How can you reverse intestinal metaplasia?
If doctors suspect your intestinal metaplasia is caused by H. pylori infection, they will likely recommend a short course of antibiotics, such as amoxicillin, clarithromycin, or tetracycline, along with over-the-counter or prescription acid-suppressing medications. Eradicating the infection appears to help reverse some cases of intestinal metaplasia altogether and may keep …
Does metaplasia always turn into cancer?
In GIM with visible dysplasia and early-stage GAC, endoscopic resection improves quality of life without reducing survival compared with surgery. Endoscopic ablation therapies have shown promise for invisible or extensive dysplasia. Summary: Endoscopic resection is appropriate for visible dysplasia and early-stage GAC without high-risk features that persists despite H. pylori …
Is intestinal metaplasia of the stomach reversible?
Quitting smoking and drinking alcohol, treating acid reflux and eradicating H. pylori infection gives your tissues a chance to recover from the chronic inflammation that triggers metaplasia. If metaplasia progresses to dysplasia, healthcare providers may recommend removing the affected tissue to prevent it from progressing to cancer.
Is intestinal metaplasia the same as Barretts?
Aug 12, 2019 · Probe-based confocal laser endomicroscopy (pCLE) provides high-level magnification (×1,000) of the gastrointestinal tract epithelium, and has been used for real-time evaluation of gastric lesions. 51 pCLE requires the intravenous administration of fluorescein, an organic fluorophore which is administered prior to the examination.

Should I worry about intestinal metaplasia?
Perhaps the biggest concern for those with intestinal metaplasia is that it might be precancerous. The abnormal cells in the digestive tract may go through a stage called dysplasia if left untreated. These abnormal cells may or may not progress to cancerous cells.
What is the treatment for gastric intestinal metaplasia?
After confirming a diagnosis of intestinal metaplasia, the doctor can begin treatment. Currently, the most effective treatment is to remove the H. pylori infection completely. This removal is done in combination with the use of antioxidant agents.
What percentage of intestinal metaplasia becomes cancer?
Atrophic gastritis, intestinal metaplasia, mild-moderate dysplasia, and severe dysplasia were associated with annual incidences of gastric cancer of 0.1%, 0.25%, 0.6%, and 6.0%, respectively.
Is intestinal metaplasia curable?
In the long term, with follow up of at least five years, there is epidemiological evidence that IM may be reversible although a combination of antioxidant agents and eradication of H pylori may be necessary to achieve this.
How common is intestinal metaplasia?
Intestinal metaplasia (IM) is recognized as a precancerous lesion for gastric cancer, increasing the risk by 6-fold. IM is highly prevalent in the general population, being detected in nearly 1 of every 4 patients undergoing upper endoscopy.Mar 15, 2012
How do you get intestinal metaplasia?
Intestinal metaplasia (IM) of the stomach is associated with a very small increased risk of developing gastric cancer. Known risk factors for IM include Helicobacter pylori infection, high salt intake, smoking, alcohol consumption, and chronic bile reflux.
How often does metaplasia turn into cancer?
1 Introduction. Gastric intestinal metaplasia (GIM) is a premalignant stage in the Correa's cascade and recognised as a point of no return in this pathway. 10 However, there exists a variation, in the progression rate from GIM to gastric cancer over 5 years ranging from 0.25% to 42%.Apr 27, 2017
What foods can you eat to prevent intestinal metaplasia?
Foods to eat. Some of the foods for prevention of intestinal metaplasia include the following. (Opt for organic tomatoes, berries, apples, grapes, cherries, peaches, and bell peppers since these fruits and vegetables are noted to have high pesticide residues.) apples (peel included) apricots. artichoke, kale, and bell peppers (these have ...
What causes intestinal metaplasia?
The exact causes of intestinal metaplasia are still being researched. However, there are some factors known to increase your risk. These risk factors may include: 1 smoking 2 H. pylori infection 3 genetics (having a close, first-degree relative with gastric cancer) 4 environmental factors
What is the camera on the end of an endoscope?
There is a camera on the end that allows doctors to get a close look at your gastric lining in this case. A tool cam also be added to the end of the endoscope that will allow the doctor to take a small sample of a lesion or the gastric lining for a biopsy. After confirming a diagnosis of intestinal metaplasia, the doctor can begin treatment.
Can intestinal metaplasia cause cancer?
Intestinal metaplasia is believed to be a precancerous lesion that may lead to gastric cancer. If you have intestinal metaplasia, then your risk of getting gastric cancer is increased six times. Trusted Source.
What are the best foods to eat to reduce oxidative stress?
These include eating lots of plant-based foods such as fresh fruits and vegetables because they are full of antioxidants. Antioxidants include vitamin C, vitamin E, flavonoids, carotenoids, and phenols.
What fruits have the most antioxidants?
apples (peel included) apricots. artichoke, kale, and bell peppers (these have the highest antioxidant content of all vegetables) bananas. beets. berries (the best fruits for antioxidants) broccoli. cherries. cocoa and dark chocolate.
Is intestinal metaplasia asymptomatic?
While some people may have acid reflux problems or symptoms relating to an H. pylori infection, intestinal metaplasia is primarily asymptomatic. This means that there aren’t any visible symptoms related to this condition. It’s discovered by screenings through endoscopy procedures and biopsies.
What are the risk factors for intestinal metaplasia?
The progression of intestinal metaplasia to cancer may be more likely to occur when the following risk factors exist. Genetics: having a family history of stomach cancer or other conditions of the intestinal tract. Alcohol consumption. Long-term incidence of acid reflux.
What is bland diet?
A bland diet (a non-spicy diet, low in fats and oils) A high-fiber, whole foods diet (rich in fresh fruits and vegetables, without processed, sugary, or fatty foods) A diet with plenty of fresh vegetables, nuts, and fruits. A diet with whole grains (instead of foods made from white flour)
What is the function of goblet cells?
The function of goblet cells is to preserve and protect the intestines by producing and secreting a thick mucus layer. Many medical experts consider intestinal metaplasia to be a precancerous condition.
Is intestinal metaplasia common?
Intestinal metaplasia is very common across the globe; one in every four people who have had an upper endoscopy (a flexible tube inserted into the nose, then down into the upper digestive system for diagnostic purposes), are found to have intestinal metaplasia. 1 Aside from the presence of an H. pylori infection, specific factors that increase the risk of intestinal metaplasia include:
Does smoking cause acid reflux?
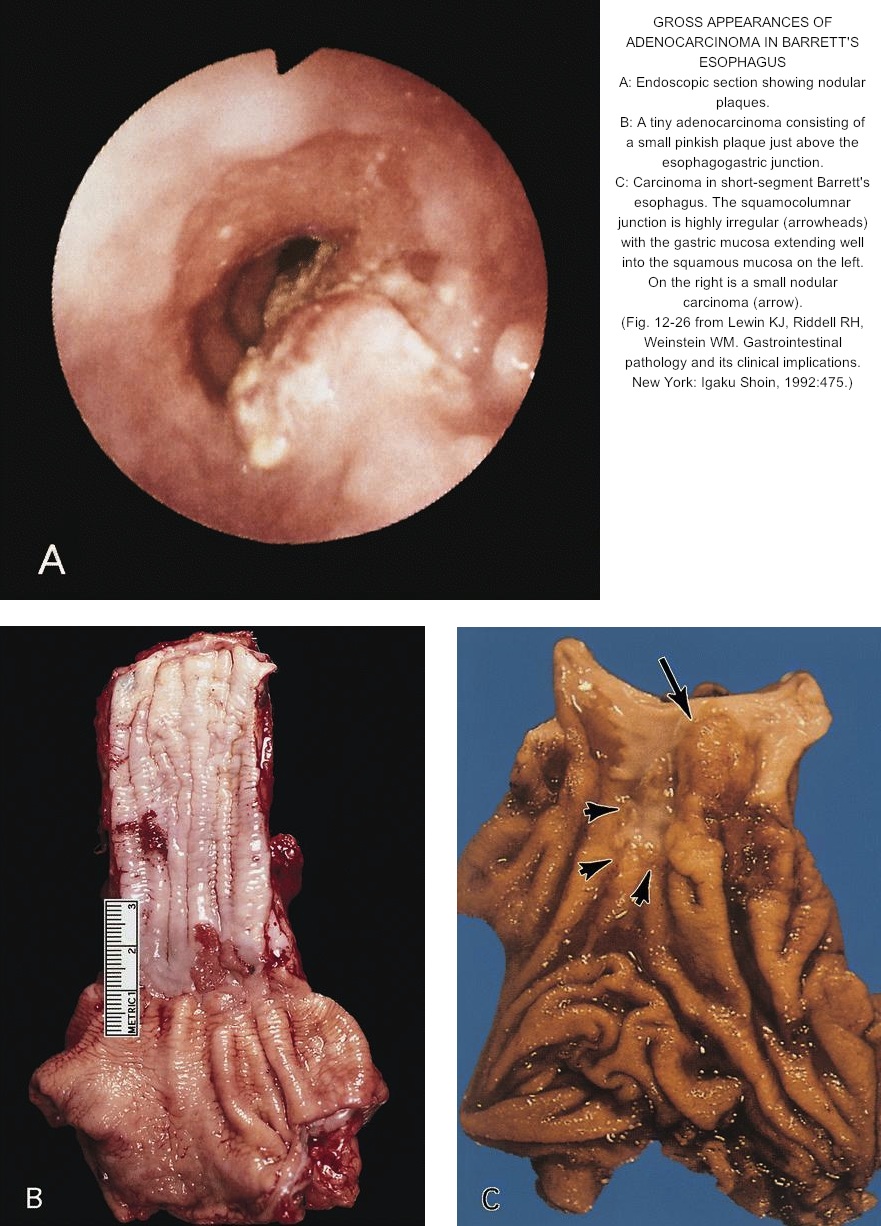
Long-term incidence of acid reflux. Secondhand smoke (and other toxins in the environment) Smoking: This lifestyle factor may increase the risk of developing many health-related conditions, including increasing the risk of intestinal metaplasia in the esophagus—known as Barrett’s esophagus .
Is stomach cancer a cancer?
According to a study in the World Journal of Gastrointestinal Oncology, gastric (stomach) cancer is the second most common cause of cancer-related death in the world. In addition, the study noted that intestinal metaplasia increases the risk of stomach cancer six-fold. 1 Therefore, screening and prevention measures are vital. Follow-up measures on precancerous lesions to ensure that cancer cells have not begun to grow, and to diagnose any cancerous cell growth early on, are a key preventive component.
What is the most common cause of peptic ulcer disease?
According to a study published in the journal Gastroenterology, over 50% of people worldwide may have an H. pylori infection. 2 H. pylori is a bacteria that infects the stomach. Infection with it usually occurs during childhood and is a very common cause of peptic (stomach) ulcer disease .
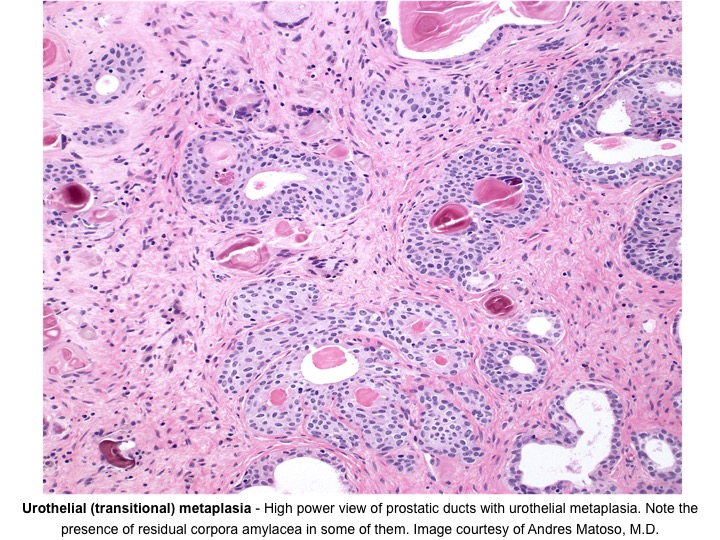
What is intestinal metaplasia?
Intestinal metaplasia occurs when cells in the tissues of the upper digestive tract, often in the stomach or esophagus, change and become more like cells from the intestines. Some doctors consider intestinal metaplasia to be a precancerous condition. Intestinal metaplasia is more common in people who have chronic acid reflux or gastroesophageal ...
What is the best medicine for stomach lining?
Doctors may also recommend drugs that reduce acid in the body to help the stomach lining or food pipe heal. This may include over-the-counter (OTC) drugs such as bismuth subsalicylate (Pepto Bismol) or prescription drugs, such as omeprazole (Prilosec).
Can H. pylori cause gastritis?
H. pylori may not cause symptoms in many people, but some people may develop digestive disorders, such as ulcers, gastritis, and GERD. The bacteria tend to attack the lining of the stomach, which is why some doctors believe they are a direct risk factor for intestinal metaplasia.
Does smoking cause metaplasia?
Smoking is a conscious lifestyle choice that may affect the progression of intestinal metaplasia. Smoking may damage the esophagus (food pipe), which could increase the risk of intestinal metaplasia in the esophagus, known as Barrett’s esophagus. One study in the United European Gastroenterol Journal.
Does smoking reduce the risk of cancer?
Quitting smoking may significantly reduce the risk for some forms of intestinal metaplasia or cancer. Other factors for intestinal metaplasia may include: environmental toxins, such as secondhand smoke or chemicals. high salt intake. alcohol consumption.
Can H pylori cause intestinal metaplasia?
An H . pylori infection may be a cause of intestinal metaplasia. The exact cause of intestinal metaplasia is still uncertain. Some healthcare professionals believe an H. pylori infection causes intestinal metaplasia, but there is also a range of risk factors that may increase the risk of developing it. Perhaps the biggest concern for those ...
What is the procedure called when you see the inside of your stomach?
Endoscopy is a procedure that uses a scope to see the inside of your stomach. A scope is a soft, flexible tube with a light and tiny camera on the end. It is passed down your throat and into your stomach. Samples of your stomach tissue may be removed and sent to a lab to be tested.
How to get rid of stomach acid?
Do not eat large meals. When you eat a lot of food at one time, your stomach needs more acid to digest it. Eat 6 small meals each day instead of 3 large meals, and eat slowly. Do not eat meals 2 to 3 hours before bedtime. Drink liquids as directed.
What is IM in the stomach?
IM is a condition that changes the cells that line your stomach or esophagus. The cells are changed into or replaced by cells that line your intestines. When IM happens in the esophagus, it is called Barrett esophagus. IM is a precancer lesion. This means it is not cancer yet, but it may develop into cancer over time.
How long does it take for H pylori to kill?
H. pylori treatment may include any of the following: Antibiotics help kill the bacteria. You may need to take this medicine for 10 to 14 days. Your healthcare provider will prescribe at least 2 antibiotics at the same time. Antiulcer medicines help decrease the amount of acid that is normally made by the stomach.
Can you sleep with more than one pillow?
You may also use more than one pillow under your head and shoulders while you sleep. Do not smoke. Nicotine can damage blood vessels and make it more difficult to manage IM. Smoking also increases your risk for new or returning cancer and delays healing after treatment.
What is the test for H pylori?
Samples of your stomach tissue may be removed and sent to a lab to be tested. A urea breath test may be used to test for H. pylori infection. You will swallow pudding, liquid, or a capsule that contains a chemical. Then you will breathe into a container.
How to increase energy level?
Drink liquids as directed. Liquids help your digestive system work correctly. Ask how much liquid to drink each day and which liquids are best for you. Exercise as directed. Exercise can help increase your energy level and appetite. Ask your healthcare provider how much exercise you need and which exercises are best for you.