Explore
The main treatments for breast cancer are:
- surgery
- radiotherapy
- chemotherapy
- hormone therapy
- targeted therapy
What are the best treatments for breast cancer?
Treatment is as follows: Neoadjuvant chemotherapy – This first line of treatment clears the breast and skin of the disease and to make the breast operable. Mastectomy and chest wall radiation. Breast reconstruction – We do not recommend immediate reconstruction because of the high risk of local recurrence of inflammatory breast cancer ...
How do I treat inflammatory breast cancer?
Surgery: The standard surgery for inflammatory breast cancer is a modified radical mastectomy. This surgery involves removal of the entire affected breast and most or all of the lymph nodes under the adjacent arm. Often, the lining over the underlying chest muscles is also removed, but the chest muscles are preserved.
What is the standard of care for inflammatory breast cancer?
Treatment
- Surgery. Surgery is recommended for the majority of stage 1 cancers. ...
- Radiation Therapy. If you have a lumpectomy, radiation therapy 12 is usually used to treat your remaining breast tissue.
- Chemotherapy. Chemotherapy is sometimes used as an adjuvant treatment for stage 1 breast cancer. ...
- Hormone Therapies. ...
- HER2 Targeted Therapies. ...
What is the plan for treating my breast cancer?

Can you survive inflammatory breast cancer?
The 5-year survival rate for people with inflammatory breast cancer is 41%. However, survival rates vary depending on the stage, tumor grade, certain features of the cancer, and the treatment given. If the cancer has spread to the regional lymph nodes, the 5-year survival rate is 56%.
How long is the treatment for inflammatory breast cancer?
Radiation is usually given 5 days a week for 6 weeks, but in some cases a more intense treatment (twice a day) can be used instead. Depending on how much tumor was found in the breast after surgery, radiation might be delayed until further chemo and/or targeted therapy (such as trastuzumab) is given.
Where does inflammatory breast cancer spread to?
Stage IV (metastatic): The inflammatory breast cancer has spread to other organs, such as the bones, lungs, brain, liver, distant lymph nodes, or chest wall (any T, any N, M1).
What were your first signs of inflammatory breast cancer?
What Are the Early Signs and Symptoms of Inflammatory Breast Cancer?Pain in the breast.Skin changes in the breast area. ... A bruise on the breast that doesn't go away.Sudden swelling of the breast.Itching of the breast.Nipple changes or discharge.Swelling of the lymph nodes under the arm or in the neck.
How quickly does inflammatory breast cancer progress?
Inflammatory breast cancer progresses rapidly, often in a matter of weeks or months. At diagnosis, inflammatory breast cancer is either stage III or IV disease, depending on whether cancer cells have spread only to nearby lymph nodes or to other tissues as well.
Who is most likely to get inflammatory breast cancer?
Being a woman. Women are more likely to be diagnosed with inflammatory breast cancer than are men — but men can develop inflammatory breast cancer, too. Being younger. Inflammatory breast cancer is more frequently diagnosed in people in their 40s and 50s.
Does inflammatory breast cancer show up in blood work?
On imaging, these sheets of tissue can resemble nests. Your doctor may be able to feel these areas of thickening on your skin, as well as possibly see areas of higher density on a mammogram. Routine blood tests may not pick up abnormalities related to inflammatory breast cancer.
Does inflammatory breast cancer hurt?
IBC causes a wide range of symptoms, including breast pain, redness, swelling, changes to the breast skin or nipples, and more. Many of the symptoms of IBC come on suddenly and may even appear to come and go. However, these symptoms will become consistently worse as the disease progresses.
How long can you live with untreated IBC?
IBC tends to have a lower survival rate than other forms of breast cancer3. The U.S. median survival rate for people with stage III IBC is approximately 57 months, or just under 5 years. The median survival rate for people with stage IV IBC is approximately 21 months, or just under 2 years.
Does inflammatory breast cancer spread quickly?
IBC grows and spreads quickly, so the cancer may have already spread to nearby lymph nodes by the time symptoms are noticed. This spread can cause swollen lymph nodes under your arm or above your collar bone. If the diagnosis is delayed, the cancer can spread to distant sites.
Is inflammatory breast cancer the most aggressive?
IBC is among the most aggressive types of breast cancer, and it can progress over the course of months or even just a few weeks. Because of this, early diagnosis and care are crucial. All too often, however, IBC isn't diagnosed until later stages, when it's harder to treat.
Does inflammatory breast cancer appear overnight?
Inflammatory breast cancer symptoms can appear quite suddenly. Inflammatory breast cancer is often confused with an infection of the breast (mastitis).
What is inflammatory breast cancer?
Inflammatory breast cancer is a rare and very aggressive disease in which cancer cells block lymph vessels in the skin of the breast. This type of...
What are the symptoms of inflammatory breast cancer?
Symptoms of inflammatory breast cancer include swelling (edema) and redness (erythema) that affect a third or more of the breast. The skin of the b...
How is inflammatory breast cancer diagnosed?
Inflammatory breast cancer can be difficult to diagnose. Often, there is no lump that can be felt during a physical exam or seen in a screening ma...
How is inflammatory breast cancer treated?
Inflammatory breast cancer is generally treated first with systemic chemotherapy to help shrink the tumor, then with surgery to remove the tumor,...
What is the prognosis of patients with inflammatory breast cancer?
The prognosis, or likely outcome, for a patient diagnosed with cancer is often viewed as the chance that the cancer will be treated successfully an...
What clinical trials are available for women with inflammatory breast cancer?
NCI sponsors clinical trials of new treatments for all types of cancer, as well as trials that test better ways to use existing treatments. Partici...
Where is radiation used for breast cancer?
The radiation is aimed at your chest, armpit and shoulder.
What is the procedure to remove breast tissue?
The operation usually includes: Surgery to remove the breast (mastectomy). A total mastectomy includes removing all of the breast tissue — the lobules, ducts, fatty tissue and some skin, including the nipple and areola. Surgery to remove the nearby lymph nodes.
How does chemotherapy work?
Chemotherapy uses drugs to destroy fast-growing cells, such as cancer cells. You may receive chemotherapy drugs through a vein (intravenously), in pill form or both. Chemotherapy is used prior to surgery for inflammatory breast cancer.
What is the best way to check for breast cancer?
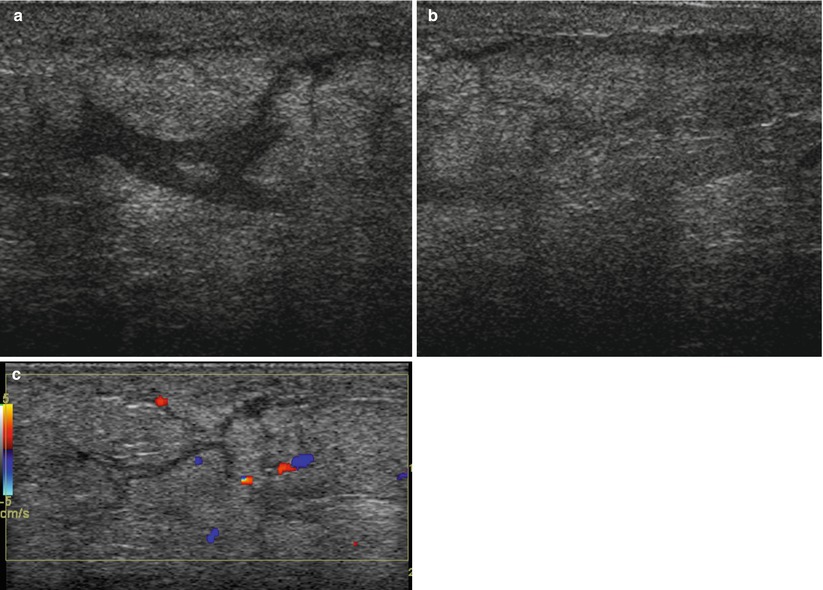
Your doctor examines your breast to look for redness and other signs of inflammatory breast cancer. Imaging tests. Your doctor may recommend a breast X-ray (mammogram) or a breast ultrasound to look for signs of cancer in your breast, such as thickened skin. Additional imaging tests, such as an MRI, may be recommended in certain situations.
What is the procedure to remove a small sample of breast tissue for testing?
Additional imaging tests, such as an MRI, may be recommended in certain situations. Removing a sample of tissue for testing. A biopsy is a procedure to remove a small sample of suspicious breast tissue for testing. The tissue is analyzed in a laboratory to look for signs of cancer.
Why do you need chemotherapy after cancer treatment?
If your cancer has a high risk of returning or spreading to another part of your body, your doctor may recommend additional chemotherapy after you've completed other treatments in order to decrease the chance that the cancer will recur.
What to do if cancer hasn't spread?
If the cancer hasn't spread to other areas of the body, treatment continues with surgery and radiation therapy. If the cancer has spread to other areas of the body, your doctor may recommend other drug treatments in addition to chemotherapy to slow the growth of the cancer.
What is the best treatment for inflammatory breast cancer?
Hormone therapy: If the cells of a woman’s inflammatory breast cancer contain hormone receptors, hormone therapy is another treatment option. Drugs such as tamoxifen, which prevent estrogen from binding to its receptor, and aromatase inhibitors such as letrozole, which block the body’s ability to make estrogen, can cause estrogen-dependent cancer cells to stop growing and die.
How is inflammatory breast cancer treated?
Inflammatory breast cancer is generally treated first with systemic chemotherapy to help shrink the tumor, then with surgery to remove the tumor, followed by radiation therapy. This approach to treatment is called a multimodal approach. Studies have found that women with inflammatory breast cancer who are treated with a multimodal approach have better responses to therapy and longer survival. Treatments used in a multimodal approach may include those described below.
What is the best test to see if you have breast cancer?
Imaging and staging tests include the following: A diagnostic mammogram and an ultrasound of the breast and regional (nearby) lymph nodes. A PET scan or a CT scan and a bone scan to see if the cancer has spread to other parts of the body.
Why is breast cancer called inflammatory?
This type of breast cancer is called “inflammatory” because the breast often looks swollen and red, or inflamed.
Why does breast cancer build up fluid?
This fluid buildup occurs because cancer cells have blocked lymph vessels in the skin, preventing the normal flow of lymph through the tissue. Sometimes the breast may contain a solid tumor that can be felt during a physical exam, but more often a tumor cannot be felt. Other symptoms of inflammatory breast cancer include a rapid increase in breast ...
What percentage of breast cancer is inflammatory?
Inflammatory breast cancer is rare, accounting for 1 to 5 percent of all breast cancers diagnosed in the United States. Most inflammatory breast cancers are invasive ductal carcinomas, which means they developed from cells that line the milk ducts of the breast and then spread beyond the ducts.
Why is my breast pink?
These symptoms are caused by the buildup of fluid (lymph) in the skin of the breast.
How is inflammatory breast cancer treated?
Inflammatory breast cancer is generally treated first with systemic chemotherapy to help shrink the tumor, then with surgery to remove the tumor, followed by radiation therapy. This approach to treatment is called a multimodal approach. Studies have found that women with inflammatory breast cancer who are treated with a multimodal approach have better responses to therapy and longer survival. Treatments used in a multimodal approach may include those described below.
What is the research on inflammatory breast cancer?
Recent research on inflammatory breast cancer has focused on the work on genetic determinants that underlie the inflammatory breast cancer phenotype.
How long does radiation treatment last after breast surgery?
If breast radiation isnt given before surgery, it is given after surgery, even if no cancer is thought to remain. This is called adjuvant radiation. It lowers the chance that the cancer will come back. Radiation is usually given 5 days a week for 6 weeks, but in some cases a more intense treatment can be used instead. Depending on how much tumor was found in the breast after surgery, radiation might be delayed until further chemo and/or targeted therapy is given. If breast reconstruction is to be done, it is usually delayed until after the radiation therapy that most often follows surgery.
What is DCIS in breast cancer?
Tis : DCIS is a condition in which abnormal cells are found in the lining of a breast duct. The abnormal cells have not spread outside the duct to other tissues in the breast. In some cases, DCIS may become invasive breast cancer that is able to spread to other tissues. At this time, there is no way to know which lesions can become invasive.
What type of cancer is blocking lymph vessels?
In most cases of inflammatory cancer, the type of cancer cells blocking the lymph vessels are invasive ductal carcinomas. This means they developed from the cells lining the milk ducts of the breast and then spread beyond the ducts.
How long does it take for breast cancer to spread?
Inflammatory breast cancer spreads quickly, often in a matter of weeks or months. For most patients, their cancer is either stage III — meaning its spread throughout the breast, but not to the nearby lymph nodes. If the cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes, its stage IV.
What is targeted therapy?
Targeted therapy refers to a variety of medication that input the bloodstream and treats cancer all through the frame. Targeted remedy pills goal to assault most cancers cells without harming healthy cells, and tend to have fewer aspect consequences than chemotherapy pills.
What is the treatment for inflammatory breast cancer?
Inflammatory breast cancer treatment usually starts with chemotherapy . Chemotherapy before surgery is called neoadjuvant or preoperative therapy. After chemotherapy , people with inflammatory breast cancer usually have surgery to remove the breast.
Why is chemo given first for inflammatory breast cancer?
Any cancer left behind during surgery increases the chances of recurrence in the breast and affects healing. Because of this, chemotherapy is typically given first for inflammatory breast cancer to shrink and destroy the cancer in the breast, improving the chance that surgery will be successful.
What is the term for a regimen of chemotherapy?
A chemotherapy regimen, or schedule, consists of a specific treatment schedule of drugs given at repeating intervals for a set number of times. Chemotherapy for inflammatory breast cancer is usually given before surgery, called preoperative or neoadjuvant chemotherapy.
How to give systemic therapy for breast cancer?
Common ways to give systemic therapies include an intravenous (IV) tube placed into a vein using a needle or in a pill or capsule that is swallowed (or ally). The types of systemic therapies used for inflammatory breast cancer include: Chemotherapy. Targeted therapy. Hormonal therapy.
How does chemotherapy destroy cancer cells?
Chemotherapy is the use of drugs to destroy cancer cells, usually by keeping the cancer cells from growing, dividing, and making more cells.
How is medication used to treat cancer?
Medication may be given through the bloodstream to reach cancer cells throughout the body. When a drug is given this way, it is called systemic therapy . Medication may also be given locally, which is when the medication is applied directly to the cancer or kept in a single part of the body. This type of medication is generally prescribed by a medical oncologist, a doctor who specializes in treating cancer with medication.
What is cancer care team?
In cancer care, doctors specializing in different areas of cancer treatment work together to create a patient’s overall treatment plan that combines different types of treatments. This is called a multidisciplinary team . Cancer care teams include a variety of other health care professionals, such as physician assistants, oncology nurses, social workers, pharmacists, counselors, nutritionists, and others.
Inflammatory Breast Cancer: What You Need to Know
Inflammatory breast cancer is uncommon, accounting for .5% to 2% of all breast cancers.
IBC Symptoms
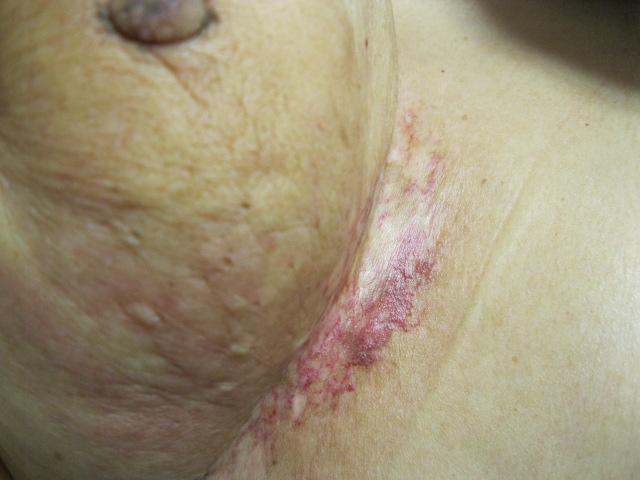
Inflammatory breast cancer causes visible changes in the skin of the breast. The skin might take on a pink hue or appear swollen and dimpled, with an “orange peel” appearance.
How is inflammatory breast cancer diagnosed?
A diagnosis of inflammatory breast cancer is confirmed by breast imaging, breast core biopsy and a skin punch biopsy. Breast biopsy and skin punch biopsy involves the doctor taking a small sample of breast tissue and breast skin, respectively.
What is the treatment for inflammatory breast cancer?
Because inflammatory breast cancer is an aggressive cancer, aggressive treatment provides the best chance of a good outcome.
What are the causes of breast cancer?
Inherited genetic mutations: Specific gene mutations increase the risk of developing cancer. These include BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations. Normal BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes repair damaged DNA. When these genes are mutated in certain ways, they fail at DNA repair, which could lead to breast and/or ovarian cancer. Other mutations that can lead to breast cancer are to PALB2, another DNA repair gene; CHEK2, a tumor suppressor gene; and PTEN, which controls how quickly cells multiply. At this time, there are no mutations associated specifically with IBC. The disease has similar rates of BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations as non-IBC breast cancers. Research into the role genetics may play in IBC is ongoing. Learn more about hereditary cancer syndromes.
What is lymph in breast?
Lymph is a clear fluid that contains tissue waste and cells that help fight infection. It travels through the body in vessels that are similar to veins. When these vessels are blocked by cancer cells, lymph builds up in the breast, causing it to swell.
What is the name of the cancer that makes your breast red?
Inflammatory Breast Cancer (IBC) I nflammatory breast cancer (IBC) is a rare, aggressive form of breast cancer. Instead of forming a lump, the disease causes the affected breast to become swollen, red and tender, often in a matter of days or weeks. Inflammatory breast cancer (IBC) is a rare, aggressive form of breast cancer.
Why is my breast red and swollen?
Instead of forming a lump, the disease causes the affected breast to become swollen, red and tender, often in a matter of days or weeks. These symptoms are not caused by inflammation. Instead, they are caused by cancer cells blocking lymph vessels in the skin and soft tissue. Lymph is a clear fluid that contains tissue waste and cells ...
How much of breast cancer is IBC?
IBC represents only 1%-5% of all breast cancer cases in the United States. Due to its aggressive nature, though, it accounts for about 10% of U.S. breast cancer deaths. Early and accurate inflammatory breast cancer diagnosis and personalized treatment by experts who specialize in IBC can make an important difference.
What are the three subtypes of breast cancer?
Like more common forms of breast cancer, IBC can be divided into three molecular subtypes that can fuel the cancer's growth and spread: HER2-positive, hormone receptor positive, and triple-negative. Compared to non-inflammatory breast cancer, IBC is more often HER2-positive or triple-negative. These subtypes impact a patient’s treatment ...
How to contact a doctor about breast cancer?
Inflammatory Breast Cancer. We're here for you. Call us at 1-877-632-6789 1-877-632-6789 or. request an appointment online. Let's get started. Request an appointment online. Diagnosis & Treatment. Cancer Types.
Diagnosis
Treatment
- Inflammatory breast cancer treatment begins with chemotherapy. If the cancer hasn't spread to other areas of the body, treatment continues with surgery and radiation therapy. If the cancer has spread to other areas of the body, your doctor may recommend other drug treatments in addition to chemotherapy to slow the growth of the cancer.
Clinical Trials
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiestesting new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.
Coping and Support
- Inflammatory breast cancer progresses rapidly. Sometimes this means you may need to start treatment before you've had time to think everything through. This can feel overwhelming. To cope, try to: 1. Learn enough about inflammatory breast cancer to make treatment decisions.Ask your doctor for the facts about your cancer and treatment. Ask what stage your cancer is and w…
Preparing For Your Appointment
- Start by first seeing your family doctor or health care provider if you have any signs or symptoms that worry you. If you're diagnosed with inflammatory breast cancer, you'll be referred to a doctor who specializes in treating cancer (oncologist). Because appointments can be brief, and because there's often a lot of information to discuss, it's a good idea to be prepared. Here's some informa…