Depending on the size and spread of the tumor (s), most women will undergo a combination of any of the following treatments:
- Lumpectomy
- Mastectomy
- Sentinel node biopsy
- Axillary node dissection
- Breast reconstruction
- Radiation
- Chemotherapy
- Hormonal therapy
- Biologic targeted therapy
How is ductal carcinoma in situ treated?
Mastectomy is a treatment for patients with multiple, very aggressive, or large invasive ductal tumors. It can be followed by breast reconstruction. Nonsurgical Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Treatment Radiation. Radiation therapy might be part of …
What you should know about invasive lobular carcinoma?
Dec 23, 2021 · Treatments for invasive ductal carcinoma include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, hormonal therapy, and targeted therapy. You and your doctor will decide what treatment or combination of treatments is right for you depending on the characteristics of the cancer and your personal preferences.
Does adenoid cystic carcinoma have a cure?
Treatment options for invasive ductal carcinoma usually depend on the severity of each case. The basic principles of treatment are to minimize the chances of local recurrence as well as to reduce the risk of metastasis. Therefore, surgical removal …
What does invasive ductal carcinoma grade 3 mean?
Feb 04, 2022 · Invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC) happens when cancerous cells begin to grow outside of the milk ducts of your breast into the surrounding fatty tissue. IDC is treated with chemotherapy, radiation ...

Does invasive ductal carcinoma require a mastectomy?
Most women with DCIS don't have the breast removed with a mastectomy. Instead, they have a lumpectomy. Most common is a lumpectomy followed by radiation. The surgeon removes the cancer and a small area of healthy tissue around it.Feb 22, 2021
What stage is invasive ductal carcinoma?
Generally, the stage of invasive ductal carcinoma is described as a number on a scale of I through IV. Stages I, II, and III describe early-stage cancers, and stage IV describes cancers that have spread outside the breast to other parts of the body, such as the bones or liver.Feb 7, 2022
What is the survival rate for invasive ductal carcinoma?
Invasive ductal carcinoma describes the type of tumor in about 80 percent of people with breast cancer. The five-year survival rate is quite high -- almost 100 percent when the tumor is caught and treated early.Jan 5, 2021
How long does it take for invasive ductal carcinoma to spread?
According to the Robert W. Franz Cancer Research Center at Providence Portland Medical Center, breast cancer cells need to divide at least 30 times before they are detectable by physical exam. Each division takes about 1 to 2 months, so a detectable tumor has likely been growing in the body for 2 to 5 years.Apr 2, 2021
What causes invasive ductal carcinoma?
Most likely, the precise cause is a complex interaction of many factors. In rare cases, the causes of invasive ductal carcinoma have been traced to inherited attributes, such as mutations of the: Breast cancer gene 1 (BRCA1), a tumor suppressor gene. Breast cancer gene 2 (BRCA2), a tumor suppressor gene.
Is invasive ductal carcinoma malignant?
What is invasive ductal carcinoma? Breast ducts are the passageways where milk from the milk glands (lobules) flows to the nipple. Invasive ductal carcinoma is cancer (carcinoma) that happens when abnormal cells growing in the lining of the milk ducts change and invade breast tissue beyond the walls of the duct.
Can invasive ductal carcinoma come back?
Invasive ductal carcinoma recurrence is possible after the completion of an initial course of treatment. In general, most physicians consider cancer to be a recurrence, rather than a progression, if a patient has exhibited no signs or symptoms for at least one year.
Does 5 year survival rate mean you have 5 years to live?
Most importantly, five-year survival doesn't mean you will only live five years. Instead it relates to the percentage of people in research studies who were still alive five years after diagnosis.Mar 16, 2007
Is a lumpectomy major surgery?
In a lumpectomy, only the affected portion of the breast is removed, without removing the surrounding healthy breast tissue. Lumpectomy is also called breast-conserving surgery. Lumpectomy is a commonly performed surgery but still major surgery with risks and potential complications.Oct 20, 2020
What is grade 3 invasive ductal carcinoma prognosis?
The grade is used to help predict your outcome (prognosis) and to help figure out what treatments might work best. A low grade number (grade 1) usually means the cancer is slower-growing and less likely to spread. A high grade number (grade 3) means a faster-growing cancer that's more likely to spread.
What is Stage 2 invasive ductal?
Specifically, the invasive ductal carcinoma stages are: Stage 1 – A breast tumor is smaller than 2 centimeters in diameter and the cancer has not spread beyond the breast. Stage 2 – A breast tumor measures 2 to 4 centimeters in diameter or cancerous cells have spread to the lymph nodes in the underarm area.
Is Stage 3 invasive ductal carcinoma curable?
With aggressive treatment, stage 3 breast cancer is curable; however, the risk that the cancer will grow back after treatment is high.
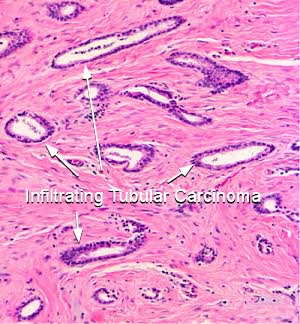
What is invasive ductal carcinoma?
Invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC), also known as infiltrating ductal carcinoma, refers to the uncontrolled growth of cancerous cells, originating fro...
How serious is invasive ductal carcinoma?
The severity of invasive ductal carcinoma mainly depends on the subtype. Tubular, mucinous, and medullary carcinomas tend to have a relatively good...
What are the causes of invasive ductal carcinoma?
The most common cause of invasive ductal carcinoma is DNA damage and genetic mutations of the breast tissue cells. Damage to DNA can cause changes...
What are the signs and symptoms of invasive ductal carcinoma?
Most individuals with early invasive ductal carcinoma are asymptomatic. However, when the size of the carcinoma is larger than 2 cm, individuals or...
How is invasive ductal carcinoma diagnosed?
To diagnose an invasive ductal carcinoma, a detailed medical history and physical examination, specifically of the breast and the underarm area, is...
How is invasive ductal carcinoma treated?
Treatment options for invasive ductal carcinoma usually depend on the severity of each case. The basic principles of treatment are to minimize the...
What are the most important facts to know about invasive ductal carcinoma?
Invasive ductal carcinoma, the most common type of breast cancer, refers to the uncontrolled growth of cancerous cells, originating from the milk d...
What is invasive ductal carcinoma?
Invasive ductal carcinoma treatment is designed to address cancer cells that initially form in a milk duct and then grow beyond the walls of the duct into the surrounding breast tissue.
How to contact Moffitt for ductal carcinoma?
If you’d like to learn more about invasive ductal carcinoma treatment option at Moffitt, call 1-888-663-3488 or complete a new patient registration form online. No referrals are required.
What is the best treatment for cancer?
Hormonal therapy – If a cancer tests positive for hormone receptors (special proteins that tell the cancer cells when to grow and divide in response to the presence of certain hormones, such as estrogen and progesterone), hormonal therapy may be used to lower the amount of hormones in the body that can potentially signal cancer cell growth. ...
What is the treatment for cancer underarms?
Radiation therapy – High-energy rays are delivered to an affected breast and underarm area to destroy cancerous cells. Chemotherapy – Anti-cancer medications are injected into a vein or taken by mouth in pill form. The medication travels through the bloodstream to reach and damage cancer cells.
How to treat a large tumor?
Additionally, to treat a large tumor (measuring more than 1 centimeter in diameter) or cancer that has spread beyond the breast tissue and lymph nodes, a physician might recommend a systemic treatment, such as chemotherapy or hormonal therapy, to destroy cancerous cells or shrink the tumor prior to surgery.
Nanotechnology In Breast Cancer
The field of nanotechnology has rapidly evolved as evidenced by the fact that there are more than 150 ongoing clinical trials investigating the efficacy of nanotechnology based drug delivery carriers targeting cancer.
Treatment For Triple Negative Breast Cancer
Treatment for triple negative breast cancer usually involves surgery , radiotherapy if breast conserving surgery was performed, and chemotherapy. If you would like to read more about the main types of breast cancer surgery, visit the surgery section of this website.
Is Infiltrating Ductal Carcinoma Curable
All together, invasive ductal carcinoma refers to cancer that has broken through the wall of the milk duct and begun to invade the tissues of the breast. Over time, invasive ductal carcinoma can spread to the lymph nodes and possibly to other areas of the body. Invasive ductal carcinoma also affects men.
What Does It Mean To Have Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Invasive Ductal Carcinoma About 80% of all breast cancers are invasive ductal carcinomas. Invasive means that the cancer has invaded or spread to the surrounding breast tissues. Ductal means that the cancer began in the milk ducts, which are the pipes that carry milk from the milk-producing lobules to the nipple.
What Can I Expect If I Have Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
If youve been diagnosed with invasive ductal carcinoma, your healthcare provider will discuss your treatment options with you in detail. For best results, youll want to begin treatment as soon as possible.
Breast Cancer Survival By Age
Five-year survival for female breast cancer shows an unusual pattern with age: survival gradually increases from 85% in women aged 15-39 and peaks at 92% in 60-69 year olds survival falls thereafter, reaching its lowest point of 70% in 80-99 year-olds for patients diagnosed with breast cancer in England during 2009-2013.
What Is Stage 1 Breast Cancer
Stage 1 breast cancer is the earliest stage of invasive breast cancer. The breast cancer has spread from its original location to the surrounding tissue but it is still contained in a relatively small area.
What is the first treatment for IDC?
Most of the time, surgery is the first treatment doctors will recommend for women with IDC. But if your tumor is very large or has spread, other options, such as chemo and hormonal therapy, may first be used to shrink the cancer. ( 2)
Why do doctors give chemotherapy after breast cancer surgery?
Chemo is also given after surgery to target any leftover cancer and to lower your chances of recurrence. ( 5)
What is the treatment for ductal carcinoma?
Hormonal therapy for invasive ductal carcinoma. Hormonal therapy is used to treat cancer cells with receptors for estrogen or progesterone, or both. The presence of these hormones can encourage breast cancer cells to multiply. Hormonal therapy removes or blocks these hormones to help prevent the cancer from growing.
How long does it take to recover from ductal carcinoma?
Chemotherapy consists of anticancer medications that are taken in pill form or injected into the bloodstream. It may take up to six months or longer after treatment has subsided to recover from the many side effects, such as nerve damage, joint pain, and fatigue.
What is the most common form of breast cancer?
The most common form of breast cancer is called invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC). It’s responsible for about 80 percent of all breast cancer diagnoses. Carcinoma refers to a type of cancer that begins in the skin cells or the tissues lining your internal organs. Adenocarcinomas are more specific types of carcinomas that originate in ...
What are the two main types of IDC?
The treatments for IDC fall into two main types: Local treatments for IDC target the cancerous tissue of the breast and the surrounding areas , such as the chest and lymph nodes. Systemic treatments for IDC are applied throughout the body, targeting any cells that may have traveled and spread from the original tumor.
What is systemic treatment for breast cancer?
Systemic treatments may be recommended depending on the characteristics of the cancer, including in situations where it has already spread beyond the breast or is at high risk of spreading to other parts of the body.
What is the treatment for IDC?
There are two main types of local treatments for IDC: surgery and radiation therapy. Surgery is used to remove the cancerous tumor and determine whether the cancer has spread to the lymph nodes. Surgery is typically the doctor’s first response when dealing with IDC.
How long does it take for a tumor to subside after radiation?
Some people treated with radiation may experience swelling or skin changes. Certain symptoms, such as fatigue, may take up to 6 to 12 weeks or longer to subside. Different kinds of surgeries and radiation therapies available for treating this IDC include: lumpectomy, or removal of the tumor.
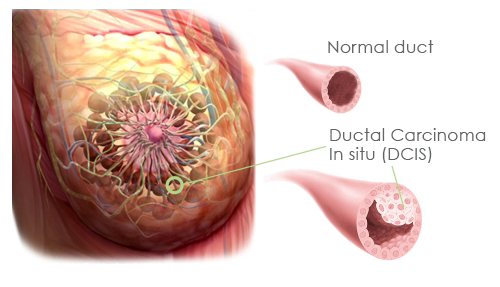
What is a DCIS?
Treatment of Ductal Carcinoma in Situ (DCIS) Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) means the cells that line the milk ducts of the breast have become cancer, but they have not spread into surrounding breast tissue. DCIS is considered non-invasive or pre-invasive breast cancer.
What is BCS in surgery?
Breast-conserving surgery (BCS) In breast-conserving surgery (BCS), the surgeon removes the tumor and a small amount of normal breast tissue around it. Lymph node removal is not always needed with BCS, but it may be done if the doctor thinks the area of DCIS might also contain invasive cancer.
Does DCIS have invasive cancer?
The chances an area of DCIS contains invasive cancer goes up with tumor size and how fast the cancer is growing. If lymph nodes are removed, this is usually done as a sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB ). If BCS is done, it is usually followed by radiation therapy. This lowers the chance of the cancer coming back in the same breast ...
Is DCIS invasive or noninvasive?
DCIS is considered non-invasive or pre-invasive breast cancer. DCIS can’t spread outside the breast, but it still needs to be treated because it can sometimes go on to become invasive breast cancer (which can spread).
Can you get BCS without radiation?
BCS without radiation therapy is not a standard treatment, but it might be an option for certain women who had small areas of low-grade DCIS that were removed with large enough cancer-free surgical margins.
Can a BCS remove DCIS?
Simple mastectomy (removal of the entire breast) may be needed if the area of DCIS is very large, if the breast has several separate areas of DCIS, or if BCS cannot remove the DCIS completely (that is, the BCS specimen and re-excision specimens still have cancer cells in or near the surgical margins).
What is the best treatment for DCIS?
Doctors recommend this type of treatment for DCIS that is hormone-receptor-positive -- which means it responds to the hormone estrogen.
How to treat DCIS?
Surgery is the most common way that doctors treat DCIS. Most often, it’s done with a procedure called a lumpectomy. A surgeon removes only the affected area of the breast while leaving healthy tissue. Doctors also call this breast-conserving surgery. Sometimes, a doctor might suggest removing the whole breast.
Why is breast cancer called DCIS?
Doctors often call this type of breast cancer ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS). It gets this name because the cancer is only in the breast ducts that carry milk.
Why do doctors recommend mastectomy?
This type of surgery is a mastectomy. Reasons why a doctor might suggest you have a mastectomy instead of a lumpectomy for DCIS include: The cancer covers a large area of the breast. The cancer is in more than one place.
What to do after a lumpectomy?
After a lumpectomy or mastectomy, some women may choose to have surgery to reconstruct their breast. The decision to have breast reconstruction is a personal one.
How long does radiation last for DCIS?
Radiation of the whole breast is the most common treatment. A machine delivers the radiation, often 5 days a week for several weeks . It might be an option to get radiation for only part of the breast. It’s not clear if this works as well as whole breast radiation.
Can chemo kill cancer cells?
No, most likely not. Chemotherapy uses drugs given throughout the body to kill fast-growing cells, including cancer. Because DCIS is only in the breast ducts, doctors don’t usually recommend chemotherapy to treat it.