacunar stroke?
According to the National Institutes of Health, lacunar stroke accounts for one-fifth of all strokes. When a stroke occurs, the brain is deprived of oxygen, causing brain cells to die within minutes. Lacunar strokes account for approximately 15 to 25 percent of all ischemic strokes in the United States and other Western countries.
What is a lacunar infarct?
Lacunar infarct is a type of stroke that occurs when one of the arteries supplying blood to the brain gets blocked. These arteries are quite small, which makes them vulnerable to damage. While most arteries in the body gradually become smaller, the arteries of the lacunar stroke branch off a large high-pressure artery.
What is a pure sensory stroke?
Pure sensory stroke. This type of stroke involves losing sensory aspects of the body, presenting as numbness or an unusual perception of pain, temperature, or pressure. A pure sensory stroke occurs as a result of damaged or destroyed regions of the brain that are responsible for controlling these sensations, typically the thalamus.
How long does it take for aspirin to work on a lacunar infarct?
Aspirin is also given within 48 hours to reduce the chance for additional clotting.
Why does a stroke happen on one side of the body?
This happens because the stroke has damaged or destroyed brains cells in that region of the brain used for sending signals for muscle control. It usually occurs on one side of the body, and often presents as a combination of arm and leg weakness, sparing the face; or a combination of arm, leg, and facial weakness.
How to identify lacunar stroke?
Lacunar strokes usually are identified by a computed tomography (CT) scan or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan of your brain. An MRI technique known as diffusion weighted imaging is particularly sensitive for identifying very new lacunar strokes.
How long does it take for a lacunar stroke to go away?
If medicines restore circulation to the brain quickly, symptoms of a lacunar stroke may go away within hours. If blood supply is interrupted for a longer time, brain injury may be more severe, and symptoms may last for many weeks or months, requiring physical rehabilitation. There may be permanent disability.
What is a stroke in the brain called?
A stroke in a deep area of the brain (for example, a stroke in the thalamus, the basal ganglia or pons) is called a lacunar stroke. These deeper structures receive their blood flow through a unique set of arteries.
Why do lacunar strokes happen?
Because of the characteristics of these arteries, lacunar strokes happen a little bit differently from other strokes. A lacunar stroke occurs when one of the arteri es that provide blood to the brain's deep structures is blocked. These arteries are small, and are uniquely vulnerable. Unlike most arteries, which gradually taper to a smaller size, ...
How long does a stroke last?
If blood supply is interrupted for a longer time, brain injury may be more severe, and symptoms may last for many weeks or months, requiring physical rehabilitation. There may be permanent disability.
What are the symptoms of a stroke?
Other neurological symptoms. In a person with prolonged, untreated high blood pressure, multiple lacunar strokes can occur. This can cause additional symptoms to develop, including emotional behavior and dementia.
How long does it take to recover from a stroke?
People often begin to recover within hours or days of a lacunar stroke. Lacunar strokes have a better rate of recovery than other strokes that involve larger blood vessels. More than 90 percent of people with a lacunar stroke will recover substantially within the first three months following the stroke.
What is the best treatment for lacunar stroke?
Antiplatelet drugs such as aspirin are routinely prescribed to help prevent new strokes in people with a history of lacunar stroke. These drugs interfere with the formation of blood clots that can cause strokes. Dr.
What is a lacunar stroke?
Strokes occur when blood vessels that supply the brain rupture or become blocked. Lacunar strokes often arise from chronic high blood pressure, which leads to progressive narrowing and finally blockage of small arteries that supply deep brain structures. Lacunar strokes account for up to one-fifth of all strokes.
What is the best medication for stroke?
Current clinical practice guidelines recommend aspirin alone, clopidogrel alone, or aspirin plus dipyridamole for secondary prevention after most types of stroke. These study results are consistent with those guidelines.
Why do lacunar strokes happen?
A lacunar stroke occurs when one of the arteries that provide blood to the brain's deep structures is blocked. These arteries are small, and are uniquely vulnerable.
What is a stroke in the brain called?
A stroke in a deep area of the brain (for example, a stroke in the thalamus, the basal ganglia or pons) is called a lacunar stroke.
Is a lacunar stroke a small artery?
Unlike most arteries, which gradually taper to a smaller size, the small arteries of a lacunar stroke branch directly off of a large, high-pressure, heavily muscled main artery.
