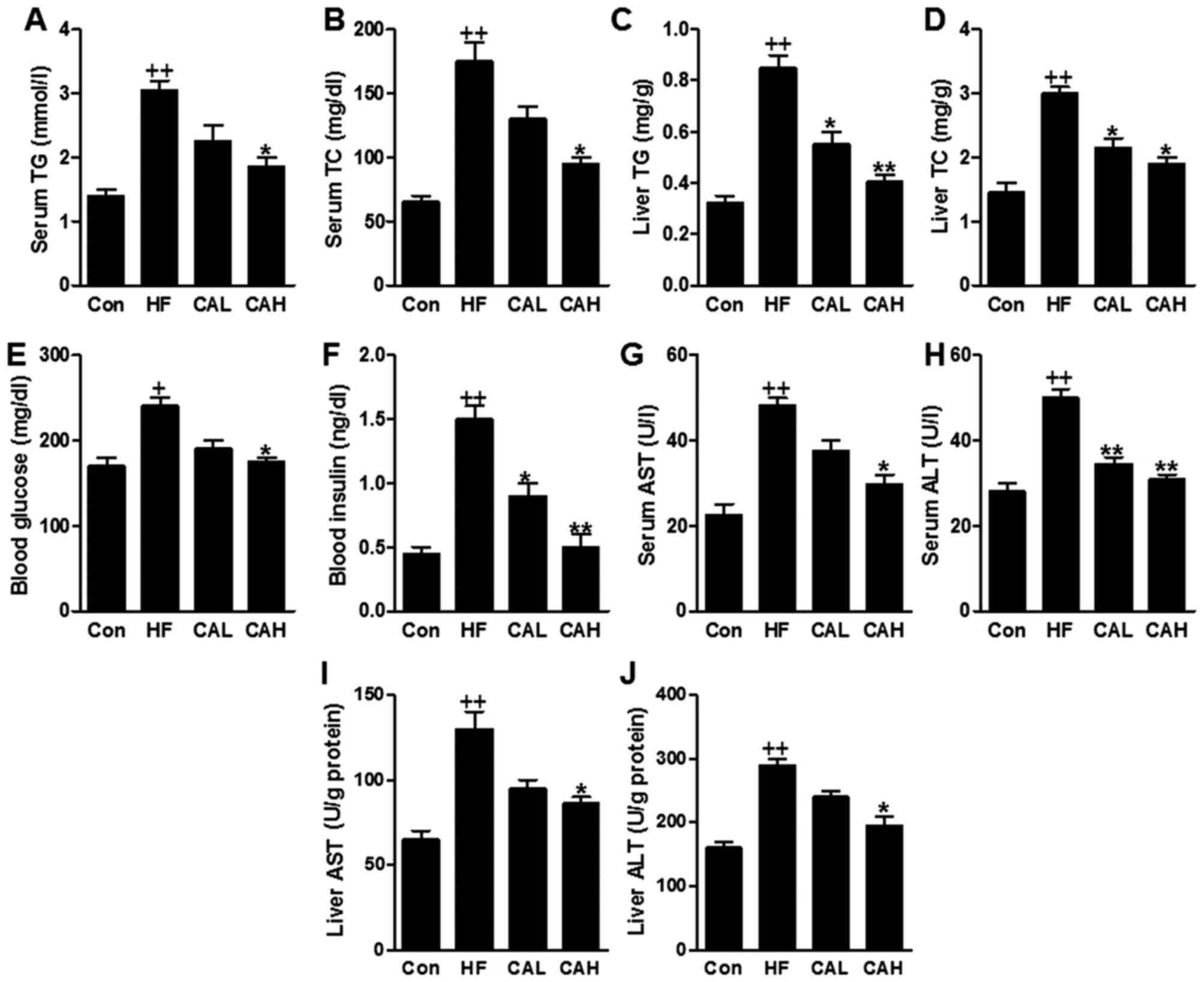
What could be causing elevated levels of AST and ALT levels?
The most common diseases causing abnormally elevated ALT and AST are acute viral hepatitis , such as hemochromatosis (a genetic condition causing long standing liver damage due to iron build up in the liver), and diminished blood flow to the liver (from shock or heart failure).
What does it mean if AST is higher than ALT?
What does it mean when AST is higher than ALT? An AST/ALT ratio higher than one (where the AST is higher than ALT) is suggestive of cirrhosis. An AST/ALT ratio higher than 2:1 (where the AST is more than twice as high as the ALT) is suggestive of alcoholic liver disease.
What is considered slightly elevated AST and Alt?
Specifically, a slight elevation to AST and ALT. For example, on a routine Comprehensive Metabolic Panel (CMP), a woman will have an AST level of 54 U/L and an ALT level of 47 U/L.
What are dangerous Alt and AST levels?
AST and ALT serum levels in some liver conditions can range anywhere from ten times the upper limits of normal to thousands of units/liter. The highest levels of AST and ALT are found with disorders that cause rapid death of numerous liver cells (extensive hepatic necrosis).

How long does it take for AST and ALT to return to normal?
TRADITIONAL BIOMARKERSMarkerTime to return to normal limitsAspartate aminotransferase7 days, but considerable variability in declines with abstinenceAlanine aminotransferaseUnknownMacrocytic volumeUnknown but half–life ∼ 40 daysCarbohydrate–deficient transferrin2–4 weeks of abstinence1 more row
What happens if you have high ALT and AST?
If your AST levels are too high, it might be a sign of an injury affecting tissues other than the liver. High ALT levels may mean you have a liver injury. It could also be a sign that you have an infection or short-term illness. The ratio of the two enzymes can help diagnose specific liver diseases.
When should I worry about AST and ALT?
Persistent mild elevation of ALT and AST in asymptomatic persons should be followed up and if the levels go above 2 times the normal range, further evaluation is necessary.
How do doctors treat elevated liver enzymes?
How is it treated? Treatment depends on what is causing your liver enzymes to be elevated. If your doctor thinks you have nonalcoholic fatty liver disease or the metabolic syndrome, you will need to watch your diet, stop drinking alcohol, lose weight, and control your cholesterol.
Which is worse high AST or ALT?
In addition, patients with Wilson's disease or cirrhosis due to viral hepatitis may have an AST that is greater than the ALT, though the ratio typically is not greater than two. When the AST is higher than ALT, a muscle source of these enzymes should be considered....AST/ALT ratioLOINC16325-3, 1916-6
How do you treat high ALT levels?
For most causes of high ALT, treatment involves lifestyle changes, such as exercise, a modified diet, and reducing alcohol intake. Depending on the results of your liver panel and your medical history, your healthcare professional may recommend checking them again at a later date.
What is an alarming AST level?
Your doctor may order follow-up tests to rule out another diagnosis. The normal range of an SGOT test is generally between 8 and 45 units per liter of serum. In general, men may naturally have higher amounts of AST in the blood. A score above 50 for men and 45 for women is high and may indicate damage.
Does high AST and ALT mean liver damage?
When the liver is damaged, ALT is released into the bloodstream and levels increase. Aspartate transaminase (AST). AST is an enzyme that helps metabolize amino acids. Like ALT, AST is normally present in blood at low levels. An increase in AST levels may indicate liver damage, disease or muscle damage.
Can liver damage reversed?
Liver transplants In the most serious cases of ARLD, the liver loses its ability to function, leading to liver failure. A liver transplant is currently the only way to cure irreversible liver failure.
How can I lower my AST and ALT levels?
Natural ways to lower ALT levelsDrinking coffee. Drinking coffee can help to lower ALT levels. ... Exercising regularly. ... Losing excess weight. ... Increasing folic acid intake. ... Making dietary changes. ... Reducing high cholesterol. ... Taking care with medications or supplements. ... Avoiding alcohol, smoking, and environmental toxins.
What is a critical ALT level?
Standard medical education dictates that the vast majority of cases of an alanine aminotransferase (ALT) level >1,000 IU/l will be due to acute ischaemia, acute drug-induced liver injury (DILI) (usually paracetamol) or acute viral hepatitis.
Should I be worried about elevated liver enzymes?
Elevated liver enzymes might be discovered during routine blood testing. In most cases, liver enzyme levels are only mildly and temporarily elevated. Most of the time, elevated liver enzymes don't signal a chronic, serious liver problem.
What is the treatment for high AST and high ALT?
What Is the Treatment for High AST (SGOT) and High ALT (SGPT)? Treatment for high AST and ALT varies greatly and is entirely dependent on the cause, states Cleveland Clinic and Healthline. When high levels are detected, further testing to determine the cause is common. High AST and high ALT may be linked to liver damage or skeletal ...
Why is AST high?
When high levels are detected, further testing to determine the cause is common. High AST and high ALT may be linked to liver damage or skeletal and cardiac muscles. ALT is an enzyme which is produced by the cells of the liver, according to Healthline. When the liver is damaged to some degree, ALT is released into the blood.
Where is the AST found?
AST is an enzyme present in many parts of the body, with the greatest amount found in the muscles, the heart and liver, states Healthline. An AST test is commonly done with an ALT test to give a person's doctor an AST to ALT ratio.
Why do doctors test for elevated liver enzymes?
Doctors test people for elevated liver enzymes if they have symptoms of conditions that typically cause liver damage. In this article, learn about the causes of elevated liver enzymes, as well as the symptoms and treatment of each of these conditions.
What test can be used to check liver enzymes?
Doctors use a blood test to check for elevated liver enzymes. They may test anyone with symptoms of one of the conditions that they know to raise liver enzyme levels. If a person’s blood test results reveal that they have elevated liver enzymes, the doctor will investigate the underlying cause.
Can Wilson's disease cause elevated liver enzymes?
polymyositis, which involves inflammation of the muscles. Certain medications, including some pain relievers and statins, can also cause elevated liver enzymes. Elevated liver enzymes are themselves asymptomatic, but the underlying conditions responsible for them may cause symptoms.
Can fatty liver disease cause elevated liver function?
Once they make a diagnosis, the doctor will recommend suitable treatments. Fatty liver disease is the most common cause of elevated liver damage. People with fatty liver disease can manage their condition by losing weight, if necessary, or reducing their alcohol consumption.
How to lower ALT levels?
To help lower ALT levels, consider adding more folate-rich foods to your diet, such as: You can also try taking a folic acid supplement. Most folic acid supplements contain doses of either 400 or 800 micrograms. Aim for a daily dose of 800 micrograms, which is the equivalent of 0.8 milligrams.
What causes elevated ALT levels?
obesity. hepatitis A, B, or C. heart failure. Regardless of what’s causing your elevated ALT levels, it’s important to work with your doctor to find and address the underlying cause. But in the meantime, there are a few things you can try that may help to lower your ALT levels.
What does it mean when your ALT is high?
A high ALT level is usually a sign of some type of liver issue. It’s important to work with your doctor to find the underlying cause of your elevated ALT, even if you don’t have any symptoms. Lowering your ALT will require treating the cause, but certain dietary changes can help.
Why is ALT important?
Liver enzymes, including ALT, help your liver break down proteins to make them easier for your body to absorb. When your liver is damaged or inflamed, it can release ALT into your bloodstream. This causes your ALT levels to rise. A high ALT level can indicate a liver problem, which is why doctors often use an ALT test when diagnosing liver ...
How to reduce a fatty liver?
avoid fruits and vegetables served with high-calorie sauces or added sugar and salt. eat fish at least twice a week, ideally those high in omega-3 fatty acids, such as salmon or trout. opt for fat-free or low-fat milk and dairy products. replace saturated and trans fats with monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats.
Does eating a diet lower your ALT?
An earlier study similarly found that eating a diet lower in calories and carbohydrates was effective for lowering ALT levels in overweight adults with insulin resistance. To improve liver health and help lower ALT, you don’t necessarily need to make drastic changes to your diet.
Does folic acid lower ALT?
Consuming more folate-rich foods and adding a folic acid supplement to your diet are both linked to lower ALT levels. While the terms folate and folic acid are often used interchangeably, they’re aren’t quite the same. They’re two different forms of vitamin B-9. Folate is naturally occurring B-9 found in certain foods.
What does it mean when your liver enzymes are elevated?
What does it mean to have elevated liver enzymes? If you have high levels of liver enzymes in your blood , you have elevated liver enzymes. High liver enzyme levels may be temporary, or they may be a sign of a medical condition like hepatitis or liver disease. Certain medications can also cause elevated liver enzymes.
What does it mean when your liver is high?
High levels of liver enzymes and other chemicals in the blood might mean that you have hepatitis, liver disease or cirrhosis. Signs of hepatitis include stools that are pale in color, fatigue, pain or swelling in the abdomen, and jaundice.
How long does it take for liver enzymes to go up?
About one-third of people with elevated liver enzymes will have normal liver enzyme levels after two to four weeks. If your liver enzymes stay high, your provider may order more blood tests, or imaging tests such as ultrasound, CT scan or MRI. They may also refer you to a liver specialist (hepatologist). Treatment will depend on what’s causing the ...
What are the enzymes in the liver?
Liver enzymes are proteins that speed up chemical reactions in your body. These chemical reactions include producing bile and substances that help your blood clot, breaking down food and toxins, and fighting infection. Common liver enzymes include: Alkaline phosphatase (ALP). Alanine transaminase (ALT).
What is the liver enzyme test?
Your healthcare provider may check your liver enzyme levels with a liver function test (LFT) or liver panel. A liver function test is a type of blood test. Your provider may order an LFT during a regular checkup if you’re at risk for liver injury or disease or if you have symptoms of liver damage.
What are the symptoms of elevated liver enzymes?
If liver damage is the cause of elevated liver enzymes, you may have symptoms such as: Abdominal (stomach) pain. Dark urine (pee). Fatigue (feeling tired). Itching. Jaundice (yellowing of your skin or eyes). Light-colored stools (poop). Loss of appetite. Nausea and vomiting.
What causes ALT and AST to be elevated?
Non-hepatic causes of raised ALT and AST include polymyositis, acute muscles injury, acute myocardial infarction and hypothyroidism. In the primary care setting, the doctor should obtain a complete history regarding the risk factors for viral hepatitis, substance abuse and request investigations accordingly.
What is the most common abnormality in liver function test?
The most common abnormalities of liver function test in an asymptomatic person is raised alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and raised aspartate aminotransferase (AST).
What is liver function test?
Liver function test is one of the most common blood tests requested by primary care doctors in clinical practice. Abnormal results in the liver function test often cause considerable anxiety in asymptomatic subjects.
Does liver enzyme elevation correlate with liver damage?
In chronic viral hepatitis, the elevation of liver enzyme may not correlate well with the degree of liver damage. Other non-hepatic medical diseases associated with raised ALT and AST include musculoskeletal disorder such as polymyositis, acute muscles injury, acute myocardial infarction and hypothyroidism. 2.
Is liver ultrasound invasive?
Ultrasound of the liver is a non-invasive procedure which can assist in the diagnosis of liver cirrhosis, NASH and any associated hepatobiliary diseases.
What happens to the AST when the liver is damaged?
As these organs are damaged, the AST will begin to rise.
What is liver enzyme?
Liver enzymes are substances produced by the liver that can be measured with a blood test. Any elevation in an enzyme level may be a sign of a liver problem, and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and alanine aminotransferase (ALT) are two of the enzymes central to such an investigation. When used comparatively, AST and ALT can help identify liver ...
What is the AST and ALT?
AST and ALT are measured in international units per liter (IU/L). The normal levels vary based on a person's body mass index (BMI) as well as the individual lab's reference value. Generally speaking, the normal reference value for adults is: 1 AST: 8 to 48 IU/L 2 ALT: 7 to 55 IU/L
What are the roles of AST and ALT?
Roles of AST and ALT. Aminotransferases are chemicals that the liver uses to make glycogen. Glycogen is the stored form of glucose, a sugar that the body uses for energy. Any glucose not immediately used will be converted into glycogen and stored in cells for future use.
What does AST/ALT ratio mean?
An AST/ALT ratio of less than one (where the ALT is significantly higher than the AST) is suggestive of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. An AST/ALT ratio equal to one (where the ALT is equal to the AST) is suggestive of acute viral hepatitis or drug-related liver toxicity. An AST/ALT ratio higher than one (where the AST is higher than ALT) ...
Where is aspartate aminotransferase found?
Aspartate aminotransferase (AST) is found in a variety of tissues, including the liver, brain, pancreas, heart, kidneys, lungs, and skeletal muscles. If any of these tissues are damaged, AST will be released into the bloodstream. While increased AST levels are indicative of a tissue injury, it is not specific to the liver per se.
What is the reference range for liver enzymes?
Generally speaking, the normal reference value for adults is: The high end of the reference range is referred to as the upper limit of normal (ULN). This number is used to establish how elevated your liver enzymes are. Mild elevations are generally considered to be two to three times the ULN.
Why does AST rise with ALT?
AST tends to rise with ALT if liver damage is present . Alkaline Phosphatase (or ALP for short): ALP is produced by the cells lining the bile ducts or the "plumbing" of the liver. A rise in ALT is commonly seen in conditions that caused blocked "ducts" such as bile stones or direct damage to the bile ducts. Gamma-glutamyl transferase (or GGT ...
What is the AST and ALT range?
Patients with chronic hepatitis tend to have AST and ALT levels in the 30-120 range , those with autoimmune hepatitis tend to have levels in the 100-600 range. Perhaps more important than these two causes is liver damage caused by a condition known as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
What is the AST of alcohol?
Alcoholic Liver disease (AST and ALT in the 70-700 range) Alcoholic liver disease used to be the #1 cause of liver failure in the United States until it was taken out by non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and obesity. Having said that it is still an important cause of liver damage in many people.
What is the difference between ALT and AST?
The standard "liver function tests" include: Alanine Transaminase (or ALT for short): ALT is produced in the liver cells known as hepatocytes and is a very specific marker of liver cell damage. Aspartate Transaminase (or AST for short): AST is not quite as specific as ALT for liver damage as it is also found in skeletal muscle, heart muscle, ...
How to treat alcoholic liver damage?
The primary treatment for alcoholic liver damage is to stop consuming alcohol, in some cases, this is enough to completely reverse the condition or at least stop further damage. #3. Prescription Medications (Low-grade elevation of AST/ALT) Certain prescription medications can also cause liver damage.
Does milk thistle help with liver problems?
In animal studies (21), silymarin (the active ingredient in milk thistle) has been shown to reduce liver injury caused by Tylenol, iron overload, alcohol, and other causes. With this in mind, milk thistle may be considered in many individuals with elevated liver enzymes.
Can Tylenol cause liver failure?
In small doses, your liver can metabolize it without issues, but once doses become excessive Tylenol metabolites can cause serious damage to your body and even result in acute liver failure. In the case of Tylenol, even daily doses of 5 to 8 grams per day may lead to liver damage over time.
How to lower AST and ALT?
But not to worry, lowering your AST and ALT levels can be achieved by changing lifestyle habits. For instance, cultivating a habit of regular exercise would improve insulin sensitivity and reduce liver inflammation. Another way to keep your AST and ALT levels in check is to review your diet.
Why is it important to keep your AST and ALT levels in check?
When it comes to protecting your liver, it’s crucial to keep your AST and ALT levels in check to be aware of potential infections or diseases you might have contracted. If your AST and ALT levels have been persistently high, consult a professional as soon as possible to steer clear of any dangerous developments.
Why is my AST and ALT high?
When there are high levels of ALT and AST, it signals that the liver is infected and inflamed, hence releasing both enzymes into the bloodstream at a rate higher than usual. Possible causes include hepatitis B and C, side effects from medication, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and alcohol. As one of the most common chronic liver ...
What is the AST/ALT ratio?
The AST/ALT ratio tells you the relative concentrations of the enzymes aspartate transaminase (AST) and alanine transaminase (ALT) in your blood. A typical AST/ALT ratio would be less than 1.
How to help liver function?
These foods can over-work your liver cells. Instead, consume foods rich in folate and the water-soluble B vitamin. Folate is key in helping your liver function at its best, so include foods such as avocado and spinach as part of your diet.
What is the most common blood test?
Out of which, one such common blood test to undergo is the liver function test (LFT).
Can NAFLD cause AST?
As one of the most common chronic liver disorders in Singapore, NAFLD is a possible cause of an abnormal ALT and AST. Most patients with NAFLD do not have symptoms. In some patients, they may experience upper abdominal discomfort or tiredness.
