
What is the pathophysiology of hypophosphatasia?
Supportive treatment is important for HPP patients, including mechanical ventilation, accurate fracture treatment, physical therapy, dental monitoring, and follow-up care to avoid subsequent problems. A causal enzyme therapy replacement with asfotase-alfa was approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2015.
Can I participate in a clinical study if I have hypophosphatasia?
Asfotase alfa is a recombinant human alkaline phosphatase, used as treatment for the underlying cause of HPP. Asfotase alfa enhances the survival in life-threatening HPP and improves bone mineralization, muscle strength, and pulmonary function. However, discontinuation of asfotase alfa leads to reap …
What are the most severe forms of hypophosphatasia?
Adults with hypophosphatasia have taken a drug called teriparatide (parathyroid hormone 1-34). This drug has been given “off-label” to many adults to help with stress fractures. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can be given to help with bone and joint pain.
What is the role of asfotase alfa in the treatment of hypophosphatasia?
Feb 01, 2016 · Treatment Hydration, restriction of dietary calcium, vitamin D, and sometimes thiazide diuretics for hypercalcemia Ventilatory support for severely affected infants, some of which need a tracheostomy, which can lead to problems with... Physiotherapy, occupational therapy and chronic pain management ...
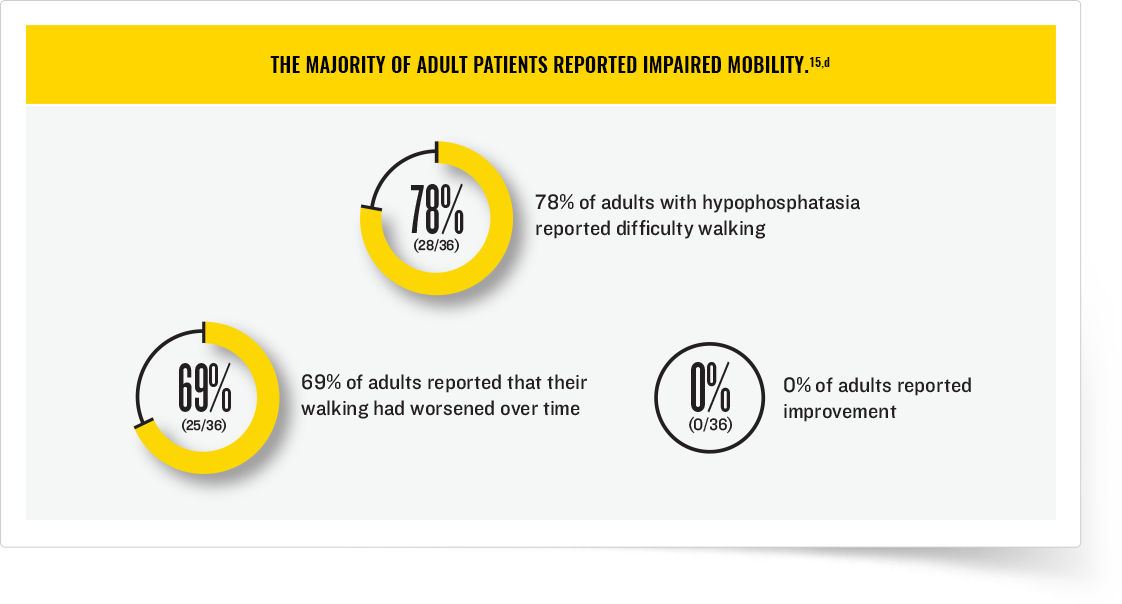
Is there a treatment for hypophosphatasia?
In 2015, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved asfotase alfa (Strensiq) as the first medical treatment for perinatal, infantile and juvenile-onset HPP. In the US, patients of any age with pediatric-onset HPP are eligible for this bone-targeted TNSALP replacement therapy given by subcutaneous injection.
What type of doctor treats hypophosphatasia?
Patients may initially present to orthopedists, neurologists, nephrologists, neonatologists, pulmonologists, dentists, endocrinologists, rheumatologists and others before an accurate diagnosis is obtained, making it important for many specialists to become familiar with key hypophosphatasia warning signs and ...Sep 26, 2019
How does someone get hypophosphatasia?
Cause. Hypophosphatasia (HPP) is a genetic condition caused by mutations in the ALPL gene . This gene gives the body instructions to make an enzyme called alkaline phosphatase, which is needed for mineralization of the bones and teeth.
What are symptoms of hypophosphatasia?
Affected children may have short stature with bowed legs or knock knees , enlarged wrist and ankle joints, and an abnormal skull shape. Adult forms of hypophosphatasia are characterized by a softening of the bones known as osteomalacia.
How is hypophosphatasia diagnosed in adults?
X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans can help diagnose HPP at all stages of life—from birth into adulthood. They can also help determine the severity of the condition based on how affected bones are. X-rays: X-rays can reveal bone abnormalities common in childhood HPP and severe forms of perinatal and infantile HPP types.Sep 21, 2021
Is hypophosphatasia a disability?
Hypophosphatasia (perinatal and infantile onset types) is a disabling condition on the Compassionate Allowance List, which qualifies an individual for an expedited approval process.
What is the cause of hypophosphatasia?
Hypophosphatasia (HPP) is a genetic condition caused by mutations in the ALPL gene. This gene gives the body instructions to make an enzyme called alkaline phosphatase, which is needed for mineralization of the bones and teeth. Mutations in this gene lead to an abnormal version of the enzyme, thus affecting the mineralization process.
When does hypophosphatasia occur?
Listen. The signs and symptoms of hypophosphatasia vary widely and can appear anywhere from before birth to adulthood. The most severe forms of the disorder tend to occur before birth and in early infancy.
What are the signs of hypophosphatasia in children?
Early loss of primary (baby) teeth is one of the first signs of the condition in children. Affected children may have short stature with bowed legs or knock knees, enlarged wrist and ankle joints, and an abnormal skull shape. Adult forms of hypophosphatasia are characterized by a softening of the bones known as osteomalacia.
How are perinatal hypophosphatasia and infantile hypophosphatasia inherited?
Perinatal (onset before birth) and infantile hypophosphatasia (HPP) are inherited in an autosomal recessive manner. [2] This means that to be affected, a person must have a mutation in both copies of the responsible gene ( ALPL) in each cell. Affected people inherit one mutated copy of the gene from each parent, who is referred to as a carrier. Carriers of an autosomal recessive condition typically do not have any signs or symptoms (they are unaffected). When 2 carriers of an autosomal recessive condition have children, each child has a:
How does a registry help research?
A registry supports research by collecting of information about patients that share something in common, such as being diagnosed with Hypophosphatasia. The type of data collected can vary from registry to registry and is based on the goals and purpose of that registry.
What is the NORD organization?
NORD is a patient advocacy organization for individuals with rare diseases and the organizations that serve them. The MAGIC Foundation has an information page about hypophosphatasia.
What is an orphanet?
Orphanet is a European reference portal for information on rare diseases and orphan drugs. Access to this database is free of charge. Orphanet. Orphanet. PubMed is a searchable database of medical literature and lists journal articles that discuss Hypophosphatasia.
What is the Hypophosphatasia?
Hypophosphatasia is an autosomal recessive rare genetic disorder of the bones and teeth. The disorder is a metabolic one where there is abnormal mineralisation of the bones and teeth. Calcium and phosphorus are the main minerals required for bone formation in the body. The genetic disease mainly impairs the bones to take up these minerals.
How is the Hypophosphatasia treatment done?
Hypophosphatasia in any form cannot be treated completely as it is a rare genetic disorder. Management of symptoms include pain management with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), the bones in adults are more prone to stress fractures which is treated with the drugs against osteoporosis known as teriparatide.
Who is eligible for the treatment? (When is the treatment done?)
When a fetus is diagnosed with skeletal deformities while in the womb but is not born dead, will be eligible for treatment, children and adults diagnosed with the disease is eligible or treatment for the particular type of deformity that he/she is affected with.
Who is not eligible for the treatment?
Every person with bowed legs, fractures and osteoporosis are not eligible for the treatments for this disorder.
Are there any side effects?
Some common side effects of asfotase alfa can be reaction on the injection site that include pain, itching, soreness, discoloration, redness, bruising, hard lump or swelling, redistribution of body fat after the injection, calcification of soft tissues and difficulty breathing, puffy eyes, nausea, vomiting, irritability etc.
What are the post-treatment guidelines?
It is recommended to these patients to avoid contact sports after monitoring and treatment for the disease and light exercises can be done.
How long does it take to recover?
The treatment options related to this disorder mainly focus on managing the symptoms. So, each symptom’s recovery time will vary depending upon the severity of the defect, type of defect and the type of treatment that it requires. There is no permanent cure for the disease.
What is hypophosphatasia in metabolism?
Hypophosphatasia (HPP) is an inborn error of metabolism with a broad spectrum of clinical severity caused by loss of function mutations in the gene encoding tissue nonspecific alkaline phosphatase ( TNSALP). To date, more than 400 distinct mutations in the TNSALP gene ( ALPL) have been identified in patients with HPP, leading to highly variable clinical phenotypes. Peter J. Tebben, M.D., Pediatric and Adolescent Medicine, at Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minnesota, explains: "The prevalence of severe forms is estimated to be 1 in 100,000, while mild forms are likely much more prevalent."
When is HPP diagnosed?
Infantile HPP is diagnosed within the first six months of life. Characteristic changes of rickets are seen on radiographs, and fractures are often present. Infants fail to grow appropriately and some experience vitamin B 6 -responsive seizures. Hypercalcemia and nephrocalcinosis also are common.
What is perinatal HPP?
Perinatal HPP presents with clinical features noted either at birth or in utero based on prenatal ultrasound. Clinical exam reveals obvious skeletal abnormalities including chest wall deformities, as well as long bones that are short or bowed or both. The skeleton is hypomineralized.
What is hypomineralized bone?
Severely hypomineralized bone is seen in patients with the perinatal and infantile forms of the disease. Those with childhood HPP exhibit metaphyseal changes of rickets and bands of radiolucency extending from the growth plate into the metaphysis. In adults, metatarsal fractures, pseudofractures in the femur and calcium pyrophosphate deposition disease are commonly identified. Enlarged pulp chambers can be seen on dental X-rays.
Is asfotase alfa approved for HPP?
Asfotase alfa is approved for the treatment of children with HPP and for adults with childhood-onset disease. "Treatment has had a significant impact on the natural history of the more-severe perinatal, infantile and childhood forms of HPP ," Dr. Tebben expands.
What is the bone histology of HPP?
Bone histology varies depending on both the age of presentation and the severity of disease. Infantile HPP is characterized by severely defective skeletal mineralization, with osteoid composing the majority of bone tissue. On the other hand, patients with the childhood and adult forms of HPP with less severe manifestations may have no evidence of mineralization defects.
What is the iliac crest bone biopsy?
Iliac crest bone biopsies from patients with more-severe forms of childhood and adult HPP generally demonstrate osteomalacia, with areas of unmineralized osteoid and the absence of tetracycline label uptake.

Home Remedies and Lifestyle
- Management of HPP at home will depend on how significant the symptoms are. There are a variety of at-home and lifestyle remedies that might help to reduce the effects of the condition on your day-to-day life.
Over-The-Counter (OTC) Therapies
- Some nonprescription medicines can help lessen symptoms of bone or joint pain linked to HPP. Additionally, orthopedic devices can help people with HPP move and function better.
Summary
- Hypophosphatasia can have wide-ranging effects on people with the condition and their families. Fortunately, most of the time the condition is treatable and manageable. Treatment includes a wide range of therapies, including at-home remedies and lifestyle therapies, over-the-counter and prescription medicines, surgeries, medical procedures, and therapies. One of the newest therapi…
A Word from Verywell
- Hypophosphatasia is a lifelong condition. It comes with many different symptoms and complications. Treatment for the condition requires a multidisciplinary team of specialists. This team may include specialists in pediatrics, endocrinology, genetics, rheumatology, orthopedics, pain management, physical and occupational therapy, neurology, periodontics, and oral surgery. …