Acute treatment for hereditary angioedema.
- Every patient should have an acute care plan.
- C1 inhibitor (plasma-derived or recombinant), ecallantide, or icatibant are effective acute treatments.
- Best acute treatment should be decided on an individual basis.
- Best acute treatment may vary between attacks for a given patient.
How does danazol treat hereditary angioedema?
Treatment of Hereditary Angioedema with Danazol — Reversal of Clinical and Biochemical Abnormalities
- Materials and Methods. Five women (25 to 38 years of age) and four men (28 to 63 years of age) with hereditary angioedema were selected for the study.
- Results. Results of Study. ...
- Discussion. ...
- References (26) Hereditary angio-neurotic oedema . ...
- Citing Articles (409)
- Letters
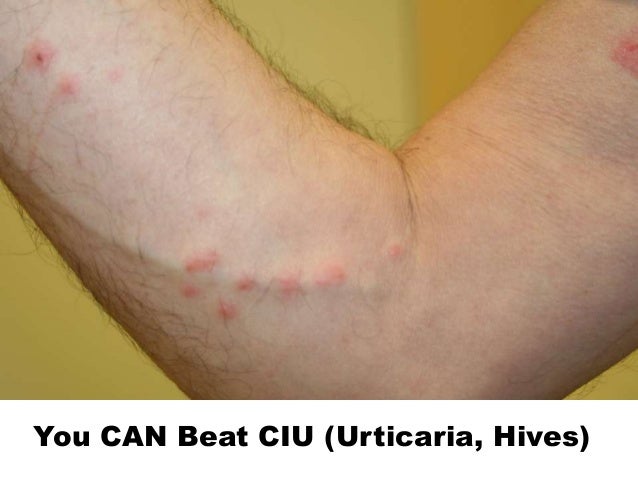
How do I know if I have hereditary angioedema?
Hereditary angioedema is a genetic disease that occurs because of a defect or mutation in the gene that controls C1-inhibitor, and is rare disease, affecting 1 in 50,000 people. Sufferers of this disease will experience unexplained swelling in the extremities, and may also have to deal with stomach pain and cramping that seems to come on without explanation. Fortunately, there are treatments ...
What are treatment options for hereditary angioedema (HAE)?
Treatments to Prevent HAE Attacks
- Cinryze. Cinryze (C1 esterase inhibitor) is a plasma-derived concentrate of C1 esterase inhibitor that works by increasing the plasma levels of C1 inhibitor activity in your body.
- Haegarda. Haegarda (C1 esterase inhibitor) is a plasma-derived concentrate of C1 esterase inhibitor. ...
- Takhzyro. ...
How is hereditary angioedema (HAE) treated?
Hereditary angioedema is a rare disorder identified by episodes of swelling under the skin, gut lining, and the lungs. Learn its triggers, treatments and more.

What medication is used for hereditary angioedema?
Doctors can use medications to treat or prevent attacks:Berotralstat (Orladeyo)C1 esterase inhibitor (Berinert, Cinryze, Haegarda)Conestat alfa (Ruconest)Ecallantide (Kalbitor)Icatibant (Firazyr)Lanadelumab-flyo (Takhzyro)
What triggers hereditary angioedema?
Hereditary angioedema (HAE) is caused by a low level or improper function of a protein called the C1 inhibitor. It affects the blood vessels. An HAE attack can result in rapid swelling of the hands, feet, limbs, face, intestinal tract, larynx (voicebox), or trachea (windpipe).
Does hereditary angioedema go away?
Attacks may involve one area of the body at a time, or they may involve a combination of areas. They always go away on their own but last from 2 to 4 days. While people with HAE have reported various triggers of attacks, emotional stress, physical stress, and dental procedures are the most commonly reported triggers.
Is there a cure for HAE?
There is no cure for HAE, but there are things you can do to help manage your condition. Your doctor can help you understand the 2 main treatment types, preventive and on-demand, and how they might play a role in your management plan.
How serious is hereditary angioedema?
The symptoms of hereditary angioedema may recur and can become more severe. Injury, severe pain, surgery, dental procedures, viral illness, and/or stress can trigger or worsen the recurring symptoms.
How long does hereditary angioedema last?
On average, untreated individuals have an attack every 1 to 2 weeks, and most episodes last for about 3 to 4 days. The frequency and duration of attacks vary greatly among people with hereditary angioedema, even among people in the same family.
What is the best antihistamine for angioedema?
Oral Antihistamines Antihistamines such as diphenhydramine (Benadryl), hydroxyzine (Visatril), and cetirizine (Zyrtec) are often helpful in managing and preventing episodes of angioedema.
Which antihistamine is best for swollen eyes?
Over-the-counter options include loratadine (Claritin), cetirizine (Zyrtec) and fexofenadine (Allegra). Others are available by prescription. Another option is eye drops that contain mast cell stabilizers, which limit release of the inflammation-causing chemicals.
Which antihistamine is best for swollen lips?
If your doctor determines your swollen lips are due to environmental allergies, he or she may recommend an over-the-counter (OTC) or prescription antihistamine medication, such as: Loratadine (Claritin) Cetirizine (Zyrtec) Diphenhydramine (Benadryl)
Are you born with hereditary angioedema?
Hereditary angioedema is genetic (a trait inherited from a parent). The condition is present at birth, but symptoms usually start when you're a child or teenager. Acquired angioedema can develop after you get certain cancers or autoimmune diseases.
Is hereditary angioedema an autoimmune disease?
It is caused by the deficiency of CI esterase inhibitor. Hereditary angioedema may be associated with autoimmune diseases, such as systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, autoimmune thyroiditis and glomerulonephritis.
Is angioedema an autoimmune disease?
Hereditary angioedema (a genetic disorder) and acquired angioedema (acquired C1 inhibitor deficiency) are caused by a deficiency or malfunction of C1 inhibitor, which is part of the immune system. Both disorders result in repeated episodes of swelling under the skin.
Can stress and anxiety cause angioedema?
Cases of angioedema without an identifiable cause are known as idiopathic angioedema. It may be that a problem with the immune system sometimes causes it to "misfire". In cases of idiopathic angioedema, certain triggers may lead to swelling, such as: anxiety or stress.
What age does hereditary angioedema start?
Background. Hereditary angioedema with C1 inhibitor deficiency (C1-INH-HAE) is characterized by recurrent swelling in subcutaneous or submucosal tissues. Symptoms often begin by age 5–11 years and worsen during puberty, but attacks can occur at any age and recur throughout life.
Can emotional stress cause angioedema?
Recently, emotional stress has been reported by patients as the most common trigger factor for angioedema attacks, and chronic stress seems to modify disease activity too [6,7,8].
Is hereditary angioedema an autoimmune disease?
It is caused by the deficiency of CI esterase inhibitor. Hereditary angioedema may be associated with autoimmune diseases, such as systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, autoimmune thyroiditis and glomerulonephritis.
What was the only treatment for HAE before 2009?
Before 2009, the only treatment available was anabolic steroids. These seven relatively new medications treat HAE differently, and their administration and dosing recommendations vary. Three of the medications are used to prevent symptoms, and four of them are used when you experience the onset of HAE symptoms.
How to prevent HAE?
Your doctor may also recommend implementing certain lifestyle modifications to help you avoid HAE triggers. Together, medications and avoiding triggers can help you effectively manage your condition.
What are the triggers for a HAE attack?
Triggers for HAE attacks may include: repetitive physical activities like typing, writing, and doing yard work. certain medications like oral contraceptives, hormone replacement therapy, and ACE inhibitors.
How many medications can you take for a HAE?
There are four medications you can use during an HAE attack. You can use some at home, while a healthcare professional needs to administer others. Remember that swelling in your throat can be life-threatening. Seek immediate medical attention in addition to using these medications if you experience this.
How long does it take to get a HAE shot?
You can also receive it under the supervision of a healthcare professional. The average dose is 50 U/kg, and it takes about five minutes to receive the injection.
Where to inject B2 bradykinin?
This B2 bradykinin receptor antagonist is for use in adults only. You can inject the dose at home under the skin of your abdomen when you experience signs of an acute HAE attack.
Can you take a C1 inhibitor at home?
C1 esterase inhibitor, human (Berinert) This is a C1 inhibitor that you administer intravenously at home or in a doctor’s office. You take it when you experience the first symptoms of an HAE attack. Both adults and children can use the medication, and your dose depends on your body weight.
What to do if your child has a HAE attack?
If your child has HAE, note any changes in behavior that you see before an attack. As they get older, they'll need to learn their triggers and treatment needs. Make sure all caregivers and family members know about the condition and what to do if an attack happens. Remember: Any swelling in the throat is an emergency.
How often do you have a HAE attack?
The frequency of attacks can vary. You can have attacks as often as every 1 to 2 weeks or 1 to 2 per year, and they can be hard to manage.
When does HAE get worse?
Symptoms most often initially show up in childhood and get worse during the teen years. Many people don't know HAE is causing their swelling until they're adults. Where you have it on your body, how often the bouts happen, and how strong they are different for everyone.
Can you be born with angioedema?
You are born with hereditary angioedema (HAE). Although you’ll always have it, treatment helps you manage it . There have been big improvements in treatment, and researchers continue to look for new solutions. Symptoms most often initially show up in childhood and get worse during the teen years.
Do you need blood tests for HAE?
You'll need blood tests, too, to confirm that it’s HAE. If you do have it, ask your doctor to refer you to a specialist familiar with the condition. You should also ask your doctor about having other members of your family tested, even if no one has symptoms. Questions for Your Doctor.
Can C1 inhibitor cause HAE?
A problem with a gene that makes a blood protein called C1 inhibitor often causes HAE. In most cases, you don’t have enough of this protein. In others, you have normal levels but it doesn't work right. For the most common form of HAE, if one of your parents has HAE, you have a 50% change of having it, too.
Is there a cure for HAE?
There's no cure for HAE, but new treatments have made it possible for people to manage their symptoms and enjoy active lives. Getting Support. To learn more about HAE and to find the support of others who have it, visit the website of the U.S. Hereditary Angioedema Association at www.haea.org.
What is the treatment for hereditary angioedema?
There are two kinds of hereditary angioedema (HAE) treatments: preventive and on demand. Preventive therapies Also known as prophylactic medication, this type of medication is taken regularly to help ward off an HAE attack. These drugs might also reduce the frequency and severity of your symptoms.
What kind of therapy is used for HAE?
The severity of your attacks and your general health will also factor into your doctor’s recommendations. The FDA-approved therapies are typically used to treat the most common kinds of HAE: type 1 and type 2.
What is Haegarda used for?
It raises your working C1 inhibitor level. It is used to prevent an HAE attack in adolescents and adults. It’s an injectable drug that you may give yourself at home about twice a week.
What is HAE in medicine?
Hereditary angioedema (HAE) is a rare, genetic disease that causes episodes of swelling in different areas of the body. Medication can help prevent attacks... By Julie Marks June 29, 2020.
How many medications are available for HAE?
All people with HAE should have access to an on-demand therapy. ( 1) Currently, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved seven medicines to prevent or treat HAE attacks.
Does Haegarda cause rash?
In a clinical study, Haegarda reduced the number of HAE attacks by 95 percent. (5) Common side effects of Haegarda include injection-site reactions, itching, rash, dizziness, and stuffy nose. (6) The FDA approved this medicine in 2017. (2)
What are the two types of hereditary angioedema?
Types of hereditary angioedema. There are two main types of HAE: type 1 and type 2. The third type, HAE with normal C1 inhibitor, is rare and not fully understood.
How many people have hereditary angioedema?
Without treatment, the condition can be life threatening. HAE affects an estimated 1 in 10,000 to 1 in 50,000 people. However, the true number of cases is not well-documented. Reasons for this may include the limited awareness ...
What is the difference between Haegarda and Cinryze?
Cinryze: This drug is an intravenous C1 esterase inhibitor that helps prevent HAE attacks in children, teens, and adults. Haegarda: People self-administer this plasma-derived concentrate of C1-esterase inhibitor.
What percentage of HAE cases are type 2?
Type 2 HAE accounts for 15% of all cases. In type 2 cases, a person’s C1 inhibitor level is normal or close to normal, but the protein does not function properly.
What causes HAE?
Causes. HAE has two primary causes. According to UC San Diego Health, the two most common causes are an inherited gene defect (about 80% of cases) and a spontaneous mutation in the C1 inhibitor (about 20% of cases). Type 3 HAE does not occur due to C1 inhibitor mutations. Instead, research.
Where does HAE occur?
Researchers characterize HAE as recurrent, severe swelling of the mucous membranes and skin. It can also occur in the gastrointestinal tract or upper airway. The swelling may occur on or in the following body parts: hands and feet. face (commonly the lips and eyes) genitals. buttocks.
Is C1 inhibitor hereditary?
Scientists consider the condition hereditary, but up to 25% of cases are the result of a spontaneous mutation at the time of conception. This mutation affects the gene responsible for the production of C1 inhibitor. In those cases, the genetic trait can then pass from a person to their children.
How to treat angioedema?
The 2 main treatments used to treat swelling caused by hereditary angioedema are: 1 icatibant – a medicine given by injection that blocks the effects of some of the chemicals responsible for the swelling 2 C1 esterase inhibitor replacement – a treatment given by injection that boosts the levels of C1 esterase inhibitor in your blood
What is the best medicine for angioedema?
Medicines called danazol and oxandrolone can help reduce the chances of swelling occurring if you have hereditary angioedema. These medicines boost the levels of C1 esterase inhibitor in your blood. Low levels of this substance are what causes the swelling. Side effects of these medicines can include: weight gain.
What is the best medicine for swelling?
If your symptoms of swelling occur during the day, it's best to take non-drowsy medicines such as cetirizine and loratadine. Other side effects of antihistamines can include: headaches. a dry mouth. a dry nose. If the swelling is severe, your GP may prescribe a short course of steroid medicine.
What is C1 replacement?
C1 esterase inhibitor replacement – a treatment given by injection that boosts the levels of C1 esterase inhibitor in your blood. Occasionally, C1 esterase inhibitor replacement may also be used shortly before surgery or dental treatment, as it can reduce the risk of these triggering swelling.
Can you use adrenaline injections for anaphylaxis?
If you have a particularly serious allergy, you may be given adrenaline auto-injectors to use if you experience a severe allergic reaction (anaphylaxis). There are several types of auto-injector, which are used in slightly different ways. Read about preventing anaphylaxis for more information.
Can you stop taking medication for angioedema?
Drug-induced angioedema. If a certain medicine you're taking is thought to be responsible for your angioedema, your doctor will usually advise stopping it. They can prescribe a different medicine for you to take instead. This is usually all that needs to be done.
Can angioedema be treated at home?
There are several different types of angioedema, each of which has a different cause. Angioedema can usually be treated at home, although severe cases may need to be treated in hospital.
What are the best treatments for HAE?
Before there were approved treatments for HAE, anabolic steroids (also known as androgens) such as danazol, oxandrolone, and stanozolol were the most commonly prescribed preventive HAE therapies. While anabolic steroids have been shown to be useful, they are not well-tolerated by many women, directly linked to liver toxicity, and can cause an increase in cholesterol levels. In addition, these drugs should not be used to treat children. Research indicates that patients treated with anabolic steroids can experience breakthrough laryngeal or abdominal attacks that require hospitalization.
How many products are approved for HAE?
Approved HAE Treatments. With eight products currently approved by the FDA for preventing and treating Hereditary Angioedema (HAE) attacks, and several therapies approved for generic use, people with HAE and their physicians have options for developing an HAE treatment plan tailored to meet each person's unique needs.
Is Heagarda a B2 receptor antagonist?
For more information visit: www.haegarda.com. ICATIBANT (GENERIC) is a bradykinin B2 receptor antagonist indicated for treatment of acute attacks of Hereditary Angioedema (HAE) in adults 18 years of age and older.
What is angioedema in childhood?
Hereditary angioedema (HAE) is a disease characterized by recurrent episodes (also called attacks) of severe swelling of the skin and mucous membranes. [1] . The age at which attacks begin varies, but most people have their first one in childhood or adolescence. [2] . The frequency of attacks usually increases after puberty.
What are the two types of HAE?
There are several types of HAE. [1] . Types I and II are caused by mutations in the C1NH gene (also called the SERPING1 gene ), which provides instructions for making the C1 inhibitor protein. [1] [3] Type I is due to deficiency of C1 inhibitor, and type II is due to dysfunction of C1 inhibitor. [1] .
How long does it take for a HAE to go away?
They always go away on their own but last from 2 to 4 days. While people with HAE have reported various triggers of attacks, emotional stress, physical stress, and dental procedures are the most commonly reported triggers. [2] There are several types of HAE. [1] .
What is the most common type of hereditary angioedema?
The most common type of hereditary angioedema is associated with a deficiency of functional C1-esterase inhibitor (C1-INH), a serine protease inhibitor that regulates the activation of the classic complement pathway and suppresses spontaneous activation of complement component C1 (figure 1). C1-INH also regulates the contact (kallikrein-kinin) ...
How often does angioedema occur?
Symptoms of hereditary angioedema typically begin in childhood, worsen in puberty, and persist throughout life. Untreated patients have attacks every 7–14 days on average, with a range from every 3 days to almost never [3].
What is the type of angioedema that is caused by mutations?
Type III hereditary angioedema shows a similar clinical picture to type I and II but has normal levels of functional C1-INH. Type III hereditary angioedema is caused by at least three known gene mutations, including a mutation of the F12 gene, which codes for factor XII to activation by plasmin. Figure 2.
How long does it take for angioedema to subside?
The angioedema generally increases over the first 24 hours and then subsides over the next 2–5 days. Oedema may affect an arm, leg, hand, foot, or the abdomen. Oropharyngeal swelling is less common.
What complement levels are normal for angioedema?
Investigations should include complement levels (figure 3). Most patients with hereditary angioedema have low C4 levels with normal C1 and C3 levels. Occasionally C4 may be normal between attacks and patients need to be tested during an acute attack.
Can angioedema cause nausea?
An abdominal attack of hereditary angioedema can cause severe abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting; it is often mistaken for an ' acute abdomen'. Bowel sounds may be absent, and guarding (muscle spasms) may be present on examination.
Does tranexamic acid cause angioedema?
The lowest possible dose should be used to control hereditary angioedema to minimise side effects. The mechanism of action of tranexamic acid in hereditary angioedema is unknown. Side effects included nausea, diarrhoea, myalgia, and thrombosis.
Drugs used to treat Hereditary Angioedema
The following list of medications are in some way related to, or used in the treatment of this condition.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.